Abstract
Objective:
To describe the presentation and identify the cause of a new clinical phenotype, characterized by early severe neurodegeneration with myopathic and myasthenic features.
Methods:
This case study of 5 patients from 3 families includes clinical phenotype, serial MRI, electrophysiologic testing, muscle biopsy, and full autopsy. Genetic workup included whole exome sequencing and segregation analysis of the likely causal mutation.
Results:
All 5 patients showed severe muscular hypotonia, progressive cerebral atrophy, and therapy-refractory epilepsy. Three patients had congenital contractures. All patients died during their first year of life. In 2 of our patients, electrophysiologic testing showed abnormal decrement, but treatment with pyridostigmine led only to temporary improvement. Causative mutations in ALG14 were identified in all patients. The mutation c.220 G>A (p.Asp74Asn) was homozygous in 2 patients and heterozygous in the other 3 patients. Additional heterozygous mutations were c.422T>G (p.Val141Gly) and c.326G>A (p.Arg109Gln). In all cases, parents were found to be heterozygous carriers. None of the identified variants has been described previously.
Conclusions:
We report a genetic syndrome combining myasthenic features and severe neurodegeneration with therapy-refractory epilepsy. The underlying cause is a glycosylation defect due to mutations in ALG14. These cases broaden the phenotypic spectrum associated with ALG14 congenital disorders of glycosylation as previously only isolated myasthenia has been described.
Congenital disorders of glycosylation (CDG) were first identified in the mid-1990s and form a steadily growing group of heterogeneous phenotypes.1 As the correct posttranslational modification of proteins by N-glycans in the endoplasmic reticulum and Golgi apparatus appears to be crucial for different organs, CDGs are predominantly multisystem disorders. The degree of impairment, however, varies remarkably and ranges from mild signs to complex and severe disorders. Functionality of the CNS is often affected and a variety of neurologic symptoms in CDG has been reported.2
Within the group of CDG, most of the identified disorders affect the well-studied pathway of N-linked glycosylation, which designates the process of covalent attachment of oligosaccharides to asparagine residues of emerging proteins.
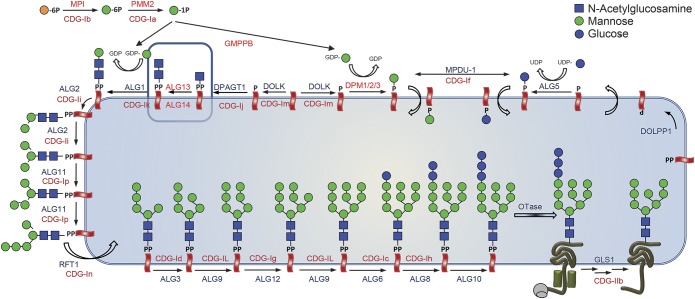
After the first step of this pathway, the formation of GlcNAc-PP-dolichol by DPAGT1, the 2 proteins ALG13 and ALG14 catalyze the addition of a second N-acetylglucosamine (GlcNAc) to form GlcNAc2-PP-dolichol.3 This glycan is subsequently extended by ALG1, ALG2, and other enzymes to the Glc3Man9GlcNAc2-PP-dolichol precursor for protein N-glycosylation (figure 1 for a schematic overview of protein N-glycosylation).
Figure 1. Metabolic pathway of protein N-glycosylation in the endoplasmic reticulum with known associated clinical syndromes for each involved protein.
The CDG-I gene defects that have been associated with congenital myasthenic syndrome (CMS) symptoms are located in the earliest steps of the Glc3Man9GlcNAc2-PP-dolichol biosynthesis. These include DPAGT1, ALG14, and ALG2. Thus far, CMS symptoms have not been identified in ALG1-CDG and ALG13-CDG.
Mutations in DPAGT1 are known to cause a severe multisystem disorder (DPAGT1-CDG4), but also a myasthenic syndrome with limb-girdle pattern.5 Mutations in ALG1 (ALG1-CDG) cause a complex and typically severe neurologic phenotype often involving epileptic seizures, structural abnormalities of the CNS, and muscular hypotonia6,7 without myasthenic signs. Mutations in ALG2 were found in 2003 to be causative for another severe multisystem disorder (ALG2-CDG) involving intellectual disability with seizures, delayed myelination, hepatomegaly, and eye anomalies including iris coloboma and cataract,8 but can also cause a predominantly myasthenic syndrome with myopathic features and varying onset.9,10 Mutations in ALG14 were identified only recently as cause of a childhood-onset isolated myasthenic syndrome with a limb-girdle pattern by Cossins et al.9
In this study, we report a rapidly progressive severe and early lethal phenotype caused by mutations in ALG14 not described before.
