Figure 3.
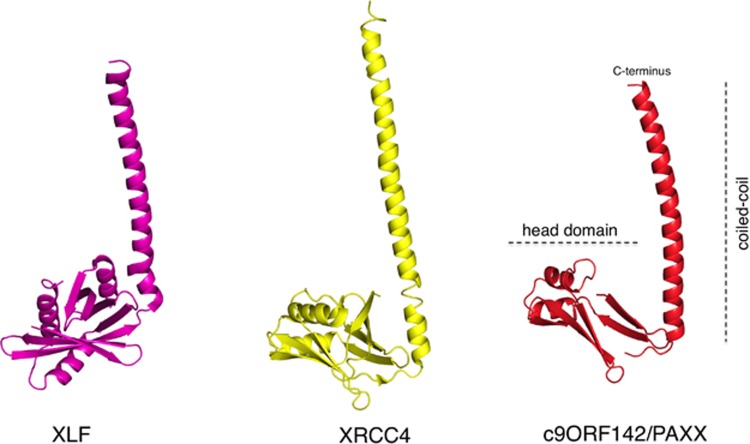
Newly discovered c-NHEJ factor c9orf142/PAXX structurally resembles XRCC4. Figure shows computer models of XLF, XRCC4 and c9orf142/PAXX (adapted from Craxton et al., 2015). These proteins typically form dimers, however, here for simplicity and to highlight their structural similarity monomers are depicted. For XLF C-terminal portion of the coiled-coil has been shortened. The overall structure of a typical XRCC4 paralog includes a globular head domain, a centrally located coiled-coil and the C-terminal region (CTR, not shown). The CTRs are intrinsically disordered and not visible on available crystal structures. The head domain of XLF and XRCC4 is responsible for the formation of XLF/XRCC4 filaments, whereas the head domain of PAXX has an unknown function. The coiled-coils include regions necessary for dimerization. CTRs of XLF and PAXX mediate the interaction with Ku (not shown).