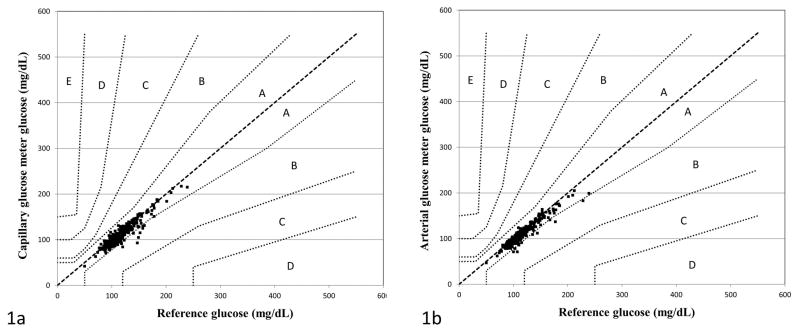
Figure 1.
Clinical concordance between capillary glucose meter (1a) and arterial glucose meter (1b) and reference glucose values as demonstrated by the Parkes error grid for Type 1 Diabetes. To meet ISO 15197:2013 accuracy guidelines, 99% of glucose meter values must fall within zone A (no effect on clinical action) or zone B (altered clinical action—little or no effect on clinical outcome). Zones C-E on the error grid represent progressively more serious insulin dosing errors that may lead to patient harm.