Abstract
Background
Blocks of duplicated genomic DNA sequence longer than 1000 base pairs are known as low copy repeats (LCRs). Identified by their sequence similarity, LCRs are abundant in the human genome, and are interesting because they may represent recent adaptive events, or potential future adaptive opportunities within the human lineage. Sequence analysis tools are needed, however, to decide whether these interpretations are likely, whether a particular set of LCRs represents nearly neutral drift creating junk DNA, or whether the appearance of LCRs reflects assembly error. Here we investigate an LCR family containing the sulfotransferase (SULT) 1A genes involved in drug metabolism, cancer, hormone regulation, and neurotransmitter biology as a first step for defining the problems that those tools must manage.
Results
Sequence analysis here identified a fourth sulfotransferase gene, which may be transcriptionally active, located on human chromosome 16. Four regions of genomic sequence containing the four human SULT1A paralogs defined a new LCR family. The stem hominoid SULT1A progenitor locus was identified by comparative genomics involving complete human and rodent genomes, and a draft chimpanzee genome. SULT1A expansion in hominoid genomes was followed by positive selection acting on specific protein sites. This episode of adaptive evolution appears to be responsible for the dopamine sulfonation function of some SULT enzymes. Each of the conclusions that this bioinformatic analysis generated using data that has uncertain reliability (such as that from the chimpanzee genome sequencing project) has been confirmed experimentally or by a "finished" chromosome 16 assembly, both of which were published after the submission of this manuscript.
Conclusion
SULT1A genes expanded from one to four copies in hominoids during intra-chromosomal LCR duplications, including (apparently) one after the divergence of chimpanzees and humans. Thus, LCRs may provide a means for amplifying genes (and other genetic elements) that are adaptively useful. Being located on and among LCRs, however, could make the human SULT1A genes susceptible to further duplications or deletions resulting in 'genomic diseases' for some individuals. Pharmacogenomic studies of SULT1Asingle nucleotide polymorphisms, therefore, should also consider examining SULT1A copy number variability when searching for genotype-phenotype associations. The latest duplication is, however, only a substantiated hypothesis; an alternative explanation, disfavored by the majority of evidence, is that the duplication is an artifact of incorrect genome assembly.
Background
Experimental and computational results estimate that 5–10% of the human genome has recently duplicated [1-4]. These estimates represent the total proportion of low-copy repeats (LCRs), which are defined as homologous blocks of sequence from two distinct genomic locations (non-allelic) >1000 base pairs in length. LCRs, which are also referred to in the literature as recent segmental duplications, may contain all of the various sequence elements, such as genes, pseudogenes, and high-copy repeats. A set of homologous LCRs make up an LCR family. Non-allelic homologous recombination between members of an LCR family can cause chromosomal rearrangements with health-related consequences [5-7]. While data are not yet available to understand the mechanistic basis of LCR duplication, mechanisms will emerge through the study of individual cases [8].
At the same time, the appearance of LCR duplicates may be an artifact arising from one of a number of problems in the assembly of a genome of interest. Especially when classical repetitive sequences are involved, it is conceivable that mistaken assembly of sequencing contigs might create in a draft sequence of a genome a repeat where none exists. In the post-genomic world, rules have not yet become accepted in the community to decide when the burden of proof favors one interpretation (a true repeat) over another (an artifact of assembly). Again, these rules will emerge over time through the study of individual cases.
Through the assembly of many case studies, more general features of duplication and evolutionary processes that retain duplicates should emerge. Although each LCR family originates from one progenitor locus, no universal features explain why the particular current progenitor loci have been duplicated instead of other genomic regions. From an evolutionary perspective, duplicated material is central to creating new function, and to speciation. One intriguing hypothesis is that genes whose duplication and recruitment have been useful to meet current Darwinian challenges find themselves in regions of the chromosome that favor the generation of LCRs.
Browsing a naturally organized database of biological sequences, we identified human cytosolic sulfotransferase (SULT) 1A as a recently expanded gene family with biomedically related functions. SULT1A enzymes conjugate sulfuryl groups to hydroxyl or amino groups on exogenous substrates (sulfonation), which typically facilitates elimination of the xenobiotic by the excretory system [9]. Sulfonation, however, also bioactivates certain pro-mutagenic and pro-carcinogenic molecules encountered in the diet and air, making it of interest to cancer epidemiologists [10,11]. These enzymes also function physiologically by sulfonating a range of endogenous molecules, such as steroid and thyroid hormones, neurotransmitters, bile salts, and cholesterol [9].
Three human SULT1A genes have been reported [12,13]. The human SULT1A1 and 1A2 enzymes are ~98% identical and recognize many different phenolic compounds such as p-nitrophenol and α-naphthol [14-19]. The human SULT1A3 enzyme is ~93% identical to SULT1A1 and 1A2, but preferentially recognizes dopamine and other catecholamines over other phenolic compounds [19-23]. High resolution crystal structures of SULT1A1 and 1A3 enzymes have been solved [24-26]. Amino acid differences that contribute to the phenolic and dopamine substrate preferences of the SULT1A1 and 1A3 enzymes, respectively, have been localized to the active site [27-30].
Polymorphic alleles of SULT1A1, 1A2, and 1A3 exist in the human population [31-33]. An allele known as SULT1A1*2 contains a non-synonymous polymorphism, displays only ~15% of wild type sulfonation activity in platelets, and is found in ~30% of individuals in some populations [31]. Numerous studies comparing SULT1A1 genotypes in cancer versus control cohorts demonstrate that the low-activity SULT1A1*2 allele is a cancer risk factor [34-36], although other studies have failed to find an association [12]. Ironically, the protection from carcinogens conferred by the high activity SULT1A1*1 allele is counterbalanced by risks associated with its activation of pro-carcinogens. For example, SULT1A enzymes bioactivate the pro-carcinogen 2-amino-α-carboline found in cooked food, cigarette smoke and diesel exhaust [37]. The sulfate conjugates of aromatic parent compounds convert to reactive electrophiles by losing electron-withdrawing sulfate groups. The resulting electrophilic cations form mutagenic DNA adducts leading to cancer.
Recently, it has become widely understood that placing a complex biomolecular system within an evolutionary model helps generate hypotheses concerning function. This process has been termed "phylogenomics" [38]. Through our bioinformatic and phylogenomic efforts on the sulfotransferase 1A system, we detected a previously unidentified human gene that is very similar to SULT1A3, transcriptionally active, and not found in the chimpanzee. In addition, we report that all four human SULT1A genes are located on LCRs in a region of chromosome 16 replete with other LCRs. A model of SULT1A gene family expansion in the hominoid lineage (humans and great apes) is presented, complete with date estimates of three preserved duplication events and identification of the progenitor locus. Positively selected protein sites were identified that might have been central in adapting the SULT1A3 and 1A4 enzymes to their role in sulfonating catecholamines such as dopamine and other structurally related drugs.
Results and Discussion
Four human SULT1A genes on chromosome 16 LCRs
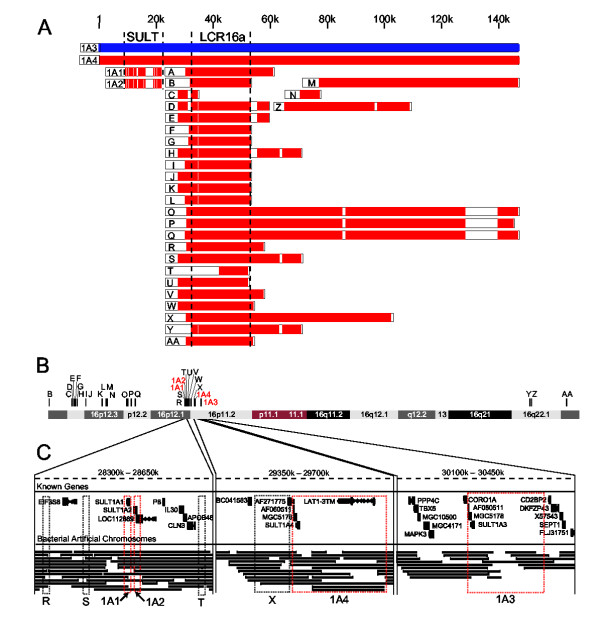
The human SULT1A1 and 1A2 genes are tandemly arranged 10 kilobase pairs (kbp) apart in the pericentromeric region of chromosome 16, while the SULT1A3 gene is located ~1.7 million base pairs (Mbp) away (Figure 1B and 1C). In addition to the three known SULT1A genes, we found a fourth gene, SULT1A4, by searching the human genome with the BLAST-like alignment tool [39]. SULT1A4 was located midway between the SULT1A1/1A2 gene cluster and the SULT1A3 gene (Figure 1B and 1C).
Figure 1.
Genomic organization of the SULT1A LCR family. (A) 30 LCRs (red) aligned to the SULT1A3 LCR (blue). Core sequences of SULT1A and LCR16a families are shown between dashed lines. (B) Chromosome 16 positions of 29 SULT1A3-related LCRs. (C) Known genes, bacterial sequencing contigs, and LCRs (outlined in boxes) in three 350 kbp regions of chromosome 16.
The SULT1A4 gene resided on 148 kbp of sequence that was highly identical to 148 kbp of sequence surrounding the SULT1A3 gene (Figure 1A and Table 1). The high sequence identity between the SULT1A3 and 1A4 genomic regions suggested that they were part of a low copy repeat (LCR) family. This suspicion was confirmed by mining the Recent Segmental Duplication Database of human LCR families [40]. In addition to the four-member SULT1A LCR family, the 148 kbp SULT1A3 LCR was related to 27 other LCRs (Figure 1A and Table 1). Many of the SULT1A3-related LCRs are members of the previously identified LCR16a family [41,42]. The SULT1A3-related LCRs mapping to chromosome 16 collectively amounted to 1.4 Mbp of sequence – or 1.5% of chromosome 16.
Table 1.
