Abstract
This protocol describes the ex vivo characterization of zebrafish hematopoietic progenitors. We show how to isolate zebrafish hematopoietic cells for cultivation and differentiation in colony assays in semi-solid media. We also describe procedures for the generation of recombinant zebrafish cytokines and for the isolation of carp serum, which are essential components of the medium required to grow zebrafish hematopoietic cells ex vivo. The outcome of these clonal assays can easily be evaluated using standard microscopy techniques after 3–10 d in culture. In addition, we describe how to isolate individual colonies for further imaging and gene expression profiling. In other vertebrate model organisms, ex vivo assays have been crucial for elucidating the relationships among hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs), progenitor cells and their mature progeny. The present protocol should facilitate such studies on cells derived from zebrafish.
INTRODUCTION
The use of zebrafish to study the genetic underpinnings of hematopoiesis has become increasingly popular over the past 20 years1–3 because of several unique features, including their embryonic optical transparency, genetic amenability, and fecundity. Furthermore, the value of zebrafish as a model organism has also been demonstrated in numerous other biological studies4–7. The popularity and utility of zebrafish as a model organism are attributable to the development and refinement of crucial techniques that allow efficient genetic manipulation, in vivo visualization of development in real time, and methods for high-throughput screening3–7. For example, zebrafish were used to map the origins of HSCs using real-time in vivo fate mapping8 and in the elucidation of the signaling pathways that are involved in these processes9–11.
In other model organisms such as the mouse and chicken, in vivo observations are routinely complemented by ex vivo experiments12–14, including culturing of hematopoietic cells in tissue culture. These ex vivo approaches that offer the possibility to perform the experiments in a cell-autonomous manner were unavailable for zebrafish until recently because of the incompatibility of broadly used mammalian or avian culture media with zebrafish cell culture, and the high divergence of mammalian and zebrafish growth factors and cytokines15,16.
Development of the protocol
Initially, we established a method for culturing zebrafish hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells (HSPCs) in suspension on top of zebrafish kidney stromal (ZKS) cells15. The ZKS cell layer was used to encourage growth and multilineage differentiation of HSPCs by cell–cell interaction and the production of a broad range of growth factors and cytokines. In order to manipulate cell fates more specifically and more efficiently, we generated several zebrafish recombinant cytokines that further increased the self-renewal and differentiation of HSPCs15. However, although we observed the terminal differentiation of zebrafish erythro-myeloid cells, this technique did not allow the study of differentiation and self-renewal potential of HSPCs at the single-cell level. Therefore, we developed zebrafish methylcellulose clonal assays, which enabled the analysis of clonal HSPC ontogeny in semisolid media for the first time16,17. These methods, which are based on mammalian clonal assays, were the first description of culture conditions that support primary zebrafish HSPCs in semisolid media18. This protocol describes these substantial improvements in detail, including an improved strategy for fish euthanasia and a simplified procedure for zebrafish kidney marrow dissection. In addition, we describe an optimized composition of methylcellulose medium. We provide a guide for utilization of various cell populations that can be grown in various different plate formats, and we offer an optimized procedure for plating hematopoietic cells. Furthermore, this procedure describes an extended downstream application guide and instructions for the preparation of some of the important culture components, such as carp serum and cytokines, in Boxes 1 and 2. Our improved protocol has been used to produce research demonstrating clonal hematopoietic progenitor assays in the zebrafish and differentiation of hematopoietic progenitors ex vivo in real time17,18.
Box 1. Preparation of carp serum ● TIMING 1.5 d.
Carp serum49 is an ideal substitution for zebrafish serum30 when added at a final concentration of 2% (vol/vol) together with 10% (vol/vol) FBS. Here we describe the protocol for its preparation. Blood collection is done by heart puncture (Supplementary Fig. 2). Blood can be collected by other methods, such as caudal vein or dorsal aorta puncture (not described). Typical yields of blood are ~6 ml/kg, which yields ~2–4 ml of serum.
Additional materials
Carp (Cyprinus carpio), size between 2 and 3 kg ! CAUTION All animal procedures must be carried out in accordance with the guidelines outlined by local and national committees for animal experiments ! CAUTION Euthanasia via cranial concussion should be conducted by a person who is experienced in the proper application of this technique ▲CRITICAL If you use smaller carp, the blood yield will be smaller. If you use older carp, the blood yield is higher, but it is more difficult to reach the heart for blood collection.
Procedure
Blood collection ● TIMING 15 min per carp
-
1
Euthanize the carp (medium size, 2–3 kg) with a sharp blow to the cranium above the eyes using a blunt wooden or rubber stick or hammer. When this step is properly performed, the fish stops moving. Alternatively, apply electrocution.
! CAUTION Cranial concussion should be conducted by a person who is experienced in the proper application of the technique.
! CAUTION Electrocution may be hazardous and must be performed by a person who is familiar with appropriate placement of electrodes and use of equipment. Purpose-built equipment must be used.
! CAUTION Blood collection (steps 1–4) should be performed by two people. The second person helps to stabilize the fish and increases blood flow by abdominal and lateral compression massage.
-
2
Position the animal on its back in an ice groove.
-
3
Insert the needle (20-gauge × 40 mm) connected to a 12-ml syringe 2–3 cm deep inside perpendicularly to the ventral surface in the midline between pectoral fins. Needle and syringe should be held 10–20° off horizontal with the tip pointing to the head (Supplementary Fig. 2). Apply negative pressure. If no blood appears, slowly withdraw the needle so that it remains just under the skin and re-direct it in a slightly different direction. Wait until the syringe is entirely filled.
▲ CRITICAL STEP If blood stops flowing, it is still possible to improve yields by pressurizing the heart. This is done by bending the tail and by massaging the abdomen in the anterior direction.
▲ CRITICAL STEP If the syringe is full, replace it gently while the needle is still inside the animal.
-
4
Perform a secondary method of euthanasia to ensure that the animal is deceased by decapitation.
Serum preparation ● TIMING 1 d
-
5
Coagulate blood for 4–6 h at RT and then incubate at 4 °C overnight.
▲ CRITICAL STEP Manipulate the syringes containing blood very gently, as any excessive manipulation can cause hemolysis.
-
6
Gently open the syringe and carefully filter the supernatant through a 70-μm nylon mesh.
▲ CRITICAL STEP The supernatant should be slightly yellow and clear. If hemolysis occurs, the supernatant is red to dark red.
Do not pool nonhemolytic and hemolytic sera. Be careful not to contaminate clear supernatant with blood clots during its filtration.
▲ CRITICAL STEP Perform steps 6–7 in a tissue culture hood using sterile technique.
-
7
Spin the supernatant for 10 min at 300g, RT and filter it with a 0.22-μm filter.
▲ CRITICAL STEP If the supernatant contains hemolytic cells, filtration could take a long time. Proceed through several subsequent filtration steps, starting with 5-μm, 0.44-μm, and 0.22-μm filters.
▲ CRITICAL STEP Be aware of any contamination. Test the serum before use for any signs of microbial infection by its cultivation at 37 °C. Directly use the serum or divide it into aliquots and freeze the aliquots in liquid N2; store them at −20 °C for at least 1 year.
Box 2. Generation of cytokines ● TIMING weeks to months.
Additional materials
Denaturing purification buffer A (pH 8.0): Combine 6 M guanidine hydrochloride, 100 mM NaH2PO4, and 10 mM Tris. Store the buffer at RT for up to 6 months, and re-adjust the pH before use. Add 10 mM 2-mercaptoethanol before use, after adjusting the pH.
Denaturing purification wash buffers B (pH 8.0) and C (pH 6.3) and elution buffer E (pH 4.0): combine 8 M urea, 100 mM NaH2PO4, and 10 mM Tris. Store it at RT for up to 6 months, and re-adjust to the required pH before use. Add 10 mM 2-mercaptoethanol before use, after adjusting the pH.
Native wash buffer (pH 8.0): combine 300 mM NaCl and 50 mM NaH2PO4. Store it at RT for up to 6 months and add 20 mM imidazole before use.
Native elution buffer (pH 8.0): combine 300 mM NaCl and 50 mM NaH2PO4. Store it at RT for up to 6 months and add 250 mM imidazole before use.
Procedure
-
1
Design or select cytokine CDS and amplify the region of interest or order the particular cDNA clone. Introduce N-terminal hexahistidine sequence by cloning cytokine CDS into pQE-30/31/32 vector (included in QIAexpress Type IV Kit). Determine the expression system to be used. For protein expression in E. coli, follow option A. For protein expression in the baculovirus system, follow option B; see Supplementary Figure 3.
▲ CRITICAL STEP Be careful not to introduce a frameshift in the cytokine open reading frame during ligation; choose a proper pQE vector.
(A) E. coli expression ● TIMING 1 week
Express the protein of interest using the QIAexpress Type IV Kit according to the manufacturer’s protocol.
Lyse the resulting bacterial pellet using denaturing purification buffer A.
Purify the protein under denaturing or native conditions using Ni-NTA agarose and according to the manufacturer’s protocol.
