Abstract
A growing body of evidence suggests glutamate excess in schizophrenia and that N-methyl-d-aspartate receptor (NMDAR) hypofunction on γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA) interneurons disinhibiting pyramidal cells may be relevant to this hyperglutamatergic state. To better understand how NMDAR hypofunction affects the brain, we used Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy and resting state functional MRI to study the effects of ketamine on hippocampal neurometabolite levels and functional connectivity in 15 healthy human subjects. We observed a ketamine induced increase of hippocampal Glx (glutamate+glutamine; F= 3.76; p= 0.04), a decrease in fronto-temporal (t=4.92, pFDR< .05, kE= 2198, x= -30, y= 52, z= 14) and temporo-parietal functional connectivity (t=5.07, pFDR< .05, kE= 6094, x= -28, y= -36, z= -2), and a possible link between connectivity changes and elevated Glx. Our data empirically support that hippocampal glutamatergic elevation and resting state network alterations may arise from NMDAR hypofunction and establish a proof of principle whereby experimental modelling of a disorder can help mechanistically integrate distinct neuroimaging abnormalities in schizophrenia.
Keywords: schizophrenia, Glx (glutamate+glutamine), N-methyl-d-aspartate receptor (NMDAR), GABA, psychosis, fronto-temporal, temporo-parietal
INTRODUCTION
Although the dopamine model of schizophrenia remains heuristically valuable, this phenotypically complex illness cannot be explained by dopaminergic dysfunction alone. A growing body of evidence suggests glutamate excess in schizophrenia1-3 and that N-methyl-d-aspartate receptor (NMDAR) hypofunction on γ -aminobutyric acid (GABA) interneurons disinhibiting pyramidal cells may be relevant to this hyperglutamatergic state4-6.
Due to its unique composition, with approximately 90% of its neurons being pyramidal cells, the hippocampus is a region that may be especially vulnerable to shifts in the excitation/inhibition balance secondary to NMDAR hypofunction as opposed to the cerebral cortex where the number of pyramidal neurons and interneurons is more similar7. Post-mortem and neuroimaging studies suggest extensive hippocampal pathology in schizophrenia7-11. We recently reported evidence of glutamatergic excess in the hippocampus in unmedicated patients1 using Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy (MRS), a technique that allows neurometabolite quantification in vivo. Glutamatergic hyperactivity has been shown to result in disorganized neuronal activity in animal models4. Resting state functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging (fMRI) allows approximation of neuronal activity by measuring the temporal covariation of low frequency fluctuations of the blood oxygen level dependent (BOLD) signal12. In schizophrenia, aberrant hippocampal resting state connectivity to frontal areas including the anterior cingulate cortex (ACC), medial prefrontal cortex (MPFC), parietal areas including the posterior cingulate cortex (PCC) and precuneus, as well as the thalamus13, 14 and striatum15-18 suggests disorganized neuronal activity, possibly related to NMDAR hypofunction15. Unfortunately, even contemporary imaging techniques cannot readily quantify NMDAR function in vivo. Alternatively, experimental manipulation of the NMDAR could provide proof of principal and advance our mechanistic understanding of the illness.
Subanesthetic doses of ketamine preferentially block NMDAR on GABAergic interneurons19-21 and have been shown to transiently induce a behavioral phenotype similar to that seen in schizophrenia22-26, without long term adverse effects27. However, previous neuroimaging studies have not mapped ketamine’s effect on hippocampal glutamate and functional connectivity in the same population, which could inform a mechanistically based and clinically relevant model integrating different patterns of brain abnormalities. To programmatically build upon our recent studies in schizophrenia1, 10, 15, 16, 28, 29, we enrolled a group of healthy volunteers to contrast (1) hippocampal Glx (glutamate+glutamine) using MRS and (2) hippocampal connectivity using resting state fMRI during a saline infusion and during a ketamine challenge. We hypothesized that experimentally induced NMDAR blockage would result in an increase of hippocampal Glx and in fronto-temporal and temporo-parietal functional dysconnectivity, resembling abnormalities seen in the disorder. Additionally, we conducted exploratory analyses investigating relationships between Glx, functional connectivity, and psychosis severity.
METHODS
Subjects
We recruited 19 healthy volunteers who gave written informed consent for this Institutional Review Board approved study. Exclusion criteria were a history of an Axis I disorder or a psychotic disorder in a first-degree family member, major medical or neurological conditions, lifetime use of psychotropic medications, prior exposure to ketamine, and pregnancy or breastfeeding.
Subjects meeting eligibility criteria during a phone screen were invited to complete a Diagnostic Interview for Genetic Studies and a psychiatric assessment and physical exam conducted by a board certified psychiatrist (NVK). Urine drug screens and, if applicable, pregnancy tests were completed during the screen and before each ketamine infusion. The Hamilton Rating Scale for Depression (HRSD)30 and Young Mania Rating Scale (YMRS)31 were used to assess mood symptoms before each infusion. The Clinician Administered Dissociative States Scale (CADSS)32 and the Brief Psychiatric Rating Scale (BPRS)33 were completed before and after the ketamine challenge (subjects were asked to retrospectively report symptoms at the time drug effects were the most prominent).
To ensure drug tolerability and minimize novelty, subjects received an intravenous racemic ketamine challenge (0.27mg/kg bolus over 10 minutes, followed by a continuous infusion of 0.25mg/kg/hour for 50 minutes) in the Clinical Research Unit at least one week prior to imaging. Ten milliliters of blood were collected immediately after completion of the bolus and 50 minutes after start of the challenge during the drug tolerability assessment rather than scanning to avoid potential delays in our scanning timeline due to complications during the blood draws. Blood samples were centrifuged to obtain plasma and stored at -40°C. Ketamine plasma levels were assayed (Nathan Klein Institute) using a liquid chromatographic procedure. During the ketamine challenge, vital signs including heart rate, blood pressure, peripheral oxygen saturation, and respiratory rate (CO2 monitoring during scanning) were monitored by an anaesthesiology fellow under supervision of a board certified anaesthesiologist according to the standards for basic anaesthetic monitoring. Monitoring was continued for one hour after infusion completion. Prior to discharge into the care of an accompanying driver, subjects were medically cleared by the fellow and psychiatrist.
Two subjects withdrew from the study because they developed emesis, and two subjects revoked consent after the initial ketamine challenge, citing time constraints as their reason (both denied adverse drug effects); 15 subjects completed imaging.