METHODS
Molecular analyses.
Genomic DNA was extracted from leukocytes of all members of family A and whole human exome enrichment was performed by a NimbleGenV3 64 Mb kit followed by paired-end 100 bp sequencing on a HighSeq2000 (Illumina, San Diego, CA). Coverage was between 31× and 34× with 49.7–55.7 million mapped reads per sample. For variant analysis, the software package GenSearchNGS (PhenoSystems, Wallonia, Belgium) was used. Details on how mutations were detected are given in the e-Methods at Neurology.org.
Exome sequencing of patient B-1 in family B was performed as described before.11,12The data were filtered for compound heterozygous and homozygous variants, and against known single nucleotide polymorphisms with an allele frequency above 1% in dbSNP, 1000 Genomes, Exome Variant Server, and an in-house variant database.
Exome sequencing of patient C-1 in family C was performed using a trio design with exon targets isolated by capture using the Agilent (Santa Clara, CA) SureSelect Human All Exon V4 (50 Mb) kit as previously described.13
All identified mutations in ALG14 were subsequently validated by Sanger sequencing. Conservation studies were performed using the PRALINE alignment application for conservation studies.14 Common splice prediction software was used for further analysis. Alamut Visual (Interactive Biosoftware, Rouen, France) was used for in silico prediction of identified variants.
Immunohistochemistry and electron microscopy.
Preparation and staining of muscle biopsies was performed using standard procedures. Immunostaining was done as described for proteolipid protein.15 See the e-Methods for more details.
Standard protocol approvals, registrations, and patient consents.
Written informed consent for publication of patient data was obtained from parents or guardians of deceased patients.
RESULTS
Clinical features.
Patients A-1 and A-2 from family A were sisters of German ancestry. There was no known consanguinity in the pedigree.
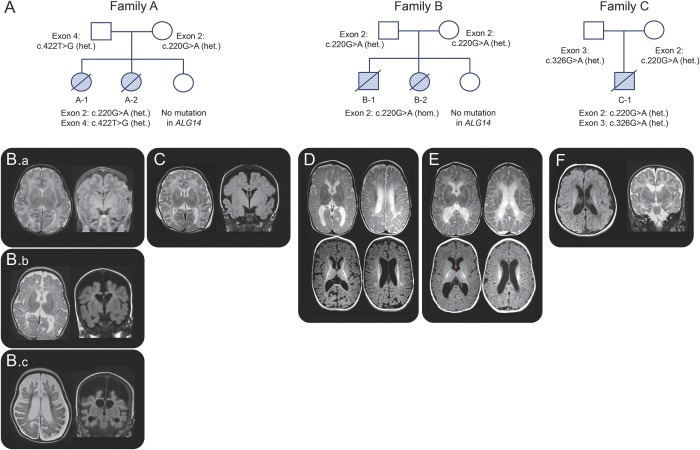
Patient A-1 was born at 34 + 2/7 weeks via cesarean delivery because of abnormal cardiotocogram, breech presentation, and polyhydramnios. Her mother reported reduced fetal movements during pregnancy. Amniocentesis had been performed in week 17 because of suspicious nuchal fold measurement but numeric chromosomal analysis was found to be normal. After birth, the girl presented with marked muscular hypotonia and pronounced contractures of elbows and knees. Lack of spontaneous breathing made primary intubation necessary. First cranial ultrasound at age 2 weeks and MRI at age 3 weeks were unremarkable (figure 2A). Creatine kinase (CK) was normal since the second week of life and SMN1 deficiency was excluded by genetic analysis. As congenital nemaline myopathy was suspected by the clinical picture, genetic testing for ACTA1 mutations was done and was negative. Nerve conduction velocity showed abnormal decrement after repetitive stimulation and treatment with pyridostigmine was initiated (started orally with 5 mg/kg/d in 6 single doses; later, continuous IV administration of 4.5 μg/kg/h). This treatment led to remarkable improvement of muscle activity, allowing spontaneous breathing for a period of weeks. However, this effect was temporary, even after adding 3,4-diaminopyridin. Diagnostic workup for congenital myasthenia was negative for acetylcholine receptor antibodies and most frequent genetic causes (RAPSN, CHRND, CHRNA1, CHRNB1, DOK7). 3,4-Diaminopyridin was discontinued when seizures became evident. EEG initially resembled tracé alternant but later developed into frank burst-suppression with continuously decreasing amplitudes. Seizures were refractory to antiepileptic drugs, including phenobarbital, carbamazepine, levetiracetam, topiramate, and corticosteroids. Comprehensive neurometabolic testing, including assessment of organic acids, neurotransmitters, and biogenous amines in serum and CSF, revealed no abnormalities. The initially good effect of pyridostigmine decreased over time and the girl remained dependent on invasive ventilation. Serial cranial MRI showed progressive and in the end severe supratentorial atrophy ages 3 and 5.5 months (figure 2, B and C). Due to the progressive nature of the disease, ventilator support was withdrawn with parental consent. She died at age 6.5 months. Autopsy of the brain showed severe parenchymal atrophy compatible with Alpers syndrome. However, genetic analysis for POLG1 mutations, accounting for 95% of Alpers syndrome cases, was negative.
