Abstract
The future of nanomedicines in oncology requires leveraging more than just the passive drug accumulation in tumors through the enhanced permeability and retention effect. Promising results combining mild hyperthermia (HT) with lyso-thermosensitive liposomal doxorubicin (LTSL-DOX) has led to improved drug delivery and potent antitumor effects in pre-clinical studies. The ultimate patient benefit from these treatments can only be realized when robust methods of HT can be achieved clinically. One of the most promising methods of non-invasive HT is the use of focused ultrasound (FUS) with MRI thermometry for anatomical targeting and feedback. MRI-guided focused ultrasound (MRgFUS) is limited by respiratory motion and large blood vessel cooling. In order to translate exciting pre-clinical results to the clinic, novel heating approaches capable of overcoming the limitations on clinical MRgFUS+HT must be tested and evaluated on their ability to locally release drug from LTSL-DOX.
Methods: In this work, a new system is described to integrate focused ultrasound (FUS) into a two-photon microscopy (2PM) setting to image the release of drug from LTSL-DOX in real-time during FUS+HT in vivo. A candidate scheme for overcoming the limitations of respiratory motion and large blood vessel cooling during MRgFUS+HT involves applying FUS+HT to 42°C in short ~30s bursts. The spatiotemporal drug release pattern from LTSL-DOX as a result is quantified using 2PM and compared against continuous (3.5min and 20min at 42°C) FUS+HT schemes and unheated controls.
Results: It was observed for the first time in vivo that these short duration temperature elevations could produce substantial drug release from LTSL-DOX. Ten 30s bursts of FUS+HT was able to achieve almost half of the interstitial drug concentration as 20min of continuous FUS+HT. There was no significant difference between the intravascular area under the concentration-time curve for ten 30s bursts of FUS+HT and 3.5min of continuous FUS+HT.
Conclusion: We have successfully combined 2PM with FUS+HT for imaging the release of DOX from LTSL-DOX in vivo in real-time, which will permit the investigation of FUS+HT heating schemes to improve drug delivery from LTSL-DOX. We have evaluated the ability to release DOX in short 30s FUS+HT bursts to 42°C as a method to overcome limitations on clinical MRgFUS+HT and have found that such exposures are capable of releasing measurable amounts of drug. Such an exposure has the potential to overcome limitations that hamper conventional MRgFUS+HT treatments in targets that are associated with substantial tissue motion.
Keywords: Focused ultrasound hyperthermia, two-photon microscopy, thermosensitive liposomes, heat-targeted cancer therapy, doxorubicin.
Introduction
Decades of intensive research on nanomedicines for oncology have produced a wealth of preclinical data, along with a number of clinical formulations. The most prevalent of these are based on liposomal platforms which due to their small sizes and long circulation times result in preferential accumulation within tumor tissue. Nanomedicines have however come under increasing scrutiny for relying heavily on the enhanced permeability and retention (EPR) effect 1-3 in order to achieve localized delivery to solid tumors and improve patient outcome. The EPR effect has been shown in human tumors 4, but the heterogeneity of this effect between patients and cancer types makes it unreliable in and of itself as the primary mechanism through which to leverage targeted drug delivery. There remains a strong need to improve the clinical outcome of nanoparticle therapeutics 5 through the development of novel strategies capable of overcoming the many obstacles related to tumor drug delivery 6, 7.
A significant advance to passively-targeted long-circulating liposomes 8-10 has been the development of temperature sensitive liposome formulations, first suggested by Yatvin et al. 11. These liposomes can be loaded with anticancer drugs such as anthracycline doxorubicin (DOX) 12, 13 or platinum-based agents such as cisplatin 14, 15 and their content release is triggered by the local application of heat within the hyperthermia (HT) regime (39-45°C). Mild HT treatments have the additional benefit of increasing the size of endothelial pores 16, increasing blood flow 17-19 and allowing increased liposome extravasation 20, 21 all of which increase the amount of bioavailable drug in the tumor. Furthermore, it has been shown that the toxicity of chemotherapy is enhanced at elevated temperatures 22 so the HT treatment has the potential to improve local efficacy without increasing systemic toxicity. In preclinical studies the combination of HT and temperature sensitive liposomes has shown great promise 12. With these studies, HT was induced in superficial tumors for periods of tens of minutes.
A central challenge that must be overcome to enable widespread clinical adoption of thermosensitive drug carriers is to achieve controlled, targeted HT treatments with a view to localizing drug release and bioeffects while minimizing the exposure of healthy tissue. Thermal therapy has a long history in oncology 23-25, with currently employed methods involving the use of radiofrequency (RF) catheters, microwaves, lasers or ultrasound 26-28. To date, the only clinical trials for thermosensitive drugs have been with ThermoDox® (Celsion, Columbia, MD), an FDA-approved lyso-thermosensitive liposomal doxorubicin (LTSL-DOX) formulation. This drug is involved in several clinical trials using different heating modalities (see review 29) and is in Phase III clinical trials for the treatment of liver tumors in combination with RF ablation 30. This approach causes thermal coagulation of the tissue near the RF electrodes and the rational is that temperature-sensitive drug delivery would then occur in the periphery of the ablated region, albeit in an uncontrolled manner.
A promising method for achieving controlled hyperthermic exposures is focused ultrasound (FUS) which has been employed for decades in thermal therapy for both HT and ablative purposes 31-34. It has also shown strong preclinical and clinical performance when combined with magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) for precise anatomical targeting and temperature feedback 35. Recent preclinical studies have shown that MRI-guided focused ultrasound (MRgFUS) can achieve spatially localized thermal exposures in the range of 41-43°C. It has been demonstrated through histology that MRgFUS is capable of inducing the targeted uptake and release of DOX from LTSL-DOX in a superficial animal tumor model using 20-30 minute exposure durations and that this gives rise to potent antitumor effects 36-38.
Unfortunately, the approach of using prolonged (tens of minutes) exposure periods, which have dominated preclinical work to date, will likely not be viable in a clinical context for a range of cancers such as liver, kidney and head and neck tumors. In these situations, respiratory motion will impact targeting and can cause artifacts in MRI thermometry images which will present as errors in the temperature measurements. Larger blood vessels near the targeted tumor will act as convective heat sinks, making sustained temperature elevations difficult 39-41. Therefore, in order to make MRgFUS+HT in combination with LTSL-DOX a more robust treatment option, new exposure approaches must be developed to overcome these issues.
A necessary element of the development of novel heating methods is to investigate their effects on microscale drug distribution patterns. Intravital microscopy studies of dorsal skinfold window chamber (DSWC) tumors have been central to understanding drug delivery from LTSL-DOX. These studies have generally employed resistive coil and water bath heating to achieve HT 13, 42 while assessing the extravasation of autofluorescent DOX with confocal microscopy. This method is well suited to creating uniform thermal exposures in a DSWC but lacks the ability to precisely control the temperature elevation on a time scale below the order of minutes. Thus, studies to date have been conducted with longer timescales of HT, on the order of 20 minutes or more.
In this study we report the development and investigation of the first preclinical system to combine FUS with a DSWC murine tumor model to investigate the release of thermosensitive drug carriers with microscopy. FUS has been used previously with two-photon microscopy (2PM) for rodent brain studies 43-46 involving non-thermal treatments using acoustically stimulated microbubbles (MB) to promote drug delivery. The present system enables real time 2PM imaging of a tumor during rapid and controlled temperature changes by using a custom transducer mounted to the DSWC and thermocouple based temperature feedback. The system is used to investigate a novel proposed exposure scheme, consisting of a series of short duration (30s) heating bursts, to release DOX from systemically injected ThermoDox®. Previous in vitro work has reported that ThermoDox® releases 80-100% of its DOX payload within 20-40s at 41.3°C 47 however this has not been empirically validated in vivo as to date, DSWC microscopy studies have been limited to longer timescales due to the manner in which heating is achieved. The short duration exposure strategy may be a means by which to overcome the limitations identified above related to thermometry, targeting and vessel cooling.
Materials and Methods
Tumor cell line and cell culture
Human FaDu squamous cell carcinoma cells expressing green fluorescent protein (FaDu-GFP, AntiCancer Inc., San Diego, CA) were cultured at 37°C in 5% CO2/95% air. For in vitro cultures, cells were propagated in RPMI 1640 with L-glutamine (MultiCell), supplemented with 10% FBS, penicillin (100 U/mL) and streptomycin (100 µg/mL). Cells were trypsinized before reaching confluency and harvested.
Animal Preparation and in vivo Tumor Model
Six-eight week old BALB/c nu/nu mice were purchased from Charles River, sterile rodent food and water were given ad libitum. All animal procedures were approved by the Animal Care Committee at Sunnybrook Research Institute, Toronto, Canada.