Dialyze eluted protein against PBS at RT overnight. If the protein precipitates during dialysis, spin the supernatant for 10 min at 10,000g, 4 °C. Resuspend the pellet in denaturing purification buffer B. Dialyze against HEPES at RT overnight. Spin the supernatant for 10 min at 10,000g, 4 °C to remove any residual precipitate.
Determine the protein concentration using BCA protein assay. Analyze the purity using polyacrylamide electrophoresis.
(B) Baculovirus expression ● TIMING 3–4 weeks
-
Clone cytokine CDS including N-terminal histidine tag from the pQE vector into the pAcGP-67A baculovirus transfer vector using EcoRI restriction site on the 5′ end. This generates a fusion with glycoprotein-67 that mediates the forced secretion of the recombinant protein. The signal peptide is cleaved during transport, and the recombinant protein can be purified from the supernatant.
▲ CRITICAL STEP Be careful not to introduce a frameshift in the cytokine open reading frame during ligation.
Co-infect sf21 insect cells with baculovirus transfer vector and Baculogold DNA. Propagate virus-infected cells and express the protein. Proceed according to the manufacturer’s (sf21 and Baculogold DNA) protocol.
Collect the supernatant from infected cells. This supernatant contains expressed protein, as well as viral particles. Spin the supernatant for 10 min at 300g, RT and filter it with a 0.22-μm filter.
Dialyze the supernatant against PBS at 4 °C. Add imidazole to a final concentration of 20 mM. Purify the protein under native conditions using Ni-NTA agarose and according to the manufacturer’s protocol. Elute the protein using elution buffer.
Dialyze eluted protein against PBS (this removes imidazole that is presented in elution buffer), and concentrate the protein using Amicon Ultra-15 Centrifugal Filter Units according to the manufacturer’s protocol. Select proper Ultracel regenerated cellulose membrane according to the protein size. Generally, we use Ultracel-10 membrane with a 10-kDa cutoff.
Determine the protein concentration using BCA protein assay. Analyze purity using polyacrylamide electrophoresis.
Applications of the method
Clonal assays are routinely used for the study of steady-state or aberrant hematopoiesis at the single-cell level19,20. Cells are essentially plated in a suspension of semisolid media such as methylcellulose to prevent their movement. In such conditions, cells stay together and form distinct colonies. If optimal plating density is attained, every HSPC generates a single colony19,20.
The approach can be used for the study of developmental differentiation relationships between hematopoietic cells via ex vivo fate-mapping experiments18,21. With these experiments, it is possible to decipher the hierarchy of most HSPCs by ex vivo fate-mapping experiments when tracking individual cells and colonies. These procedures also enable a thorough and functional characterization of intrinsic and extrinsic regulators that affect normal and malignant hematopoiesis18,19,22–24. Clonal assays facilitate the detailed characterization of various mutant phenotypes19, and therefore they are a valuable tool for phenotyping hematopoietic defects generated in the zebrafish model system.
Experimental design
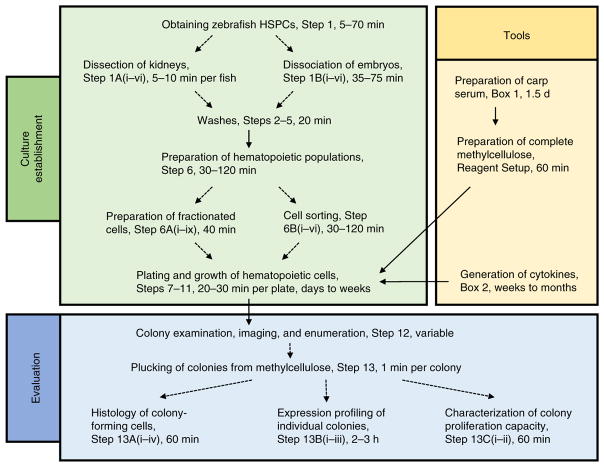
The overall experimental schematic in Figure 1 shows a summary of the stages required to establish cell culture, the tools that are necessary to accomplish this and the evaluation of outcomes of clonal assays by standard microscopy techniques or gene expression profiling. Colonies can be directly imaged, enumerated, and then plucked from the methylcellulose for subsequent analysis such as histology, gene expression profiling, and characterization of proliferative capacity. The protocols for these assays are described in the PROCEDURE section. The following points should be considered before starting the experiment.
Figure 1.
Flowchart of the described experimental procedures. This flowchart highlights major steps and timings that need to be considered during culture establishment (green box); the generation of important tools, such as the preparation of carp serum and the generation of recombinant cytokines (yellow box); and necessary steps for evaluating the outcomes of the clonal assays (blue box).
Choice of fish
The choice of fish depends on the purpose of your study. It is possible to use adult fish whole kidney marrow (WKM)16,25, as well as embryonic fish, as a source of HSPCs17. When you are using adults, use fish that are 3–9 months old, preferably ~6 months of age. At this age, fish are fully developed, and the kidneys contain high numbers of blood progenitors; if you are using younger fish, expect smaller kidney sizes and reduced cell yields. Our preliminary data suggest that the same is true for older fish; the cellularity of the kidney and functional number of HSPCs seem to drop as the fish age. If embryos are used as a source of hematopoietic cells, collect the cells between 24 and 36 h post-fertilization (h.p.f.) for primitive hematopoiesis studies, or use embryos older than 36 h.p.f. for definitive hematopoiesis studies. As a multitude of zebrafish mutant and transgenic reporter lines have been created and described, it is possible to use these fish for experimental procedures. For example, numerous fish have been generated that express fluorescent genes under the control of tissue-specific promoters, such as gata1:dsRed fish that have dsRed+ erythrocytes26, cd41:GFP fish that have GFP+ progenitors/thrombocytes27, mpx:GFP fish that have GFP+ neutrophils28, and cmyb:GFP fish that have GFP+ progenitors8. These animals can be further mated to generate double-transgenic reporters, such as gata1:dsRed; cd41:gfp18 animals, which are essential for observing erythroid and thrombocytic development in the same animal. When these transgenic animals are used, the lineage commitment of HSPCs is easily visualized without any staining. Examples of the most common transgenic strains that are suitable for the detection of individual colony types are listed in Table 1. This protocol also enables the study of HSPCs from mutant fish with various hematopoietic defects. A number of mutant phenotypes have been described so far29 (e.g., vlad tepes, cloche, and moonshine), many of which have yet to be mapped to defects in HSPC lineage decisions. The use of these functional HSPC assays will probably lead to functional characterization of genes altered in prior (and future) mutant screens.
TABLE 1.
Colony generation depends on zebrafish cytokines present in the medium.
| Cytokines added | Colony type detected | Suitable zebrafish strain for colony detection | Note |
|---|---|---|---|
| Epo | CFU-E, BFU-E | Tg(b-globin:GFP)41, Tg(gata1:dsRed)26 | |
| Gcsfa/b | CFU-G, CFU-M | Tg(mpx:GFP)28, Tg(lyz:dsRed)42, Tg(mpeg1:GFP)43 | |
| Tpo | CFU-T | Tg(cd41:GFP)27 | |
| Epo, Gcsfa/b | CFU-GEM | Tg(gata1:dsRed, mpx:GFP)16 | |
| Epo, Scfa | CFU-E, BFU-E | Tg(b-globin:GFP)41, Tg(gata1:dsRed)26 | Addition of Scfa increases the proliferation capacity of erythroid colonies |
| Epo, Tpo | CFU-E, BFU-E, CFU-T, CFU-TE | Tg(gata1:dsRed; cd41:GFP)18 | |
| Epo, Gcsfa/b, Tpo | CFU-E, BFU-E, CFU-G, CFU-M, CFU-T, CFU-TE, CFU-GEM, CFU-GEMT | Tg(lyz:dsRed; cd41:GFP)18 | Erythroid colonies can be detected on the basis of hemoglobinization |
CFU-E, colony-forming unit erythroid; BFU-E, burst-forming unit erythroid; CFU-G, colony-forming unit granulocyte; CFU-M, colony-forming unit macrophage; CFU-T, colony-forming unit thrombocyte; CFU-TE, colony-forming unit thrombocyte, erythroid; CFU-GEM, colony-forming unit granulocyte, erythroid, macrophage; CFU-GEMT, colony-forming unit granulocyte, erythroid, macrophage, thrombocyte.