Figure 2. Pedigrees with indication of ALG14 mutations and cranial MRI of reported patients.
(A) Pedigrees of families A, B, and C with indication of identified mutations in ALG14. Cranial MRI of patient A-1 at age 4 weeks (B.a), 3 months (B.b), and 5.5 months (B.c) and cranial MRI of patient A-2 at age 3 weeks (C) show delayed myelination and severe rapidly progressive cerebral atrophy with resulting increase in arachnoid space. Note the turricephalic cranial shape. Cranial MRI of patient B-1 at age 6 months (D) and patient B-2 at 3 months (E) show atrophy and lack of myelination. MRI of patient C-1 at 5 weeks (F) shows ventriculomegaly and white matter volume loss. het. = heterozygous; hom. = homozygous.
Patient A-2 was born 2 years later at 36 + 2/7 weeks via cesarean delivery because of decreased fetal movements and polyhydramnios. In contrast with the preceding pregnancy, fetal movements were felt to be normal in the beginning but decreased later in pregnancy. She presented like her sister with muscular hypotonia and contractures of elbows and knees and required intubation directly after birth. She was also found to have bilateral chylothorax and insertion of chest tubes was necessary. Cranial MRI showed delayed myelination and beginning frontoparietal atrophy at age 3 months (figure 2D). EEG was abnormal with a burst-suppression pattern. Pleural effusions reappeared after removing the chest tubes and made reinsertion necessary. Oral treatment with pyridostigmine (5–8 mg/kg/d in 6 single doses) was initiated and led to an improvement of muscle strength and facilitated extubation. In contrast to her sister's course of disease, her respiratory situation remained stable under continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) support and continuation of pyridostigmine. As tonic-clonic seizures became more frequent, anticonvulsive therapy with levetiracetam and phenobarbital was started, with only temporary improvement. At age 3 months, she developed sudden bradycardia and died minutes later. Autopsy was not performed.
Patients B-1 and B-2 of family B were brother and sister of Dutch ancestry. There was no known consanguinity in the pedigree. They had a healthy sister.
Patient B-1 was born at 40 + 5/7 weeks by Cesarean section because of breech position. During the last few weeks of pregnancy, fetal movements were decreased. Directly after birth, hypotonia and severe lack of movements were noted. He needed respiratory support with CPAP and oxygen for the first few weeks. Cranial ultrasounds, EEG, karyotyping, metabolic screening of urine and plasma, as well as DNA analysis for spinal muscular atrophy and Prader Willi syndrome were unrevealing. At 6 months, he developed infantile spasms. EEG showed a burst-suppression pattern that later developed into hypsarrhythmia. The epilepsy was treated with vigabatrin and clonazepam, without success. Nerve conduction studies were normal; EMG showed evidence of denervation and reinnervation, suggestive of anterior horn cell disease. MRI at 6 months revealed delayed myelination and cerebral atrophy (figure 2E). Studies of respiratory chain function in fibroblasts were inconclusive. He had increasing respiratory problems and died at age 8 months. Autopsy was performed.
Patient B-2 was born at 39 + 5/7 weeks by vaginal delivery. Fetal movements had been normal. After birth, a mild hypotonia and mild contractures of elbows and knees were observed. Lack of movements was noted, but less impressive than in her brother. She had some difficulty swallowing, but respiration was normal. Extensive metabolic screening revealed no cause. CK was normal. MRI of the brain at 3 months revealed delayed myelination and beginning cerebral atrophy (figure 2F). EEG at 3 months was severely abnormal and described as beginning hypsarrhythmia. Phenobarbital was started, after which she became more alert and interactive. Feeding difficulties remained present and necessitated a percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy tube. She deteriorated further, and became more hypotonic with generalized muscle atrophy and a myopathic face. Because of this, no further treatment was initiated and she died at 6 months. No autopsy was performed.