FaDu-GFP cells were routinely cultured as described above. Tumor cells (2x106) suspended in 30µL of media were injected in the fascia of a dorsal skin flap placed in a window chamber in mice 48. Following tumor inoculation mice carrying window chambers were housed individually. Imaging studies were performed 9-12 days after inoculation when tumors were visually perfused.
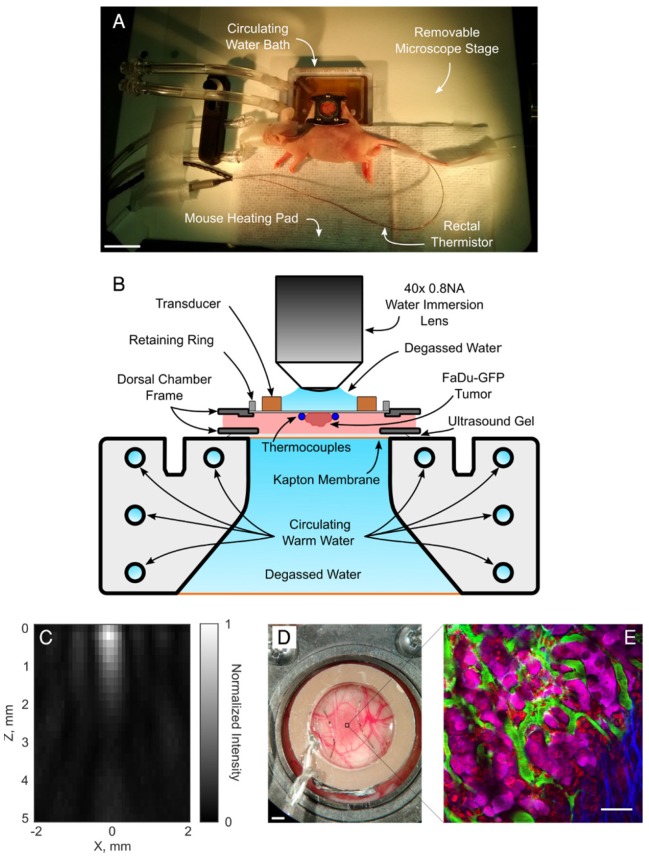
On the imaging day, mice with tumor-bearing DSWCs were anesthetized with isoflurane. The tail veins were cannulated for the injection of fluorescent dextran (2MDa FITC, 33mg/kg, dissolved in PBS; ThermoFisher Scientific) and LTSL-DOX (ThermoDox®, 10mg/kg of doxorubicin, in equal parts of 5% dextrose solution). The doxorubicin dose prescribed here was chosen to correspond to a human equivalent dose of approximately 30mg/m2 49. This is similar to that used in rats (30mg/m2 50), rabbits (30mg/m2 51) and on the low end of what has been administered in clinical trials (20-60mg/m2 52) with ThermoDox®. The animals were placed on a heating pad atop a removable microscope stage which used feedback from a rectal thermistor to maintain the animal core body temperature at 37°C during the experiment (TC-1000, CWE Inc., Ardmore, PA). The glass coverslip of the DSWC was then removed to allow the insertion of two bare-junction type-T thermocouples into the DSWC adjacent to the tumor to provide temperature feedback. The thermocouples were fabricated by soldering the tips of a copper and a constantan wire (diameter 0.05mm) in a twisted pair (California Fine Wire Company, Grover Beach, CA). Thermocouples were inserted such that they did not puncture large vessels in the DSWC, but were able to bracket the tumor, i.e. one inferior and one superior, and to be close to the center of the DSWC. Thermocouples were not placed directly in the center of the DSWC because this would cause a large viscous heating artifact from the focus of the ring transducer making temperature measurements inaccurate 53. Following thermocouple insertion, a new 12mm diameter 150µm thick coverslip with the transducer attached to the top surface with cyanoacrylate adhesive was placed in the DSWC with an internal retaining ring. The underside of the DSWC was coupled to a reservoir of degassed water with ultrasound gel to minimize acoustic reflections. The reservoir was heated with a circulating water heater (T/Pump Model TP-500, Gaymar, Orchard Park, NY) to maintain the temperature of the DSWC tissue at 36-37°C for the duration of the imaging study. Once the preparation was complete the removable microscope stage was transferred to the microscope for concurrent FUS+HT and 2PM imaging. An overview of the experimental apparatus and an example 2PM image is shown in Figure 1.
Figure 1.
A, Removable microscope stage with a DSWC-bearing nude mouse in position for 2PM imaging, scale bar = 2cm. B, DSWC mount for use during 2PM for imaging drug release from LTSL-DOX during FUS+HT, missing from the diagram labels is the optically transparent coverslip glass which is glued to the bottom surface of the transducer. C, The acoustic intensity distribution produced by the ring transducer below the coverslip surface. D, A close up of the DSWC with the ring transducer mounted in position and thermocouples visible near the tumor boundaries, scale bar = 1mm. E, Representative image illustrating the capability of the 2PM imaging setup to visualize the release of DOX from LTSL-DOX following FUS+HT in a murine tumor model. In this image the FITC-labelled vasculature is green, FaDu-GFP tumor cells are false-coloured magenta, DOX is red and collagen is blue, scale bar = 50µm.
FUS Parameters for HT
A PZT-4 cylindrical transducer (diameter = 10mm, thickness = 1.5mm, height = 1.1mm) was used for sonication. Four physically identical transducers were used in this study to expedite experiment throughput with a driving frequency of 1.189 ± 0.015MHz (mean ± SD) in the thickness mode. A full characterization of the transducer design is presented here 54. The normalized acoustic intensity profile can be seen in Figure 1C. Each transducer was driven by a function generator (33210A, Agilent, Palo Alto, CA) and a 53dB RF power amplifier (NP Technologies Inc., Newbury Park, CA). The applied forward and reflected electrical power was monitored using an RF power meter (E4419B, Agilent, Palo Alto, CA) and each transducer had its own custom impedance matching circuit to minimize the reflected power along the transmission line. Temperature monitoring of DSWC tissue was performed using a thermocouple data acquisition system (DT9828, Data Translation Inc., Marlboro, MA).
Temperature Feedback Control
The temperature elevation in the DSWC was controlled by adjusting the applied electrical power to the transducer based on the temperature feedback from implanted thermocouples at a rate of 1 Hz using a PID control algorithm with empirically determined gain constants (KP = 0.09, KI = 0.001, KD = 0.5). The output power was given by:
| Pi+1 = Pi + ΔPi ≤ Pmax(1) |
| ΔPi= ( KP·ei ) + ( KI·Σej ) + ( KD·(ei - ei-1) ) |
| ei = Tg - Ti |
The integral summation index (index j) was initialized to zero when FUS was turned on and only operated when the measured temperature (Ti) was within ±1°C of the desired temperature (Tg). To reduce the initial accumulation of error, the desired temperature rise was prescribed as an exponential ramp instead of a step function 55.
Four HT exposure schemes were investigated in this study; three groups used FUS+HT to a target temperature of 42°C and the fourth served as an unheated control. As has been investigated in previous literature 38,42, the first group measured the drug release and penetration following 20min of sustained FUS+HT. In this group the exponential ramp was 6min in duration and the maximum electrical power was 1.5W. The second group used a novel short duration HT format of 10x 30s heating 'bursts' separated by 5min to allow the tissue to return to baseline temperature and quantitative 2PM imaging to be performed. In this case the exponential ramp was 15s in duration. The third heating group involved a continuous temperature elevation, 3.5min duration, with the same exponential ramp as the short duration bursts. The purpose of this group was to expose the DSWC tissue to the same accumulated duration above 41.3°C (the ideal release temperature from the LTSL-DOX formulation 47) as the short duration bursts over the course of 60min. In the two previously mentioned heating schemes the Pmax value from equation (1) during sonication was determined based on threshold criteria as follows. Pmax began at 4W until either thermocouple read above 41°C and below 42°C at which point Pmax was dropped to 2W. Then when either thermocouple read above 42°C for the first time, Pmax was dropped again to its final value of 1W.
During a pilot thermocouple pullback experiment, a third thermocouple was placed in the center of the DSWC such that it could provide a temperature reading from the focus of the transducer during a fixed power exposure. In this experiment it was found that the temperature reading at the focus was +0.25°C warmer than the reading from the other two thermocouples, following subtraction of the +0.28°C viscous heating artifact 56. This difference became +0.21°C when the middle thermocouple was translated ±1mm from the focus providing an indication of the temperature uniformity within the imaging field-of-view (FOV).