Following anatomical, spectroscopy, and resting state fMRI scans during a saline infusion (flow rate of 0.01ml/s), subjects were given a short break. After repeat anatomical scans, subjects received a ketamine challenge consisting of a bolus (0.27mg/kg over 10 minutes), followed by a continuous infusion (0.25mg/kg/hour, flow rate of 0.01ml/s). Spectroscopy acquisition was started approximately 13 minutes after start of the challenge (10 minutes for bolus administration and 3 minutes for shimming, this also allowed for stabilization of ketamine plasma levels) and lasted for 21.3 minutes and followed by resting state scans that were started approximately 45 minutes after the start of the challenge and lasted for 7.5 minutes.
Image acquisition
Imaging was performed on a 3T head-only scanner (Magnetom Allegra, Siemens). A high-resolution structural scan was acquired (MPRAGE, TR/TE/TI=2300/3.93/1100msec, 1mm isotropic voxels).
A series of T1-weighted anatomical scans (TR/TE= 250/3.48ms, 5mm slice thickness) were acquired to aid placement of the left hippocampus spectroscopy voxel (2.7×1.5×1cm; Figure 1). Voxel placement for the second acquisition was guided by an image of the voxel placement during the first scan. After manual shimming, CHESS pulses were used to suppress the water signal. Spectra were acquired using a PRESS sequence (TR/TE= 2000/80ms to optimize the glutamate signal34 and minimize macromolecule contribution; 1200 Hz spectral bandwidth; 1024 points; 640 averages, and 8 averages without water suppression).
Figure 1.
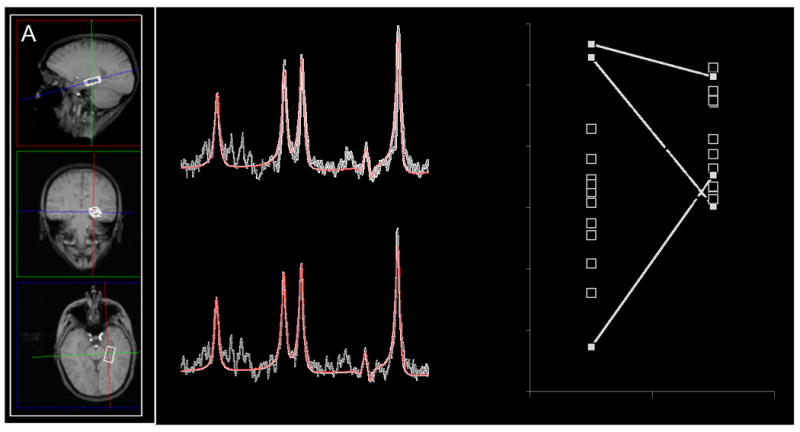
(A) Example of magnetic resonance spectroscopy (MRS) voxel placement in the left hippocampus (2.7×1.5×1cm). The image is displayed in radiological convention (right side of image is subject’s left side). (B+C) Example spectra of the same subject during (B) saline infusion and (C) ketamine infusion. The black line is a spectrum (640 averages) obtained from the left hippocampus voxel, the red line is an overlay of spectral fit. (D) Hippocampal Glx during saline and ketamine infusion (n= 15). Squares represent individual measurements. Lines connect saline and ketamine measurements of individual subjects. Boxplots indicated that Glx measures during saline the infusion for three subjects were outliers (no outliers detected during ketamine challenge). Repeating analyses excluding these subjects did not alter results, Glx remained significantly higher during ketamine challenge compared to saline infusion (n= 12; F= 9.408; p< 0.01). Grey indicates that Glx value during saline infusion was an outlier. Cho, choline; Cr, creatine; Glx, glutamate + glutamine; NAA, N-acetyl-aspartate; ppm, parts per million.
Resting state fMRI scans were acquired during a gradient recalled echo-planar imaging sequence (TR/TE= 2000/30msec, flip angle= 70°, field of view= 192×192mm2, 64×64 matrix, 6mm slice thickness, 1mm gap, 30 axial slices, 225 acquisitions). Subjects were instructed to keep their eyes open and stare passively ahead. No subject reported falling asleep during the resting state scan.
MRS data processing
MRS data were quantified in the time domain with AMARES35 in jMRUI (version 5.2); prior knowledge derived from in vitro and in vivo metabolite spectra was included in the model, as reported elsewhere1, 28. Exclusion criteria were (1) line width of the magnitude signal during manual shimming >20 Hz at FWHM and (2) Cramer-Rao lower bounds (CRLB) >20%. No spectra were excluded. Metabolites were quantified with respect to creatine (Cr/ internal water (W) did not differ between conditions; F= 0.517; p= .48); for the sake of brevity they will be referred to as Glx, NAA (N-acetyl-aspartate+ N-acetylaspartylglutamate), and Cho (glycerophosphocholine+ phosphocholine) hereafter. Structural scans were segmented into grey matter (GM), white matter (WM), and cerebrospinal fluid to calculate voxel tissue fractions, using in house Matlab codes.
Resting state data processing
After removing the first five frames from each run to allow for signal equilibration, data were slice timing corrected, realigned, co-registered, normalized, and spatially smoothed with a 6mm Gaussian kernel using the conn toolbox in SPM8.36 Physiological and other spurious sources of noise were estimated with aCompcor, and the first five principal temporal components each from white matter and CSF were removed37. No global signal regression was performed. Frames with movement >0.5mm or global signal z score change >3 were identified with artifact detection (ART), scrubbed38, and excluded from analyses. Residual data were band-pass filtered (0.009-0.08 Hz). The entire time series was excluded if >50% of frames were contaminated by movement, or if mean framewise displacement exceeded 0.5mm. No scans met these criteria. We observed no differences in mean framewise displacement (saline: 0.18+/-0.06mm; ketamine: 0.20+/-0.08mm; t= -1.17; p= 0.26), or mean proportion of frames scrubbed (saline: 6.71+/- 5.46%; ketamine: 8.31+/-7.71%; t= -0.70; p= 0.50) across time points. The first eigenvariate of the BOLD time series from a left hippocampus seed region, defined by the AAL atlas, was extracted and correlated to the time series of all other voxels to create seed-to-voxel correlation maps for each subject.
Statistical Analyses
To investigate change in metabolites between saline and ketamine infusions, we used a mixed repeated measures design with neurometabolites as dependent variables, experimental condition (saline vs ketamine) as fixed factor, and voxel GM fraction (GM%/ GM%+ WM%)39 as covariate. Given directionality in hypothesis for changes in Glx, we conducted a one-sided test; changes in other metabolites were examined with two-sided tests. Results were considered statistically significant at p< .05. In an exploratory fashion, we also examined relationships between Glx and clinical observations using Pearson’s correlations.