Patient C-1 of family C was the only son of healthy and nonconsanguineous parents (Australian father and Canadian mother).
Patient C-1 was born at 39 + 3/7 weeks by vaginal delivery. Decreased fetal movements were noted during the last few months of the pregnancy. Antenatal ultrasound showed bilateral talipes equinovarus and tricuspid valve thickening with some regurgitation. Examination at birth revealed hypotonia with very little proximal muscle movement in the upper and lower extremities. Cranial nerve examination demonstrated mild ptosis and bifacial weakness and normal pupillary response and fundi. In addition to the talipes equinovarus, bilateral contractures of the elbows, knees, and ankles were noted and he had micrognathia and a very high arched palate. His CK was initially elevated at 2,230 U/L but decreased to normal levels after 7 days (<220 U/L). MRI done at 5 weeks of age showed mild ventriculomegaly and white matter volume loss. EEG was done at 1 month to investigate episodes of eye fluttering and desaturation and showed a dysmature background with frequent positive and negative bilateral rolandic sharp waves. An EEG done at 3½ months of age showed multiple seizures ranging from 20 seconds to 4.5 minutes in duration, primarily originating from the right occipital or temporal region, a pattern consistent with migrating partial seizures of infancy. He was treated with incomplete clinical response with phenobarbital, levetiracetam, topiramate, and pyridoxine. Chest X-ray at 3½ months of age showed mild enlargement of the cardiothymic silhouette. He further deteriorated with increasing frequency of seizures, feeding intolerance, and frequent apneic spells. Care was withdrawn and he died at 4 months of age. No autopsy was performed.
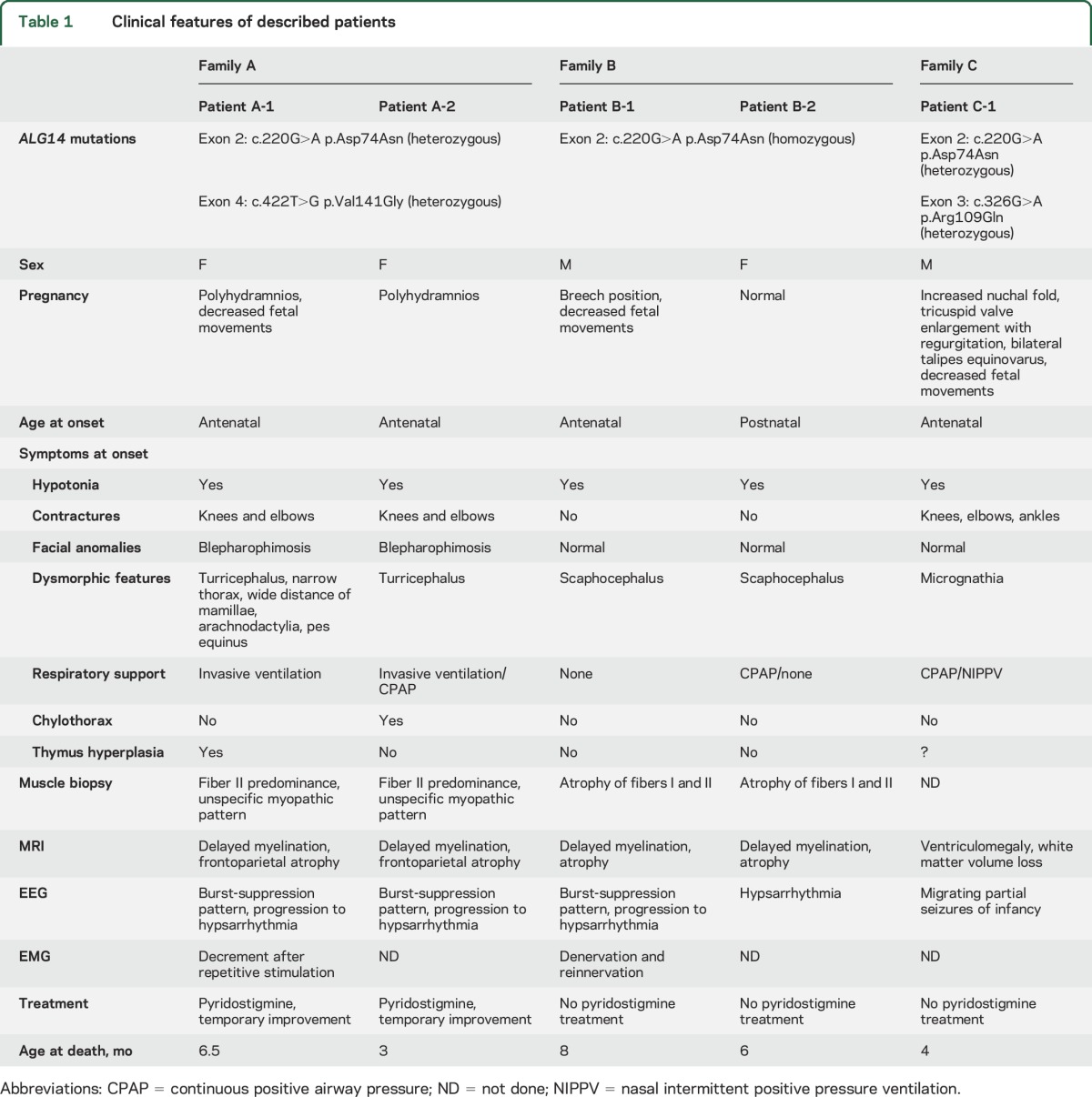
See table 1 for comprehension of clinical features of all described patients.