2PM Imaging of DOX Release
On the experiment day, the DSWC was placed under a water immersion 40× 0.80NA objective lens with a working distance of 3.3mm and a FOV of 318µm×318µm (LUMPLFLN 40XW, Olympus, Tokyo, Japan). Laser scanning was performed using a multiphoton microscope (FV1000MPE, Olympus, Tokyo, Japan) and a Mai-Tai mode-locked Titanium Sapphire tunable laser (690-1040nm; Newport Corp., Irvine, CA) was used to excite the FaDu-GFP cells and collagen at 900nm, as well as to excite the FITC-labelled vasculature and doxorubicin at 810nm. An external photomultiplier tube (Hamamatsu, Hamamatsu City, Japan) collected the fluorescent emissions following bandpass filtering of 420/460nm for collagen, 495/540nm for FITC and FaDu-GFP and 575/630nm for doxorubicin.
To visualize the tumor vasculature 2MDa dextran-conjugated FITC was injected as a bolus through the tail vein. Tumor vessels were confirmed by imaging the tissue at 900nm in order to excite the FaDu-GFP as well as the FITC dextran. Tumor vessels near the surface of the DSWC and the center of the ring transducer were selected to maintain high SNR and close proximity to the acoustic focus of the transducer.
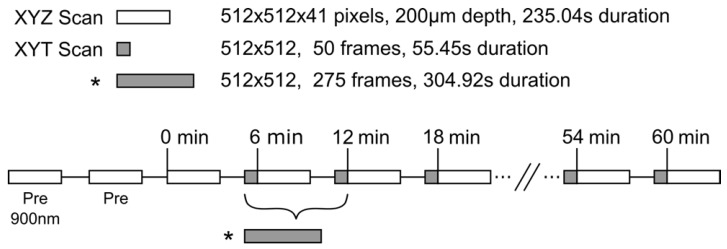
Once a vessel bed was selected a baseline XYZ volume stack was acquired at 810nm to create a 3D vascular map of the tumor vessels. Lateral images of 512×512 pixels (0.602µm/pixel, 8µs/pixel, Kalman 2× line filter) were acquired below the coverslip surface to 200µm depth in 5µm increments for an acquisition time of 235.04s for each volume stack. These volumes were acquired in an XYZT order every 6min. In the 2min between stacks, a single plane XYT acquisition was taken.
For each animal, the XY plane of the time series scan was selected to be between 35µm-100µm in depth where tumor vessels could be visualized with good SNR. Single plane acquisitions were acquired with the same lateral resolution as the depth scans but with a greater temporal resolution of 0.902Hz (512×512 pixels, 0.602µm/pixel, 2µs/pixel, no Kalman filter). Time scans of 50 frames were acquired between each depth stack for an imaging duration of 55.44s per scan, with the exception of the first time scan in the 3.5min of FUS+HT group, in which 275 frames were acquired in 5min to cover the duration of FUS. A timing diagram of the 2PM imaging paradigm is shown in Figure 2.
Figure 2.
Experimental timing diagram describing the 2PM imaging paradigm used to image the release of DOX from LTSL-DOX during FUS+HT to 42°C. The asterisk (*) indicates a longer time series which replaces the first two time series and the first depth scan in the standard imaging paradigm, this is to image the release of DOX during the entire sonication in the 3.5min of FUS+HT group. The LTSL-DOX is administered in a 5min infusion starting at time 0 in all groups except the 20min FUS+HT group, in which case the tumor tissue is heated to 42°C in the first 6min at which point the LTSL-DOX in infused. All imaging scans were performed with an excitation wavelength of 810nm unless indicated otherwise.
Analysis of 2PM Data
All of the 2PM image data was processed in Matlab (2016b, The MathWorks, Natick, MA) to segment the intravascular and extravascular spaces as described in 42. DOX fluorescence is proportional to its concentration in tissue.
Drug release as a function of time was reported from the analysis of the XYT scan data. The DOX fluorescence at time t (denoted as It) was corrected for FITC bleed-through and normalized with respect to the baseline fluorescent signal (I0) in each compartment (intravascular and extravascular). It was expressed in terms of percentage increase (%I0) using the following relationship.
| %I0 = (It - I0)/I0 × 100% (2) |
First, 2D vascular masks were created and the baseline fluorescent signal (I0) was calculated from the average of the first 5 frames (spanning 5.5s) in each XYT acquisition prior to the start of FUS in each short duration and continuous 3.5min FUS+HT exposures, and similarly in unheated controls. For a given exposure (i.e. every 6min in the case of short duration bursts - see Figure 2) this permitted an examination of the release as a function of time within the exposure time scale. It was also of interest to estimate the average release for each exposure in both compartments which was calculated relative to the baseline immediately preceding a FUS exposure (i.e. mean of %I0). This provided a metric for the incremental drug release and uptake associated with a particular exposure (either short duration of 3.5min continuous). The area under the concentration-time curve (AUC) was calculated by trapezoidal integration of the percent increase from the baseline signal level (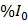 ) as a function of time. The AUC provides a measure of the amount of drug present in the tissue over time, which is a frequently employed metric of bioavailability 42. This data is reported for all groups except the 20min of FUS+HT group, where the entire duration of FUS was not recorded in real-time.
) as a function of time. The AUC provides a measure of the amount of drug present in the tissue over time, which is a frequently employed metric of bioavailability 42. This data is reported for all groups except the 20min of FUS+HT group, where the entire duration of FUS was not recorded in real-time.
Drug penetration depth was measured for the XYZT data by performing a Euclidean distance transform of the segmented 3D vascular mask to create a distance map from each extravascular pixel to the nearest vascular structure. The baseline fluorescent signal in this case was measured prior to the first XYZT acquisition. Boundary effects were removed by truncating the dataset by 50 pixels on all sides in the XY plane. The mean fluorescent signal for pixels at each distance from the nearest vessel were reported up to 17.5µm. This penetration depth was the furthest distance that was reliably discernable across all DSWC due to the heterogeneity of tumor vessel spacing between animals.
Statistical Analysis
Data comparison of DOX release and penetration among heating groups was performed using one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) followed by a multiple comparison test in Matlab. For all analyses, a value of p < 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
Results
Temperature Control of FUS+HT During 2PM
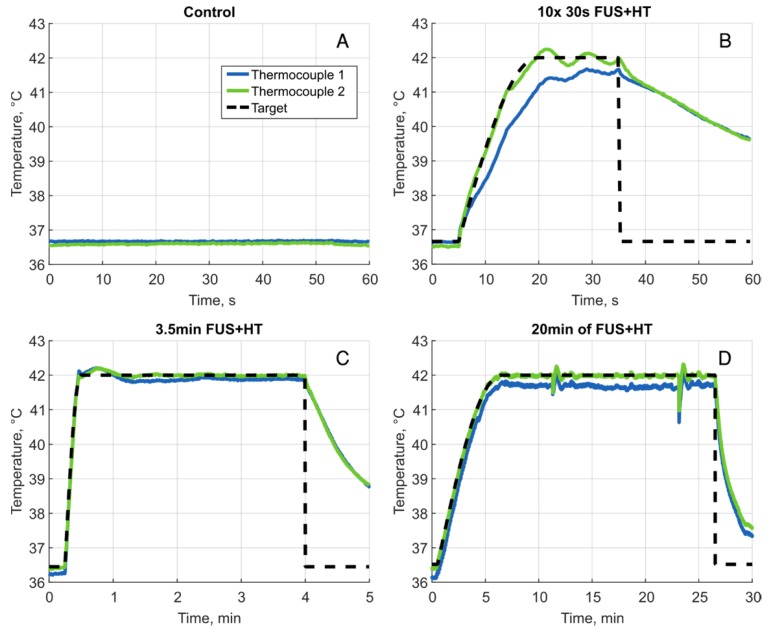
Using the feedback system the temperature elevation in a tumor-bearing DSWC was successfully controlled during concurrent FUS+HT and 2PM in real-time. Four different FUS+HT schemes were investigated. A summary of the performance of the temperature controller is provided in Table 1 and a graphical summary of temperature versus time curves in each group are shown in Figure 3.
Table 1.