Input cell strategy
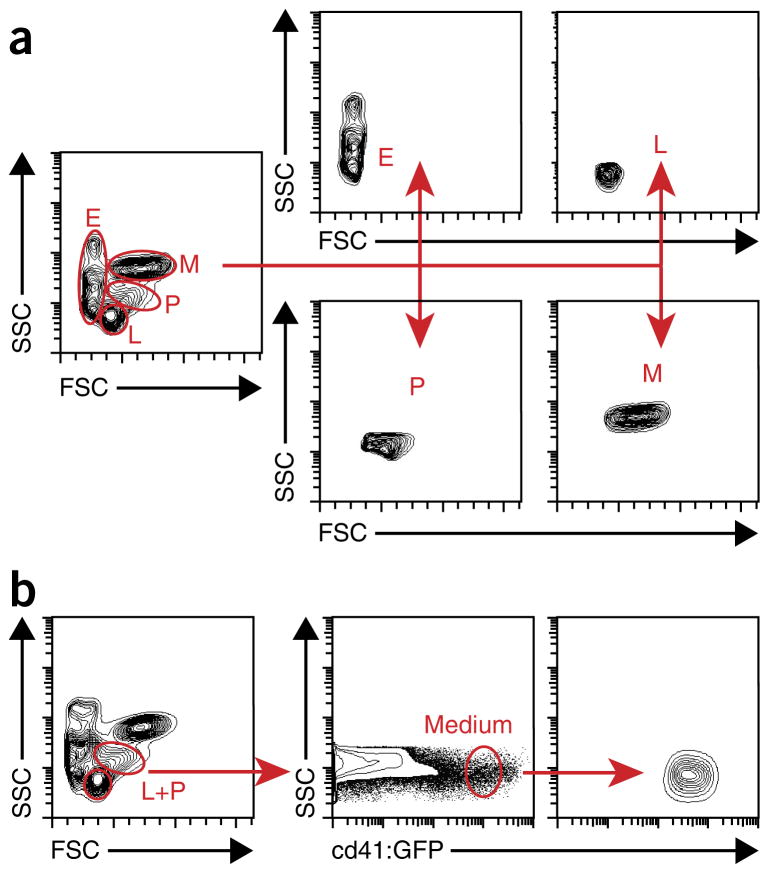
Treatment of cells before plating is one of the most variable factors, and it should be considered carefully depending on the experimental design. Cells can be plated directly after their dissociation from tissues (termed ‘unfractionated cells’), but preferably Ficoll-Hypaque/Biocoll (density 1.077 g/ml) centrifugation should be used to remove unwanted mature erythrocytes and dead cells. These cells are referred to as ‘fractionated cells’. Between 1 and 3 adult fish or 100 and 500 embryos should provide enough cells for seeding one multiwell plate (ANTICIPATED RESULTS). Another method is to sort cells with fluorescence-activated cell sorting (FACS). With FACS, several distinct scatter populations, termed ‘erythroid’, ‘lymphoid’, ‘precursor’, and ‘myeloid’, are resolved by light-scatter characteristics26 (Fig. 2a). Although the sorting strategy depends on your interests, it will influence the composition and number of different HSPCs isolated. For example, we were able to characterize cd41medium cells from the combined ‘lymphoid’ and ‘precursor’ fraction (Fig. 2b) that were significantly enriched in bipotent thrombocytic-erythroid progenitors (TEPs)18.
Figure 2.
Gating strategy for the isolation of specific cell populations via FACS. (a) Representative illustration of the gating for the isolation of distinct fractions of kidney marrow cells: erythroid (E), lymphoid (L), precursor (P), and myeloid (M) populations. (b) Schematic illustration of gating for the isolation of cd41:GFPmedium cells from the combined lymphoid and progenitor (L+P) scatter fractions of adult WKM. Contour plots represent results obtained from analysis of kidneys of five adult Tg(cd41:GFP) fish. Modified from ref. 17; originally published in Blood. Svoboda et al. Dissection of vertebrate hematopoiesis using zebrafish thrombopoietin. Blood. 2014;124:220–228. © The American Society of Hematology.
Culture plates
Which culture plates are best for plating progenitors is another factor that depends on the experimental aims. Generally, it is recommended to use non-tissue-culture-treated dishes that are used for suspension cell culture, which prevents adhesive interactions between the cells and the plate. With this approach, the cultures are more likely to grow colonies as opposed to adherent monolayer cultures. The optimal size of the culture plates depends on the experiment. Generally, multiwell plates work well, because they enable the plating of cells in different cytokine conditions in replicates. However, if high quantities of certain colony types are required, 3- to 6-cm culture dishes also work well. The recommended volume of methylcellulose medium and seeding density vary depending on the size of the plate, as listed in Table 2.
TABLE 2.
Recommended methylcellulose volume and seeding density for selected multiwell plates.
| Type of plate | Methylcellulose volume per well (ml) | Number of seeded cells per well | |
|---|---|---|---|
|
| |||
| Fractionated WKM cells | Sorted cd41medium HSPCs from lymphoid and progenitor scatter fraction | ||
| 6-Well plate | 3 | 40,000 | 4,000 |
| 12-Well plate | 1.6 | 20,000 | 2,000 |
| 24-Well plate | 0.9 | 10,000 | 1,000 |
Culture conditions
Zebrafish hematopoietic cells grow best at 32 °C, in a humidified 5% CO2 environment. Although cells are healthy at the physiological temperature of zebrafish (28 °C), they divide faster and appear similarly healthy at 32 °C. However, raising the temperature to 37 °C for extended periods of time is toxic15.
Medium
Serum is a crucial component of most culture media. It contains growth factors and endogenous cytokines, along with exogenously added cytokines, which cooperatively ensures the optimal growth and differentiation of cells. Presumably because of the high genetic divergence between mammals and teleosts, we observed that our culture conditions required fish serum in addition to FBS. As isolation of sufficient amounts of zebrafish serum is technically challenging30,31, we experimentally tested the serum from other larger but phylogenetically related teleosts. Our experiments indicated that sera derived from multiple fish species such as European perch, salmonids (SeaGrow JJ80), and northern pike were ineffective, whereas serum from the common carp stimulated the most cell survival and proliferation in vitro (Supplementary Fig. 1). We base our experimental conditions for zebrafish culture experiments on chicken culture medium13 and use 10% (vol/vol) FBS and 2% (vol/vol) carp serum. We describe how to prepare carp serum in Box 1 (Supplementary Fig. 2). Even though zebrafish cells can be cultured at concentrations as low as 1% (vol/vol) carp serum, we have found 2% (vol/vol) carp serum to be optimal for hematopoietic progenitor cell self-renewal and differentiation. Given that preparation of carp serum is challenging, we do not recommend decreasing the proportion of FBS and increasing the proportion of carp serum.
Transferrin is an essential mediator of iron transport during erythrocyte differentiation32. Because of the divergence between vertebrate transferrin genes and a lack of available recombinant zebrafish transferrin, we have determined that it is best to include a synthetic iron supplement, ferric salicylaldehyde isonicotinoyl hydrazine (Fe-SIH), in the medium. The addition of Fe-SIH into HSPC cultures enables full erythroid maturation.
Cytokines are essential proteins for manipulating the differentiation of hematopoietic cells ex vivo. Because of their divergence among vertebrates, most mammalian and avian factors are not effective in fish cultures15,16,18,23,33–36. Many genes were duplicated during the evolution of the teleost genome37,38; thus multiple copies of genes that express cytokines are present in zebrafish. It will be essential to identify the functional orthologs of mammalian genes to fully understand their role in zebrafish; this work is ongoing. We have identified, cloned, recombinantly expressed, and purified a number of these genes, such as those encoding erythropoietin (Epo), granulocyte colony–stimulating factor a and b (Gcsfa/b)16,23, and thrombopoietin (Tpo)18. Because cytokines control cell proliferation and differentiation, the choice of particular factors to include in the medium depends on the experimental goals. Erythro-myeloid maturation can be studied with zebrafish Epo and Gcsfa/b15,16,23, and the combination of Epo and Tpo is essential for investigating zebrafish thrombopoiesis18. Individual combinations of cytokines that yield particular types of colonies are listed in Table 1. A negative control, such as PBS or control baculovirus supernatant, should be included in the individual treatments. It is also essential to perform these experiments in replicate.
Because of the evolutionary distance and lack of cross-reactivity between mammalian and zebrafish cytokines, it is necessary to produce them. This includes sequence design, protein expression, and protein purification. For recombinant expression, remove the leader sequence and transmembrane domain from the gene’s coding sequence (CDS), and tag the construct with an N-terminal hexahistidine sequence to allow affinity chromatography purification. For protein expression, first try expression in Escherichia coli, which offers the best protein yield. As an alternative, if the E. coli expression system yields suboptimal results because of low expression levels, recombinant protein toxicity, or issues with protein solubility, the baculovirus expression system can be used (Supplementary Fig. 3). Protein expression levels and purification yields often vary and depend on several factors, such as protein toxicity for host cells and the protein’s size and physiochemical properties. Expression plasmids that can be used to produce recombinant cytokines (Epo, Gcsfa/b and Tpo) in E. coli or insect cells are available through Addgene (IDs 64309, 65611, 65612, and 65613).
MATERIALS
REAGENTS
Animals
Wild-type or transgenic zebrafish, 3–9 months of age, or Zebrafish embryos, 24 h.p.f. and older ! CAUTION All animal procedures must be carried out in accordance with guidelines outlined by the local and national committees for animal experiments.
Cells and media
BL21-CodonPlus (DE3)-RIL competent cells (Agilent Technologies, cat. no. 230245-41)
LB broth, Miller (Sigma-Aldrich, cat. no. L2542)
sf21 insect cells (Gibco, cat. no. 11497-013)
Sf-900 II SFM insect medium (Gibco, cat. no. 10902-096)
Top10 competent cells (Invitrogen, cat. no. C4040-10)
Chemical stocks/reagents
Pierce BCA protein assay kit (Thermo Scientific, cat. no. 23225)
Ethanol (Merck/Mecomm, cat. no. 1009831011) ! CAUTION Ethanol is a flammable liquid and vapor. Handle it with care.