Table 1.
Clinical features of described patients
Isoelectric focusing studies.
Analysis of transferrin glycosylation status by isoelectric focusing was not done in patients A-1, A-2, or C-1.
Glycosylation studies for patients B-1 and B-2 included isoelectrofocusing and mass spectrometry16 of transferrin. Only for patient B-1, a minimal increase in the lack of a single N-glycan was observed by mass spectrometry (6%, reference: <4%).
Histologic findings in muscle biopsies.
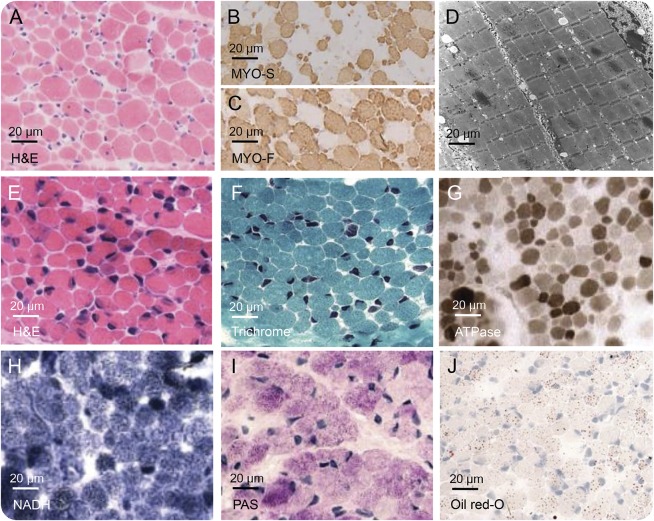
In patients A-1 and A-2, biopsies of quadriceps muscle were performed and showed a marked variation of fiber diameter with dominance of type II fibers but no increase of central nuclei and no structural anomalies like nemaline rods, cores, or sarcotubular aggregates (figure 3, E–J).
Figure 3. Findings of muscle biopsy.
Histologic specimens of muscle biopsies of patient B-1 (A–D) and patient A-1 (E–J).
In patients B-1 and B-2, muscle biopsies revealed variation of fiber diameter with atrophy of both type I and type II fibers and mild glycogen accumulation. No muscle structural anomalies were present. In patient B-2, muscle biopsy showed moderate accumulation of fat and intracellular presence of myelin figures and lipofuscin (figure 3, A–D, for muscle biopsy of patient B-2). Mitochondrial density and morphology were examined and normal; studies of respiratory chain function in muscle were unrevealing.
No muscle biopsy was performed for patient C-1.
Autopsy findings.
In patient A-1, autopsy of the brain was performed. On macroscopic analysis, the brain was small (280 g, normal value for age 725 ± 72 g). In line with MRI findings, the corpus callosum was thin and lateral ventricles were dilated. Microscopic analysis revealed generalized neurodegeneration of neocortex and archicortex with marked activation of microglia and astrocytes. No ischemic or inflammatory lesions were found.