Summary of the FUS+HT PID controller in the 4 treatment groups.
| Experimental Group | Temperature Response (Mean ± SD) |
Thermal Dose CEM43°C |
Time above 41.3°C |
|---|---|---|---|
| Control (n=3) | 36.79 ± 0.15 °C | 0.00 ± 0.00 | 0 ± 0 s |
| 10× 30s FUS+HT to 42°C (n=6) | 42.07 ± 0.09 °C | 1.04 ± 0.15 | 221 ± 37 s |
| 3.5min FUS+HT to 42°C (n=4) | 41.97 ± 0.06 °C | 0.78 ± 0.08 | 218 ± 4s |
| 20min FUS+HT to 42°C (n=4) | 41.99 ± 0.01 °C | 4.55 ± 0.20 | 1287 ± 22s |
The temperature response was measured here as the mean temperature reading from the max temperature thermocouple while the prescribed temperature was at the target of 42°C. Thermal dose was calculated as in 70 when both thermocouples read greater than 39°C. The time above 41.3°C was measured as the total time both thermocouples read greater than 41.3°C. Data are presented as the mean ± SEM.
Figure 3.
Sample heating curves for all 4 heating groups. A, Unheated control, B, one example of a 30s FUS+HT burst to 42°C, there were 10 bursts in total for each mouse in this group separated by 5 minutes. C, A heating curve during 3.5min of FUS+HT and D 20min of FUS+HT with a 6 minute exponential ramp to the target temperature. The large perturbations of the temperature response in this case occurred as a result of adding water to the coverslip glass in order to maintain water coupling to the objective lens, this sudden cooling of the tumor tissue was promptly corrected for by the controller.
Release of DOX in Real-Time During FUS+HT
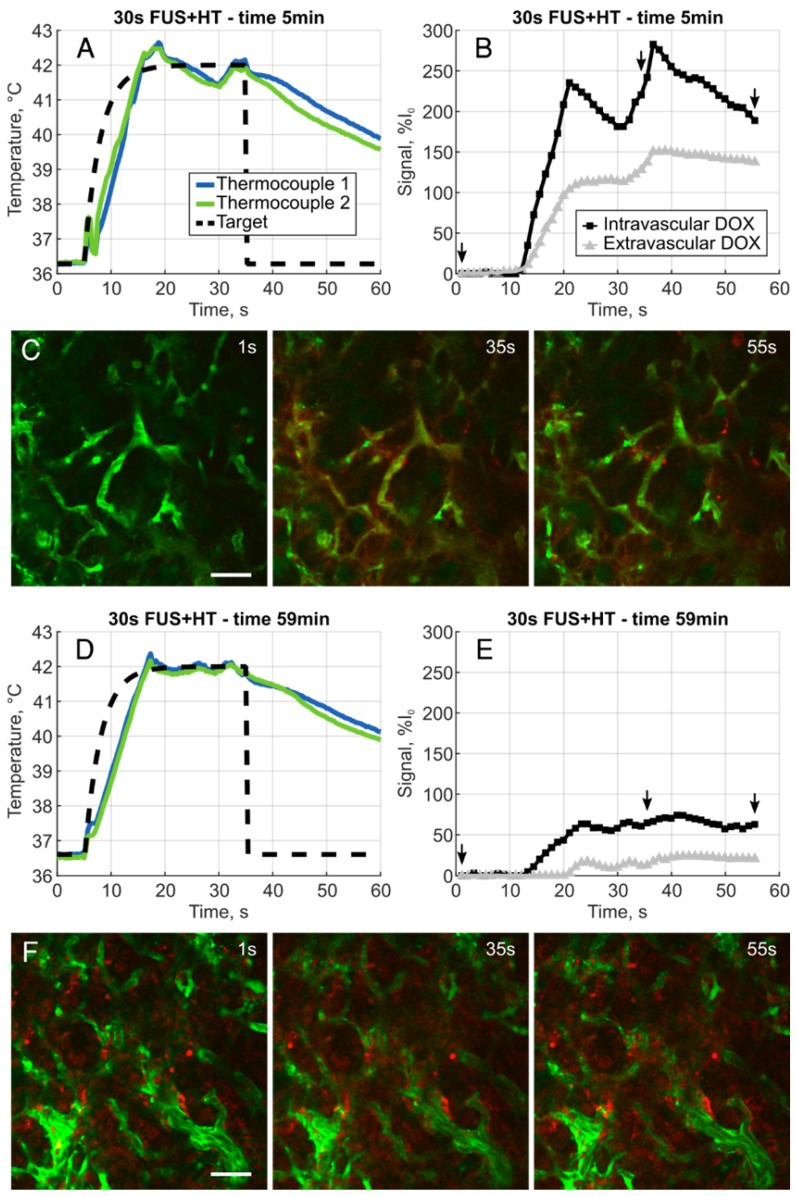
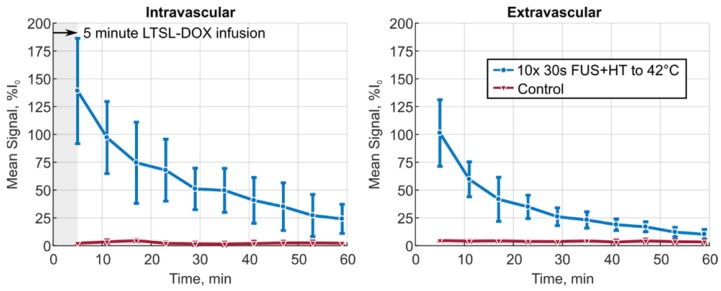
The XYT data provided the opportunity to visualize the spatiotemporal DOX release patterns during the course of exposures for the short duration and continuous 3.5min of heating cases as well as in unheated controls. The measured DOX signal in unheated controls in both the intra- and extravascular compartments remains flat for the entire acquisition. In the short duration exposure case, as seen in Figure 4, there is clear evidence of DOX release which persists even 59min after the beginning of drug infusion. The variable temperature response in Figure 4A is a result of controller behaviour in this case, but the sensitivity of the 2PM system can be seen in Figure 4B, where the intravascular release profile mimics the shape of the temperature curve. The mean signal change that was measured during each XYT scan for both the unheated controls and the 30s FUS+HT bursts is shown in Figure 5. The amplitude in both compartments decreases as a function of time from the end of LTSL-DOX infusion in the short duration heating case. This is most likely a result of the reduction in circulating LTSL-DOX in the plasma.
Figure 4.
A, Example heating curve during the first 30s burst of FUS+HT at the 5 minute time point immediately following the infusion of drug. B, Clear evidence of the release of DOX is seen from the measured intra- and extravascular signal changes and images representing this acquisition, denoted by the small arrows, are shown in C. D, Example heating curve during the tenth and final 30s burst of FUS+HT at the 59 minute time point. E, There are still measureable amounts of DOX being released, but the amplitude of the signal change has diminished as seen in F due to the reduction in circulating LTSL-DOX. In all 2PM images green is the FITC-labelled vasculature, DOX is red, scale bar = 50µm.
Figure 5.
The mean signal amplitude measured during each of the 10 XYT scans for the 30s of FUS+HT to 42°C group versus the unheated control group in both the intra- and extravascular compartments. Data are reported as mean ± SD.
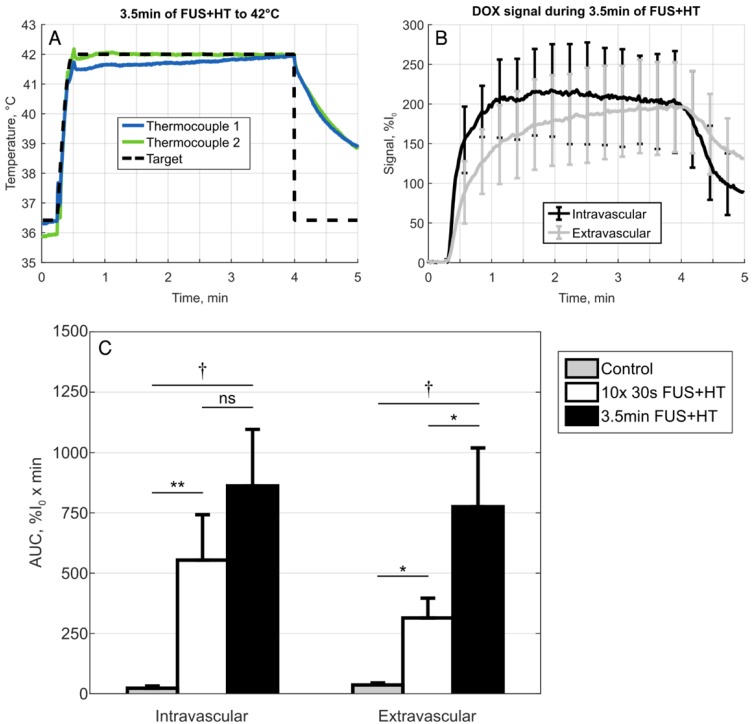
In the continuous 3.5min heating case, similar results as in previous work looking at the release of DOX from this formulation of LTSL-DOX 42 were observed. In particular, the extravascular signal continued to increase for the entire duration of HT and the intravascular signal reached a peak in the first 2min of HT and began to slowly decay, seen in Figure 6. A comparison of the AUC in the 3.5min heating case to the short duration heating and unheated controls revealed no statistically significant difference between the 10x 30s FUS+HT and the continuous 3.5min FUS+HT group when looking in the intravascular compartment.