Ethanol 70% (vol/vol) in dH2O ! CAUTION Ethanol 70% (vol/vol) in dH2O is a flammable liquid and vapor. Handle it with care.
Biocoll separating solution (Millipore, cat. no. L6115)
Guanidine hydrochloride (Serva, cat. no. 24200)
HEPES (Gibco, cat. no. 15630-106), 20 mM
Imidazole (Sigma-Aldrich, cat. no. I5513)
Agarose (Amresco, cat. no. J234)
Giemsa stain (Sigma-Aldrich, cat. no. G5637)
NaCl (Roth, cat. no. 3957)
NaH2PO4 (Sigma-Aldrich, cat. no. S3139)
NaHCO3 (Sigma-Aldrich, cat. no. S5761), 5.6% (wt/vol)
NaOH (Sigma-Aldrich, cat. no. S8045)
Ni-NTA agarose (Qiagen, cat. no. 30410)
PBS, 1× (Sigma-Aldrich, cat. no. P4417)
HBSS with Ca2+, Mg2+ (Gibco, cat. no. 14025092)
SYTOXRed (Molecular Probes, cat. no. S34859)
Tris (Roth, cat. no. 4855)
Urea (Serva, cat. no. 24524)
Media components
-
2-Mercaptoethanol (Sigma-Aldrich, cat. no. M6250)
! CAUTION 2-Mercaptoethanol is toxic; avoid inhalation, ingestion, or contact with skin.
BSA, 10% (wt/vol) (StemCell Technologies, cat. no. 09300) ▲ CRITICAL It is crucial to use high-quality BSA that was optimized for growth of human hematopoietic progenitor cells.
Carp serum (Box 1)
DMEM (1×) with high glucose from powder (Gibco, cat. no. 12800)
DMEM (2×) with high glucose from powder (Gibco, cat. no. 12800)
FBS (Gibco, 10270)
-
FBS, embryonic-stem-cell qualified (Biosera, cat. no. FB-1001S/500)
▲ CRITICAL It is crucial to use ES-cell-qualified FBS, as HSPCs are highly sensitive.
FE-SIH iron supplement (Sigma-Aldrich, cat. no. I3153)
H2O (Gibco, cat. no. 15230-097)
L-Glutamine, 0.2 M (Gibco, cat. no. 25030-081)
Methylcellulose powder (Sigma-Aldrich, cat. no. M0387)
Penicillin-streptomycin, 100× (Gibco, cat. no. 15140122)
Molecular biology
Baculogold Bright DNA (BD Biosciences, cat. no. 552846)
Ice
pAcGP-67 A, B, C baculovirus transfer vector set (BD Biosciences, cat. no. 554759)
Liberase TM (Roche, cat. no. 05401119001)
QIAexpress Type IV Kit (Qiagen, cat. no. 32149)
PureLink RNA Micro Kit (Invitrogen, cat. no. 12183016)
Primers (Table 3)
LightCycler DNA Master SYBR Green I (Roche, cat. no. 12015099001)
SuperScript VILO cDNA Synthesis Kit (Invitrogen, cat. no. 11754-050)
TABLE 3.
Primer sequences.
| Gene | Forward primer sequence (5′-3′) | Reverse primer sequence (5′-3′) | Product size (bp) | Note |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| cd41 (ref. 44) | CTGAAGGCAGTAACGTCAAC | TCCTTCTTCTGACCACACAC | 197 | Thrombocytic, HSPC marker |
| c-mpl44 | CGCCAACCAAAGCCAGAGTTA | ACTTTTCAACAGGTGCATCCCA | 103 | Thrombocytic, HSPC marker |
| c-myb | GAGCTGTTCCGAACTCCCAA | TTAATCGTGCCGACCACTCC | 161 | HSPC marker |
| ccr9 (ref. 45) | AACCTCACTCACTCCTCAAAC | CAGACCACCAGAGTGTTACC | 189 | T cell, eosinophilic marker |
| csf1r46 | ATGACCATACCCAACTTTCC- | AGTTTGTTGGTCTGGATGTG | 148 | Macrophage marker |
| csf3r45 | TGAAGGATCTTCAACCACAC | GGGAATTATAGGCCACAAAC | 233 | Granulocytic marker |
| ef1a44 | GAGAAGTTCGAGAAGGAAGC | CGTAGTATTTGCTGGTCTCG | 142 | Housekeeping gene |
| fli1 (ref. 18) | CCGAGGTCCTGCTCTCACAT | GGGACTGGTCAGCGTGAGAT | 87 | Lymphoid, thrombocytic marker |
| gata1 (ref. 44) | TGAATGTGTGAATTGTGGTG | ATTGCGTCTCCATAGTGTTG | 211 | Erythroid marker |
| gata2 (ref. 47) | CCTGCGGGCTCTACTACAAACT | GTCTTGTCCTGCATGCACTTG | 160 | Endothelial, HSC, eosinophilic marker |
| hbA48 | CTGATACGGACAAGGCTGTTGT | AGACGGTCAGCATTCTGGCGA | 99 | Marker of adult erythrocytes |
| hbB48 | ATGGTTGAGTGGACAGATGC | TACACGATCAGACATCTGGATA | 107 | Marker of adult erythrocytes |
| hbBe3 (ref. 47) | TTTCCGGCTGTTAGCGGACT | TTGCCTTCTGAGGGCTGACA | 127 | Marker of primitive erythrocytes |
| lyz | CTGGTGGGAAGAATTTGTG | CCGTCCATTTTCACAATCAG | 100 | Neutrophilic marker |
| marco | ACGACAGCTTCGATAATTTG | AAAATACTGCTCTCGGTTCC | 145 | Macrophage marker |
| mhc2dab45 | CAGGCCTACTTGCATCAATTG | CAGACCAGATGCTCCGATG | 429 | B cell, macrophage, dendritic cell marker |
| mpeg1 (ref. 46) | CCCACCAAGTGAAAGAGG | GTGTTTGATTGTTTTCAATGG | 150 | Macrophage marker |
| mpx44 | TGATGTTTGGTTAGGAGGTG | GAGCTGTTTTCTGTTTGGTG | 161 | Neutrophilic marker |
| pax5 | CTGATTACAAACGCCAAAAC | CTAAATTATGCGCAGAAACG | 177 | B cell marker |
| pu.1 (ref. 44) | AGAGAGGGTAACCTGGACT | AAGTCCACTGGATGAATGTG | 204 | Myeloid marker |
| runx1 (ref. 44) | CGGTGAACGGTTAATATGAC | CTTTTCATCACGGTTTATGC | 139 | HSPC marker |
| tcra | TCGTTTTCAATGTGCTGGTG | GATGATCTGGAATGGGATGC | 139 | T cell marker |
Annealing temperature of listed primers is 60 °C. HSC, hematopoietic stem cell; HSPC, hematopoietic stem and progenitor cell.
EQUIPMENT
12-Well plates
24-Well plates
Absorbent paper towels
Amicon Ultra-15 Centrifugal Filter Unit (Millipore, cat. no. UFC901024)
Bacteriological incubator shaker, 37 °C
Biological cell culture hood with laminar flow and UV light
Burner
Cell culture centrifuge (Beckman Coulter)
Cell culture incubator shaker, 28 °C, humidified
Cell culture incubator, 32 °C, 0–5% CO2, humidified
CASY cell counter (Roche)
Dialysis membrane
Dialysis clips
Amicon ultraspin tubes
Dissecting microscope (Olympus)
Erlenmeyer flask, 1 liter
FACS tubes with filter tops
Falcon conical tubes, 15 ml and 50 ml
Filter units with low-protein-absorption cellulose acetate or polyethersulfone membrane, 0.22, 0.44, and 5 μm (Corning)
Fluoresence-activated cell sorter. We use an Influx cytometer (BD Biosciences)
Glass beaker, 50 ml
Glass slides and coverslips
Hemocytometer
Inverted microscope
Laboratory balance
Needles, 20-gauge × 40 mm (B. Braun, cat. no. 465 7519)
Ni-NTA columns
Nutator
Nylon mesh filter, 70 μm
Polystyrene round-bottom tube with cell-strainer cap, 5 ml (Corning, cat. no. 352235)
Pasteur pipettes
Pestle
Pipetboy (Integra, cat. no. 155 000)
PIPETMAN tips for 1,000, 200, and 30 μl (Gilson)
PIPETMAN filter tips for 1,000, 200, 20, and 10 μl (Gilson, cat. nos. F81004, F81003 and F81002, F81001)
Repetman (Gilson)
Repet-tips, 12.5 ml (Gilson, cat. no. F164560)
Serological pipettes for 2, 10, and 25 ml
Stainless steel microscissors
Stainless steel fine forceps, Dumont positive tweezers, style 55 (Electron Microscopy Sciences, cat. no. 72707-01)
Standard microcentrifuge for 1.5-ml microcentrifuge tubes
Sterile Eppendorf tubes, 1.5 ml
Sterile Eppendorf tubes, 2 ml
Syringes, 12 ml
REAGENT SETUP
Washing medium
To 435 ml of DMEM, add 50 ml of FBS, 10 ml of 0.2 M L-glutamine, and 5 ml of 100× penicillin–streptomycin. Store the medium at 4 °C for up to 3 months.