SULT1A3-related LCRs
| LCR Name* | Chromosome | Strand | Start | End | Length | % Identity† |
| A | chr18p | + | 11605429 | 11633851 | 28422 | 97.8 |
| B | chr16p | + | 11985022 | 12003971 | 18949 | 97.6 |
| C | chr16p | - | 14747420 | 14753000 | 5580 | 94.8 |
| D | chr16p | - | 14766628 | 14792117 | 25489 | 96.5 |
| E | chr16p | - | 14805750 | 14832437 | 26687 | 96.6 |
| F | chr16p | - | 14996007 | 15072649 | 76642 | 96.9 |
| G | chr16p | + | 15161625 | 15185467 | 23842 | 95.6 |
| H | chr16p | - | 15417052 | 15453865 | 36813 | 95.9 |
| I | chr16p | - | 16394409 | 16416404 | 21995 | 96.4 |
| J | chr16p | + | 16437719 | 16461029 | 23310 | 96.5 |
| K | chr16p | + | 18371484 | 18394809 | 23325 | 96.4 |
| L | chr16p | + | 18414255 | 18434928 | 20673 | 96.4 |
| M | chr16p | - | 18834216 | 18904410 | 70194 | 96.5 |
| N | chr16p | + | 18962854 | 18969729 | 6875 | 95.2 |
| O | chr16p | + | 21376182 | 21480283 | 104101 | 97.8 |
| P | chr16p | + | 21808293 | 21910109 | 101816 | 98.3 |
| Q | chr16p | - | 22414809 | 22523008 | 108199 | 97.1 |
| R | chr16p | + | 28316465 | 28341127 | 24662 | 97.8 |
| S | chr16p | + | 28427424 | 28467064 | 39640 | 97.3 |
| 1A1 | chr16p | + | 28481970 | 28490644 | 8674 | 86.0 |
| 1A2 | chr16p | + | 28494950 | 28502357 | 7407 | 86.6 |
| T | chr16p | - | 28621035 | 28630803 | 9768 | 97.7 |
| U | chr16p | - | 28692200 | 28714506 | 22306 | 98.1 |
| V | chr16p | - | 28800873 | 28828646 | 27773 | 97.7 |
| W | chr16p | - | 29084138 | 29108487 | 24349 | 97.8 |
| X | chr16p | + | 29426409 | 29498137 | 71728 | 97.6 |
| 1A4 | chr16p | + | 29498152 | 29644489 | 146337 | 99.1 |
| 1A3 | chr16p | + | 30236110 | 30388351 | 152241 | 100 |
| Y | chr16q | + | 69784235 | 69818803 | 34568 | 96.2 |
| Z | chr16q | + | 70016088 | 70061019 | 44931 | 97.4 |
| AA | chr16q | - | 74188141 | 74209430 | 21289 | 97.4 |
*LCR names are as in Figure 1. †Percent identity is relative to the 1A3 LCR.
To determine if other genes in the SULT super family were also recently duplicated during LCR expansions, we searched the Segmental Duplication Database [4] for human reference genes located on LCRs. No other complete cytosolic SULT genes were located on LCRs, but 25% of the SULT2A1 open reading frame (ORF) was located on an LCR (Table 2).
Table 2.
Duplication Status of SULT Genes
| Accession | Gene | Chromosome | ORF Length | ORF Duplicated |
| NM_001055 | SULT1A1, phenol | chr16 | 895 | 895 |
| NM_001054 | SULT1A2, phenol | chr16 | 895 | 895 |
| NM_003166 | SULT1A3, dopamine | chr16 | 895 | 895 |
| NM_014465 | SULT1B1 | chr4 | 804 | 0 |
| NM_001056 | SULT1C1 | chr2 | 898 | 0 |
| NM_006588 | SULT1C2 | chr2 | 916 | 0 |
| NM_005420 | SULT1E1 | chr4 | 892 | 0 |
| NM_003167 | SULT2A1, DHEA | chr19 | 864 | 210 |
| NM_004605 | SULT2B1 | chr19 | 1059 | 0 |
| NM_014351 | SULT4A1 | chr22 | 862 | 0 |
The steroid sulfatase gene, which encodes an enzyme that removes sulfate groups from the same biomolecules recognized and sulfonated by SULT enzymes, is frequently deleted in patients with scaly skin (X-linked icthyosis) due to nonallelic homologous recombination between LCRs on chromosome X [43,44]. As demonstrated by the X-linked icthyosis example, SULT1A copy number or activity in the human population could be modified – with health-related consequences – by nonallelic homologous recombination between LCRs on chromosome 16.
SULT1A4: genomic and transcriptional evidence
The sequence of the SULT1A4 gene region from the human reference genome was so similar to that of the SULT1A3 region (>99% identity) that the differences were near those that might arise from sequencing error or allelic variation. It was conceivable, therefore, that some combination of sequence error, allelic variation, and/or faulty genome construction generated the appearance of a SULT1A4 gene that does not actually exist. We therefore searched for additional evidence that the SULT1A4 gene was material.
We asked whether any evidence was consistent with the hypothesis of an artificial SULT1A4 LCR from erroneous genome assembly, as opposed to the existence of a true duplicate region. Here, the quality of the genomic sequencing is important. The junction regions at the ends of the SULT1A4 LCR were sufficiently covered; at least nine sequencing contigs overlapped either junction boundary (Figure 1C). This amount of evidence has been used in other studies to judge the genomic placement of LCRs [45].
As another line of evidence, we compared the nucleotide sequences of the SULT1A4 and 1A3 genomic regions (Table 3). Among the 876 coding positions the only difference was at position 105, where SULT1A4 possessed adenine (A) and SULT1A3 possessed guanine (G). Thus, if two genes do exist, they differ by one silent transition at the third position of codon 35. The untranslated regions, however, contained thirteen nucleotide differences while the introns contained seven additional differences (Table 3). These 21 differences between the SULT1A4 and 1A3 genomic regions disfavor the hypothesis that sequencing errors played a role in the correct/incorrect placement of these LCRs.
Table 3.
SULT1A4 and SULT1A3 Genomic Region Differences
| Location* | Nucleotide | SULT1A4 Region | SULT1A3 Region |
| 5' UTR | -6,246 | G | C |
| 5' UTR | -6,118 | C | T |
| 5' UTR | -6,007 | G | C |
| 5' UTR | -5,246 | - | T |
| 5' UTR | -4,433 | - | T |
| Intron 1B | -2,775 | C | T |
| Intron 1B | -2,671 | - | T |
| Intron 1B | -2,670 | - | T |
| Intron 1B | -2,594 | T | G |
| Intron 1A | -91 | - | A |
| Exon 2 | +105 | A | G |
| Intron 4 | +853 | - | A |
| Intron 4 | +1,487 | A | G |
| Exon 8 | +3,569 | - | A |
| Exon 8 | +3,570 | - | A |
| Exon 8 | +3,571 | - | T |
| Exon 8 | +3,572 | - | T |
| 3' UTR | +5,379 | G | C |
| 3' UTR | +6,438 | C | - |
| 3' UTR | +6,335 | C | - |
| 3' UTR | +6,210 | C | - |
* 21 alignment positions are shown where the nucleotide/gapping (-) of the SULT1A4 region differed from that of the SULT1A3 region. Exon and intron names of the SULT1A3 gene are according to [33]. All nucleotides are numbered relative to the first nucleotide of the start codon, which has a value of +1. There was no position 'zero'. The last nucleotide of the coding sequence occurs at position +3,188. Approximately 3 kb of upstream (5' UTR) and downstream (3' UTR) nucleotides were included in the comparison.
The SULT1A4 gene was located near the junction of two LCRs (Figure 1C). For this reason, it was not clear whether SULT1A4 had a functional promoter. We took a bioinformatic approach to address this question. Expressed sequences ascribed to SULT1A3 were downloaded from the NCBI UniGene website [46]. Each sequence was aligned to SULT1A3 and SULT1A4 genomic regions. Based on the A/G polymorphism at the third position of codon 35, five expressed sequences were assigned to SULT1A4 and nine to SULT1A3 (Table 4). Other expressed sequences were unclassified because they did not overlap codon 35. If the SULT1A4 does exist, there is ample evidence from expressed sequences to make conclusions about its transcriptional activity.
Table 4.
Evidence of SULT1A4 Expression
| Accession | Gene* | Tissue† | Pos. 105 |
| [Genbank:CB147451] | SULT1A4 | Liver | A |
| [Genbank:BF087636] | SULT1A4 | head-neck | A |
| [Genbank:W76361] | SULT1A4 | fetal heart | A |
| [Genbank:W81033] | SULT1A4 | fetal heart | A |
| [Genbank:BC014471] | SULT1A4 | pancreas, epitheliod carcinoma | A |
| [Genbank:F08276] | SULT1A3 | infant brain | G |
| [Genbank:BF814073] | SULT1A3 | Colon | G |
| [Genbank:BG819342] | SULT1A3 | Brain | G |
| [Genbank:BM702343] | SULT1A3 | optic nerve | G |
| [Genbank:BQ436693] | SULT1A3 | large cell carcinoma | G |
| [Genbank:AA323148] | SULT1A3 | cerebellum | G |
| [Genbank:AA325280] | SULT1A3 | cerebellum | G |
| [Genbank:AA349131] | SULT1A3 | fetal adrenal gland | G |
| [Genbank:L25275] | SULT1A3 | placenta | G |
*Gene classifications made according to the nucleotide at position 105 as described in the text. †Tissue descriptions were taken from GenBank accessions.
The codon 35 A/G polymorphism was reported as allelic variation in SULT1A3 by Thomae et al. [33]. It is conceivable that Thomae et al. sequenced both SULT1A3 and SULT1A4 because of the identical sequences surrounding them. In their study, 89% of CAA (1A4) and 11% of CAG (1A3) codon 35 alleles were detected in one population. Why were the frequencies not more equal, as would be expected if SULT1A4 is always CAA and SULT1A3 is CAG? One hypothesis is that SULT1A3 is indeed CAG/CAA polymorphic as reported, while SULT1A4 is always CAA. Interestingly, in both the chimpanzee and gorilla, codon 35 of SULT1A3 is CAA. This implies that the ancestral SULT1A3 gene (prior to duplication) likely had a CAA codon. An A to G transition might have been fixed in a fraction of SULT1A3 genes after the divergence of humans and great apes. If this scenario is true, some transcripts assigned to SULT1A4 on the basis of codon 35 may actually be from individuals expressing the ancestral CAA version of SULT1A3.