To investigate change in functional connectivity between saline and ketamine infusions, we did paired-sample t-tests on the subject level connectivity maps. Analyses were limited (masked) to include only regions that were functionally connected to the hippocampus in at least one of the conditions (saline/ ketamine). These masks were computed by thresholding (PFDR< .05), binarizing, and then combining each within-group analysis (both conditions) producing masks of the combined connected areas. Analyses were corrected for multiple comparisons using the false discovery rate (FDR) and are reported at pFDR< 0.05. To assess the relationship between resting state connectivity changes and Glx, we created connectivity change maps using the ImCalc function in SPM8, and extracted the first eigenvariate for each cluster that showed decreased connectivity during the ketamine challenge, which was then correlated with Glx during the ketamine challenge.
In an exploratory fashion, we used regression analyses to examine relationships between connectivity during the saline infusion and ketamine induced severity of psychosis (to assess to what extent baseline functional connectivity may be related to the brain’s propensity to develop psychosis) and between connectivity during the ketamine challenge and ketamine induced severity of psychosis, defined as BPRS total score. To explore if any associations unique to symptom dimension exist, we then performed regression analysis using both BPRS positive and negative symptom scores as regressors in the same analysis.40
RESULTS
Demographics, clinical observations, and laboratory results
Fifteen subjects (10 male/ 5 female) aged 24.80+/- 3.49 years completed scanning. One subject smoked 3 cigarettes per day; all others denied smoking. None had HDRS or YMRS scores in the clinical range. BPRS and CADSS scores were significantly higher during the ketamine challenge compared to the saline infusion (Table 1). Ketamine plasma levels were 74.27+/- 22.08ng/ml and 97.47+/- 19.59ng/ml immediately after completion of the bolus and 50 minutes after start of infusion, respectively.
Table 1.
Clinical measures1
| Saline | Ketamine | t-score | p value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BPRS2 | ||||
| Total | 20.60 (0.74) | 32.73 (4.94) | -9.742 | < .01 |
| Positive | 3.00 (0.00) | 5.87 (1.69) | -6.590 | < .01 |
| Negative | 3.13 (0.35) | 6.87 (1.96) | -7.047 | < .01 |
| CADSS | ||||
| Total score | 0.07 (0.02) | 13.60 (6.50) | -8.049 | < .01 |
| Amnesia | 0.07 (0.02) | 2.07 (1.71) | -4.472 | < .01 |
| Derealization | 0.00 (0.00) | 7.27 (3.92) | -7.183 | < .01 |
| Depersonalization | 0.00 (0.00) | 3.47 (2.10) | -6.394 | < .01 |
| Confusion | 0.00 (0.00) | 0.13 (3.52) | -1.468 | 0.16 |
| HRSD | 0.20 (0.40) | |||
| YMRS | 0.20 (0.56) |
Abbreviations: BPRS Brief Psychiatric Rating Scale; CADSS Clinician Administered Dissociative States Scale; HRSD Hamilton Rating Scale for Depression; YMRS Young Mania Rating Scale
Mean (SD) unless indicated otherwise, n= 15
Brief Psychiatric Rating Scale (1 – 7 scale); positive (conceptual disorganization, hallucinatory behavior, and unusual thought content); negative (emotional withdrawal, motor retardation, and blunted affect)
MRS measurements
We found a significant increase in Glx during the ketamine challenge compared to the saline infusion, Glx/W increased at trend level (saline: 0.18, ketamine: 0.21; F 1.977 p= .09); NAA and Cho did not differ between measurements (Table 2, Figure 1). We observed no correlations between BPRS or CADSS scores and Glx at endpoint or percent change in Glx between saline and ketamine infusions (all p > .05).
Table 2.
Neurometabolites and spectral quality indices 1
| Saline | Ketamine | t/F | p value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Neurometabolite measurements | ||||
| Glx | 0.62 (0.13) | 0.69 (0.08) | 3.756 | 0.042 |
| NAA | 1.35 (0.10) | 1.38 (0.16) | 0.346 | 0.57 |
| Cho | 0.94 (0.12) | 0.96 (0.16) | 0.151 | 0.70 |
| Spectral quality indices | ||||
| Glx CRLB | 0.09 (0.02) | 0.10 (0.02) | -2.182 | 0.05 |
| NAA CRLB | 0.04 (0.01) | 0.04 (0.01) | -1.799 | 0.09 |
| Cho CRLB | 0.03 (0.01) | 0.03 (0.01) | -1.713 | 0.11 |
| FWHM | 7.42 (1.32) | 7.63 (1.46) | -0.694 | 0.50 |
| SNR | 12.57 (1.76) | 11.89 (1.85) | 1.260 | 0.23 |
| Voxel tissue fraction | ||||
| grey matter (%) | 63.67 (4.64) | 63.11 (6.00) | 0.527 | 0.61 |
| white matter (%) | 33.64 (4.81) | 34.42 (6.45) | -0.701 | 0.50 |
| cerebrospinal fluid (%) | 2.68 (0.14) | 2.47 (0.16) | 1.009 | 0.33 |
Abbreviations: Cho Choline; CRLB, Cramer Rao Lower Bounds; FWHM Full width at half maximum; Glx glutamate+glutamine; NAA N-acetyl-aspartate; SNR Signal to noise ratio
Mean (SD) unless indicated otherwise, n= 15
one-sided F test
Resting state functional connectivity
Left hippocampus functional connectivity patterns during the saline infusion were consistent with prior reports in healthy subjects (supplemental Figure). During the ketamine challenge, we found two clusters of decreased connectivity, a frontal cluster spanning across the ACC, MPFC, and middle cingulate (t=4.92, kE [cluster extent]= 2198, x= -30, y= 52, z= 14) and a largely temporo-parietal cluster spanning from the bilateral hippocampus to the right insula, bilateral precuneus, PCC, lingual gyrus, and calcarine sulcus (t=5.07, kE= 6094, x= -28, y= -36, z= -2). No areas showed increased hippocampus connectivity during the ketamine challenge. We observed a significant negative correlation between Glx during the ketamine challenge and hippocampus connectivity change with ketamine in the frontal cluster (r= 0.52; p<.05) and a trend-level negative correlation between Glx during the ketamine challenge and hippocampus connectivity change with ketamine in the temporo-parietal cluster (r= 0.51; p= .05; Figure 2). No correlations between connectivity change and change in Glx were observed.
Figure 2.
