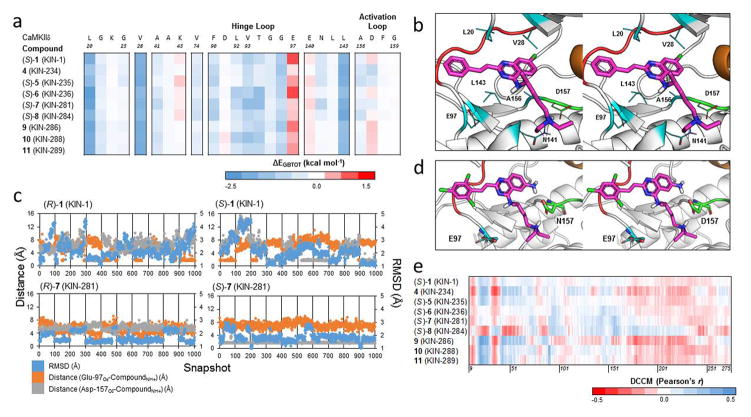
Figure 6.
(a) Decomposition energies of key residues of binding for 1 and derivatives against CaMKIIδ. For compounds with a chiral center in the N-akylamine moiety, only the S configuration shown. Each row is a compound while each column is an individual residue. (b) A snapshot from the simulation of (S)-1 bound to CaMKIIδ, showing the sidechains of key residues from the interaction in line format. The crystal structure of CaMKIIδ (PDB ID: 2WEL, 1.90 Å) is shown as cartoon (gray) with the hinge loop (red), DFG-motif (green), and αC helix (orange) highlighted. The protein is shown with part of the glycine-rich loop removed (Residues Gly-21 to Ser-26) to expose the ATP binding pocket. (c) Plot of the RMSD of the compound (blue) and the distance from the positively charged amine hydrogen on the N-akylamine moiety of the compound from the negatively charged epsilon and delta oxygen atoms of Glu-97 (orange) and Asp-157 (gray), respectively, across 1000 snapshots for the R and S configurations of 1 and 7. (d) A snapshot from the simulation of (S)-7 (KIN-281) bound to CaMKIIδ, showing the additional hydrogen bond created by the amine group on the quinazoline core of the compound. The crystal structure of CaMKIIδ (PDB ID: 2WEL, 1.90 Å) is shown as cartoon (gray) with the hinge loop (red), DFG-motif (green), and αC helix (orange) highlighted. The protein is shown with the glycine-rich loop removed (residues Glu-19 to Arg-29) to expose the ATP binding pocket. Asp-157 and Glu-97 are also shown as element-colored stick models, with carbons colored as green and cyan, respectively. (e) Dynamic cross-correlation matrix (DCCM) cross section of 1 and 8 derivatives against the protein kinase domain of CaMKIIδ.