SULT1A progenitor locus
We aligned the coding sequences of all available SULT1A genes and used various nucleotide distance metrics and tree-building algorithms to infer the gene tree without constraints. The unconstrained topology placed platypus as the out group, with the placental mammals ordered (ox,(pig,(dog,(rodents)),(rabbit,(primates)))). This differed from the topology inferred while constraining for the most likely relationships among mammalian orders (platypus,((dog,(ox,pig)), ((rabbit,(rodents)), primates))) [47]. We considered both trees, and found that the conclusions drawn throughout the paper were robust with regard to these different topologies. Therefore, only the tree inferred while constraining for most likely relationships among mammalian orders is discussed (Figure 2).
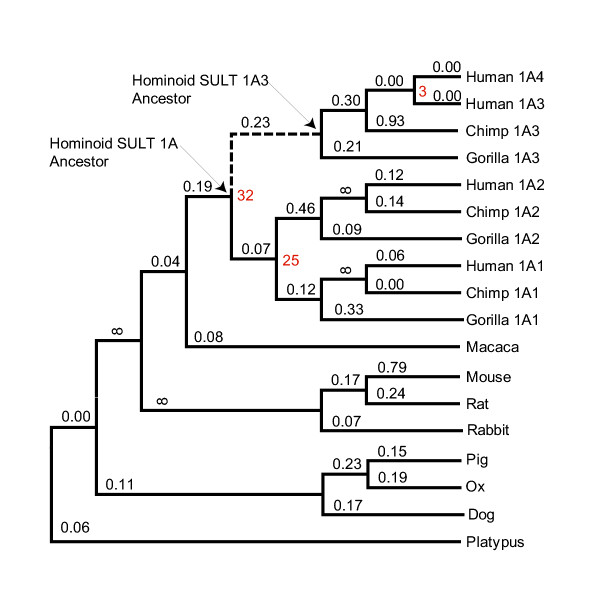
Figure 2.
SULT1A gene tree. TREx upper-limit date estimates of hominoid SULT1A duplications are shown as Ma in red. KA/KS values estimated by PAML are shown above branches. Infinity (8) indicates a non-reliable KA/KS value greater than 100. The 1A3/1A4 branch is dashed. NCBI accession numbers of sequences used: chimpanzee 1A1 [Genbank:BK004887], chimpanzee 1A2 [Genbank:BK004888], chimpanzee 1A3 [Genbank:BK004889], ox [Genbank:U34753], dog [Genbank:AY069922], gorilla 1A1 [Genbank:BK004890], gorilla 1A2 [Genbank:BK004891], gorilla 1A3 [Genbank:BK004892], human 1A1 [Genbank:L19999], human 1A2 [Genbank:U34804], human 1A3 [Genbank:L25275], human 1A4 [Genbank:BK004132], macaque [Genbank:D85514], mouse [Genbank:L02331], pig [Genbank:AY193893], platypus [Genbank:AY044182], rabbit [Genbank:AF360872], rat [Genbank:X52883].
Using the transition redundant exchange (TREx) molecular dating tool [48], we placed upper-limit date estimates at the SULT1A duplication nodes (Figure 2). The SULT1A gene family appears to have expanded ~32, 25, and 3 million years ago (Ma). Therefore, the SULT1A duplications likely occurred after the divergence of hominoids and old world monkeys, with the most recent duplication occurring even after the divergence of humans and great apes.
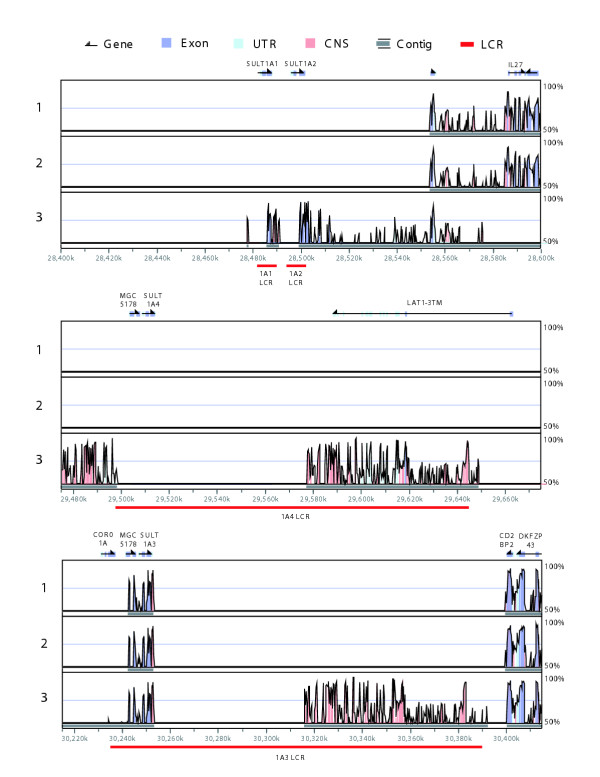
Mouse, rat, and dog genomes each contained a single SULT1A gene. The simplest evolutionary model, therefore, predicted that one of the four hominoid SULT1A loci was orthologous to the rodent SULT1A1 gene. Syntenic regions have conserved order of genetic elements along a chromosomal segment and evidence of synteny between homologous regions is useful for establishing relationships of orthology and paralogy. Human SULT1A1 is most like rodent Sult1a1 in sequence and function and before the advent of whole genome sequencing it was assumed that they were syntenic and therefore orthologous [49]. Complete genome sequences have since emerged and alignments between them are available in the visualization tool for alignments (VISTA) database of human-rodent genome alignments [50,51]. The VISTA database contains mouse-human pairwise alignments and mouse-rat-human multiple alignments. The multiple alignments were found to be more sensitive for predicting true orthologous regions between rodent and human genomes [51]. We searched the VISTA database for evidence of any human-rodent syntenic regions involving the four SULT1A loci. The more sensitive multiple alignments failed to record any human-rodent syntenic regions involving the SULT1A1, SULT1A2, or SULT1A4 loci but detected synteny involving the SULT1A3 loci and both rodent genomes (Figure 3). These results are indicative of a hominoid specific SULT1A family expansion from a progenitor locus corresponding to the genomic region that now contains SULT1A3. The results from the VISTA database were not as clear when the less sensitive alignment method was employed (Figure 3).
Figure 3.
Synteny plots demonstrating SULT1A3 is the progenitor locus of the hominoid SULT1A family. Each box shows a VISTA percent identity plot between a section of the human genome and a section of a rodent genome. Different rodent genomes and alignment methods are indicated as follows: 1 = mouse (Oct. 2003 build) multiple alignment method (MLAGAN); 2 = rat (June 2003 build) multiple alignment method (MLAGAN); 3 = mouse (October 2003 build) pairwise alignment method (LAGAN). Human gene locations are shown above and human chromosome 16 coordinates below.
SULT1A3 and 1A4 LCRs were 99.1% identical overall (Table 1). More careful inspection revealed that the SULT1A3 and 1A4 LCRs were 99.8% identical over the first 120 kbp, but only 98.0% identical over the last 28 kbp (data not shown). This 10-fold difference in percent identities (0.2% vs. 2.0%) suggested that the SULT1A4-containing LCR was produced by two independent duplications. The chimpanzee draft genome assembly aligned with the human genome [52] provides evidence in support of this hypothesis. There is conserved synteny between human and chimp genomes over the last 28 kbp of the 1A4-containing LCR, but no synteny over the first 120 kbp where the SULT1A4 gene is located (data not shown). This finding and the TREx date estimate for the SULT1A3/1A4 duplication event at ~3 Ma indicate that SULT1A4 is a human invention not shared by chimpanzees – our closest living relatives.
It should be noted that the chimpanzee genome assembly is less reliable than the assembly of the human genome. The coverage is significantly lower, and the methods used for assembly are viewed by many as being less reliable, in part because they relied on the human assembly. Other possibilities, less supported the available evidence, should be considered, including deletion of the chimpanzee SULT1A4 gene since the human-chimp divergence, or failure of the draft chimpanzee genome assembly to detect the 120 kbp segment on which the SULT1A4 gene resides.
Adaptive evolution in hominoids
From an analysis of gene sequence change over time, molecular evolutionary theory can generate hypotheses about whether duplication has led to functional redundancy, or whether the duplicates have adopted separate functional roles. If the latter, molecular evolutionary theory can suggest how different the functional roles might be by seeking evidence for positive (adaptive) selection for mutant forms of the native proteins better able to contribute to fitness.
Positive selection of protein function can best be hypothesized when the ratio of non-synonymous (replacement) to synonymous (silent) changes normalized to the number of non-synonymous and synonymous sites throughout the entire gene sequence (KA/KS) is greater than unity. Various models of evolutionary sequence change can be used to calculate these ratios. The simplest assumes a single KA/KS ratio over the entire tree (one-ratio). More complex models assume an independent ratio for each lineage (free-ratios), variable ratios for specific classes of sequence sites (site-specific), or variable ratios for specific classes of sequence sites along specified branches (branch-site specific) [53-57].
Estimating the free parameters in each of these models by the maximum likelihood method [58] enables testing two nested evolutionary models as competing hypotheses, where one model is a special case of another model. The likelihood ratio test (LRT) statistic, which is twice the log likelihood difference between the nested models, is comparable to a χ2 distribution with degrees of freedom equal to the difference in free parameters between the models [59]. Evidence for adaptive evolution typically requires a KA/KS ratio >1 and a statistically significant LRT [60].