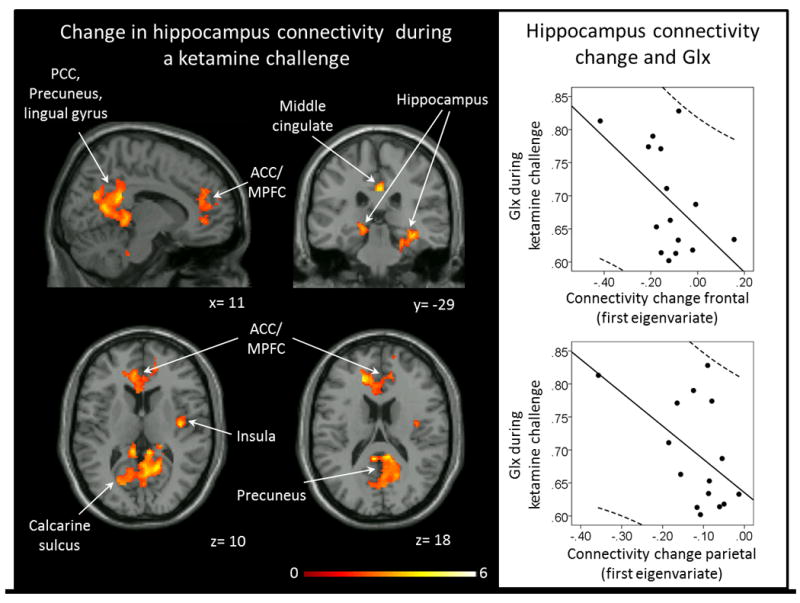
Left: Areas of decreased functional connectivity during a ketamine challenge compared to a saline infusion (pFDR< .05). No areas of increased connectivity during the ketamine challenge were detected. Clusters were overlaid on the Xjview single subject T1 template. Numbers indicate MNI coordinates. Color bar indicates t values. Right: Correlations between ketamine induced connectivity change (first eigenvariate) and Glx during a ketamine challenge. ACC: anterior cingulate cortex, MPFC: medial prefrontal cortex, Glx: glutamate+glutamine, PCC: posterior cingulate cortex.
BPRS total score during the ketamine challenge was negatively correlated with hippocampus connectivity during saline infusion to a cluster spanning across the ACC, MPFC, insula and rolandic operculum (t=5.68, kE= 2626, x= -6, y= 44, z= -18) and to a cluster spanning across the temporal lobe and cerebellum (t=5.50, kE= 4053, x= -66, y= -38, z= -22). BPRS total scores during the ketamine challenge were negatively correlated with hippocampus connectivity during the ketamine challenge to a cluster spanning across the superior frontal gyrus, middle cingulum, PCC, and precuneus (t=7.06, kE= 5916, x= 4, y= 10, z= 42) and to a cluster spanning across the bilateral parahippocamus, superior/ inferior parietal cortices, superior and middle occipital cortices, and lingual gyrus (t=5.07, kE= 6094, x= -28, y= -36, z= -2; Figure 3). None of the associations were unique to a specific symptom dimension.
Figure 3.
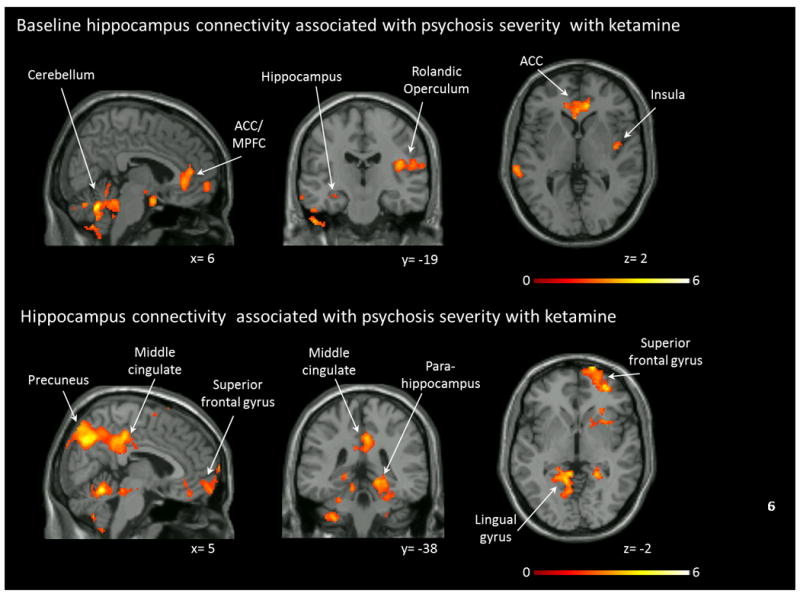
Resting state functional connectivity in relation to symptom severity. Top row: Functional connectivity during a saline infusion in relationship to Brief Psychiatric Rating Scale (BPRS) total scores during a ketamine challenge. Clusters indicate regions where connectivity was negatively correlated with symptom severity (pFDR< .05). No clusters were detected that showed positive correlations between connectivity and symptom severity. Bottom row: Functional connectivity during a ketamine challenge in relationship to BPRS total scores during the ketamine challenge. Clusters indicate regions where connectivity was negatively correlated with symptom severity (pFDR< .05). No clusters were detected that showed positive correlations between connectivity and symptom severity. Clusters were overlaid on the Xjview single subject T1 template. Numbers indicate MNI coordinates. Color bar indicates t values. ACC: anterior cingulate cortex, MPFC: medial prefrontal cortex.
DISCUSSION
To our knowledge, this is the first study to date combining MRS and resting state fMRI to probe the effects of experimentally induced NMDAR hypofunction in vivo in healthy human subjects, and the first to report elevated subcortical glutamatergic levels after ketamine administration. We observed a ketamine induced increase of hippocampal Glx, a decrease in fronto-temporal and temporo-parietal functional connectivity, and a possible link between connectivity changes and elevated Glx. It is important to note that alterations closely resemble hippocampal neurometabolic and network-level abnormalities we have previously reported in unmedicated patients with schizophrenia1, 15. Our experiment adds to the efforts in bridging the gap between contemporary mechanistic models and findings from in vivo neuroimaging studies in schizophrenia, suggesting that hippocampal glutamate excess and functional network disturbances may reflect a disrupted excitation/ inhibition balance.
In agreement with this, prior studies have reported elevated hippocampal rCBF in unmedicated patients41 and elevated hippocampal blood volume in medicated patients42. Linking cellular-level mechanisms and neuroimaging findings, Schobel and colleagues reported a series of experiments in a mouse model of schizophrenia, showing that ketamine administration causes an increase in extracellular glutamate, hippocampal hypermetabolism, and atrophy. In parallel, they identified a relationship between hippocampal hypermetabolism and structural deficits in patients transitioning from a prodromal state to syndromal psychosis43. The authors concluded that glutamate acts as a pathogenic driver of hippocampal pathology.