CFU-erythroid medium
Combine the reagents listed below to obtain 100 ml of CFU-erythroid (CFU-E) medium. All reagents should be stored according to the manufacturer’s directions.
| Components | Volume | Final concentration |
|---|---|---|
| DMEM | 69.3 ml | |
| H2O | 7 ml | |
| FBS | 10 ml | 10% (vol/vol) |
| Carp serum (Box 1) | 2 ml | 2% (vol/vol) |
| 10% BSA | 5 ml | 0.5% (wt/vol) |
| 5.6% NaHCO3 | 3.6 ml | 0.2% (wt/vol) |
| Fe-SIH, 1,000× | 0.1 ml | |
| 1 M 2-mercaptoethanol | 10 μl | 100 μM |
| Penicillin–streptomycin, 100× | 1 ml | Penicillin (100 U/ml), streptomycin (100 μg/ml) |
| 0.2 M L-glutamine | 2 ml | 4 mM |
After mixing the reagents, saturate the medium with CO2. For this, swirl the medium and introduce the CO2 by gently foaming the gas above the liquid level until the medium becomes orange in color. Sterilize the solution using a 0.2-μm filter. Store it at 4 °C for at least 3 months.
Methylcellulose stock, 2% (wt/vol)
Weigh 10 g of methylcellulose and sterilize it under UV light for 30 min. Transfer the methylcellulose powder into a 1-liter Erlenmeyer flask and add 225 ml of sterile H2O. Mix the solution and bring it to a boil. Swirl the flask vigorously and then cool it to below 50 °C, and then add 225 ml of 2× DMEM. Adjust the weight of the mixture to 503 g with sterile water. Stir the stock overnight at 4 °C, and allow it to thicken before dividing the stocks into aliquots and storing them at −20 °C.
Complete methylcellulose medium
Combine the reagents listed below to obtain 100 ml of complete methylcellulose medium. Store the mixture at 4 °C for up to 3 months. All reagents except methylcellulose stock and carp serum should be stored according to the manufacturer’s directions. The carp serum should be stored according to the instructions in Box 1.
| Components | Volume | Final concentration |
|---|---|---|
| Methylcellulose stock | 60 ml | 1.2% (wt/vol) |
| H2O | 16.3 ml | |
| FBS | 10 ml | 10% (vol/vol) |
| Carp serum | 2 ml | 2% (vol/vol) |
| 10% BSA | 5 ml | 0.5% (wt/vol) |
| 5.6% NaHCO3 | 3.6 ml | 0.2% (wt/vol) |
| Fe-SIH, 1,000× | 0.1 ml | |
| 1 M 2-mercaptoethanol | 10 μl | 100 μM |
| Penicillin–streptomycin, 100× | 1 ml | Penicillin (100 U/ml), streptomycin (100 μg/ml) |
| 0.2 M L-glutamine | 2 ml | 4 mM |
PROCEDURE
Obtaining zebrafish HSPCs ● TIMING 5–70 min
-
1|
To isolate zebrafish HSPCs from adult fish, follow option A. To isolate HSPCs from embryos, follow option B.
! CAUTION All animal procedures must be carried out in accordance with ethical guidelines outlined by local and national committees for animal experiments.
▲ CRITICAL STEP Isolation must be performed on a clean lab bench using sterile instruments and filter pipette tips.
(A) Dissection of zebrafish kidneys ● TIMING 5–10 min per fish
-
Place fish in ice-cold water until no signs of life are visible, as determined by cessation of opercula movement (2–3 min).
▲ CRITICAL STEP Fish euthanasia with low toxicity and high efficacy is crucial. We do not recommend euthanizing the fish with common anesthetics such as tricaine methanesulfonate because of the potential molecular and cellular off-target effects of the drug. As a substitution, we recommend using rapid cooling with ice water for zebrafish euthanasia39,40.
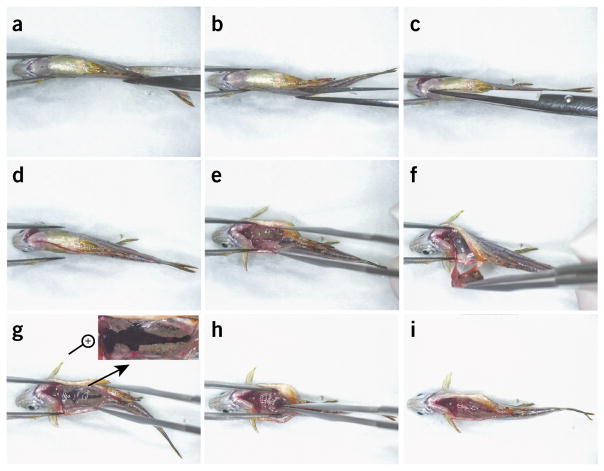
Briefly dip fish into 70% (vol/vol) ethanol to sterilize the skin, and place it on absorbent paper towels under a dissecting microscope (Fig. 3a). Remove any residual ethanol droplets using absorbent paper towels.
-
Use scissors to make an opening anteriorly from the anus along the ventral midline for the entire length of the abdomen (Fig. 3b–d and Supplementary Video 1).
▲ CRITICAL STEP Take care not to damage the intestines, as this might cause contamination of samples.
Use forceps to remove the internal organs. Take care not to damage the kidney (black and silver tissue along the spine, Fig. 3e,f and Supplementary Video 1).
Collect the head, body, and tail kidney (anterior to posterior) using sterile forceps, and pull out the whole organ (Fig. 3g–i and Supplementary Video 1).
Transfer the kidney into 2-ml Eppendorf tubes prefilled with 400 μl of FBS.
Figure 3.
Dissection of zebrafish kidney. (a–i) Screenshots from the full dissection video (Supplementary Video 1). (a) Position the anesthetized fish under a dissecting microscope. (b–d) Make an opening using scissors along the entire length of the abdomen. (e,f) Remove the internal organs; take care not to rupture intestines. (g–i) A magnified view of the kidney structure is shown at the top right corner in g, and collection of the kidney marrow, from anterior to posterior, is shown in h and i.
(B) Dissociation of zebrafish embryos ● TIMING 35–70 min
Collect as many embryos as possible, and place them into ice-cold water until no signs of life are present (5–15 min).
Transfer the embryos into 1.5-ml Eppendorf tubes. Use ~100 embryos per tube.
Remove any liquid from embryos with a pipette.
Wash the embryos three times with PBS and once with washing medium (Reagent Setup).
-
Homogenize the embryos with a pestle several times.
▲ CRITICAL STEP If you are using embryos younger than 48 h.p.f., proceed directly to Step 2. If you are using embryos older than 48 h.p.f., proceed with enzymatic digestion, Step 1B(vi).
Incubate the embryos in HBSS containing Liberase TM enzymes at a final concentration of 50 μg/ml for 30 min at 37 °C under high agitation.
Washes ● TIMING 20 min
▲ CRITICAL Perform Steps 2–10 in a tissue culture hood using sterile technique.
-
2|
Disaggregate tissues by repeated trituration with a 1,000-μl filter tip.
-
3|
Filter cells through the 70-μm nylon mesh into a 15-ml tube.
-
4|
Wash the filter with 10 ml of washing medium.
-
5|
Spin down the cells for 4 min at 400g.
▲ CRITICAL STEP Perform all centrifugation steps at room temperature (RT; 20 °C).
Preparation of individual hematopoietic populations ● TIMING 30–120 min
-
6|
Prepare the population of unsorted fractionated WKM cells using Biocoll density centrifugation (option A) or proceed with FACS to sort individual cell populations (option B).
(A) Preparation of fractionated WKM or embryo-derived cells ● TIMING 40 min
▲ CRITICAL If you plan to use unfractionated WKM cells, omit Step 6A(iii–vi).
Wash the pellet with 10 ml of washing medium and spin down the cells for 4 min at 400g, RT to pellet cells.
Resuspend the pellet in 10 ml of washing medium in a 15-ml conical Falcon tube.
Slowly layer 1.5 ml of Biocoll solution underneath the cells by placing the Pasteur pipette at the bottom of the sample. Alternatively, slowly layer the cells over the Biocoll solution using a serological pipette.
Spin down the cells for 9 min at 1,100g, RT.
-
Transfer the interface using a Pasteur pipette into another 15-ml tube.
▲ CRITICAL STEP The interface may not appear if a low amount of starting material was used. If this is the case, collect the interface together with Biocoll solution, without touching the pellet.
? TROUBLESHOOTING
Fill the tube with washing medium.
Spin down the cells for 4 min at 400g, RT.
Discard the supernatant and resuspend the cell pellet in 100 μl of ES-cell-qualified FBS per fish or per 100 embryos.
-
Count cells using a cell counter or a hemocytometer.
? TROUBLESHOOTING
(B) Cell sorting ● TIMING 30–120 min
Wash the pellet with 10 ml of PBS, and spin down the cells for 4 min at 400g, RT to pellet cells.
Resuspend the cell pellet in 500 μl of PBS per fish or per 100 embryos.