In patient B-1, a full autopsy was performed. On macroscopic analysis, the brain was small (665 g, normal value for age 767 ± 32 g). On cut, the lateral ventricles were dilated with a thin corpus callosum, indicative of white matter atrophy (figure e-1A). Microscopy revealed multiple lesions in the gray and white matter with loss of cells, reactive astrocytes and microglia, and accruing of macrophages and extravasated lymphocytes (figure e-1, B–D). In these lesions, the vascular endothelial cells were swollen but the vessels were otherwise normal with no thrombotic occlusion of the lumen. The white matter throughout the brain and cerebellum showed lack of myelin, reactive astrocytes and microglia, sparse lymphocytes in the perivascular spaces, and some axonal spheroid (figure e-1, E–I). The cortex and basal ganglia also showed reactive astrocytes and microglia (figure e-1, I–L).There were no neuronal migration disorders or cortical dysplasia. Body autopsy was unremarkable.
Genetic findings.
Family A.
Exome sequence was performed in both deceased sisters and revealed compound heterozygous missense mutations in exons 2 and 4 of ALG14 (exon 2: c.220G>A; p.Asp74Asn; exon 4: c.422T>G; p.Val141Gly). Both parents were found to be heterozygous carriers of either one of these mutations. The identified mutations have not been reported before. In the healthy sister, no mutation in ALG14 was found.
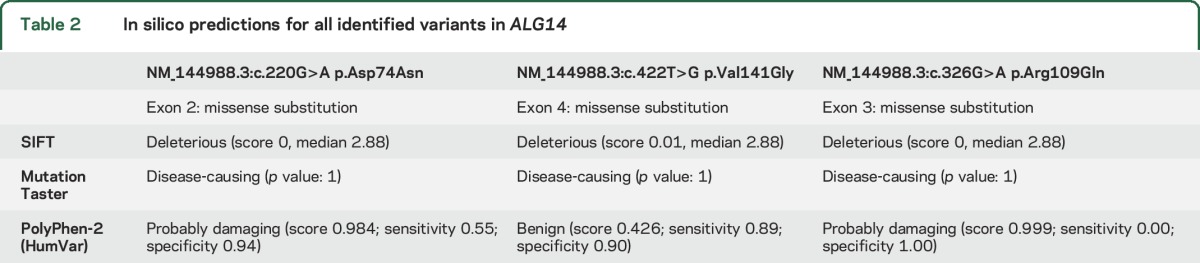
Prediction algorithms indicate the c.220g>A variant to be deleterious (SIFT), disease-causing (MutationTaster), and probably damaging (Polyphen-2), respectively. The c.422T>G variant was also predicted to be deleterious (SIFT) and disease-causing (MutationTaster), but benign by Polyphen-2.
Family B.
Exome sequencing of patient B-1 revealed a homozygous variant (c.220G>A; p.Asp74Asn) in exon 2 of ALG14 (NM_144988). The variant was also present in the affected sibling patient B-2. The parents were both heterozygous carriers of this variant.
Family C.
Exome sequencing of patient C-1 revealed compound heterozygous missense mutations in exons 2 and 3 of ALG14 (exon 2: c.220.G>A; p.Asp74Asn, exon 3: c.326G>A; p.Arg109Gln). Both parents were confirmed to be carriers. The novel c.326G>A variant was predicted to be deleterious (SIFT), disease-causing (MutationTaster), and probably damaging (Polyphen-2).
Analysis of variants.
The c.220G>A variant is also known in dbSNP (rs769114543). The allele frequency in ExAC is 0.017% in the total population and 0.024% in the European non-Finnish population. There are no data in the ESP database.
The c.422T>G variant is known in dbSNP (rs139005007). The allele frequency of the variant in the ExAC database is 0.0085% of the total population and 0.014% in the European (non-Finnish) population. In the ESP database, the allele frequency is 0.008%.
The c.326G>A variant is also known in dbSNP (rs199689080). The allele frequency in ExAC is 0.0099% (total population) and 0.015% (European [non-Finnish] population).
Analysis of splice prediction (NNSPLICE, GeneSplicer, Human Splicing Finder, MaxEntScan, SpliceSiteFinder-like) showed only minimal effects on splicing for all variants.
A summary of in silico predictions for all identified variants is shown in table 2.
Table 2.
In silico predictions for all identified variants in ALG14
DISCUSSION
We present a new phenotype of severe early lethal neurodegeneration with myasthenic and myopathic features in 3 separate families due to previously unreported mutations in the ALG14 gene. To our knowledge, this is the first report of congenital myasthenic features as part of a complex neurologic disorder. The phenotype of 5 affected individuals from 3 independent families includes progressive cerebral atrophy and concomitant intractable epilepsy.