Because neuronal composition is variable across the brain, it is conceivable that disparate regions express differential vulnerability to disease mechanisms. Probing sensitivity to ketamine induced NMDAR hypofunction, two prior studies reported increases of glutamatergic indices in the ACC44, 45, but others found no change in the ACC46 and occipital cortex47. Like us, Rowland and colleagues reported no relationship between glutamatergic indices and BPRS or CADSS scores, which is consistent with many studies in schizophrenia that fail to establish a direct link between glutamate excess and symptom severity48. While it is possible that these indices reflect a more general marker of psychopathology that is not readily captured by behavioral scales, an alternative interpretation is that clinical symptoms may emerge from disrupted network-level functional connectivity patterns related to glutamate excess. In other words, it is possible that glutamate acts as moderating variable between resting state connectivity and behavioral symptoms.
Ketamine induced NMDAR hypofunction on GABA interneurons has been shown to disrupt gamma oscillations49, which are thought to regulate synchronized brain activity50, and in turn could also affect resting state connectivity. Several studies have reported ketamine induced connectivity changes, including increased whole brain global connectivity51, increased cortico-thalamic connectivity52, decreased default mode network connectivity53, and mixed increases and decreases among eight large scale networks54. Examining prefrontal-hippocampal connectivity using region-of-interest masks in the dorsolateral prefrontal cortices and bilateral hippocampi, Grimm and colleagues reported hyperconnectivity after a ketamine challenge55. While this may appear to be inconsistent with our finding of a decrease in hippocampus connectivity, we may have simply captured a different window in the temporal dynamic56 of ketamine induced network changes (we scanned during the ketamine administration, whereas Grimm scanned 20 minutes after completion of the challenge). Preclinical models suggest a dose dependent ketamine induced extracellular glutamate increase of up to 200-300% of baseline levels within 20 minutes of administration with the effect subsiding between 60 and 100 minutes of administration57. Similarly, an MRS study examining ketamine effects in the MPFC suggests a 17+/-25% increase of Glx within 30 minutes of administration that subsided within one hour58, which is consistent findings of a 13C-MRS study reporting an increase of 3C enrichment of glutamate-C4 of approximately 15%59, and similar to our report of a mean increase of 15.9+/-28% of hippocampal Glx.
Ketamine induced decreases in cortico-hippocampal functional connectivity spanning to the ACC, MPFC, insula, precuneus, and lingual gyrus reported here recapitulate preclinical findings of NMDAR hypofunction related hippocampal connectivity changes to homologous areas of the rat brain60. In parallel, ketamine modulates cerebral blood flow (rCBF) in the hippocampus, ACC, MPFC, and lingual gyrus in both healthy controls and volunteers with schizophrenia41, 42, again implicating vulnerability to NMDAR blockage in this functional circuit.
It is intriguing that ketamine induces cortico-hippocampal circuitry alterations that are similar to those seen in schizophrenia15-18 but does not replicate hippocampal connectivity abnormalities to the thalamus and to the striatum13-15, 61, an area rich in dopaminergic innervation. This possibly reflects a dissociation of glutamate and dopamine system abnormalities, which is in agreement with prior studies failing to reverse ketamine induced psychosis with haloperidol, a dopamine D2 receptor antagonist, in healthy subjects and volunteers with schizophrenia22, 62. Alternatively, it may be related to the ketamine dose63 or to the statistical threshold set for image analyses, since fronto-striatal-thalamic connectivity has been shown to increase with ketamine64, and preclinical models have established a link between hippocampal glutamate and dopamine firing in the ventral tegmental area65. Taken together, findings argue against a simplistic interpretation of ketamine as a schizophrenia model but rather for a model of a hyperglutamatergic stage66 or subtype of the illness. A recent report of elevated cortical glutamate (though no data exists for the hippocampus) in patients with treatment-resistant schizophrenia compared to treatment-responsive patients67 underscores the value of this pharmacological neuroimaging phenotype as translational target for novel drug development.
Interestingly, lower hippocampus connectivity during saline infusion to the ACC and insula, both regions part of a network responding to behaviourally salient events and reported abnormal in schizophrenia68, 69, was related to higher symptom severity during the ketamine challenge. Putting this in context of NMDAR blockage induced reductions in connectivity, it is tempting to interpret findings akin to a cognitive reserve model70, where greater hippocampal functional connectivity during saline infusion to the salience network may provide a higher threshold for clinical symptoms to emerge and thus reflect the brain’s resilience to developing psychosis. The possibility of leveraging neuroimaging data to predict behaviour, disease vulnerability, or propensity to treatment response is of great interest to the field71. For example, the predictive value of imaging biomarkers for antipsychotic response in schizophrenia is beginning to be explored68, 72. As this area of research matures, we can hope to be able to derive illness models that can bridge mechanisms of brain function and pathology at the macroscopic scale to disease vulnerability and behavioral phenotypes.
Several strengths and limitations need to be considered. To be able to compare spectroscopy and resting state data with our previous studies, imaging and data analysis parameters replicated those we had implemented previously (except for more stringent movement correction of resting state data here). We did not include a placebo control. Because of ketamine’s unique side effect profile, including dissociative effects and nystagmus, the risk of “unblinding” is substantial73. We acknowledge that it would be ideal to include a study arm with an active placebo that could mitigate these concerns74, but any drug producing similar side effects could also confound neurometabolite measurements and resting state connectivity, making interpretation of findings difficult. Additionally, a counterbalance design and randomization of subjects to the different conditions could have better controlled for anticipation and expectancy effects. We reported a significant increase in Glx using a one sided t-test given the directionality of our hypothesis based on our report in schizophrenia, but we were underpowered to detect significant abnormalities in Glx/W and in Glx assuming the directionality of the change had been unknown a priori. Also, MRS data was collected only once, which precludes us to directly comment on the temporal dynamics of hippocampal Glx changes.
In summary, our data empirically support that hippocampal glutamatergic elevation and resting state network alterations may arise from NMDAR hypofunction and establish a proof of principle whereby experimental modelling of a disorder can help mechanistically integrate distinct neuroimaging abnormalities in schizophrenia. The results of this study also have potential clinical implications. Medications attenuating the impact of hippocampal glutamatergic hyperactivity could conceivably diminish functional dysconnectivity and perhaps alleviate disease burden across symptom dimensions in this profoundly disabling neuropsychiatric disorder. Future studies investigating the utility of these translational biomarkers to assess target engagement, circuit-relevant pharmacodynamic activity, and efficacy of novel pharmacotherapies will be important to inform this question.
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank Ariel Kidwell for her assistance in data collection and the BRAMILA lab for providing the tool for calculation of framewise displacements. This work was supported by the National Institute of Mental Health (K23MH106683, NVK; R01MH102951, ACL) and the UAB Civitan International Research Center and UAB Center for Clinical and Translational Science (NVK).
Footnotes
Conflict of Interest:
ACL has received an investigator initiated grant from Janssen Pharmaceuticals. All other authors declare no conflicts of interest, including relevant financial interests, activities, relationships, and affiliations.