Figure 6.
A, Temperature profile of a 3.5min continuous FUS+HT to 42°C group and B, the subsequent release of DOX (n=3). C, A comparison of the sum of each discrete AUC measurement in the 10x 30s of FUS+HT and unheated controls as well as the continuous AUC measured from the 3.5min continuous FUS+HT group. There is no significance between the intravascular AUC in the short duration and 3.5min heating group. However, there is a significant difference in the extravascular compartment. Significance was evaluated using one-way ANOVA following by a multiple comparison test in Matlab between the 30s FUS+HT and unheated controls at each time point, (*) p < 0.05, (**) p < 0.01, (†) p < 0.001.
Depth Penetration of DOX in Tumor Tissue
The penetration of DOX into the tumor interstitium following the release from LTSL-DOX during FUS+HT was measured using 2PM up to 60min following the start of drug infusion. This was the case for all groups except the 20min FUS+HT group in which the start of drug infusion was delayed 6min to allow the tumor tissue to reach 42°C before drug administration as this is the optimal condition for maximizing drug release 42. Representative images can be seen in Figure 7 and surface plots of the drug penetration as a function of time can be found in Figure 8.
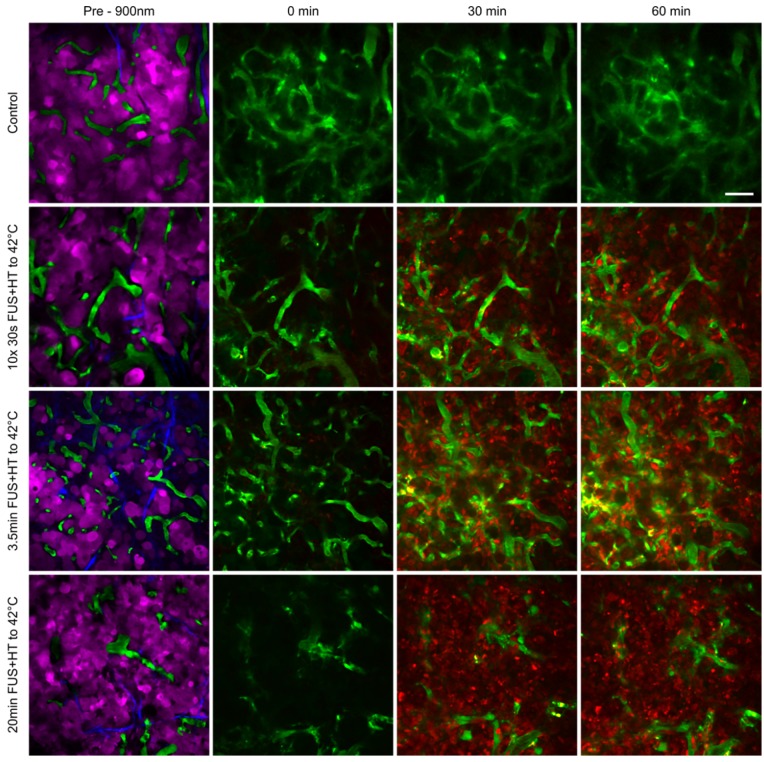
Figure 7.
Tumor cell localization and uptake of DOX at serial time points following FUS+HT to 42°C and in an unheated control. In the top row we see that no appreciable drug is taken up by the tumor cells as evidenced by the absence of red signal. In the second row we see an increase in the 30min time point in relation to the 0min, and even more signal increase in the 60min time point as a result of more 30s FUS+HT bursts being applied to 42°C. In the bottom two rows we see a large signal change in the 30min time point compared to time 0min which remains up to the 60min time point and this is because the FUS+HT exposure to 42°C in these cases had reached completion within 30min. Scale bar = 50µm.
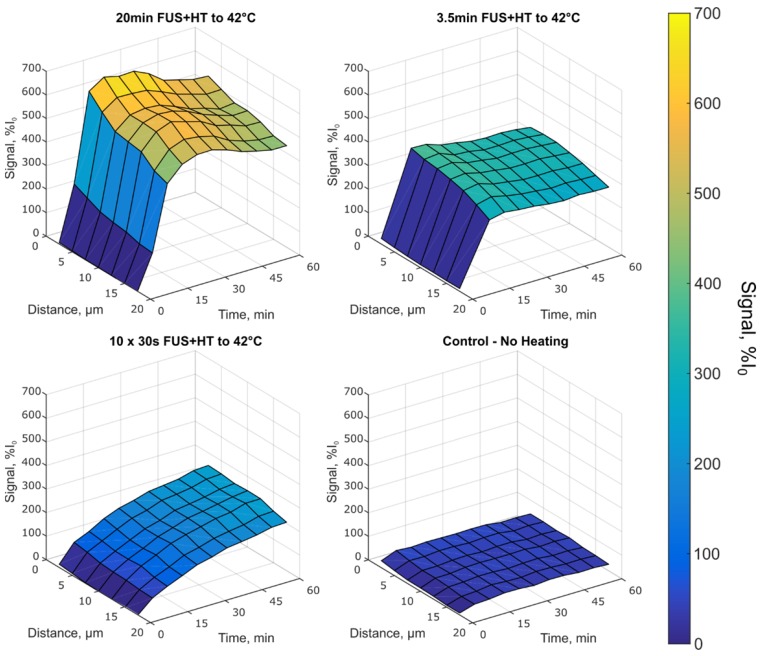
Figure 8.
Depth penetration of DOX up to 17.5µm in tumor tissue in each heating group. The 10x 30s FUS+HT group shows an increase in the drug signal following each hyperthermia burst, whereas in the case of continuous sonications, the signal increases until FUS is off at which point the signal slowly decays and begins to plateau. The unheated control group shows very little increase in extravascular signal as a function of time and distance in the tumor tissue.
In the 10x 30s FUS+HT group we see the drug penetration increased following each 30s heating burst. In the continuous heating groups the drug penetration was seen to increase for the duration of FUS+HT and slowly decay once FUS was off before steadily approaching a plateau. This implies that while DOX was measured to be within the extravascular space following FUS+HT, some of that signal was lost at the later time points, either from the washout of DOX back into the vasculature and away from the tumor, or from DOX fluorescence quenching. The observed signal plateau provides evidence for the former. In the unheated control group the drug penetration slowly increases in the first 5 minutes following drug infusion and then slowly plateaus with very little absolute signal change. The average DOX signal as a function of time in this case is presented in Figure 9A.
Figure 9.
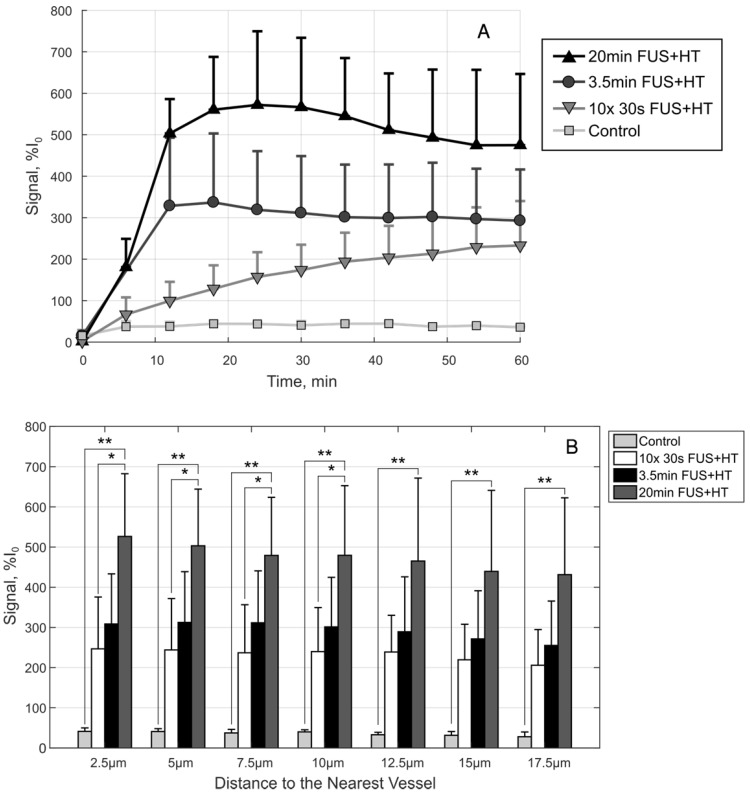
A, The drug penetration averaged along the depth direction to give an indication of the average drug signal in each group as a function of time. B, A comparison of the drug penetration as a function of distance to the nearest vessel at the 60min time point. The drug penetration is nearly homogeneous up to 17.5µm in each case, but there is a significant difference between the 20min FUS+HT group and the 10x 30s FUS+HT group up to 10µm. At each penetration distance examined here, the 20min FUS+HT group showed significantly more DOX signal than unheated controls. Significance was evaluated using one-way ANOVA following by a multiple comparison test in Matlab between the 30s FUS+HT and unheated controls at each time point, (*) p < 0.05, (**) p < 0.01.