ALG14 forms a heterodimer with the catalytic subunit ALG13, and acts in the second step of N-linked glycosylation in the endoplasmic reticulum, catalyzing the transfer of the second N-acetylglucosamine to dolichol-PP-GlcNAc.3,13
Mutations in ALG14 have been identified in a single family with congenital myasthenic syndrome by Cossins et al.9 The described phenotype, however, was considerably milder, with an onset of isolated myasthenic symptoms age 7 and 40 years in 2 affected sisters. Both reported patients were still ambulatory and did not exhibit epilepsy nor did they show any abnormalities on cranial MRI. The identified variants in those 2 siblings included a c.310C>T (p.Arg104*) truncating mutation and a c.194C>T (p.Pro65Leu) missense mutation, which was shown to reduce expression of ALG14 in cultured cells. Interestingly, both reported patients showed long-term benefit from treatment with cholinesterase inhibitors. Furthermore, the group was able to demonstrate in vitro that ALG14 localizes at endplate regions and plays an important role for correct expression of the acetylcholine receptor.9
We are aware that myasthenia was only documented in 2 of our patients (A-1 and A-2). Repetitive stimulation was not performed in the other 3 patients. However, the combination of myasthenic findings and a clear—albeit only temporary—therapeutic benefit of pyridostigmine treatment in the mentioned sisters underlines the importance of focused examination in future patients to straighten out this feature. In one patient (B-1), EMG revealed evidence of denervation and reinnervation, so that affection of motoneurons might also be part of this multisystem phenotype.
Surprisingly, autopsy of the brain of patient B-1 revealed multiple lesions in the white and gray matter with marked neuronal rarefication, suggestive of ischemic brain injury. However, coagulation studies revealed no abnormalities and cerebral imaging showed no ischemic lesions—either in this or in the other 4 reported patients. Infarctions are described in other glycosylation defects (PMM2-CDG and ALG1-CDG), where they are usually due to thrombotic events due to coagulation disorders.17
No truncating mutations were identified in our patients. All identified mutations are predicted to be damaging by different prediction tools, except for the c.422T>G variant, which is predicted to be benign using PolyPhen 2. However, due to the similarity of the phenotype and heterozygosity of the parents, we assume that this mutation is also disease-causing.
No clear glycosylation abnormalities could be observed of transferrin in the patients from family B. This has been observed in an increasing number of CDG-I gene defects, including ALG13-CDG presenting with encephalopathic epilepsy18 and GMPPB-CDG.19
We present an early severe and lethal phenotype caused by mutations in ALG14, which involves myasthenic and myopathic features as well as cerebral atrophy and therapy-refractory epilepsy. Whereas complex multisystem disorders have been described for other key genes in early N-glycosylation this is, to our knowledge, the first report of a multisystem disorder caused by mutations in ALG14.
Supplementary Material
ACKNOWLEDGMENT
The authors thank the Genome Technology Center at the Radboud UMC and BGI Copenhagen for providing the exome sequencing service; and the families of the patients for giving consent to publish this data.
GLOSSARY
- CDG
congenital disorders of glycosylation
- CK
creatine kinase
- CPAP
continuous positive airway pressure
Footnotes
Supplemental data at Neurology.org
AUTHOR CONTRIBUTIONS
David Schorling: writing of manuscript, acquisition and interpretation of clinical data. Simone Rost: molecular analysis of patients and interpretation, critical review of manuscript. Dirk J. Lefeber: molecular analysis of patients and interpretation, drafting of manuscript, making of N-glycosylation pathway scheme (figure 1). Lauren Brady: molecular analysis and clinical description of patients, review of manuscript. Clemens R. Müller: molecular analysis of patients and interpretation, critical review of manuscript. Rudolf Korinthenberg: clinical data of patients, interpretation of data, reviewing manuscript. Mark Tarnopolsky: clinical data of patients, interpretation of data, reviewing manuscript. Carsten G. Bönnemann: molecular analysis of patients, interpretation of clinical and molecular data. Richard J. Rodenburg: molecular analysis of patients, interpretation of data, review of manuscript. Marianna Bugiani: clinical and histologic data, interpretation, review of manuscript. Maria Beytia: molecular analysis and clinical description of patients, review of manuscript. Marcus Krüger: clinical description of patients, critical review of manuscript. Marjo van der Knaap: clinical and molecular data of patients, reviewing manuscript. Janbernd Kirschner: clinical data of patients, acquisition of clinical data, writing and reviewing manuscript.
STUDY FUNDING
No targeted funding reported.