References
- 1.Kraguljac NV, White DM, Reid MA, Lahti AC. Increased hippocampal glutamate and volumetric deficits in unmedicated patients with schizophrenia. JAMA Psychiatry. 2013;70(12):1294–1302. doi: 10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2013.2437. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.de la Fuente-Sandoval C, Leon-Ortiz P, Favila R, Stephano S, Mamo D, Ramirez-Bermudez J, et al. Higher levels of glutamate in the associative-striatum of subjects with prodromal symptoms of schizophrenia and patients with first-episode psychosis. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2011;36(9):1781–1791. doi: 10.1038/npp.2011.65. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Kegeles LS, Mao X, Stanford AD, Girgis R, Ojeil N, Xu X, et al. Elevated prefrontal cortex gamma-aminobutyric acid and glutamate-glutamine levels in schizophrenia measured in vivo with proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2012;69(5):449–459. doi: 10.1001/archgenpsychiatry.2011.1519. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Moghaddam B, Javitt D. From revolution to evolution: the glutamate hypothesis of schizophrenia and its implication for treatment. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2012;37(1):4–15. doi: 10.1038/npp.2011.181. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Olney JW, Farber NB. Glutamate receptor dysfunction and schizophrenia. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1995;52(12):998–1007. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.1995.03950240016004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Javitt DC. Twenty-five years of glutamate in schizophrenia: are we there yet? Schizophr Bull. 2012;38(5):911–913. doi: 10.1093/schbul/sbs100. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Heckers S, Konradi C. GABAergic mechanisms of hippocampal hyperactivity in schizophrenia. Schizophr Res. 2014 doi: 10.1016/j.schres.2014.09.041. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Kraguljac NV, Reid M, White D, Jones R, den Hollander J, Lowman D, et al. Neurometabolites in schizophrenia and bipolar disorder - a systematic review and meta-analysis. Psychiatry Res. 2012;203(2-3):111–125. doi: 10.1016/j.pscychresns.2012.02.003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Benes FM, Khan Y, Vincent SL, Wickramasinghe R. Differences in the subregional and cellular distribution of GABAA receptor binding in the hippocampal formation of schizophrenic brain. Synapse. 1996;22(4):338–349. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1098-2396(199604)22:4<338::AID-SYN5>3.0.CO;2-C. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Hutcheson NL, Reid MA, White DM, Kraguljac NV, Avsar KB, Bolding MS, et al. Multimodal analysis of the hippocampus in schizophrenia using proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy and functional magnetic resonance imaging. Schizophr Res. 2012;140(1-3):136–142. doi: 10.1016/j.schres.2012.06.039. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Lahti AC, Weiler MA, Holcomb HH, Tamminga CA, Carpenter WT, McMahon R. Correlations between rCBF and symptoms in two independent cohorts of drug-free patients with schizophrenia. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2006;31(1):221–230. doi: 10.1038/sj.npp.1300837. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Biswal B, Yetkin FZ, Haughton VM, Hyde JS. Functional connectivity in the motor cortex of resting human brain using echo-planar MRI. Magn Reson Med. 1995;34(4):537–541. doi: 10.1002/mrm.1910340409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Samudra N, Ivleva EI, Hubbard NA, Rypma B, Sweeney JA, Clementz BA, et al. Alterations in hippocampal connectivity across the psychosis dimension. Psychiatry Res. 2015;233(2):148–157. doi: 10.1016/j.pscychresns.2015.06.004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Knochel C, Stablein M, Storchak H, Reinke B, Jurcoane A, Prvulovic D, et al. Multimodal assessments of the hippocampal formation in schizophrenia and bipolar disorder: evidences from neurobehavioral measures and functional and structural MRI. Neuroimage Clin. 2014;6:134–144. doi: 10.1016/j.nicl.2014.08.015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Kraguljac NV, White DM, Hadley N, Hadley JA, Ver Hoef L, Davis E, et al. Aberrant hippocampal circuitry in unmedicated patients with schizophrenia and effects of antipsychotic medication: a longitudinal resting state functional MRI study. Schizophr Bull. 2016 doi: 10.1093/schbul/sbv228. in press. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Kraguljac NV, White DM, Hadley J, Reid MA, Lahti AC. Hippocampal-parietal dysconnectivity and glutamate abnormalities in unmedicated patients with schizophrenia. Hippocampus. 2014;24(12):1524–1532. doi: 10.1002/hipo.22332. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Zhou Y, Shu N, Liu Y, Song M, Hao Y, Liu H, et al. Altered resting-state functional connectivity and anatomical connectivity of hippocampus in schizophrenia. Schizophr Res. 2008;100(1-3):120–132. doi: 10.1016/j.schres.2007.11.039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Duan HF, Gan JL, Yang JM, Cheng ZX, Gao CY, Shi ZJ, et al. A longitudinal study on intrinsic connectivity of hippocampus associated with positive symptom in first-episode schizophrenia. Behav Brain Res. 2015;283:78–86. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2015.01.022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Sapkota K, Mao Z, Synowicki P, Lieber D, Liu M, Ikezu T, et al. GluN2D N-Methyl-d-Aspartate Receptor Subunit Contribution to the Stimulation of Brain Activity and Gamma Oscillations by Ketamine: Implications for Schizophrenia. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2016;356(3):702–711. doi: 10.1124/jpet.115.230391. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Yamamoto T, Nakayama T, Yamaguchi J, Matsuzawa M, Mishina M, Ikeda K, et al. Role of the NMDA receptor GluN2D subunit in the expression of ketamine-induced behavioral sensitization and region-specific activation of neuronal nitric oxide synthase. Neurosci Lett. 2016;610:48–53. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2015.10.049. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.von Engelhardt J, Bocklisch C, Tonges L, Herb A, Mishina M, Monyer H. GluN2D-containing NMDA receptors-mediate synaptic currents in hippocampal interneurons and pyramidal cells in juvenile mice. Front Cell Neurosci. 2015;9:95. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2015.00095. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Lahti AC, Koffel B, LaPorte D, Tamminga CA. Subanesthetic doses of ketamine stimulate psychosis in schizophrenia. Neuropsychopharmacology. 1995;13(1):9–19. doi: 10.1016/0893-133X(94)00131-I. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Lahti AC, Weiler MA, Tamara Michaelidis BA, Parwani A, Tamminga CA. Effects of ketamine in normal and schizophrenic volunteers. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2001;25(4):455–467. doi: 10.1016/S0893-133X(01)00243-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Lahti AC, Holcomb HH. Schizophrenia, VIII: pharmacologic models. Am J Psychiatry. 2003;160(12):2091. doi: 10.1176/appi.ajp.160.12.2091. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Parwani A, Weiler MA, Blaxton TA, Warfel D, Hardin M, Frey K, et al. The effects of a subanesthetic dose of ketamine on verbal memory in normal volunteers. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 2005;183(3):265–274. doi: 10.1007/s00213-005-0177-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Weiler MA, Thaker GK, Lahti AC, Tamminga CA. Ketamine effects on eye movements. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2000;23(6):645–653. doi: 10.1016/S0893-133X(00)00156-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Lahti AC, Warfel D, Michaelidis T, Weiler MA, Frey K, Tamminga CA. Long-term outcome of patients who receive ketamine during research. Biol Psychiatry. 2001;49(10):869–875. doi: 10.1016/s0006-3223(00)01037-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Kraguljac NV, Reid MA, White DM, den Hollander J, Lahti AC. Regional decoupling of N-acetyl-aspartate and glutamate in schizophrenia. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2012;37(12):2635–2642. doi: 10.1038/npp.2012.126. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Hutcheson NL, Sreenivasan KR, Deshpande G, Reid MA, Hadley J, White DM, et al. Effective connectivity during episodic memory retrieval in schizophrenia participants before and after antipsychotic medication. Hum Brain Mapp. 2015;36(4):1442–1457. doi: 10.1002/hbm.22714. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Hamilton M. Rating depressive patients. J Clin Psychiatry. 1980;41(12 Pt 2):21–24. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Young RC, Biggs JT, Ziegler VE, Meyer DA. A rating scale for mania: reliability, validity and sensitivity. Br J Psychiatry. 1978;133:429–435. doi: 10.1192/bjp.133.5.429. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Bremner JD, Krystal JH, Putnam FW, Southwick SM, Marmar C, Charney DS, et al. Measurement of dissociative states with the Clinician-Administered Dissociative States Scale (CADSS) J Trauma Stress. 1998;11(1):125–136. doi: 10.1023/A:1024465317902. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Overall J, Gorham D. The brief psychiatric rating scale. Psychology Report. 1962;10:799–812. [Google Scholar]
- 34.Schubert F, Gallinat J, Seifert F, Rinneberg H. Glutamate concentrations in human brain using single voxel proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy at 3 Tesla. Neuroimage. 2004;21(4):1762–1771. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2003.11.014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Vanhamme L, van den Boogaart A, Van Huffel S. Improved method for accurate and efficient quantification of MRS data with use of prior knowledge. J Magn Reson. 1997;129(1):35–43. doi: 10.1006/jmre.1997.1244. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Whitfield-Gabrieli S, Nieto-Castanon A. Conn: a functional connectivity toolbox for correlated and anticorrelated brain networks. Brain Connect. 2012;2(3):125–141. doi: 10.1089/brain.2012.0073. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Behzadi Y, Restom K, Liau J, Liu TT. A component based noise correction method (CompCor) for BOLD and perfusion based fMRI. Neuroimage. 2007;37(1):90–101. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2007.04.042. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Power JD, Barnes KA, Snyder AZ, Schlaggar BL, Petersen SE. Steps toward optimizing motion artifact removal in functional connectivity MRI; a reply to Carp. Neuroimage. 2012 doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2012.03.017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Caprihan A, Jones T, Chen H, Lemke N, Abbott C, Qualls C, et al. The Paradoxical Relationship between White Matter, Psychopathology and Cognition in Schizophrenia: A Diffusion Tensor and Proton Spectroscopic Imaging Study. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2015 doi: 10.1038/npp.2015.72. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Fornito A, Harrison BJ, Goodby E, Dean A, Ooi C, Nathan PJ, et al. Functional dysconnectivity of corticostriatal circuitry as a risk phenotype for psychosis. JAMA Psychiatry. 2013;70(11):1143–1151. doi: 10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2013.1976. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Medoff DR, Holcomb HH, Lahti AC, Tamminga CA. Probing the human hippocampus using rCBF: contrasts in schizophrenia. Hippocampus. 2001;11(5):543–550. doi: 10.1002/hipo.1070. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Talati P, Rane S, Skinner J, Gore J, Heckers S. Increased hippocampal blood volume and normal blood flow in schizophrenia. Psychiatry Res. 2015;232(3):219–225. doi: 10.1016/j.pscychresns.2015.03.007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Schobel SA, Chaudhury NH, Khan UA, Paniagua B, Styner MA, Asllani I, et al. Imaging patients with psychosis and a mouse model establishes a spreading pattern of hippocampal dysfunction and implicates glutamate as a driver. Neuron. 2013;78(1):81–93. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2013.02.011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Rowland LM, Bustillo JR, Mullins PG, Jung RE, Lenroot R, Landgraf E, et al. Effects of ketamine on anterior cingulate glutamate metabolism in healthy humans: a 4-T proton MRS study. Am J Psychiatry. 2005;162(2):394–396. doi: 10.1176/appi.ajp.162.2.394. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Stone JM, Dietrich C, Edden R, Mehta MA, De Simoni S, Reed LJ, et al. Ketamine effects on brain GABA and glutamate levels with 1H-MRS: relationship to ketamine-induced psychopathology. Mol Psychiatry. 2012;17(7):664–665. doi: 10.1038/mp.2011.171. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Taylor MJ, Tiangga ER, Mhuircheartaigh RN, Cowen PJ. Lack of effect of ketamine on cortical glutamate and glutamine in healthy volunteers: a proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy study. J Psychopharmacol. 2012;26(5):733–737. doi: 10.1177/0269881111405359. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Valentine GW, Mason GF, Gomez R, Fasula M, Watzl J, Pittman B, et al. The antidepressant effect of ketamine is not associated with changes in occipital amino acid neurotransmitter content as measured by [(1)H]-MRS. Psychiatry Res. 2011;191(2):122–127. doi: 10.1016/j.pscychresns.2010.10.009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Poels EM, Kegeles LS, Kantrowitz JT, Javitt DC, Lieberman JA, Abi-Dargham A, et al. Glutamatergic abnormalities in schizophrenia: A review of proton MRS findings. Schizophr Res. 2014 doi: 10.1016/j.schres.2013.12.013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Hong LE, Summerfelt A, Buchanan RW, O’Donnell P, Thaker GK, Weiler MA, et al. Gamma and delta neural oscillations and association with clinical symptoms under subanesthetic ketamine. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2010;35(3):632–640. doi: 10.1038/npp.2009.168. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Symond MP, Harris AW, Gordon E, Williams LM. “Gamma synchrony” in first-episode schizophrenia: a disorder of temporal connectivity? Am J Psychiatry. 2005;162(3):459–465. doi: 10.1176/appi.ajp.162.3.459. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Driesen NR, McCarthy G, Bhagwagar Z, Bloch M, Calhoun V, D’Souza DC, et al. Relationship of resting brain hyperconnectivity and schizophrenia-like symptoms produced by the NMDA receptor antagonist ketamine in humans. Mol Psychiatry. 