Stain the cells using a dead cell probe such as SYTOXRed (final concentration, 5 nM), which does not interfere with GFP or dsRed fluorescence.
-
Filter the cells using a polystyrene round-bottom tube with a 35-μm cell-strainer cap. Analyze and sort cells by influx cytometer or equivalent (e.g., BD Aria). Collect the sorted cells into a 2-ml Eppendorf tube prefilled with 500 μl of ES-cell-qualified FBS chilled to 4 °C.
▲ CRITICAL STEP Precoat the tube with FBS. This will prevent sorted droplets from drying out on the tube’s wall.
Spin down the cells for 4 min at 400g, RT.
-
Discard the supernatant and resuspend the cell pellet in ES-cell-qualified FBS to a final concentration of up to 1 × 106 cells per ml. Confirm the number of sorted cells using a hemocytometer.
? TROUBLESHOOTING
Plating of hematopoietic cells ● TIMING 20–30 min per plate
-
7|
Mix cells with methylcellulose in 50-ml Falcon tubes to reach the desired final cell density (see Experimental design section and Table 2).
-
8|
Tightly cap the tubes and gently vortex or nutate (rock) them for 15 min at RT.
▲ CRITICAL STEP Take care to prevent introducing air bubbles.
-
9|
Pipette appropriate cytokines (Table 1) to the bottom of wells in a multiwell plate. For all cytokines, start with a volume that will give a final concentration of 100 ng/ml for recombinant purified proteins or 50× dilution for baculovirus supernatants.
▲ CRITICAL STEP This approach significantly reduces the number of individual Falcon tubes that are needed for the preparation of cell-methylcellulose solution when multiple combinations of cytokines are used. Cytokines loaded in small droplets can evaporate quickly; proceed quickly or dilute cytokines in PBS before pipetting.
-
10|
Divide the cell–methylcellulose solution into plates containing cytokines using Repetman and a 12.5-ml RepetTip (for recommended volumes, see Table 2).
▲ CRITICAL STEP Be careful not to introduce any bubbles.
▲ CRITICAL STEP Certain cytokines are extremely active even at very low concentrations. Be aware of any potential cytokine cross-contamination when using a single RepetTip.
▲ CRITICAL STEP If there are any empty wells in your plates, fill them with sterile water. This will help preserve the humidity inside the plates.
Growth and evaluation of hematopoietic colonies ● TIMING variable; days to weeks
-
11|
Maintain the plates at 32 °C in a humidified atmosphere of 5% CO2.
-
12|
Remove the plates after 3–21 d (3 d for early myeloid and erythroid colonies; 7, 10, 14, and 21 d for mixed, thrombocytic, erythroid, and myeloid colonies) for colony examination, imaging, and enumeration.
▲ CRITICAL STEP When you are growing the colonies for extended periods of time (>14 d), overlay the cells every 7th d with 100 μl of CFU-E medium (Reagent Setup) containing required growth factors. For subsequent analysis of individual colonies, proceed to Step 13 (optional).
? TROUBLESHOOTING
-
13|
Pluck colonies from methylcellulose using a pipette and a fine 30-μl tip (Supplementary Fig. 4). Be careful to pick only individual colonies. If needed, colonies of similar morphology may be pooled together. For histology of colony-forming cells, follow option A. For expression profiling of individual colonies, follow option B. To characterize colony proliferation capacity, follow option C
? TROUBLESHOOTING
(A) Histology of colony-forming cells ● TIMING 60 min
Place colonies into a 1.5-ml Eppendorf tube prefilled with 200 μl of FBS, and dissociate them by repeated trituration.
Spin down the cells for 30 s at 16,000g, RT.
Discard the supernatant and resuspend the cell pellet in 1–5 μl of FBS to obtain highly concentrated cell suspension.
Cytospin or smear cells and stain them with Giemsa stain according to the manufacturer’s protocol.
(B) Gene expression profiling of individual colonies ● TIMING 2–3 h
Place colonies into a 1.5-ml Eppendorf tube prefilled with 200 μl of FBS.
Spin down the cells for 4 min at 400g, RT and resuspend the pellet in PureLink lysis buffer.
Extract and purify total RNA using the PureLink RNA Micro Kit according to the manufacturer’s protocol.
Generate the first-strand cDNA using the SuperScript VILO cDNA Synthesis Kit according to the manufacturer’s protocol. A 20-μl reaction volume works well.
Perform PCR using LightCycler DNA Master SYBR Green I according to the manufacturer’s protocol. Use 1 μl of cDNA as a template. Primers are listed in Table 3. Use ef1a as a housekeeping reference gene. The annealing temperature is 55 °C.
(C) Characterization of colony proliferation capacity ● TIMING 60 min
-
Place colonies into a 1.5-ml Eppendorf tube prefilled with 50 μl of PBS, and dissociate them by repeated trituration.
▲ CRITICAL STEP Certain erythroid colonies are resistant to mechanical dissociation, and their disruption requires enzymatic treatment. For this, incubate colonies in 50 μl of HBSS containing Liberase TM enzyme at a final concentration of 100 μg/ml for 10 min at 37 °C and dissociate again by repeated trituration.
-
Count the number of colony-forming cells with a cell counter or hemocytometer.
▲ CRITICAL STEP Avoid any washing steps during this protocol, as any washes might cause cell loss.
▲ CRITICAL STEP Sometimes, even after enzymatic digestions, some cells remain in clumps. If the clumps contain more than eight cells, accurate counting will be hindered.
? TROUBLESHOOTING
Troubleshooting advice can be found in Table 4.
TABLE 4.
Troubleshooting table.
| Step | Problem | Possible reason | Solution |
|---|---|---|---|
| 6A(v) | No visible cells in the interface | Low amount of starting material | Collect the interface together with Biocoll solution |
| 6A(ix) | Low yield of isolated cells | Low amount of starting material | Increase the number of animals; use older or larger animals |
| Insufficient dissociation of kidney marrow | Dissociate the marrow more extensively, and split kidney marrow from multiple animals into several tubes | ||
| 6B(vi) | Low number of sorted cells | Rare population of gated cells | Change the gating strategy |
| Cells do not enter the sorting tube | Recalibrate the FACS instrument | ||
| Cells stick to the wall of the sorting tube, dying during the sorting process | Coat the wall of collection tubes with medium, and re-coat it during the sort if needed | ||
| Cells die during the sorting process | Make sure to keep the cells chilled during the sorting process | ||
| 12 | No or low colony growth | Low number of seeded cells | Increase the number of seeded cells |
| Ineffective cytokine stimulation | Increase the effective concentration of cytokine tested or test cooperation between several cytokines | ||
| Unhealthy or inbred fish | Test different fish | ||
| Methylcellulose too dense | Prepare fresh 2% (wt/vol) methylcellulose stock and mix new complete methylcellulose | ||
| Colonies are present even in a negative control | Colony density is too high | Plate fewer cells; when over-plated, cells often generate microenvironments that help them survive and proliferate even without the presence of exogenous supporting factors | |
| Yeast or bacterial contamination producing microbial colonies | Follow sterile techniques, especially during kidney dissection; use sterile forceps when removing kidney marrow; test for the presence of microbial organisms in a culture medium, especially in carp serum | ||
| Large chunks present in methylcellulose | Methylcellulose stock contains insoluble pieces of methocel | Swirl methylcellulose vigorously after bringing it to a boil during its preparation. Allow the methylcellulose stock to sediment for 1–2 d before using it for mixing the complete methylcellulose. Note: it is common for methylcellulose to contain a small amount of insoluble clumps | |
| Cells are concentrated on a single area within the well | Inefficient mixing of cell– methylcellulose mixture | Mix the cell–methylcellulose mixture more thoroughly | |
| 13 | Inability to isolate single colonies | Colony density is too high | Plate fewer cells |
● TIMING
Step 1, obtaining zebrafish HSPCs: 5–70 min
Step 1A, dissection of zebrafish kidneys: 5–10 min per fish
Step 1B, dissociation of zebrafish embryos: 35–70 min
Steps 2–5, washes: 20 min
Step 6, preparation of individual hematopoietic population: 30–120 min
Step 6A, preparation of fractionated WKM cells or embryo-derived cells: 40 min
Step 6B, cell sorting: 30–120 min
Steps 7–10, plating of hematopoietic cells: 20–30 min per plate
Steps 11–13, growth and evaluation of hematopoietic colonies: variable; days to weeks
Step 13A, histology of colony-forming cells: 60 min
Step 13B, gene expression profiling of individual colonies: 2–3 h
Step 13C, characterization of colony proliferation capacity: 60 min
Box 1, preparation of carp serum: 1.5 d
Box 2, generation of cytokines: weeks to months
ANTICIPATED RESULTS
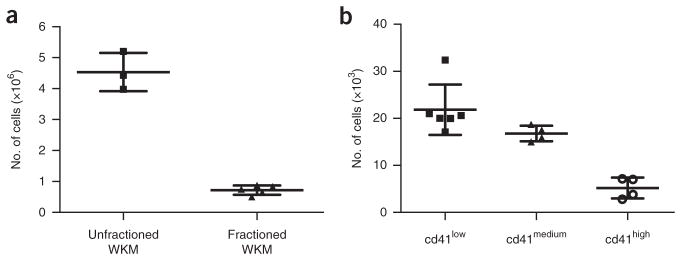
This protocol allows the isolation of zebrafish HSPCs from kidney marrow or embryos and their subsequent growth and differentiation into distinct blood lineages. A typical cell yield from kidney marrow is demonstrated in Figure 4. Unfractionated cell fractions consist predominantly of mature erythrocytes, whereas the fractionated population consists mainly of HSPCs and myeloid cells. Cell yields and composition are influenced by the fish’s age and size16. In our experience, the number of mature myeloid cells increases over time in the WKM at the expense of the number of progenitor cells. However, we also have noted that fish size positively correlates with the number of progenitor cells in kidneys. An average number of isolatable, unfractionated WKM cells is ~4–5 × 106 per fish, whereas the number of fractionated WKM cells will be only 0.5–1 × 106 cells per fish (Fig. 4a). The number of sorted cells depends on the desired gating strategy. As an example, cd41:GFP reporter fish have, on average, 21 × 103 cd41low, 18 × 103 cd41medium and 4 × 103 cd41high isolatable cells (Fig. 4b). Similarly, the number and composition of isolatable embryonic cells varies according to the developmental stage and gating strategy.