By comparison at the 60min time point, shown in Figure 9B, there is no significant difference in the short duration heating case and the 3.5min of continuous FUS+HT at each depth from the nearest vessel. The 20min continuous FUS+HT group had a statistically significant difference from the unheated control at all distances and a differed significantly from the 10x 30s FUS+HT group up to a distance of 10µm.
Discussion
The use of controlled HT to effect the targeted release and potentiation of thermosensitive nanodrugs holds enormous clinical potential for oncology. However the ultimate patient benefit of combining HT with LTSL-DOX is far from being realized due to the limitations on robust clinical implementation of HT treatments. Non-invasive MRgFUS is a prime candidate for delivering HT. Using a novel FUS+HT 2PM system, short duration heating bursts were evaluated here as a potential method of overcoming the limitations of continuous HT during clinical MRgFUS+HT treatments with LTSL-DOX. It was observed for the first time in vivo that these short temperature elevations could produce substantial drug release, a finding that was previously suggested only by in vitro work 47.
The interstitial drug concentration with 10x 30s sonications was about half of what was observed with a continuous 20min sonication, which corresponded to an almost 6-fold longer integrated exposure time. Prior in vivo studies have shown that up to 26.7-fold 37 drug delivery enhancement is achieved with 20min of MRgFUS+HT in animal tumors. If a similar ratio of enhancement (50%) were achieved in tumors, this would still be a potent level of drug enhancement and motivates further optimization of this treatment strategy. Having an alternate strategy besides continuous heating to potentiate drug release would help to overcome some of the issues related to treating heterogeneous tumors with MRgFUS+HT.
In the short duration heating case the measured DOX release using 2PM decreases with each successive HT burst. This progressive drop in release is most likely the result of a reduction in circulating liposomes, consistent with DOX being released from the liposomes while they are within the vasculature 42. In mice the LTSL-DOX formulation was found to have a circulation half-life of 1.34hrs 57, but was also found to be rather unstable at physiological temperatures in dose escalation studies 52, 58. This suggests that modifying the exposure scheme such that there were more short duration bursts close to the end of the drug infusion would result in a greater amount of released DOX. This was not carried out in the present study as a cool down period between pulses was desired to demonstrate the principle of this approach. Indeed, when an equivalent duration of heating was applied in the form of a single 3.5min exposure immediately following the LTSL-DOX infusion, a higher level of drug extravasation (+26%) was achieved. The AUC data also suggests a higher level of tissue exposure to the drug, however it should be noted that the times between exposures were not accounted for in the short duration heating case, nor was the time after the 3.5min exposure ended. The AUC was included as a point of reference to previous work, however in future work it would be of interest to sample images more regularly throughout the duration of the experiment for the AUC to reflect the tissue drug exposure levels.
The short duration exposures were evaluated as we envision that they are a strategy to overcome current obstacles to treating a range of tumor types with MRgFUS+HT. By applying short duration exposures issues related to convective cooling in proximity to large thermally significant vessels, or in regions of high perfusion, could be overcome 41. Heating biological tissue in short durations has been shown to mitigate the effects of perfusion 59 and can also be applied during a breath hold to limit motion. The idea originated from the use of FUS for lesion formation in the late 1970's and early 1980's 60, 61 and was later proposed for HT treatments in 1984 by Britt et al. 62. A 30s breath hold may be a difficult task for patients with advanced disease, but we envision that shorter durations of heating applied for more repetitions near the end of drug infusion would yield comparable drug release. Furthermore, with modern phased-array FUS technology and precise anatomical targeting with MRI, multiple HT treatment cells can be defined 63 and heated in rapid succession without prolonged cooldown time to both overcome perfusion and maximize the amount of drug released.
The work reported in this study was carried out using a novel system that was developed to combine FUS+HT and 2PM for imaging drug release in vivo. Due to the uniformity of the temperature elevation in the optical FOV, minor variations in thermocouple placement between animals were not likely to affect the nature of the results. Controlled heating exposures were achieved with temperature elevations from a baseline of 36°C to a target of 42°C, induced on a timescale of tens of seconds. By using the same DSWC tumor model, LTSL-DOX formulation and a comparable 20min HT exposure as employed in previous work 42, we are afforded a point of reference for the results shown here. Consistent with previous work, the 20min exposure resulted in substantial and rapid drug extravasation. Supplementing previous studies, we extended the observation time to 34min post-exposure and found a decrease in drug signal (-17%) with respect to the peak concentration. In the present work, drug penetration up to 17.5µm from vessel boundaries was examined, which is lower than what has been studied previously (27.5µm 13, 35µm 42, 55µm 64). In the present case, a higher magnification objective lens with a smaller FOV was used compared to that in previous literature. In future work, a different objective lens with a higher numerical aperture, lower magnification and larger FOV could be used to image more of the tumor and quantify a further penetration depth. It is also notable that with this approach we have been able to observe the co-localization of DOX within GFP-labelled tumor cells, whereas with previous confocal work it was not possible to establish this directly.
Finally, it should be noted that the system described here could be employed to investigate a range of basic drug delivery questions. As a starting point, higher temperature short duration exposures are of interest, which can readily be achieved with the FUS+HT system by increasing transducer power levels and the desired temperature set-point. Temperatures below 45°C for durations of ~30s are not expected to cause damage, but would expose the tissue to longer durations at the ideal release temperature from this LTSL-DOX formulation if the heat-up and exponential cooldown period are considered. The effects of administering contrast agent microbubbles (MB) into the circulation prior to the application of FUS can also be examined in order to improve drug delivery. FUS stimulated MBs can elicit a wide variety of therapeutically relevant bioeffects 65 such as increasing microvascular permeability 66, 67 and enhancing the thermal deposition of ultrasound 68, 69. The aforementioned treatment strategies have the potential to improve the release of DOX from LTSL-DOX following FUS+HT and their impact at the microvascular level can be observed and quantified with 2PM in the setup discussed here.
Conclusion
We have successfully combined 2PM with FUS+HT for imaging the release of DOX from LTSL-DOX in vivo in real-time. We have evaluated the ability to release DOX in short 30s FUS+HT bursts to 42°C as a method to overcome limitations on clinical MRgFUS+HT and have found that such exposures are capable of releasing measurable amounts of drug. This was the case for up to 60min following the infusion of the LTSL-DOX. Approximately half the amount of DOX was released, however, compared to 20min of continuous FUS+HT to 42°C, but these results are unsurprising and may prove to be clinically adequate for inducing an enhanced tumor response. By overcoming the motion induced limitations on MRgFUS+HT this treatment method could be clinically usable and could be applied on a more broad spectrum of tumor indications.
Acknowledgments
ThermoDox® was provided by the Celsion Corporation. The authors would like to thank Shawna Rideout-Gros and Sharshi Bulner for their help with the animal surgeries and tumor cell culture; Lynsie A. M. Thomason for her guidance in using the two-photon microscope for our in vivo studies; Moe Kazem, Rooke Reyes and Michael Pozzobon for their help manufacturing the removable microscope stage; and Charissa Poon for editing the manuscript. This work was supported by a Canadian Cancer Society Research Institute Impact Grant and the Canada Research Chair program.
Abbreviations
- 2PM
two-photon microscopy
- ANOVA
analysis of variance
- DOX
doxorubicin
- DSWC
dorsal skinfold window chamber
- EPR
enhanced permeability and retention
- FOV
field-of-view
- FUS
focused ultrasound
- HT
hyperthermia
- LTSL-DOX
lyso-thermosensitive liposomal doxorubicin
- MB
microbubble
- MRgFUS
MRI-guided focused ultrasound
- MRI
magnetic resonance imaging
- RF
radiofrequency.