We estimated KA/KS ratios for each branch in the 1A gene tree by maximum likelihood with the PAML program [61]. A typical branch in the SULT1A gene tree had a ratio of 0.16, and the ratio was 0.23 on the branch separating extant SULT1A3/1A4 genes from the single SULT1A gene in the last common ancestor of hominoids (Figure 2). Thus, the KA/KS ratio estimated as an average over all sites did not suggest adaptive evolution along the 1A3/1A4 branch.
We then implemented three site-specific and two branch-site evolutionary models that allow KA/KS ratios to vary among sites. Four of the five models estimated that a proportion of sites (2–8%) had KA/KS >1 (Table 5). Each model was statistically better at the 99 or 95% confidence level than the appropriate null model as determined using the LRT statistic (Table 6). Table 6 lists the specific sites that various analyses identified as being potentially involved in positive selection and a subset of these sites that are changing along the SULT1A3/1A4 branch.
Table 5.
Likelihood Values and Parameter Estimates for SULT1A Genes
| Model | f.p.* | Log L | Parameter Estimates† | ||
| One-ratio | 39 | - 5,047.81 | KA/KS = 0.15 | ||
| Free-ratios | 69 | - 5,005.18 | KA/KS ratios for each branch shown in Figure 2 | ||
| Site-specific | |||||
| Neutral | 36 | - 5,021.14 | p0 = 0.48 | (p1 = 0.52) | |
| KA/KS 0 = 0 | KA/KS 1 = 1 | ||||
| Selection | 38 | - 4,884.89 | p0 = 0.41 | p1 = 0.13 | (p2 = 0.46) |
| KA/KS 0 = 0 | KA/KS 1 = 1 | KA/KS2 = 0.19 | |||
| Discrete (k = 2) | 37 | - 4,931.05 | p0 = 0.68 | p1 = 0.32 | |
| KA/KS 0 = 0.06 | KA/KS 1 = 0.77 | ||||
| Discrete (k = 3) | 40 | - 4,880.78 | p0 = 0.59 | p1 = 0.33 | (p2 = 0.08) |
| KA/KS 0 = 0.02 | KA/KS 1 = 0.31 | KA/KS2 = 1.24 | |||
| Beta | 37 | - 4,884.27 | p = 0.27 | q = 1.07 | |
| Beta+selection | 39 | - 4,879.97 | p = 0.30 | q = 1.33 | |
| p0 = 0.98 | p1 = 0.02 | KA/KS = > 2.0 | |||
| Branch-site specific | |||||
| Model A | 38 | - 5,013.29 | p0 = 0.48 | p1 = 0.49 | (p2 = 0.03) |
| KA/KS 0 = 0 | KA/KS 1 = 1 | KA/KS2 = > 2.0 | |||
| Model B | 40 | - 4,886.52 | p0 = 0.68 | p1 = 0.30 | (p2 = 0.02) |
| KA/KS 0 = 0.04 | KA/KS1 = 0.56 | KA/KS2 = > 2.0 | |||
*f.p. is the number of free parameters in each model. †Evidence for positive selection is shown in boldface. Proportions of sites in each KA/KS class, p0, p1, and p2, were not free parameters when in parentheses. Neutral site-specific model assumes two site classes having fixed KA/KS ratios of 0 and 1, with the proportion of sites in each class estimated as free parameters. Selection site-specific model assumes a third proportion of sites with KA/KS estimated from the data. Discrete model assumes 2 or 3 site classes (k) with the proportion of sites, and KA/KS ratios for each proportion, estimated as free parameters. Beta model assumes a beta distribution of sites, where the distribution is shaped by the parameters p and q. Beta+selection model assumes an additional class of sites having a KA/KS ratio estimated from the data. Model A, an extension of the neutral model, assumes a third site class on the 1A3/1A4 branch with KA/KS estimated from the data. Model B, an extension of the discrete model with two site classes (k = 2), also assumes a third site class on the 1A3/1A4 branch with KA/KS estimated from the data.
Table 6.
Likelihood Ratio Tests for the SULT1A Genes
| Selection vs. Neutral | Discrete (k = 3) vs. One-ratio | Beta+selection vs. Beta | Model A vs. Neutral | Model B vs. Discrete (k = 2) | |
| Log L1 | - 4,884.89 | - 4,880.78 | - 4,879.97 | - 5,013.29 | - 4,886.52 |
| Log L0 | - 5,021.14 | - 5,047.81 | - 4,884.27 | - 5,021.14 | - 4,931.05 |
| 2ΔLog L | 272.50 | 334.06 | 8.60 | 15.70 | 89.06 |
| d.f. | 2 | 4 | 2 | 2 | 2 |
| P-value | P < 0.001 | P < 0.001 | 0.01 < P < 0.05 | P < 0.001 | P < 0.001 |
| Positively selected sites* | |||||
| 3 (0.86) | |||||
| 7 (0.63) | |||||
| 30 (0.71) | |||||
| 35 (0.73) | |||||
| 71 (0.88) | |||||
| 77(0.92) | |||||
| 84(0.92) | |||||
| 85(0.95) | |||||
| 86(0.97) | |||||
| 89(0.99) | 89 (0.88) | 89(0.99) | 89(0.99) | ||
| 93(0.97) | |||||
| 105 (0.72) | 105 (0.53) | ||||
| 107 (0.82) | 107 (0.75) | ||||
| 132 (0.87) | 132 (0.78) | ||||
| 143 (0.51) | |||||
| 146 (0.80) | 146(0.97) | ||||
| 222(0.99) | 222 (0.58) | ||||
| 236 (0.53) | |||||
| 245 (0.99) | 245 (0.99) | ||||
| 261 (0.90) | |||||
| 275 (0.70) | |||||
| 288 (0.89) | |||||
| 290 (0.95) | |||||
| 293 (0.72) |
*In parentheses for each positively selected site is the posterior probability that the site belongs to the class with KA/KS >1. Posterior probabilities >90% are bold-face. Positively selected sites also experiencing non-synonymous change on the 1A3/1A4 branch are underlined.
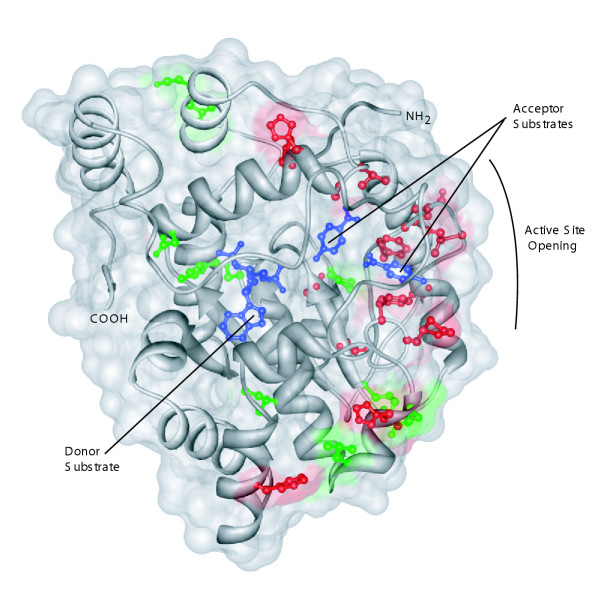
A hypothesis of adaptive change that is based on the use of KA/KSvalues can be strengthened by joining the molecular evolutionary analysis to an analysis based on structural biology [62,63]. Here, we ask whether the sites possibly involved in an episode of sequence evolution are, or are not, randomly distributed in the three dimensional structure. To ask this question, we mapped the sites to the SULT1A structure (Figure 4). Sites holding amino acids whose codons had suffered synonymous replacements were evenly distributed throughout the three-dimensional structure of the enzyme, as expected for silent changes that have no impact on the protein structure and therefore cannot be selected for or against at the protein level (Figure 4). In contrast, sites experiencing non-synonymous replacements during the episode following the duplication that created the new hominoid gene are clustered on the side of the protein near the substrate binding site and the channel through which the substrate gains access to the active site (Figure 4 and Table 7). This strengthens the hypothesis that replacements at the sites are indeed adaptive. The approach employed here based on structural biology does not lend itself easily to evaluation using statistical metrics. Rather, the results are valuable based on the visual impression that they give, and the hypotheses that they generate.
Figure 4.
Non-synonymous changes along the 1A3/1A4 branch cluster on the SULT1A1 enzyme structure [PDB: 1LS6] [26]. Red sites experienced non-synonymous changes, green sites experienced synonymous changes. The PAPS donor substrate and p-nitrophenol acceptor substrates are shown in blue. Image was generated using Chimera [86].
Table 7.
Non-synonymous Changes on the 1A3/1A4 Branch
| Site* | Nucleotide Changes/Site | Hominoid SULT1A Ancestor | Hominoid SULT1A3 Ancestor | |||||
| Residue | PP† | Physicochemical Properties | Residue | PP | Physicochemical Properties | |||
| 44 | 1 | Ser | (1.00) | tiny polar | → | Asn | (1.00) | small polar |
| 71 | 1 | His | (0.99) | non-polar aromatic positive | → | Asn | (1.00) | small polar |
| 76 | 1 | Phe | (1.00) | non-polar aromatic | → | Tyr | (1.00) | aromatic |
| 77 | 2 | Met | (0.99) | non-polar | → | Val | (1.00) | small non-polar aliphatic |
| 84 | 1 | Phe | (1.00) | non-polar aromatic | → | Val | (1.00) | small non-polar aliphatic |
| 85 | 1 | Lys | (1.00) | Positive | → | Asn | (1.00) | small polar |
| 86 | 2 | Val | (0.98) | small non-polar aliphatic | → | Asp | (1.00) | small polar negative |
| 89 | 3 | Ile | (0.98) | non-polar aliphatic | → | Glu | (1.00) | polar negative |
| 93 | 1 | Met | (0.00) | non-polar | → | Leu | (1.00) | non-polar aliphatic |
| 101 | 1 | Ala | (1.00) | tiny non-polar | → | Pro | (1.00) | small |
| 105 | 1 | Leu | (1.00) | non-polar aliphatic | → | Ile | (1.00) | son-polar aliphatic |
| 107 | 1 | Thr | (1.00) | tiny polar | → | Ser | (1.00) | tiny polar |
| 132 | 1 | Ala | (1.00) | tiny non-polar | → | Pro | (1.00) | small |
| 143 | 1 | Tyr | (1.00) | aromatic | → | His | (1.00) | non-polar aromatic positive |
| 144 | 2 | His | (0.99) | non-polar aromatic positive | → | Arg | (1.00) | polar positive |
| 146 | 2 | Ala | (1.00) | tiny non-polar | → | Glu | (1.00) | polar negative |
| 148 | 1 | Val | (1.00) | small non-polar aliphatic | → | Ala | (1.00) | tiny non-polar |
| 222 | 1 | Leu | (0.99) | non-polar aliphatic | → | Phe | (1.00) | non-polar aromatic |
* Sites underlined were identified as being positively selected using the branch-site specific models. †Posterior probabilities that the ancestral residues are correct, conditional on the model of sequence evolution used.
