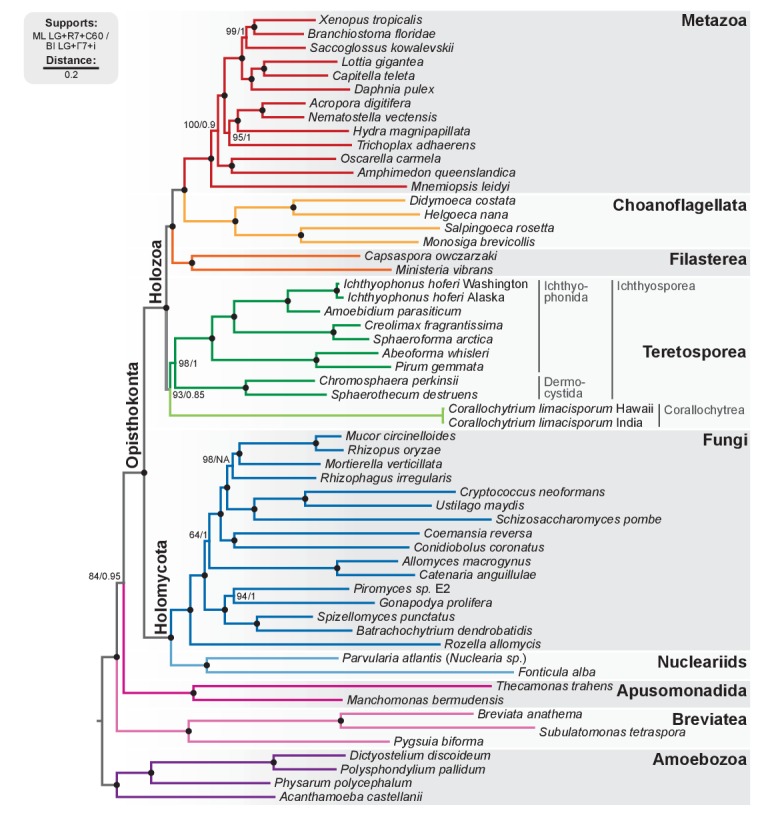
Figure 2. Phylogenomic tree of Unikonta/Amorphea.
Phylogenomic analysis of the BVD57 taxa matrix. Tree topology is the consensus of two Markov chain Monte Carlo chains run for 1231 generations, saving every 20 trees and after a burn-in of 32%. Statistical supports are indicated at each node: (i) non-parametric maximum likelihood ultrafast-bootstrap (UFBS) values obtained from 1000 replicates using IQ-TREE and the LG + R7+C60 model; (ii) Bayesian posterior probabilities (BPP) under the LG+Γ7 + CAT model as implemented in Phylobayes. Nodes with maximum support values (BPP = 1 and UFBS = 100) are indicated by a black bullet. See Figure 2—figure supplement 1 for raw trees with complete statistical supports. Figure 2—source data 1.
DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.7554/eLife.26036.007