References
- 1.Matsumura Y, Maeda H. A new concept for macromolecular therapeutics in cancer chemotherapy: mechanism of tumoritropic accumulation of proteins and the antitumor agent smancs. Cancer Res. 1986;46:6387–92. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Maeda H. The enhanced permeability and retention (EPR) effect in tumor vasculature: the key role of tumor-selective macromolecular drug targeting. Adv Enzyme Regul. 2001;41:189–207. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2571(00)00013-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Maeda H. Macromolecular therapeutics in cancer treatment: the EPR effect and beyond. J Controlled Release. 2012;164:138–44. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2012.04.038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Harrington KJ, Mohammadtaghi S, Uster PS, Glass D, Peters AM, Vile RG. et al. Effective targeting of solid tumors in patients with locally advanced cancers by radiolabeled pegylated liposomes. Clin Cancer Res. 2001;7:243–54. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Allen C. Why I'm holding onto hope for nano in oncology. Mol Pharm. 2016;13:2603–4. doi: 10.1021/acs.molpharmaceut.6b00547. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Minchinton AI, Tannock IF. Drug penetration in solid tumours. Nat Rev Cancer. 2006;6:583–92. doi: 10.1038/nrc1893. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Tan Q, Saggar JK, Yu M, Wang M, Tannock IF. Mechanisms of drug resistance related to the microenvironment of solid tumors and possible strategies to inhibit them. Cancer J. 2015;21:254–62. doi: 10.1097/PPO.0000000000000131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Needham D, Hristova K, McIntosh TJ, Dewhirst M, Wu N, Lasic DD. Polymer-grafted liposomes: physical basis for the “stealth” property. J Liposome Res. 1992;2:411–30. [Google Scholar]
- 9.Wu NZ, Da D, Rudoll TL, Needham D, Whorton AR, Dewhirst MW. Increased microvascular permeability contributes to preferential accumulation of Stealth liposomes in tumor tissue. Cancer Res. 1993;53:3765–70. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Soloman R, Gabizon AA. Clinical pharmacology of liposomal anthracyclines: focus on pegylated liposomal Doxorubicin. Clin Lymphoma Myeloma. 2008;8:21–32. doi: 10.3816/clm.2008.n.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Yatvin MB, Weinstein JN, Dennis WH, Blumenthal R. Design of liposomes for enhanced local release of drugs by hyperthermia. Science. 1978;202:1290–3. doi: 10.1126/science.364652. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Needham D, Anyarambhatla G, Kong G, Dewhirst MW. A new temperature-sensitive liposome for use with mild hyperthermia: characterization and testing in a human tumor xenograft model. Cancer Res. 2000;60:1197–201. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Li L, ten Hagen TLM, Hossann M, Süss R, van Rhoon GC, Eggermont AMM. et al. Mild hyperthermia triggered doxorubicin release from optimized stealth thermosensitive liposomes improves intratumoral drug delivery and efficacy. J Controlled Release. 2013;168:142–50. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2013.03.011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Nishimura Y, Ono K, Hiraoka M, Masunaga S, Jo S, Shibamoto Y. et al. Treatment of murine SCC VII tumors with localized hyperthermia and temperature-sensitive liposomes containing cisplatin. Radiat Res. 1990;122:161–7. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Dou YN, Zheng J, Foltz WD, Weersink R, Chaudary N, Jaffray DA. et al. Heat-activated thermosensitive liposomal cisplatin (HTLC) results in effective growth delay of cervical carcinoma in mice. J Controlled Release. 2014;178:69–78. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2014.01.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Chen B, Zhou M, Xu LX. Study of vascular endothelial cell morphology during hyperthermia. J Therm Biol. 2005;30:111–7. [Google Scholar]
- 17.Shakil A, Osborn JL, Song CW. Changes in oxygenation status and blood flow in a rat tumor model by mild temperature hyperthermia. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1999;43:859–65. doi: 10.1016/s0360-3016(98)00516-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Vujaskovic Z, Poulson JM, Gaskin AA, Thrall DE, Page RL, Charles HC. et al. Temperature-dependent changes in physiologic parameters of spontaneous canine soft tissue sarcomas after combined radiotherapy and hyperthermia treatment. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2000;46:179–85. doi: 10.1016/s0360-3016(99)00362-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Zhu D, Lu W, Weng Y, Cui H, Luo Q. Monitoring thermal-induced changes in tumor blood flow and microvessels with laser speckle contrast imaging. Appl Opt. 2007;46:1911–7. doi: 10.1364/ao.46.001911. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Kong G, Braun RD, Dewhirst MW. Hyperthermia enables tumor-specific nanoparticle delivery: effect of particle size. Cancer Res. 2000;60:4440–5. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Kong G, Braun RD, Dewhirst MW. Characterization of the effect of hyperthermia on nanoparticle extravasation from tumor vasculature. Cancer Res. 2001;61:3027–32. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Hahn GM. Potential for therapy of drugs and hyperthermia. Cancer Res. 1979;39:2264–8. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Myerson RJ, Moros EG, Diederich CJ, Haemmerich D, Hurwitz MD, Hsu I-CJ. et al. Components of a hyperthermia clinic: Recommendations for staffing, equipment, and treatment monitoring. Int J Hyperthermia. 2014;30:1–5. doi: 10.3109/02656736.2013.861520. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Datta NR, Rogers S, Ordóñez SG, Puric E, Bodis S. Hyperthermia and radiotherapy in the management of head and neck cancers: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Int J Hyperthermia. 2016;32:31–40. doi: 10.3109/02656736.2015.1099746. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Mallory M, Gogineni E, Jones GC, Greer L, Simone CB. Therapeutic hyperthermia: The old, the new, and the upcoming. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2016;97:56–64. doi: 10.1016/j.critrevonc.2015.08.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Koning GA, Eggermont AMM, Lindner LH, ten Hagen TLM. Hyperthermia and thermosensitive liposomes for improved delivery of chemotherapeutic drugs to solid tumors. Pharm Res. 2010;27:1750–4. doi: 10.1007/s11095-010-0154-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Stauffer PR, Maccarini P, Arunachalam K, Craciunescu O, Diederich C, Juang T. et al. Conformal microwave array (CMA) applicators for hyperthermia of diffuse chest wall recurrence. Int J Hyperthermia. 2010;26:686–98. doi: 10.3109/02656736.2010.501511. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Diederich CJ, Hynynen K. Ultrasound technology for hyperthermia. Ultrasound Med Biol. 1999;25:871–87. doi: 10.1016/s0301-5629(99)00048-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Dou Y, Hynynen K, Allen C. To heat or not to heat: Challenges with clinical translation of thermosensitive liposomes. J Controlled Release. 2017;249:63–73. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2017.01.025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Poon RT, Borys N. Lyso-thermosensitive liposomal doxorubicin: an adjuvant to increase the cure rate of radiofrequency ablation in liver cancer. Future Oncol. 2011;7:937–45. doi: 10.2217/fon.11.73. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Guthkelch AN, Carter LP, Cassady JR, Hynynen KH, Iacono RP, Johnson PC. et al. Treatment of malignant brain tumors with focused ultrasound hyperthermia and radiation: results of a phase I trial. J Neurooncol. 1991;10:271–84. doi: 10.1007/BF00177540. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Wu F, Wang Z-B, Cao Y-D, Chen W-Z, Bai J, Zou J-Z. et al. A randomised clinical trial of high-intensity focused ultrasound ablation for the treatment of patients with localised breast cancer. Br J Cancer. 2003;89:2227–33. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6601411. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Kennedy JE. High-intensity focused ultrasound in the treatment of solid tumours. Nat Rev Cancer. 2005;5:321–7. doi: 10.1038/nrc1591. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Elias WJ, Lipsman N, Ondo WG, Ghanouni P, Kim YG, Lee W. et al. A Randomized Trial of Focused Ultrasound Thalamotomy for Essential Tremor. N Engl J Med. 2016;375:730–9. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1600159. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Ishihara Y, Calderon A, Watanabe H, Okamoto K, Suzuki Y, Kuroda K. et al. A precise and fast temperature mapping using water proton chemical shift. Magn Reson Med. 1995;34:814–23. doi: 10.1002/mrm.1910340606. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Ranjan A, Jacobs GC, Woods DL, Negussie AH, Partanen A, Yarmolenko PS. et al. Image-guided drug delivery with magnetic resonance guided high intensity focused ultrasound and temperature sensitive liposomes in a rabbit Vx2 tumor model. J Controlled Release. 2012;158:487–94. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2011.12.011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Staruch RM, Ganguly M, Tannock IF, Hynynen K, Chopra R. Enhanced drug delivery in rabbit VX2 tumours using thermosensitive liposomes and MRI-controlled focused ultrasound hyperthermia. Int J Hyperthermia. 