Figure 4.
Number of HSPCs in zebrafish WKM. (a) Total number of unfractionated and fractionated WKM cells per fish. (b) Total number of cd41low, cd41medium, and cd41high cells isolated from the lymphoid and progenitor scatter fractions. Each dot represents the number of cells per individual fish. Error bars represent ±s.d. Figure reproduced from ref. 17; originally published in Blood. Svoboda et al. Dissection of vertebrate hematopoiesis using zebrafish thrombopoietin. Blood. 2014;124:220–228. © The American Society of Hematology.
Zebrafish hematopoietic colonies appear after only a few days in culture, and they can be grown for up to 1–2 months when supplemented with CFU-E medium and growth factors at regular intervals, which prevents the wells from drying out and provides cells with additional cytokines and nutrients. Erythroid ((burst-forming unit (BFU)-E, CFU-E; Fig. 5a), thrombocytic (CFU-T, Fig. 5a), and myeloid (CFU-macrophage/granulocyte (M/G), Fig. 5b) colonies first appear at days 2 and 3. CFU-M/G colonies should be enumerated at that time; later, the colonies become too dense, reach the bottom of the plate, and spread/dissociate. The BFU-E and CFU-E colonies can be distinguished and enumerated according to their size starting at day 4. At day 5, hemoglobinization occurs in erythroid colonies, which makes them a dark reddish color that allows easy visualization with bright-field microscopy. Mixed erythro-thrombocytic colonies (CFU-TE, Fig. 5a) can be recognized at day 4, and multipotent CFU-GEM/GEMT (granulocyte-erythroid-macrophage/granulocyte-erythroid- macrophage-thrombocyte; Fig. 5b) colonies can be identified after day 6.
Figure 5.
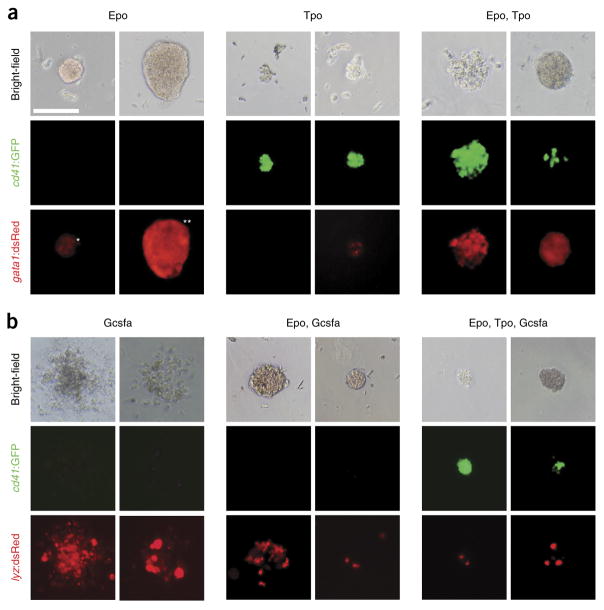
Representative images of particular colonies grown in methylcellulose. (a,b) Progenitor cells isolated from fractionated WKM of adult (a) Tg(cd41:GFP, gata1:dsRed) and (b) Tg(cd41:GFP, lyz:dsRed) fish were grown for 4 d in the presence of zebrafish cytokines. (a) Epo stimulates growth and differentiation of small CFU-E (*) and large BFU-E (**) colonies that are hemoglobinized and express gata1:dsRed (left). Tpo stimulates growth and differentiation of relatively small CFU-T colonies that express high levels of cd41: GFP and low levels of gata1:dsRed (middle). Combinatorial addition of Epo and Tpo stimulates mixed CFU-TE colonies, consisting of clusters of erythrocytes and thrombocytes that express high levels of both cd41:GFP and gata1:dsRed (right). (b) Gcsf stimulates growth and differentiation of myeloid CFU-G/M colonies that express lyz:dsRed (left), whereas the combination of Epo and Gcsf encourages differentiation of hemoglobinized lyz:dsRed CFU-GEM colonies (middle). Combinatorial addition of Epo, Tpo, and Gcsf expands hemoglobinized CFU-GEMT colonies that express both cd41:GFP and lyz:dsRed (right). All photomicrographs were taken at original magnification ×200. Scale bar (top left) represents 100 μm in all images. Modified from ref. 17; originally published in Blood. Svoboda et al. Dissection of vertebrate hematopoiesis using zebrafish thrombopoietin. Blood. 2014;124:220–228. © The American Society of Hematology.
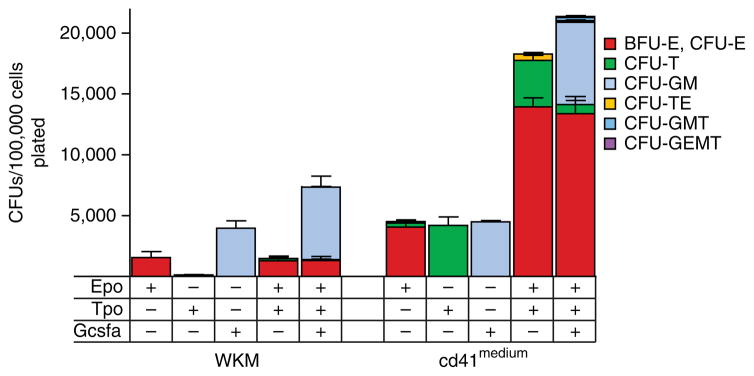
The composition and number of particular colonies depends on the particular population of cells plated and on the zebrafish cytokines present in medium, as shown in Table 1. The most abundant types of HSPCs in fractionated WKM are erythroid and myeloid progenitors (Fig. 6). For example, the cd41medium population yields myeloid progenitors and a higher number of erythroid progenitors. It also contains a significant enrichment of thrombocytic and bipotent TEPs, as well as other HSPCs, such as granulocyte-macrophage-thrombocyte (GMT) and GEMT progenitors (Fig. 6). All colonies that are described above can be easily identified using single- and double-transgenic reporter fish, as described in Table 1.
Figure 6.
Enumeration of colonies from fractionated WKM cells and cd41medium cells. Colonies were generated by cell culture in methylcellulose with Epo, Tpo, or Gcsf or with a combination of Epo and Tpo or of Epo, Tpo, and Gcsf. Overall cell differentiation potential is represented by the number of colony-forming units (CFUs) per 100,000 cells plated. Bars represent mean values of biological triplicate experiments, and error bars represent s.d. Modified from ref. 17; originally published in Blood. Svoboda et al. Dissection of vertebrate hematopoiesis using zebrafish thrombopoietin. Blood. 2014;124:220–228. © The American Society of Hematology.
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Ministry of Education, Youth and Sports—Program NPU I (LO1419), the Czech Science Foundation (16-21024S to P.B.), the Charles University Grant Agency (598712 to O.S.), and the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (NIDDK) at the National Institutes of Health (NIH; K01-DK087814-01A1 to D.L.S.).
Footnotes
AUTHOR CONTRIBUTIONS O.S., D.L.S., O.M., and P.B. performed the research; O.S., D.L.S., and P.B. designed the research; O.S., D.L.S., and P.B. wrote the manuscript; and L.I.Z. and D.T. provided critical reagents for the work, as well as suggestions on experimental design.
COMPETING FINANCIAL INTERESTS The authors declare competing financial interests: details are available in the online version of the paper.
Note: Any Supplementary Information and Source Data files are available in the online version of the paper.
