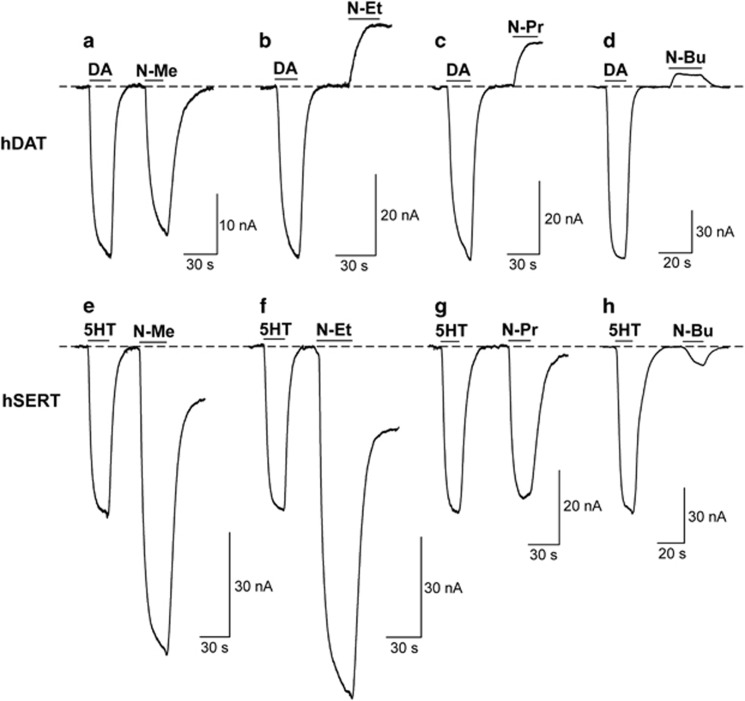
Figure 2.
Effect of N-substituted 4-MA analogs on membrane currents in oocytes transfected with hDAT or hSERT. In voltage-clamped (Vcom=–60 mV) hDAT-expressing oocytes 10 μM N-methyl 4-MA produces an inward current (a), and 10 μM N-ethyl 4-MA (b), N-propyl 4-MA (c), and N-butyl 4-MA (d) display a block of the endogenous hDAT leak current. For comparison, individual traces are adjusted to match the inward current in response to hDAT endogenous substrate DA (5 μM, shown before application of the N-substituted 4-MA analogs) (a–d). In voltage-clamped (Vcom=–60 mV) hSERT-expressing oocytes, all N-substituted 4-MA analogs produce inward currents (e–h); however, 10 μM N-methyl 4-MA (e) and N-ethyl 4-MA (f) display large responses, N-propyl 4-MA displays a moderate response (g), and N-butyl 4-MA (h) produces a small response. For comparison, individual traces are adjusted to match an inward current in response to hSERT endogenous substrate 5HT (5 μM, shown before application of the N-substituted 4-MA analogs) (e–h). Horizontal dotted lines along the baseline (ie, holding current) for hDAT and hSERT recordings are added to compare compound responses.