We then examined literature where amino acids had been exchanged between SULT1A1 and SULT1A3. One of the sites, at position 146, identified as being involved in adaptive change, is known to control substrate specificity in SULT1A1 and 1A3 [27-30]. The remaining sites identified are nearby.
Conclusion
An interesting question in post-genomic science asks how to create biological hypotheses from various drafts of whole genome sequences. In generating these hypotheses, it is important to remember that a genomic sequence is itself a hypothesis, about the chemical structure of a small number of DNA molecules. In many cases, biologists wish to move from the genomic sequence, as a hypothesis, to create hypotheses about biological function, without first "proving" the genome sequence hypothesis.
This type of process, building hypotheses upon unproven hypotheses, is actually common in science. In fact, very little of what we believe as fact is actually "proven"; formal proof is virtually unknown in science that involves observation, theory, and experiment. Rather, scientists generally accumulate data until a burden of proof is met, with the standards for that burden being determined by experience within a culture. In general, scientists have an idea in an area as to what level of validation is sufficient to avoid making mistakes an unacceptable fraction of the time, and proceed to that level in their ongoing work, until they encounter a situation where they make a mistake (indicating that a higher standard is needed), or encounter enough examples where a lower standard works, and therefore come to accept a lower standard routinely [64].
Genomics has not yet accumulated enough examples for the culture to define the standards for a burden of proof. In the example discussed here, several lines of reasoning would be applied to analyze the sulfotransferase gene family. First, the fact that the draft genome for chimpanzee contains three paralogs, while the draft genome for human contains four, would normally be interpreted (as it is here) as evidence that an additional duplication occurred in the time since chimpanzee and humans diverged. It would also, however, be consistent with the loss of one of four hypothetical genes present in the common ancestor of chimpanzee and humans in the lineage leading to chimpanzee. Another possibility is that the finishing stages of the chimpanzee genome project will uncover a SULT1A4 gene.
Normally, one would resolve this question using an out group taxon, a species that diverged from the lineage leading to chimpanzee and human before chimpanzee and human themselves diverged. The nearest taxa that might serve as an out group today are, however, rat and mouse. As noted above, they diverged so long ago (ca. 150 MY separates contemporary rodents from contemporary primates) that the comparison provides no information. And no closer out group taxon (e.g., orangutan) has had its genome completely sequenced.
Here, the two hypotheses (duplication versus loss after the chimpanzee-human speciation) are distinguished (to favor post-speciation duplication) based on an analysis of the silent nucleotide substitutions using the TREx metric. The very small number of nucleotide differences separating the SULT1A3 and SULT1A4 coding regions favors the generation of the two paralogs after chimpanzee and human diverged.
This comparison, however, potentially suffers from the statistics of small numbers. The number of differences in the coding region (exactly one) is small. By considering ~10 kbp of non-coding sequence, however, additional differences were found. It is possible that in the assembly of the human genome, a mistake was made that led to the generation of a SULT1A4 region that does not actually exist. In this hypothesis, the ~20 nucleotide differences between the SULT1A3 and SULT1A4 paralogs must be the consequence of allelic polymorphism in the only gene that exists. This is indeed how some of the data were initially interpreted.
Does the preponderance of evidence favor the hypothesis of a very recent duplication to generate a pair of paralogs (SULT1A3 and SULT1A4)? Or does the evidence favor the hypothesis that the SULT1A4 gene is an illusion arising from gene assembly error coupled to sequencing errors and/or allelic variation at ca. 20 sites? The culture does not yet have a standard of assigning the burden of proof here, although a choice of hypothesis based simply on the count of the number of mistakes that would need to have been made to generate each hypothesis (none for the first, at least three for the second) would favor the former over the latter. Thus, perhaps naively, the burden of proof now favors the former, and we may proceed to generate the biological hypothesis on top of the genomic hypothesis.
Here, the hypothesis has immediate pharmacogenomic and genomic disease implications due to the specific functional behaviors of SULT1A enzymes. LCR-mediated genomic rearrangements could disrupt or amplify human SULT1A gene copy number. Given our current environmental exposure to many forms of carcinogens and pro-carcinogens that are either eliminated or activated by SULT enzymes, respectively, it is plain to see how SULT1A copy number variability in the human population could underlie cancer susceptibilities and drug or food allergies.
The majority of evidence indicates that a new transcriptionally active human gene, which we refer to as SULT1A4, was created when 120 kbp of chromosome 16 duplicated after humans diverged from great apes. Thus, SULT1A4, or possibly another gene in this region, is likely to contribute to distinguishing humans from their closest living relatives. It is also conceivable that an advantage in gene regulation, as opposed to an advantage from gene duplication, was the driving force behind the duplication of this 120 kbp segment. While cause and effect are difficult to separate, the examples presented here support the hypothesis that genes whose duplication and recruitment are useful to meet current Darwinian challenges find themselves located on LCRs.
The SULT1A4 gene is currently the most obvious feature of the duplicated region and has been preserved for ~3 MY without significant divergence of its coding sequence. One suggestion for the usefulness of SULT1A4 is that it expanded sulfonating enzymes to new tissues. The SULT1A4 gene is located only 10 kbp upstream from the junction boundary of its LCR and 700 kbp away from the SULT1A3 locus. It is possible, therefore, that promoter elements from the new genomic context of the SULT1A4 gene would drive its expression in tissues where SULT1A3 is not expressed – a hypothesis testable by more careful transcriptional profiling.
Multiple SULT1A genes were apparently useful inventions by our stem hominoid ancestor. Following the duplication of an ancestral primate SULT1A gene ~32 Ma, positive selection acted on a small proportion of sites in one of the duplicates to create the dopamine sulfonating SULT1A3 enzyme. In the example presented here, the evidence of adaptive change at certain sites is corroborated by the ad hoc observation that the sites cluster near the active site of the protein. The well known substrate binding differences at the active sites of SULT1A1/1A2 and SULT1A3 (and now SULT1A4) substantiate these findings.
When studying well-characterized proteins as we have done here, episodes of functional change can be identified by piecing together several lines of evidence. It is not immediately possible, unfortunately, to assemble as much evidence for the majority of proteins in the biosphere. Thus, an important goal in bioinformatics is to recognize the signal of functional change from a restricted amount of evidence. Of the three lines of evidence employed here (codon-based metrics, structural biology, and experimental), structural biology, with its obvious connections to protein function and impending growth from structural genomics initiatives, will probably be the most serviceable source of information for most protein families. This should be especially true for protein families not amenable to experimental manipulation, or with deep evolutionary branches where codon-based metrics are unhelpful. If we are to exploit the incontrovertible link between structure and function, however, new structural bioinformatic tools and databases relating protein structure to sequence changes occurring on individual branches are much needed.
This bioinformatic study makes several clear predictions. First, a PCR experiment targeted against the variation between the hypothetical SULT1A3 and SULT1A4 human genes should establish the existence of the two separate genes. Second, a reverse transcription-PCR experiment would be expected to uncover transcriptional activity for the SULT1A3 and SULT1A4 human genes. Since this paper was submitted, these experiments have been done, and indeed confirm our predictions made without the experimental information [65]. Further, after this manuscript and its computationally-based predictions were submitted for publication, a largely finished sequence for chromosome 16 has emerged [66] that confirms our analysis here in every respect.
Methods
SULT1A LCR family organization in the human genome
The July 2003 human reference genome (based on NCBI build 34) was queried with the SULT1A3 coding region using the BLAST-like alignment tool [39], and search results were visualized in the UCSC genome browser [67]. Two distinct locations on chromosome 16 were identified as equally probable. One location was recognized by NCBI Map Viewer [68] as the SULT1A3 locus. The other locus was dubbed SULT1A4 following conventional naming for this family. The coding sequence and genomic location of SULT1A4, as well as expressed sequences derived from SULT1A4, have been deposited with the GenBank Third Party Annotation database under accession [Genbank:BK004132].
To determine the extent of homology between the SULT1A3 and 1A4 genomic locations, ~500 kbp of sequence surrounding SULT1A3 and ~500 kbp of sequence surrounding SULT1A4 were downloaded from NCBI and compared using PIPMAKER [69,70]. Before submitting to PIPMAKER, high-copy repeats in one of the sequences were masked with REPEATMASKER [71].
The Human Recent Segmental Duplication Page [72] was consulted to identify other LCRs related to the SULT1A3-containing LCR. Chromosomal coordinates of 30 SULT1A3-related LCRs were arranged in GFF format and submitted to the UCSC genome browser as a custom track. Sequences corresponding to the chromosomal coordinates of the 30 LCRs were then downloaded from the UCSC genome browser and parsed into separate files. Each LCR was aligned with the SULT1A3-containing LCR using MULTIPIPMAKER [73]. The Segmental Duplication Database [74] was used to examine the duplication status of each gene in the cytosolic SULT super family.
