Abstract
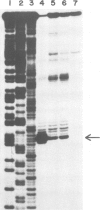
The nucleotide sequence of the 5'-flanking region of the cloned human preproenkephalin A gene, extending to 949 bp upstream of the capping site, has been determined. The preproenkephalin A gene, when joined with an SV40 vector and introduced into COS monkey cells, is efficiently transcribed from its own promoter. To assess the DNA sequence required for promoter function, we have constructed a series of 5'-deletion mutants of a fusion gene that consists of the 949-bp 5'-flanking sequence and capping site of the preproenkephalin A gene and the structural sequence of the herpes simplex virus thymidine kinase gene. The deletions up to 757-172 bp upstream of the capping site exert essentially no effect on the expression of the fusion gene, whereas the deletions up to 145, 111, 81 and 67 bp upstream of the capping site result in a gradual decrease in the transcriptional efficiency. No detectable amount of the fusion gene transcript is produced with the mutants having deletions up to 67, 43 and 28 bp upstream of the capping site. These results indicate that a functional promoter of the preproenkephalin A gene lies between 67 and 171 bp upstream of the capping site. This promoter region corresponds to a highly GC-rich segment with short repeated sequences and palindromes.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Banerji J., Rusconi S., Schaffner W. Expression of a beta-globin gene is enhanced by remote SV40 DNA sequences. Cell. 1981 Dec;27(2 Pt 1):299–308. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90413-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benoist C., Chambon P. In vivo sequence requirements of the SV40 early promotor region. Nature. 1981 Mar 26;290(5804):304–310. doi: 10.1038/290304a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berk A. J., Sharp P. A. Sizing and mapping of early adenovirus mRNAs by gel electrophoresis of S1 endonuclease-digested hybrids. Cell. 1977 Nov;12(3):721–732. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90272-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breathnach R., Chambon P. Organization and expression of eucaryotic split genes coding for proteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1981;50:349–383. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.50.070181.002025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brinster R. L., Chen H. Y., Warren R., Sarthy A., Palmiter R. D. Regulation of metallothionein--thymidine kinase fusion plasmids injected into mouse eggs. Nature. 1982 Mar 4;296(5852):39–42. doi: 10.1038/296039a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chu G., Sharp P. A. SV40 DNA transfection of cells in suspension: analysis of efficiency of transcription and translation of T-antigen. Gene. 1981 Mar;13(2):197–202. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(81)90008-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cochet M., Chang A. C., Cohen S. N. Characterization of the structural gene and putative 5'-regulatory sequences for human proopiomelanocortin. Nature. 1982 May 27;297(5864):335–339. doi: 10.1038/297335a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Comb M., Seeburg P. H., Adelman J., Eiden L., Herbert E. Primary structure of the human Met- and Leu-enkephalin precursor and its mRNA. Nature. 1982 Feb 25;295(5851):663–666. doi: 10.1038/295663a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dierks P., van Ooyen A., Cochran M. D., Dobkin C., Reiser J., Weissmann C. Three regions upstream from the cap site are required for efficient and accurate transcription of the rabbit beta-globin gene in mouse 3T6 cells. Cell. 1983 Mar;32(3):695–706. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90055-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dierks P., van Ooyen A., Mantei N., Weissmann C. DNA sequences preceding the rabbit beta-globin gene are required for formation in mouse L cells of beta-globin RNA with the correct 5' terminus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Mar;78(3):1411–1415. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.3.1411. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donahue T. F., Daves R. S., Lucchini G., Fink G. R. A short nucleotide sequence required for regulation of HIS4 by the general control system of yeast. Cell. 1983 Jan;32(1):89–98. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90499-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fromm M., Berg P. Deletion mapping of DNA regions required for SV40 early region promoter function in vivo. J Mol Appl Genet. 1982;1(5):457–481. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gluzman Y. SV40-transformed simian cells support the replication of early SV40 mutants. Cell. 1981 Jan;23(1):175–182. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90282-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., van der Eb A. J. A new technique for the assay of infectivity of human adenovirus 5 DNA. Virology. 1973 Apr;52(2):456–467. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90341-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grosschedl R., Birnstiel M. L. Identification of regulatory sequences in the prelude sequences of an H2A histone gene by the study of specific deletion mutants in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Mar;77(3):1432–1436. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.3.1432. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grosschedl R., Birnstiel M. L. Spacer DNA sequences upstream of the T-A-T-A-A-A-T-A sequence are essential for promotion of H2A histone gene transcription in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Dec;77(12):7102–7106. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.12.7102. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grosveld G. C., de Boer E., Shewmaker C. K., Flavell R. A. DNA sequences necessary for transcription of the rabbit beta-globin gene in vivo. Nature. 1982 Jan 14;295(5845):120–126. doi: 10.1038/295120a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gubler U., Seeburg P., Hoffman B. J., Gage L. P., Udenfriend S. Molecular cloning establishes proenkephalin as precursor of enkephalin-containing peptides. Nature. 1982 Jan 21;295(5846):206–208. doi: 10.1038/295206a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirt B. Selective extraction of polyoma DNA from infected mouse cell cultures. J Mol Biol. 1967 Jun 14;26(2):365–369. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90307-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmgren R., Corces V., Morimoto R., Blackman R., Meselson M. Sequence homologies in the 5' regions of four Drosophila heat-shock genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jun;78(6):3775–3778. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.6.3775. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Humphries R. K., Ley T., Turner P., Moulton A. D., Nienhuis A. W. Differences in human alpha-, beta- and delta-globin gene expression in monkey kidney cells. Cell. 1982 Aug;30(1):173–183. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90023-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ingolia T. D., Craig E. A. Primary sequence of the 5' flanking regions of the Drosophila heat shock genes in chromosome subdivision 67B. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Apr 10;9(7):1627–1642. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.7.1627. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karch F., Török I., Tissières A. Extensive regions of homology in front of the two hsp70 heat shock variant genes in Drosophila melanogaster. J Mol Biol. 1981 May 25;148(3):219–230. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90536-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kudo A., Yamamoto F., Furusawa M., Kuroiwa A., Natori S., Obinata M. Structure of thymidine kinase gene introduced into mouse Ltk- cells by a new injection method. Gene. 1982 Jul-Aug;19(1):11–19. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90184-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liebhaber S. A., Goossens M. J., Kan Y. W. Cloning and complete nucleotide sequence of human 5'-alpha-globin gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Dec;77(12):7054–7058. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.12.7054. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKnight S. L., Gavis E. R. Expression of the herpes thymidine kinase gene in Xenopus laevis oocytes: an assay for the study of deletion mutants constructed in vitro. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Dec 20;8(24):5931–5948. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.24.5931. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKnight S. L., Kingsbury R. Transcriptional control signals of a eukaryotic protein-coding gene. Science. 1982 Jul 23;217(4557):316–324. doi: 10.1126/science.6283634. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mellon P., Parker V., Gluzman Y., Maniatis T. Identification of DNA sequences required for transcription of the human alpha 1-globin gene in a new SV40 host-vector system. Cell. 1981 Dec;27(2 Pt 1):279–288. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90411-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mishina M., Kurosaki T., Yamamoto T., Notake M., Masu M., Numa S. DNA sequences required for transcription in vivo of the human corticotropin-beta-lipotropin precursor gene. EMBO J. 1982;1(12):1533–1538. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01351.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakanishi S., Teranishi Y., Watanabe Y., Notake M., Noda M., Kakidani H., Jingami H., Numa S. Isolation and characterization of the bovine corticotropin/beta-lipotropin precursor gene. Eur J Biochem. 1981 Apr;115(3):429–438. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1981.tb06220.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noda M., Furutani Y., Takahashi H., Toyosato M., Hirose T., Inayama S., Nakanishi S., Numa S. Cloning and sequence analysis of cDNA for bovine adrenal preproenkephalin. Nature. 1982 Jan 21;295(5846):202–206. doi: 10.1038/295202a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noda M., Teranishi Y., Takahashi H., Toyosato M., Notake M., Nakanishi S., Numa S. Isolation and structural organization of the human preproenkephalin gene. Nature. 1982 Jun 3;297(5865):431–434. doi: 10.1038/297431a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Notake M., Tobimatsu T., Watanabe Y., Takahashi H., Mishina M., Numa S. Isolation and characterization of the mouse corticotropin-beta-lipotropin precursor gene and a related pseudogene. FEBS Lett. 1983 May 30;156(1):67–71. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(83)80250-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelham H. R. A regulatory upstream promoter element in the Drosophila hsp 70 heat-shock gene. Cell. 1982 Sep;30(2):517–528. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90249-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelham H. R., Bienz M. A synthetic heat-shock promoter element confers heat-inducibility on the herpes simplex virus thymidine kinase gene. EMBO J. 1982;1(11):1473–1477. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01340.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin C. M., Schmid C. W. Pyrimidine-specific chemical reactions useful for DNA sequencing. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Oct 24;8(20):4613–4619. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.20.4613. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi H., Teranishi Y., Nakanishi S., Numa S. Isolation and structural organization of the human corticotropin--beta-lipotropin precursor gene. FEBS Lett. 1981 Nov 30;135(1):97–102. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(81)80952-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weaver R. F., Weissmann C. Mapping of RNA by a modification of the Berk-Sharp procedure: the 5' termini of 15 S beta-globin mRNA precursor and mature 10 s beta-globin mRNA have identical map coordinates. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 10;7(5):1175–1193. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.5.1175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitfeld P. L., Seeburg P. H., Shine J. The human pro-opiomelanocortin gene: organization, sequence, and interspersion with repetitive DNA. DNA. 1982;1(2):133–143. doi: 10.1089/dna.1.1982.1.133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wigler M., Pellicer A., Silverstein S., Axel R. Biochemical transfer of single-copy eucaryotic genes using total cellular DNA as donor. Cell. 1978 Jul;14(3):725–731. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90254-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zalkin H., Yanofsky C. Yeast gene TRP5: structure, function, regulation. J Biol Chem. 1982 Feb 10;257(3):1491–1500. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]