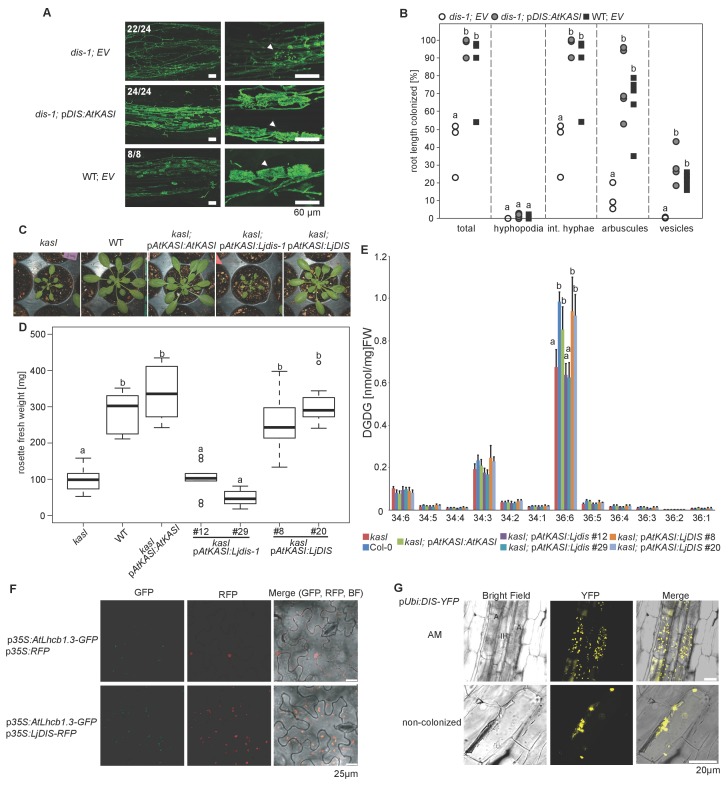
Figure 4. DIS function is equivalent to a canonical KASI.
(A) Microscopic AM phenotype of transgenic dis-1 mutant and wild-type hairy roots transformed with either an empty vector (EV) or the Arabidopsis KASI gene fused to the L. japonicus DIS promoter. White arrowheads indicate arbuscules. (B) Quantification of AM colonization in transgenic roots of dis-1 transformed with EV (open circles), dis-1 transformed with pDIS-AtKASI (grey circles) and wild-type transformed with EV (black squares). int. hyphae, intraradical hyphae. Different letters indicate significant differences (ANOVA; posthoc Tukey; n = 15; p≤0.001) among genotypes for each fungal structure separately. F2,12 = 0.809 (total and intraradical hyphae), F2,12 = 43.65 (arbuscules), F2,12 = 0.0568 (vesicles). (C) Rosettes of Arabidopsis, kasI mutant, Col-0 wild-type plants and kasI mutant plants transformed either with the native AtKASI gene, the dis-1 mutant or the DIS wild-type gene driven by the Arabidopsis KASI promoter at 31 days post planting. (D) Rosette fresh weight of kasI mutant, Col-0 wild-type plants, one transgenic pAtKASI:AtKASI complementation line (Wu and Xue, 2010) and two independent transgenic lines each of kasI mutant plants transformed either with the dis-1 mutant or the DIS wild-type gene driven by the Arabidopsis KASI promoter at 31 days post planting. Different letters indicate significant differences (ANOVA; posthoc Tukey; n = 70; p≤0.001; F6,63 = 34.06) among genotypes. (E) Q-TOF MS/MS analysis of absolute amount of digalactosyldiacylglycerols (DGDG) containing acyl chains of 16:x + 18:x(34:x DGDG) or di18:x(36:x DGDG) derived from total leaf lipids of the different Arabidopsis lines. Different letters indicate significant differences (ANOVA; posthoc Tukey; n = 32; (p≤0.05, F 6,25 = 14.48 (36:6)). (F) Subcellular localization of DIS in transiently transformed Nicotiana benthamiana leaves. Free RFP localizes to the nucleus and cytoplasm (upper panel). RFP fused to DIS co-localizes with the Arabidopsis light harvesting complex protein AtLHCB1.3-GFP in chloroplasts (lower panel). (G) Subcellular localization in plastids of DIS-YFP expressed under the control of the L. japonicus Ubiquitin promoter in R. irregularis colonized (upper panel) and non-colonized (lower panel) L. japonicus root cortex cells. BF, bright field; IH, intercellular hypha; A, arbuscule.