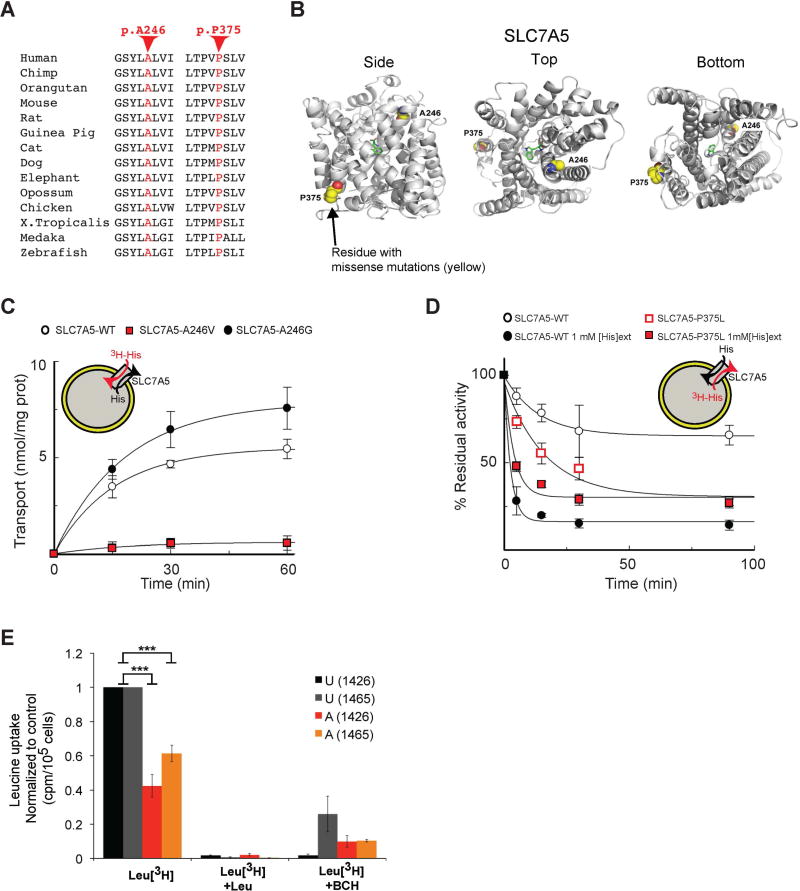
Figure 6. A246V and P375L mutations compromise SLC7A5 function.
(A) Conservation of the SLC7A5 A246 and P375 in several species.
(B) Side, top and bottom views of the predicted structure of SLC7A5 in complex with tryptophan showing SLC7A5 backbone atoms (gray ribbon), atoms of the residues constituting the missense mutations (yellow spheres) and the ligand tryptophan (green sticks); oxygen atoms (red) and nitrogen atoms (blue).
(C) SLC7A5 wild-type, A246V and A246G mutants over-expressed and purified by fast protein liquid chromatography were reconstituted in proteoliposomes. Transport is followed as uptake (red arrow) of external [3H]His in exchange with internal His. Transport was started by adding external 5 µM [3H]His at time zero to proteoliposomes containing 10 mM His reconstituted with SLC7A5-WT (○), SLC7A5-A246V (
 ) or SLC7A5-A246G (●) and stopped at the indicated times (means ± SD; n=5 experiments).
) or SLC7A5-A246G (●) and stopped at the indicated times (means ± SD; n=5 experiments).
(D) Time dependence of [3H]His efflux from proteoliposomes reconstituted with SLC7A5-WT or SLC7A5-P375L was measured. Proteoliposomes reconstituted with SLC7A5-WT (○, ●) or SLC7A5-P375L (
 ,
,
 ), containing 2 mM His were radioactivity-preloaded. Efflux was measured in absence (○,
), containing 2 mM His were radioactivity-preloaded. Efflux was measured in absence (○,
 ; uniport) or presence of external 1 mM His (●,
; uniport) or presence of external 1 mM His (●,
 ; antiport). Percentage of His efflux was calculated with respect to time 0 (means ± SD; n=4 experiments).
; antiport). Percentage of His efflux was calculated with respect to time 0 (means ± SD; n=4 experiments).
(E) Radio-labeled leucine ([3H]Leu) transport analysis in human fibroblasts from affected (A) and unaffected (U) members of families 1426 and 1465 illustrating a significant reduction in leucine uptake by the cells of affected patients. Specificity of leucine uptake was assessed by competition with 10mM cold leucine (Leu) or 10 mM 2 BCH; ***P<0.001 (means ± SEM; N≥3 experiments performed with fibroblasts from two patients and one healthy control/family).
See also Figure S7.