The bacterial artificial chromosome contigs supporting each member of the SULT1A LCR family, and the known genes within each LCR, were inspected with the UCSC genome browser [75]. The DNA sequences of nine bacterial artificial chromosome contigs supporting the SULT1A4 genomic region [NCBI Clone Registry: CTC-446K24, CTC-529P19, CTC-576G12, CTD-2253D5, CTD-2324H19, CTD-2383K24, CTD-2523J12, CTD-3191G16, RP11-28A6] and seven contigs supporting the SULT1A3 region [NCBI Clone Registry: CTD-2548B1, RP11-69O13, RP11-164O24, RP11-455F5, RP11-612G2, RP11-787F23, RP11-828J20] were downloaded from the UCSC genome browser website.
Phylogenetics
The MASTERCATALOG was used for performing initial inspections of the SULT gene family and for delivering a non-redundant collection of SULT1A genes. Additional SULT1A ORFs were extracted from gorilla working draft contigs [Genbank:AC145177] (SULT1A1 and 1A2) and [Genbank:AC145040] (SULT1A3) and chimpanzee whole genome shotgun sequences [Genbank:AACZ01082721] (SULT1A1), [Genbank:AADA01101065] (SULT1A2), and [Genbank:AACZ01241716] (SULT1A3) using PIPMAKER exon analysis. These new SULT1A genes have been deposited with the GenBank Third Party Annotation database under accession numbers [Genbank:BK004887-BK004892]. DNA sequences were aligned with CLUSTAL W [76]. The multiple sequence alignment used in all phylogenetic analyses is presented as supplementary data [see Additional file 1]. Pairwise distances were estimated under various distance metrics (Jukes-Cantor, Kimura 2-parameter, and Tamura-Nei) that account for among-site rate variation using the gamma distribution [77]. Phylogenies were inferred using both neighbor-joining and minimum evolution tree-building algorithms under the following constraints ((((primates), rodents), (artiodactyls, carnivores)), platypus). Phylogenetic analyses were conducted using the MEGA2 v2.1 [78] and PAUP* v4.0 [79] software packages.
Parameter estimates of site class proportions, KA/KS ratios, base frequencies, codon frequencies, branch lengths, and the transition/transversion bias were determined by the maximum likelihood method with the PAML v3.14 program [61]. Positively selected sites, posterior probabilities, and marginal reconstructions of ancestral sequences were also determined using PAML. Sites experiencing synonymous changes along the 1A3/1A4 branch were recorded by hand from an ancestral sequence alignment.
Molecular dating
Starting with aligned DNA sequences, the number (n) of two-fold redundant codons (Lys, Glu, Gln, Cys, Asp, Phe, His, Asn, Tyr) where the amino acid had been conserved in pairs of aligned sequences, and the number of these codons where the third position was identically conserved (c) were counted by the DARWIN bioinformatics platform [80,81]. The pairwise matrix of n and c values for all SULT1A genes is presented as supplementary data [see Additional file 2]. The c/n quotient equals the fraction of identities (f2) in this system, or the transition redundant exchange (TREx) value [48]. TREx values were converted to TREx distances (kt values) by the following equation: kt = - ln [(f2 - Eq.) / (1 - Eq.)], where k is the rate constant of nucleotide substitution, t is the time separating the two sequences, and Eq. is the equilibrium state of the TREx value [48]. The equilibrium state of the TREx value was estimated as 0.54 for primates, and the rate constant at two-fold redundant sites where the amino acid was conserved (k) was estimated as 3.0 × 10 -9 changes/site/year for placental mammals (T. Li, D. Caraco, E. Gaucher, D. Liberles, M. Thomson, and S.A.B., unpublished data). These estimates were determined by sampling all pairs of mouse:rat and mouse:human orthologs in the public databases and following accepted placental mammal phylogenies and divergence times [82,83]. Therefore, the date estimates reported are based on the contentious assumptions that (i) rates are constant at the third position of two-fold redundant codons across the genome, (ii) the fossil calibration points are correct, and (iii) the mammalian phylogeny used is correct. Branch lengths were obtained for the constrained tree topology from the pairwise matrix of TREx distances using PAUP* v4.0. Upper-limit date estimates for nodes corresponding to SULT1A duplication events were obtained by summing the longest path of branches leading to a node and dividing that value by k.
Comparative genomics
Human-chimpanzee genome alignments were inspected at the UCSC Genome Browser. Human-rodent genome alignments were examined with the VISTA Genome Browser [50,51,84]. VISTA default parameters were used for drawing curves. Alignments constructed using both the pairwise method (LAGAN) and the multiple alignment method (MLAGAN) between the human genome builds frozen on April 2003 or July 2003 and both rodent genomes were inspected.
Transcriptional profiling
All expressed sequences ascribed to SULT1A3 were downloaded from NCBI UniGene [85] and aligned with SULT1A3 and SULT1A4 genomic regions using PIPMAKER. Alignments were inspected for the polymorphism in codon 35, as well as any other potential patterns, to determine whether they were derived from SULT1A3 or SULT1A4.
Abbreviations
kbp (kilobase pairs); LCR (low copy repeat); Mbp (million base pairs); Ma (million years ago); ORF (open reading frame); SULT (sulfotransferase); TREx (transition redundant exchange); VISTA (visualization tool for alignments).
Authors' contributions
M.E.B carried out the study and drafted the manuscript. S.A.B participated in designing the study and preparing the manuscript.
Supplementary Material
Multiple sequence alignment of SULT1A genes.Multiple sequence alignment of SULT1A genes used in all phylogenetic analyses. Characters conserved in all sequences are indicated with asterisks.
Pairwise n and c values for SULT1A genes. Pairwise n and c values between SULT1A genes. The names of the sequences are the row-headers and the column-headers. Lower triangular matrix contains n values, and upper triangular matrix contains c values.
Acknowledgments
Acknowledgements
We thank the Foundation for Applied Molecular Evolution for providing computational resources. This work was supported by grant DOD 6402-202-L0-G from the USF Center for Biological Defense, and by an NIH post-doctoral fellowship to M.E.B.
Contributor Information
Michael E Bradley, Email: mebradley@chem.ufl.edu.
Steven A Benner, Email: benner@chem.ufl.edu.
References
- Lander ES, Linton LM, Birren B, Nusbaum C, Zody MC, Baldwin J, Devon K, Dewar K, Doyle M, FitzHugh W, Funke R, Gage D, Harris K, Heaford A, Howland J, Kann L, Lehoczky J, LeVine R, McEwan P, McKernan K, Meldrim J, Mesirov JP, Miranda C, Morris W, Naylor J, Raymond C, Rosetti M, Santos R, Sheridan A, Sougnez C, Stange-Thomann N, Stojanovic N, Subramanian A, Wyman D, Rogers J, Sulston J, Ainscough R, Beck S, Bentley D, Burton J, Clee C, Carter N, Coulson A, Deadman R, Deloukas P, Dunham A, Dunham I, Durbin R, French L, Grafham D, Gregory S, Hubbard T, Humphray S, Hunt A, Jones M, Lloyd C, McMurray A, Matthews L, Mercer S, Milne S, Mullikin JC, Mungall A, Plumb R, Ross M, Shownkeen R, Sims S, Waterston RH, Wilson RK, Hillier LW, McPherson JD, Marra MA, Mardis ER, Fulton LA, Chinwalla AT, Pepin KH, Gish WR, Chissoe SL, Wendl MC, Delehaunty KD, Miner TL, Delehaunty A, Kramer JB, Cook LL, Fulton RS, Johnson DL, Minx PJ, Clifton SW, Hawkins T, Branscomb E, Predki P, Richardson P, Wenning S, Slezak T, Doggett N, Cheng JF, Olsen A, Lucas S, Elkin C, Uberbacher E, Frazier M, Gibbs RA, Muzny DM, Scherer SE, Bouck JB, Sodergren EJ, Worley KC, Rives CM, Gorrell JH, Metzker ML, Naylor SL, Kucherlapati RS, Nelson DL, Weinstock GM, Sakaki Y, Fujiyama A, Hattori M, Yada T, Toyoda A, Itoh T, Kawagoe C, Watanabe H, Totoki Y, Taylor T, Weissenbach J, Heilig R, Saurin W, Artiguenave F, Brottier P, Bruls T, Pelletier E, Robert C, Wincker P, Smith DR, Doucette-Stamm L, Rubenfield M, Weinstock K, Lee HM, Dubois J, Rosenthal A, Platzer M, Nyakatura G, Taudien S, Rump A, Yang H, Yu J, Wang J, Huang G, Gu J, Hood L, Rowen L, Madan A, Qin S, Davis RW, Federspiel NA, Abola AP, Proctor MJ, Myers RM, Schmutz J, Dickson M, Grimwood J, Cox DR, Olson MV, Kaul R, Shimizu N, Kawasaki K, Minoshima S, Evans GA, Athanasiou M, Schultz R, Roe BA, Chen F, Pan H, Ramser J, Lehrach H, Reinhardt R, McCombie WR, de la Bastide M, Dedhia N, Blocker H, Hornischer K, Nordsiek G, Agarwala R, Aravind L, Bailey JA, Bateman A, Batzoglou S, Birney E, Bork P, Brown DG, Burge CB, Cerutti L, Chen HC, Church D, Clamp M, Copley RR, Doerks T, Eddy SR, Eichler EE, Furey TS, Galagan J, Gilbert JG, Harmon C, Hayashizaki Y, Haussler D, Hermjakob H, Hokamp K, Jang W, Johnson LS, Jones TA, Kasif S, Kaspryzk A, Kennedy S, Kent WJ, Kitts P, Koonin EV, Korf I, Kulp D, Lancet D, Lowe TM, McLysaght A, Mikkelsen T, Moran JV, Mulder N, Pollara VJ, Ponting CP, Schuler G, Schultz J, Slater G, Smit AF, Stupka E, Szustakowski J, Thierry-Mieg D, Thierry-Mieg J, Wagner L, Wallis J, Wheeler R, Williams A, Wolf YI, Wolfe KH, Yang SP, Yeh RF, Collins F, Guyer MS, Peterson J, Felsenfeld A, Wetterstrand KA, Patrinos A, Morgan MJ, Szustakowki J, de Jong P, Catanese JJ, Osoegawa K, Shizuya H, Choi S, Chen YJ. Initial sequencing and analysis of the human genome. Nature. 2001;409:860–921. doi: 10.1038/35057062. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheung VG, Nowak N, Jang W, Kirsch IR, Zhao S, Chen XN, Furey TS, Kim UJ, Kuo WL, Olivier M, Conroy J, Kasprzyk A, Massa H, Yonescu R, Sait S, Thoreen C, Snijders A, Lemyre E, Bailey JA, Bruzel A, Burrill WD, Clegg SM, Collins S, Dhami P, Friedman C, Han CS, Herrick S, Lee J, Ligon AH, Lowry S, Morley M, Narasimhan S, Osoegawa K, Peng Z, Plajzer-Frick I, Quade BJ, Scott D, Sirotkin K, Thorpe AA, Gray JW, Hudson J, Pinkel D, Ried T, Rowen L, Shen-Ong GL, Strausberg RL, Birney E, Callen DF, Cheng JF, Cox DR, Doggett NA, Carter NP, Eichler EE, Haussler D, Korenberg JR, Morton CC, Albertson D, Schuler G, de Jong PJ, Trask BJ. Integration of cytogenetic landmarks into the draft sequence of the human genome. Nature. 2001;409:953–958. doi: 10.1038/35057192. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eichler EE. Segmental duplications: what's missing, misassigned, and misassembled--and should we care? Genome Res. 2001;11:653–656. doi: 10.1101/gr.188901. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bailey JA, Yavor AM, Massa HF, Trask BJ, Eichler EE. Segmental duplications: organization and impact within the current human genome project assembly. Genome Res. 2001;11:1005–1017. doi: 10.1101/gr.GR-1871R. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stankiewicz P, Lupski JR. Genome architecture, rearrangements and genomic disorders. Trends Genet. 2002;18:74–82. doi: 10.1016/S0168-9525(02)02592-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emanuel BS, Shaikh TH. Segmental duplications: an 'expanding' role in genomic instability and disease. Nat Rev Genet. 2001;2:791–800. doi: 10.1038/35093500. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singleton AB, Farrer M, Johnson J, Singleton A, Hague S, Kachergus J, Hulihan M, Peuralinna T, Dutra A, Nussbaum R, Lincoln S, Crawley A, Hanson M, Maraganore D, Adler C, Cookson MR, Muenter M, Baptista M, Miller D, Blancato J, Hardy J, Gwinn-Hardy K. alpha-Synuclein locus triplication causes Parkinson's disease. Science. 2003;302:841. doi: 10.1126/science.1090278. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horvath JE, Gulden CL, Bailey JA, Yohn C, McPherson JD, Prescott A, Roe BA, de Jong PJ, Ventura M, Misceo D, Archidiacono N, Zhao S, Schwartz S, Rocchi M, Eichler EE. Using a pericentromeric interspersed repeat to recapitulate the phylogeny and expansion of human centromeric segmental duplications. Mol Biol Evol. 2003;20:1463–1479. doi: 10.1093/molbev/msg158. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falany CN. Enzymology of human cytosolic sulfotransferases. FASEB J. 1997;11:206–216. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.11.4.9068609. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller JA. Sulfonation in chemical carcinogenesis--history and present status. Chem Biol Interact. 1994;92:329–341. doi: 10.1016/0009-2797(94)90074-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glatt H. Sulfation and sulfotransferases 4: bioactivation of mutagens via sulfation. FASEB J. 1997;11:314–321. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.11.5.9141497. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coughtrie MW. Sulfation through the looking glass--recent advances in sulfotransferase research for the curious. Pharmacogenomics J. 2002;2:297–308. doi: 10.1038/sj.tpj.6500117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freimuth RR, Wiepert M, Chute CG, Wieben ED, Weinshilboum RM. Human cytosolic sulfotransferase database mining: identification of seven novel genes and pseudogenes. Pharmacogenomics J. 2004;4:54–65. doi: 10.1038/sj.tpj.6500223. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhu X, Veronese ME, Sansom LN, McManus ME. Molecular characterisation of a human aryl sulfotransferase cDNA. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1993;192:671–676. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1993.1467. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilborn TW, Comer KA, Dooley TP, Reardon IM, Heinrikson RL, Falany CN. Sequence analysis and expression of the cDNA for the phenol-sulfating form of human liver phenol sulfotransferase. Mol Pharmacol. 1993;43:70–77. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hwang SR, Kohn AB, Hook VY. Molecular cloning of an isoform of phenol sulfotransferase from human brain hippocampus. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1995;207:701–707. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1995.1244. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ozawa S, Nagata K, Shimada M, Ueda M, Tsuzuki T, Yamazoe Y, Kato R. Primary structures and properties of two related forms of aryl sulfotransferases in human liver. Pharmacogenetics. 1995;5:S135–40. doi: 10.1097/00008571-199512001-00015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhu X, Veronese ME, Iocco P, McManus ME. cDNA cloning and expression of a new form of human aryl sulfotransferase. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 1996;28:565–571. doi: 10.1016/1357-2725(95)00164-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reiter C, Mwaluko G, Dunnette J, Van Loon J, Weinshilboum R. Thermolabile and thermostable human platelet phenol sulfotransferase. Substrate specificity and physical separation. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1983;324:140–147. doi: 10.1007/BF00497020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernier F, Lopez Solache I, Labrie F, Luu-The V. Cloning and expression of cDNA encoding human placental estrogen sulfotransferase. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1994;99:R11–5. doi: 10.1016/0303-7207(94)90159-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhu X, Veronese ME, Bernard CC, Sansom LN, McManus ME. Identification of two human brain aryl sulfotransferase cDNAs. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1993;195:120–127. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1993.2018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood TC, Aksoy IA, Aksoy S, Weinshilboum RM. Human liver thermolabile phenol sulfotransferase: cDNA cloning, expression and characterization. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1994;198:1119–1127. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1994.1159. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones AL, Hagen M, Coughtrie MW, Roberts RC, Glatt H. Human platelet phenolsulfotransferases: cDNA cloning, stable expression in V79 cells and identification of a novel allelic variant of the phenol-sulfating form. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1995;208:855–862. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1995.1414. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bidwell LM, McManus ME, Gaedigk A, Kakuta Y, Negishi M, Pedersen L, Martin JL. Crystal structure of human catecholamine sulfotransferase. J Mol Biol. 1999;293:521–530. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1999.3153. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dajani R, Cleasby A, Neu M, Wonacott AJ, Jhoti H, Hood AM, Modi S, Hersey A, Taskinen J, Cooke RM, Manchee GR, Coughtrie MW. X-ray crystal structure of human dopamine sulfotransferase, SULT1A3. Molecular modeling and quantitative structure-activity relationship analysis demonstrate a molecular basis for sulfotransferase substrate specificity. J Biol Chem. 1999;274:37862–37868. doi: 10.1074/jbc.274.53.37862. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gamage NU, Duggleby RG, Barnett AC, Tresillian M, Latham CF, Liyou NE, McManus ME, Martin JL. Structure of a human carcinogen-converting enzyme, SULT1A1. Structural and kinetic implications of substrate inhibition. J Biol Chem. 2003;278:7655–7662. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M207246200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dajani R, Hood AM, Coughtrie MW. A single amino acid, glu146, governs the substrate specificity of a human dopamine sulfotransferase, SULT1A3. Mol Pharmacol. 1998;54:942–948. doi: 10.1124/mol.54.6.942. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brix LA, Barnett AC, Duggleby RG, Leggett B, McManus ME. Analysis of the substrate specificity of human sulfotransferases SULT1A1 and SULT1A3: site-directed mutagenesis and kinetic studies. Biochemistry. 1999;38:10474–10479. doi: 10.1021/bi990795q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brix LA, Duggleby RG, Gaedigk A, McManus ME. Structural characterization of human aryl sulphotransferases. Biochem J. 1999;337:337–343. doi: 10.1042/0264-6021:3370337. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brix LA, Nicoll R, Zhu X, McManus ME. Structural and functional characterisation of human sulfotransferases. Chem Biol Interact. 1998;109:123–127. doi: 10.1016/S0009-2797(97)00126-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raftogianis RB, Wood TC, Otterness DM, Van Loon JA, Weinshilboum RM. Phenol sulfotransferase pharmacogenetics in humans: association of common SULT1A1 alleles with TS PST phenotype. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1997;239:298–304. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1997.7466. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raftogianis RB, Wood TC, Weinshilboum RM. Human phenol sulfotransferases SULT1A2 and SULT1A1: genetic polymorphisms, allozyme properties, and human liver genotype-phenotype correlations. Biochem Pharmacol. 1999;58:605–616. doi: 10.1016/S0006-2952(99)00145-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomae BA, Rifki OF, Theobald MA, Eckloff BW, Wieben ED, Weinshilboum RM. Human catecholamine sulfotransferase (SULT1A3) pharmacogenetics: functional genetic polymorphism. J Neurochem. 2003;87:809–819. doi: 10.1046/j.1471-4159.2003.02027.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saintot M, Malaveille C, Hautefeuille A, Gerber M. Interactions between genetic polymorphism of cytochrome P450-1B1, sulfotransferase 1A1, catechol-o-methyltransferase and tobacco exposure in breast cancer risk. Int J Cancer. 2003;107:652–657. doi: 10.1002/ijc.11432. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu MT, Wang YT, Ho CK, Wu DC, Lee YC, Hsu HK, Kao EL, Lee JM. SULT1A1 polymorphism and esophageal cancer in males. Int J Cancer. 2003;103:101–104. doi: 10.1002/ijc.10805. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zheng W, Xie D, Cerhan JR, Sellers TA, Wen W, Folsom AR. Sulfotransferase 1A1 polymorphism, endogenous estrogen exposure, well-done meat intake, and breast cancer risk. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2001;10:89–94. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King RS, Teitel CH, Kadlubar FF. In vitro bioactivation of N-hydroxy-2-amino-alpha-carboline. Carcinogenesis. 2000;21:1347–1354. doi: 10.1093/carcin/21.7.1347. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisen JA, Fraser CM. Phylogenomics: intersection of evolution and genomics. Science. 2003;300:1706–1707. doi: 10.1126/science.1086292. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kent WJ. BLAT--the BLAST-like alignment tool. Genome Res. 2002;12:656–664. doi: 10.1101/gr.229202. 10.1101/gr.229202. Article published online before March 2002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheung J, Estivill X, Khaja R, MacDonald JR, Lau K, Tsui LC, Scherer SW. Genome-wide detection of segmental duplications and potential assembly errors in the human genome sequence. Genome Biol. 2003;4:R25. doi: 10.1186/gb-2003-4-4-r25. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson ME, Viggiano L, Bailey JA, Abdul-Rauf M, Goodwin G, Rocchi M, Eichler EE. Positive selection of a gene family during the emergence of humans and African apes. Nature. 2001;413:514–519. doi: 10.1038/35097067. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eichler EE, Johnson ME, Alkan C, Tuzun E, Sahinalp C, Misceo D, Archidiacono N, Rocchi M. Divergent origins and concerted expansion of two segmental duplications on chromosome 16. J Hered. 2001;92:462–468. doi: 10.1093/jhered/92.6.462. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonifas JM, Morley BJ, Oakey RE, Kan YW, Epstein EHJ. Cloning of a cDNA for steroid sulfatase: frequent occurrence of gene deletions in patients with recessive X chromosome-linked ichthyosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987;84:9248–9251. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.24.9248. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yen PH, Li XM, Tsai SP, Johnson C, Mohandas T, Shapiro LJ. Frequent deletions of the human X chromosome distal short arm result from recombination between low copy repetitive elements. Cell. 1990;61:603–610. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90472-Q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loftus BJ, Kim UJ, Sneddon VP, Kalush F, Brandon R, Fuhrmann J, Mason T, Crosby ML, Barnstead M, Cronin L, Deslattes Mays A, Cao Y, Xu RX, Kang HL, Mitchell S, Eichler EE, Harris PC, Venter JC, Adams MD. Genome duplications and other features in 12 Mb of DNA sequence from human chromosome 16p and 16q. Genomics. 1999;60:295–308. doi: 10.1006/geno.1999.5927. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pontius JU. Wagner L. GD S. The NCBI Handbook. Bethesda, National Center for Biotechnology Information; 2003. UniGene: a unified view of the transcriptome. pp. 21.1–21.12. [Google Scholar]
- Murphy WJ, Eizirik E, O'Brien SJ, Madsen O, Scally M, Douady CJ, Teeling E, Ryder OA, Stanhope MJ, de Jong WW, Springer MS. Resolution of the early placental mammal radiation using Bayesian phylogenetics. Science. 2001;294:2348–2351. doi: 10.1126/science.1067179. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benner SA. Interpretive proteomics--finding biological meaning in genome and proteome databases. Adv Enzyme Regul. 2003;43:271–359. doi: 10.1016/S0065-2571(02)00024-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinshilboum RM, Otterness DM, Aksoy IA, Wood TC, Her C, Raftogianis RB. Sulfation and sulfotransferases 1: Sulfotransferase molecular biology: cDNAs and genes. Faseb J. 1997;11:3–14. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Couronne O, Poliakov A, Bray N, Ishkhanov T, Ryaboy D, Rubin E, Pachter L, Dubchak I. Strategies and tools for whole-genome alignments. Genome Res. 2003;13:73–80. doi: 10.1101/gr.762503. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brudno M, Poliakov A, Salamov A, Cooper GM, Sidow A, Rubin EM, Solovyev V, Batzoglou S, Dubchak I. Automated whole-genome multiple alignment of rat, mouse, and human. Genome Res. 2004;14:685–692. doi: 10.1101/gr.2067704. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chimpanzee Genome Project http://www.nhgri.nih.gov/11509418
- Goldman N, Yang Z. A codon-based model of nucleotide substitution for protein-coding DNA sequences. Mol Biol Evol. 1994;11:725–736. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a040153. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muse SV, Gaut BS. A likelihood approach for comparing synonymous and nonsynonymous nucleotide substitution rates, with application to the chloroplast genome. Mol Biol Evol. 1994;11:715–724. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a040152. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang Z, Nielsen R. Codon-substitution models for detecting molecular adaptation at individual sites along specific lineages. Mol Biol Evol. 2002;19:908–917. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a004148. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen R, Yang Z. Likelihood models for detecting positively selected amino acid sites and applications to the HIV-1 envelope gene. Genetics. 1998;148:929–936. doi: 10.1093/genetics/148.3.929. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang Z, Nielsen R, Goldman N, Pedersen AM. Codon-substitution models for heterogeneous selection pressure at amino acid sites. Genetics. 2000;155:431–449. doi: 10.1093/genetics/155.1.431. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felsenstein J. Evolutionary trees from DNA sequences: a maximum likelihood approach. J Mol Evol. 1981;17:368–376. doi: 10.1007/BF01734359. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huelsenbeck JP, Rannala B. Phylogenetic methods come of age: testing hypotheses in an evolutionary context. Science. 1997;276:227–232. doi: 10.1126/science.276.5310.227. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bielawski JP, Yang Z. Maximum likelihood methods for detecting adaptive evolution after gene duplication. J Struct Funct Genomics. 2003;3:201–212. doi: 10.1023/A:1022642807731. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang Z. PAML: a program package for phylogenetic analysis by maximum likelihood. Comput Appl Biosci. 1997;13:555–556. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/13.5.555. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaucher EA, Das UK, Miyamoto MM, Benner SA. The crystal structure of eEF1A refines the functional predictions of an evolutionary analysis of rate changes among elongation factors. Mol Biol Evol. 2002;19:569–573. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a004113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaucher EA, Miyamoto MM, Benner SA. Evolutionary, structural and biochemical evidence for a new interaction site of the leptin obesity protein. Genetics. 2003;163:1549–1553. doi: 10.1093/genetics/163.4.1549. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galison PL. How experiments end. Chicago, University of Chicago Press; 1987. p. xii, 330 p.. [Google Scholar]
- Hildebrandt MA, Salavaggione OE, Martin YN, Flynn HC, Jalal S, Wieben ED, Weinshilboum RM. Human SULT1A3 pharmacogenetics: gene duplication and functional genomic studies. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2004;321:870–878. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2004.07.038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finishing the euchromatic sequence of the human genome. Nature. 2004;431:931–945. doi: 10.1038/nature03001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kent WJ, Sugnet CW, Furey TS, Roskin KM, Pringle TH, Zahler AM, Haussler D. The human genome browser at UCSC. Genome Res. 2002;12:996–1006. doi: 10.1101/gr.229102. 10.1101/gr.229102. Article published online before print in May 2002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NCBI MapVeiwer http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/mapview
- Schwartz S, Zhang Z, Frazer KA, Smit A, Riemer C, Bouck J, Gibbs R, Hardison R, Miller W. PipMaker--a web server for aligning two genomic DNA sequences. Genome Res. 2000;10:577–586. doi: 10.1101/gr.10.4.577. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PipMaker and MultiPipMaker http://bio.cse.psu.edu/pipmaker
- Repeat Masker http://repeatmasker.genome.washington.edu
- Human Recent Segmental Duplication Page http://chr7.ocgc.ca/humandup
- Schwartz S, Elnitski L, Li M, Weirauch M, Riemer C, Smit A, Green ED, Hardison RC, Miller W. MultiPipMaker and supporting tools: Alignments and analysis of multiple genomic DNA sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 2003;31:3518–3524. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkg579. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segmental Duplication Database http://humanparalogy.gene.cwru.edu
- UCSC Genome Bioinformatics http://genome.ucsc.edu
- Thompson JD, Higgins DG, Gibson TJ. CLUSTAL W: improving the sensitivity of progressive multiple sequence alignment through sequence weighting, position-specific gap penalties and weight matrix choice. Nucleic Acids Res. 1994;22:4673–4680. doi: 10.1093/nar/22.22.4673. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang Z. Among-site rate variation and its impact on phylogenetic analyses. Trends in Ecology and Evolution. 1996;11:367–372. doi: 10.1016/0169-5347(96)10041-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumar S, Tamura K, Jakobsen IB, Nei M. MEGA2: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis software. Bioinformatics. 2001;17:1244–1245. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/17.12.1244. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swofford DL. PAUP 4.0 - Phylogenetic Analysis Using Parsimony (And Other Methods) Sunderland, MA, Sinauer Associates; 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Gonnet GH, Benner SA. Technical Report 154 Department Informatik. Zurich, Swiss Federal Institute of Technology; 1991. Computational Biochemistry Research at ETH. [Google Scholar]
- DARWIN's Homepage http://cbrg.inf.ethz.ch/Darwin/index.html
- Liu FG, Miyamoto MM, Freire NP, Ong PQ, Tennant MR, Young TS, Gugel KF. Molecular and morphological supertrees for eutherian (placental) mammals. Science. 2001;291:1786–1789. doi: 10.1126/science.1056346. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Springer MS, Murphy WJ, Eizirik E, O'Brien SJ. Placental mammal diversification and the Cretaceous-Tertiary boundary. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003;100:1056–1061. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0334222100. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VISTA Genome Browser http://pipeline.lbl.gov
- NCBI UniGene http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/UniGene
- Huang CC, Couch GS, Pettersen EF, Ferrin TE. Chimera: an extensible molecular modeling application constructed using standard components. Pacific Symposium on Biocomputing. 1996;1:724. [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Multiple sequence alignment of SULT1A genes.Multiple sequence alignment of SULT1A genes used in all phylogenetic analyses. Characters conserved in all sequences are indicated with asterisks.
Pairwise n and c values for SULT1A genes. Pairwise n and c values between SULT1A genes. The names of the sequences are the row-headers and the column-headers. Lower triangular matrix contains n values, and upper triangular matrix contains c values.