DISCLOSURE
The authors report no disclosures relevant to the manuscript. Go to Neurology.org for full disclosures.
REFERENCES
- 1.Van Schaftingen E, Jaeken J. Phosphomannomutase deficiency is a cause of carbohydrate-deficient glycoprotein syndrome type I. FEBS Lett 1995;377:318–320. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Freeze HH, Eklund EA, Ng BG, Patterson MC. Neurology of inherited glycosylation disorders. Lancet Neurol 2012;11:453–466. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Gao X-D, Tachikawa H, Sato T, Jigami Y, Dean N. Alg14 recruits Alg13 to the cytoplasmic face of the endoplasmic reticulum to form a novel bipartite UDP-N-acetylglucosamine transferase required for the second step of N-linked glycosylation. J Biol Chem 2005;280:36254–36262. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Würde AE, Reunert J, Rust S, et al. Congenital disorder of glycosylation type Ij (CDG-Ij, DPAGT1-CDG): extending the clinical and molecular spectrum of a rare disease. Mol Genet Metab 2012;105:634–641. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Belaya K, Finlayson S, Slater CR, et al. Mutations in DPAGT1 cause a limb-girdle congenital myasthenic syndrome with tubular aggregates. Am J Hum Genet 2012;91:193–201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Grubenmann CE, Frank CG, Hülsmeier AJ, et al. Deficiency of the first mannosylation step in the N-glycosylation pathway causes congenital disorder of glycosylation type Ik. Hum Mol Genet 2004;13:535–542. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Dupré T, Vuillaumier-Barrot S, Chantret I, et al. Guanosine diphosphate-mannose:GlcNAc2-PP-dolichol mannosyltransferase deficiency (congenital disorders of glycosylation type Ik): five new patients and seven novel mutations. J Med Genet 2010;47:729–735. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Thiel C, Schwarz M, Peng J, et al. A new type of congenital disorders of glycosylation (CDG-Ii) provides new insights into the early steps of dolichol-linked oligosaccharide biosynthesis. J Biol Chem 2003;278:22498–22505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Cossins J, Belaya K, Hicks D, et al. Congenital myasthenic syndromes due to mutations in ALG2 and ALG14. Brain J Neurol 2013;136:944–956. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Monies DM, Al-Hindi HN, Al-Muhaizea MA, et al. Clinical and pathological heterogeneity of a congenital disorder of glycosylation manifesting as a myasthenic/myopathic syndrome. Neuromuscul Disord 2014;24:353–359. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Wortmann SB, Koolen DA, Smeitink JA, van den Heuvel L, Rodenburg RJ. Whole exome sequencing of suspected mitochondrial patients in clinical practice. J Inherit Metab Dis 2015;38:437–443. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Neveling K, Feenstra I, Gilissen C, et al. A post-hoc comparison of the utility of sanger sequencing and exome sequencing for the diagnosis of heterogeneous diseases. Hum Mutat 2013;34:1721–1726. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Tanaka AJ, Cho MT, Millan F, et al. Mutations in SPATA5 are associated with microcephaly, intellectual disability, seizures, and Hearing loss. Am J Hum Genet 2015;97:457–464. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Simossis VA, Heringa J. PRALINE: a multiple sequence alignment toolbox that integrates homology-extended and secondary structure information. Nucleic Acids Res 2005;33:W289–W294. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Kevelam SH, Bugiani M, Salomons GS, et al. Exome sequencing reveals mutated SLC19A3 in patients with an early-infantile, lethal encephalopathy. Brain J Neurol 2013;136:1534–1543. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.van Scherpenzeel M, Steenbergen G, Morava E, Wevers RA, Lefeber DJ. High-resolution mass spectrometry glycoprofiling of intact transferrin for diagnosis and subtype identification in the congenital disorders of glycosylation. Transl Res J Lab Clin Med 2015;166:639–649.e1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Morava E, Vodopiutz J, Lefeber DJ, et al. Defining the phenotype in congenital disorder of glycosylation due to ALG1 mutations. Pediatrics 2012;130:e1034–1039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Dimassi S, Labalme A, Ville D, et al. Whole-exome sequencing improves the diagnosis yield in sporadic infantile spasm syndrome. Clin Genet 2016;89:198–204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Carss KJ, Stevens E, Foley AR, et al. Mutations in GDP-mannose pyrophosphorylase B cause congenital and limb-girdle muscular dystrophies associated with hypoglycosylation of α-dystroglycan. Am J Hum Genet 2013;93:29–41. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.