2012;28:776–87. doi: 10.3109/02656736.2012.736670. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Staruch RM, Hynynen K, Chopra R. Hyperthermia-mediated doxorubicin release from thermosensitive liposomes using MR-HIFU: Therapeutic effect in rabbit Vx2 tumours. Int J Hyperthermia. 2015;31:118–33. doi: 10.3109/02656736.2014.992483. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Hynynen K. Effect of tissue perfusion on temperature elevation. Ultrasound Med Biol. 1989;15(Suppl 1):41–43. doi: 10.1016/0301-5629(89)90214-7. discussion 45-46. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Hynynen K, DeYoung D, Kundrat M, Moros E. The effect of blood perfusion rate on the temperature distributions induced by multiple, scanned and focused ultrasonic beams in dogs' kidneys in vivo. Int J Hyperthermia. 1989;5:485–97. doi: 10.3109/02656738909140473. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Billard BE, Hynynen K, Roemer RB. Effects of physical parameters on high temperature ultrasound hyperthermia. Ultrasound Med Biol. 1990;16:409–20. doi: 10.1016/0301-5629(90)90070-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Manzoor AA, Lindner LH, Landon CD, Park J-Y, Simnick AJ, Dreher MR. et al. Overcoming limitations in nanoparticle drug delivery: triggered, intravascular release to improve drug penetration into tumors. Cancer Res. 2012;72:5566–75. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-12-1683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Raymond SB, Skoch J, Hynynen K, Bacskai BJ. Multiphoton imaging of ultrasound/Optison mediated cerebrovascular effects in vivo. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2007;27:393–403. doi: 10.1038/sj.jcbfm.9600336. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Cho EE, Drazic J, Ganguly M, Stefanovic B, Hynynen K. Two-photon fluorescence microscopy study of cerebrovascular dynamics in ultrasound-induced blood-brain barrier opening. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2011;31:1852–62. doi: 10.1038/jcbfm.2011.59. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Nhan T, Burgess A, Cho EE, Stefanovic B, Lilge L, Hynynen K. Drug delivery to the brain by focused ultrasound induced blood-brain barrier disruption: quantitative evaluation of enhanced permeability of cerebral vasculature using two-photon microscopy. J Controlled Release. 2013;172:274–80. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2013.08.029. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Burgess A, Nhan T, Moffatt C, Klibanov AL, Hynynen K. Analysis of focused ultrasound-induced blood-brain barrier permeability in a mouse model of Alzheimer's disease using two-photon microscopy. J Controlled Release. 2014;192:243–8. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2014.07.051. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Mills JK, Needham D. Lysolipid incorporation in dipalmitoylphosphatidylcholine bilayer membranes enhances the ion permeability and drug release rates at the membrane phase transition. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2005;1716:77–96. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamem.2005.08.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Palmer GM, Fontanella AN, Shan S, Hanna G, Zhang G, Fraser CL. et al. In vivo optical molecular imaging and analysis in mice using dorsal window chamber models applied to hypoxia, vasculature and fluorescent reporters. Nat Protoc. 2011;6:1355–66. doi: 10.1038/nprot.2011.349. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Nair AB, Jacob S. A simple practice guide for dose conversion between animals and human. J Basic Clin Pharm. 2016;7:27–31. doi: 10.4103/0976-0105.177703. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Ponce AM, Viglianti BL, Yu D, Yarmolenko PS, Michelich CR, Woo J. et al. Magnetic resonance imaging of temperature-sensitive liposome release: drug dose painting and antitumor effects. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2007;99:53–63. doi: 10.1093/jnci/djk005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Staruch RM, Chopra R, Hynynen K. Localised drug release using MRI-controlled focused ultrasound hyperthermia. Int J Hyperthermia. 2011;27:156–71. doi: 10.3109/02656736.2010.518198. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Zagar TM, Vujaskovic Z, Formenti S, Rugo H, Muggia F, O'Connor B. et al. Two phase I dose-escalation/pharmacokinetics studies of low temperature liposomal doxorubicin (LTLD) and mild local hyperthermia in heavily pretreated patients with local regionally recurrent breast cancer. Int J Hyperthermia. 2014;30:285–94. doi: 10.3109/02656736.2014.936049. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Hynynen K, Edwards DK. Temperature measurements during ultrasound hyperthermia. Med Phys. 1989;16:618–26. doi: 10.1118/1.596364. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Nhan T, Burgess A, Hynynen K. Transducer design and characterization for dorsal-based ultrasound exposure and two-photon imaging of in vivo blood-brain barrier disruption in a rat model. IEEE Trans Ultrason Ferroelectr Freq Control. 2013;60:1376–85. doi: 10.1109/TUFFC.2013.2710. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Hutchinson E, Dahleh M, Hynynen K. The feasibility of MRI feedback control for intracavitary phased array hyperthermia treatments. Int J Hyperthermia. 1998;14:39–56. doi: 10.3109/02656739809018213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Hynynen K, Martin CJ, Watmough DJ, Mallard JR. Errors in temperature measurement by thermocouple probes during ultrasound induced hyperthermia. Br J Radiol. 1983;56:969–70. doi: 10.1259/0007-1285-56-672-969. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Banno B, Ickenstein LM, Chiu GNC, Bally MB, Thewalt J, Brief E. et al. The functional roles of poly(ethylene glycol)-lipid and lysolipid in the drug retention and release from lysolipid-containing thermosensitive liposomes in vitro and in vivo. J Pharm Sci. 2010;99:2295–308. doi: 10.1002/jps.21988. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Hauck ML, LaRue SM, Petros WP, Poulson JM, Yu D, Spasojevic I. et al. Phase I trial of doxorubicin-containing low temperature sensitive liposomes in spontaneous canine tumors. Clin Cancer Res. 2006;12:4004–10. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-06-0226. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Dorr LN, Hynynen K. The effects of tissue heterogeneities and large blood vessels on the thermal exposure induced by short high-power ultrasound pulses. Int J Hyperthermia. 1992;8:45–59. doi: 10.3109/02656739209052878. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Fry FJ, Johnson LK. Tumor irradiation with intense ultrasound. Ultrasound Med Biol. 1978;4:337–41. doi: 10.1016/0301-5629(78)90022-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Lizzi FL, Coleman DJ, Driller J, Ostromogilsky M, Stanley Chang, Greenall P. Ultrasonic hyperthermia for ophthalmic therapy. IEEE Trans Sonics Ultrason. 1984;31:473–81. [Google Scholar]
- 62.Britt RH, Pounds DW, Lyons BE. Feasibility of treating malignant brain tumors with focused ultrasound. Prog Exp Tumor Res. 1984;28:232–45. doi: 10.1159/000408248. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Tempany CMC, McDannold NJ, Hynynen K, Jolesz FA. Focused ultrasound surgery in oncology: overview and principles. Radiology. 2011;259:39–56. doi: 10.1148/radiol.11100155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Li L, ten Hagen TLM, Bolkestein M, Gasselhuber A, Yatvin J, van Rhoon GC. et al. Improved intratumoral nanoparticle extravasation and penetration by mild hyperthermia. J Controlled Release. 2013;167:130–7. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2013.01.026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Goertz DE. An overview of the influence of therapeutic ultrasound exposures on the vasculature: high intensity ultrasound and microbubble-mediated bioeffects. Int J Hyperthermia. 2015;31:134–44. doi: 10.3109/02656736.2015.1009179. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Skyba DM, Price RJ, Linka AZ, Skalak TC, Kaul S. Direct in vivo visualization of intravascular destruction of microbubbles by ultrasound and its local effects on tissue. Circulation. 1998;98:290–3. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.98.4.290. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Price RJ, Skyba DM, Kaul S, Skalak TC. Delivery of colloidal particles and red blood cells to tissue through microvessel ruptures created by targeted microbubble destruction with ultrasound. Circulation. 1998;98:1264–7. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.98.13.1264. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Wu J. Temperature rise generated by ultrasound in the presence of contrast agent. Ultrasound Med Biol. 1998;24:267–74. doi: 10.1016/s0301-5629(97)00246-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.McDannold NJ, Vykhodtseva NI, Hynynen K. Microbubble contrast agent with focused ultrasound to create brain lesions at low power levels: MR imaging and histologic study in rabbits. Radiology. 2006;241:95–106. doi: 10.1148/radiol.2411051170. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Sapareto SA, Dewey WC. Thermal dose determination in cancer therapy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1984;10:787–800. doi: 10.1016/0360-3016(84)90379-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]