References
- 1.de Jong JL, Zon LI. Use of the zebrafish system to study primitive and definitive hematopoiesis. Annu Rev Genet. 2005;39:481–501. doi: 10.1146/annurev.genet.39.073003.095931. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Carroll KJ, North TE. Oceans of opportunity: exploring vertebrate hematopoiesis in zebrafish. Exp Hematol. 2014;42:684–696. doi: 10.1016/j.exphem.2014.05.002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Boatman S, et al. Assaying hematopoiesis using zebrafish. Blood Cells Mol Dis. 2013;51:271–276. doi: 10.1016/j.bcmd.2013.07.009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Stewart AM, Braubach O, Spitsbergen J, Gerlai R, Kalueff AV. Zebrafish models for translational neuroscience research: from tank to bedside. Trends Neurosci. 2014;37:264–278. doi: 10.1016/j.tins.2014.02.011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Goessling W, North TE. Repairing quite swimmingly: advances in regenerative medicine using zebrafish. Dis Model Mech. 2014;7:769–776. doi: 10.1242/dmm.016352. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.White R, Rose K, Zon L. Zebrafish cancer: the state of the art and the path forward. Nat Rev Cancer. 2013;13:624–636. doi: 10.1038/nrc3589. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Yen J, White RM, Stemple DL. Zebrafish models of cancer: progress and future challenges. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2014;24:38–45. doi: 10.1016/j.gde.2013.11.003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Bertrand JY, et al. Haematopoietic stem cells derive directly from aortic endothelium during development. Nature. 2010;464:108–111. doi: 10.1038/nature08738. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Espin-Palazon R, et al. Proinflammatory signaling regulates hematopoietic stem cell emergence. Cell. 2014;159:1070–1085. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2014.10.031. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Kim AD, et al. Discrete Notch signaling requirements in the specification of hematopoietic stem cells. EMBO J. 2014;33:2363–2373. doi: 10.15252/embj.201488784. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Kim AD, Stachura DL, Traver D. Cell signaling pathways involved in hematopoietic stem cell specification. Exp Cell Res. 2014;329:227–233. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2014.10.011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Bock TA. Assay systems for hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells. Stem Cells. 1997;15:185–195. doi: 10.1002/stem.5530150824. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Beug H, Steinlein P, Bartunek P, Hayman MJ. Avian hematopoietic cell culture: in vitro model systems to study oncogenic transformation of hematopoietic cells. Methods Enzymol. 1995;254:41–76. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(95)54006-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Alexander WS, Begley CG. Thrombopoietin in vitro and in vivo. Cytokines Cell Mol Ther. 1998;4:25–34. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Stachura DL, et al. Zebrafish kidney stromal cell lines support multilineage hematopoiesis. Blood. 2009;114:279–289. doi: 10.1182/blood-2009-02-203638. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Stachura DL, et al. Clonal analysis of hematopoietic progenitor cells in the zebrafish. Blood. 2011;118:1274–1282. doi: 10.1182/blood-2011-01-331199. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Stachura DL, Traver D. Cellular dissection of zebrafish hematopoiesis. Methods Cell Biol. 2011;101:75–110. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-387036-0.00004-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Svoboda O, et al. Dissection of vertebrate hematopoiesis using zebrafish thrombopoietin. Blood. 2014;124:220–228. doi: 10.1182/blood-2014-03-564682. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Moore MA, Williams N, Metcalf D. In vitro colony formation by normal and leukemic human hematopoietic cells: characterization of the colony-forming cells. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1973;50:603–623. doi: 10.1093/jnci/50.3.603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.McCulloch EA. Stem cells in normal and leukemic hemopoiesis (Henry Stratton Lecture, 1982) Blood. 1983;62:1–13. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Coulombel L. Identification of hematopoietic stem/progenitor cells: strength and drawbacks of functional assays. Oncogene. 2004;23:7210–7222. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1207941. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Quelen C, et al. Identification of a transforming MYB-GATA1 fusion gene in acute basophilic leukemia: a new entity in male infants. Blood. 2011;117:5719–5722. doi: 10.1182/blood-2011-01-333013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Stachura DL, et al. The zebrafish granulocyte colony-stimulating factors (Gcsfs): 2 paralogous cytokines and their roles in hematopoietic development and maintenance. Blood. 2013;122:3918–3928. doi: 10.1182/blood-2012-12-475392. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Surdziel E, et al. Enforced expression of miR-125b affects myelopoiesis by targeting multiple signaling pathways. Blood. 2011;117:4338–4348. doi: 10.1182/blood-2010-06-289058. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Gerlach GF, Schrader LN, Wingert RA. Dissection of the adult zebrafish kidney. J Vis Exp. 2011;54:2839–2844. doi: 10.3791/2839. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Traver D, et al. Transplantation and in vivo imaging of multilineage engraftment in zebrafish bloodless mutants. Nat Immunol. 2003;4:1238–1246. doi: 10.1038/ni1007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Lin HF, et al. Analysis of thrombocyte development in CD41-GFP transgenic zebrafish. Blood. 2005;106:3803–3810. doi: 10.1182/blood-2005-01-0179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Renshaw SA, et al. A transgenic zebrafish model of neutrophilic inflammation. Blood. 2006;108:3976–3978. doi: 10.1182/blood-2006-05-024075. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Davidson AJ, Zon LI. The ‘definitive’ (and ‘primitive’) guide to zebrafish hematopoiesis. Oncogene. 2004;23:7233–7246. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1207943. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Murtha JM, Qi W, Keller ET. Hematologic and serum biochemical values for zebrafish (Danio rerio) Comp Med. 2003;53:37–41. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Pedroso GL, et al. Blood collection for biochemical analysis in adult zebrafish. J Vis Exp. 2012:3865–3868. doi: 10.3791/3865. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Napier I, Ponka P, Richardson DR. Iron trafficking in the mitochondrion: novel pathways revealed by disease. Blood. 2005;105:1867–1874. doi: 10.1182/blood-2004-10-3856. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Katzenback BA, Belosevic M. Molecular and functional characterization of kita and kitla of the goldfish (Carassius auratus L.) Dev Comp Immunol. 2009;33:1165–1175. doi: 10.1016/j.dci.2009.06.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Liongue C, Hall CJ, O’Connell BA, Crosier P, Ward AC. Zebrafish granulocyte colony-stimulating factor receptor signaling promotes myelopoiesis and myeloid cell migration. Blood. 2009;113:2535–2546. doi: 10.1182/blood-2008-07-171967. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Paffett-Lugassy N, et al. Functional conservation of erythropoietin signaling in zebrafish. Blood. 2007;110:2718–2726. doi: 10.1182/blood-2006-04-016535. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Santos MD, Yasuike M, Hirono I, Aoki T. The granulocyte colony-stimulating factors (CSF3s) of fish and chicken. Immunogenetics. 2006;58:422–432. doi: 10.1007/s00251-006-0106-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Meyer A, Schartl M. Gene and genome duplications in vertebrates: the one-to-four (-to-eight in fish) rule and the evolution of novel gene functions. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1999;11:699–704. doi: 10.1016/s0955-0674(99)00039-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Meyer A, Van de Peer Y. From 2R to 3R: evidence for a fish-specific genome duplication (FSGD) Bioessays. 2005;27:937–945. doi: 10.1002/bies.20293. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Chen K, et al. The evaluation of rapid cooling as an anesthetic method for the zebrafish. Zebrafish. 2014;11:71–75. doi: 10.1089/zeb.2012.0858. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Wilson JM, Bunte RM, Carty AJ. Evaluation of rapid cooling and tricaine methanesulfonate (MS222) as methods of euthanasia in zebrafish (Danio rerio) J Am Assoc Lab Anim Sci. 2009;48:785–789. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Pugach EK, Li P, White R, Zon L. Retro-orbital injection in adult zebrafish. J Vis Exp. 2009:1645–1648. doi: 10.3791/1645. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Hall C, Flores MV, Storm T, Crosier K, Crosier P. The zebrafish lysozyme C promoter drives myeloid-specific expression in transgenic fish. BMC Dev Biol. 2007;7:42. doi: 10.1186/1471-213X-7-42. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Ellett F, Pase L, Hayman JW, Andrianopoulos A, Lieschke GJ. mpeg1 promoter transgenes direct macrophage-lineage expression in zebrafish. Blood. 2011;117:49–56. doi: 10.1182/blood-2010-10-314120. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Bertrand JY, Kim AD, Teng S, Traver D. CD41+ cmyb+ precursors colonize the zebrafish pronephros by a novel migration route to initiate adult hematopoiesis. Development. 2008;135:1853–1862. doi: 10.1242/dev.015297. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Balla KM, et al. Eosinophils in the zebrafish: prospective isolation, characterization, and eosinophilia induction by helminth determinants. Blood. 2010;116:3944–3954. doi: 10.1182/blood-2010-03-267419. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Wittamer V, Bertrand JY, Gutschow PW, Traver D. Characterization of the mononuclear phagocyte system in zebrafish. Blood. 2011;117:7126–7135. doi: 10.1182/blood-2010-11-321448. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Gardiner MR, Gongora MM, Grimmond SM, Perkins AC. A global role for zebrafish klf4 in embryonic erythropoiesis. Mech Dev. 2007;124:762–774. doi: 10.1016/j.mod.2007.06.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Tiedke J, Gerlach F, Mitz SA, Hankeln T, Burmester T. Ontogeny of globin expression in zebrafish (Danio rerio) J Comp Physiol B. 2011;181:1011–1021. doi: 10.1007/s00360-011-0588-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Kondo H, Watabe S. Growth promoting effects of carp serum components on goldfish culture cells. Fisheries Sci. 2006;72:4. [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.