2013;18(11):1199–1204. doi: 10.1038/mp.2012.194. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Hoflich A, Hahn A, Kublbock M, Kranz GS, Vanicek T, Windischberger C, et al. Ketamine-Induced Modulation of the Thalamo-Cortical Network in Healthy Volunteers As a Model for Schizophrenia. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. 2015;18(9) doi: 10.1093/ijnp/pyv040. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Scheidegger M, Walter M, Lehmann M, Metzger C, Grimm S, Boeker H, et al. Ketamine decreases resting state functional network connectivity in healthy subjects: implications for antidepressant drug action. PLoS One. 2012;7(9):e44799. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0044799. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Niesters M, Khalili-Mahani N, Martini C, Aarts L, van Gerven J, van Buchem MA, et al. Effect of subanesthetic ketamine on intrinsic functional brain connectivity: a placebo-controlled functional magnetic resonance imaging study in healthy male volunteers. Anesthesiology. 2012;117(4):868–877. doi: 10.1097/ALN.0b013e31826a0db3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Grimm O, Gass N, Weber-Fahr W, Sartorius A, Schenker E, Spedding M, et al. Acute ketamine challenge increases resting state prefrontal-hippocampal connectivity in both humans and rats. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 2015;232(21-22):4231–4241. doi: 10.1007/s00213-015-4022-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Chen JE, Chang C, Greicius MD, Glover GH. Introducing co-activation pattern metrics to quantify spontaneous brain network dynamics. Neuroimage. 2015;111:476–488. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2015.01.057. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Moghaddam B, Adams B, Verma A, Daly D. Activation of glutamatergic neurotransmission by ketamine: a novel step in the pathway from NMDA receptor blockade to dopaminergic and cognitive disruptions associated with the prefrontal cortex. J Neurosci. 1997;17(8):2921–2927. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.17-08-02921.1997. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Kegeles LS, Mao X, Ojeil N, Massuda R, Pedrini M, Chen C, et al. J-editing/MEGA-PRESS time-course study of the neurochemical effects of ketamine administration in healthy humans. Proc Intl Soc Mag Reson Med. 2013;21(2013):1206. [Google Scholar]
- 59.Chowdhury GM, Behar KL, Cho W, Thomas MA, Rothman DL, Sanacora G. (1)H-[(1)(3)C]-nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy measures of ketamine’s effect on amino acid neurotransmitter metabolism. Biol Psychiatry. 2012;71(11):1022–1025. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2011.11.006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Gass N, Schwarz AJ, Sartorius A, Schenker E, Risterucci C, Spedding M, et al. Sub-anesthetic ketamine modulates intrinsic BOLD connectivity within the hippocampal-prefrontal circuit in the rat. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2014;39(4):895–906. doi: 10.1038/npp.2013.290. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Sarpal DK, Argyelan M, Robinson DG, Szeszko PR, Karlsgodt KH, John M, et al. Baseline Striatal Functional Connectivity as a Predictor of Response to Antipsychotic Drug Treatment. Am J Psychiatry. 2015 doi: 10.1176/appi.ajp.2015.14121571. appiajp201514121571. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Krystal JH, D’Souza DC, Karper LP, Bennett A, Abi-Dargham A, Abi-Saab D, et al. Interactive effects of subanesthetic ketamine and haloperidol in healthy humans. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 1999;145(2):193–204. doi: 10.1007/s002130051049. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Vollenweider FX, Vontobel P, Oye I, Hell D, Leenders KL. Effects of (S)-ketamine on striatal dopamine: a [11C]raclopride PET study of a model psychosis in humans. J Psychiatr Res. 2000;34(1):35–43. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3956(99)00031-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Dandash O, Harrison BJ, Adapa R, Gaillard R, Giorlando F, Wood SJ, et al. Selective augmentation of striatal functional connectivity following NMDA receptor antagonism: implications for psychosis. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2015;40(3):622–631. doi: 10.1038/npp.2014.210. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Floresco SB, Todd CL, Grace AA. Glutamatergic afferents from the hippocampus to the nucleus accumbens regulate activity of ventral tegmental area dopamine neurons. J Neurosci. 2001;21(13):4915–4922. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.21-13-04915.2001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Anticevic A, Corlett PR, Cole MW, Savic A, Gancsos M, Tang Y, et al. N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor antagonist effects on prefrontal cortical connectivity better model early than chronic schizophrenia. Biol Psychiatry. 2015;77(6):569–580. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2014.07.022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Mouchlianitis E, Bloomfield MA, Law V, Beck K, Selvaraj S, Rasquinha N, et al. Treatment-Resistant Schizophrenia Patients Show Elevated Anterior Cingulate Cortex Glutamate Compared to Treatment-Responsive. Schizophr Bull. 2015 doi: 10.1093/schbul/sbv151. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Kraguljac NV, White DM, Hadley JA, Visscher KM, Knight D, Ver Hoef L, et al. Abnormalities in large scale functional networks in unmedicated patients with schizophrenia and effects of risperidone. Neuroimage: Clinical. 2016;10:146–158. doi: 10.1016/j.nicl.2015.11.015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Palaniyappan L, Liddle PF. Does the salience network play a cardinal role in psychosis? An emerging hypothesis of insular dysfunction. J Psychiatry Neurosci. 2012;37(1):17–27. doi: 10.1503/jpn.100176. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Stern Y. The concept of cognitive reserve: a catalyst for research. J Clin Exp Neuropsychol. 2003;25(5):589–593. doi: 10.1076/jcen.25.5.589.14571. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Van Essen DC, Smith SM, Barch DM, Behrens TE, Yacoub E, Ugurbil K, et al. The WU-Minn Human Connectome Project: an overview. Neuroimage. 2013;80:62–79. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2013.05.041. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Lahti AC, Weiler MA, Holcomb HH, Tamminga CA, Cropsey KL. Modulation of limbic circuitry predicts treatment response to antipsychotic medication: a functional imaging study in schizophrenia. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2009;34(13):2675–2690. doi: 10.1038/npp.2009.94. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Perlis RH, Ostacher M, Fava M, Nierenberg AA, Sachs GS, Rosenbaum JF. Assuring that double-blind is blind. Am J Psychiatry. 2010;167(3):250–252. doi: 10.1176/appi.ajp.2009.09060820. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Enck P, Bingel U, Schedlowski M, Rief W. The placebo response in medicine: minimize, maximize or personalize? Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2013;12(3):191–204. doi: 10.1038/nrd3923. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.


