Abstract
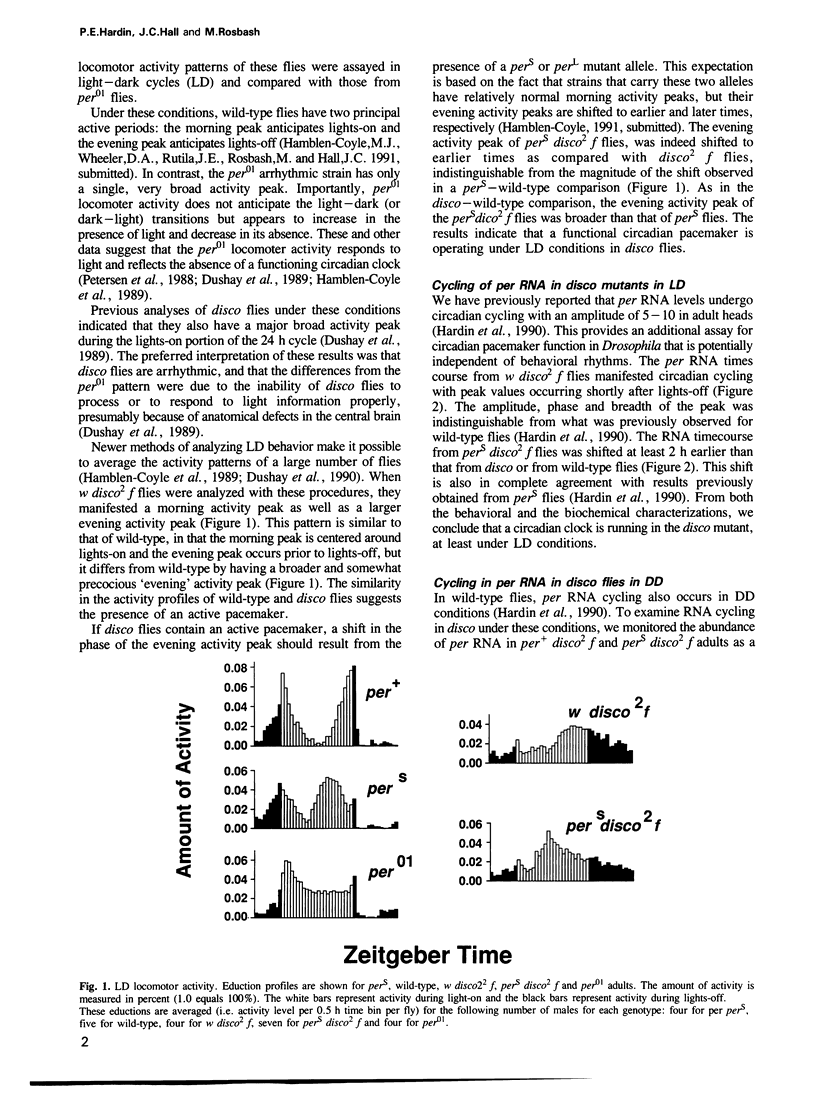
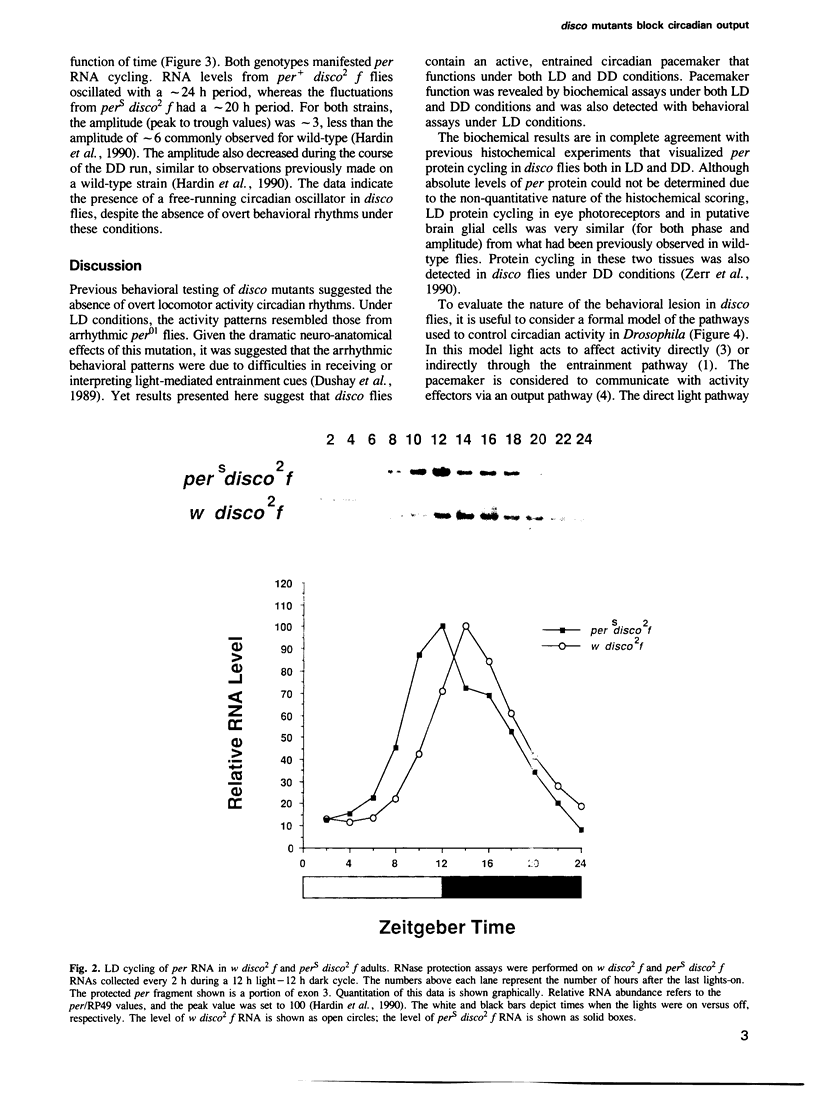
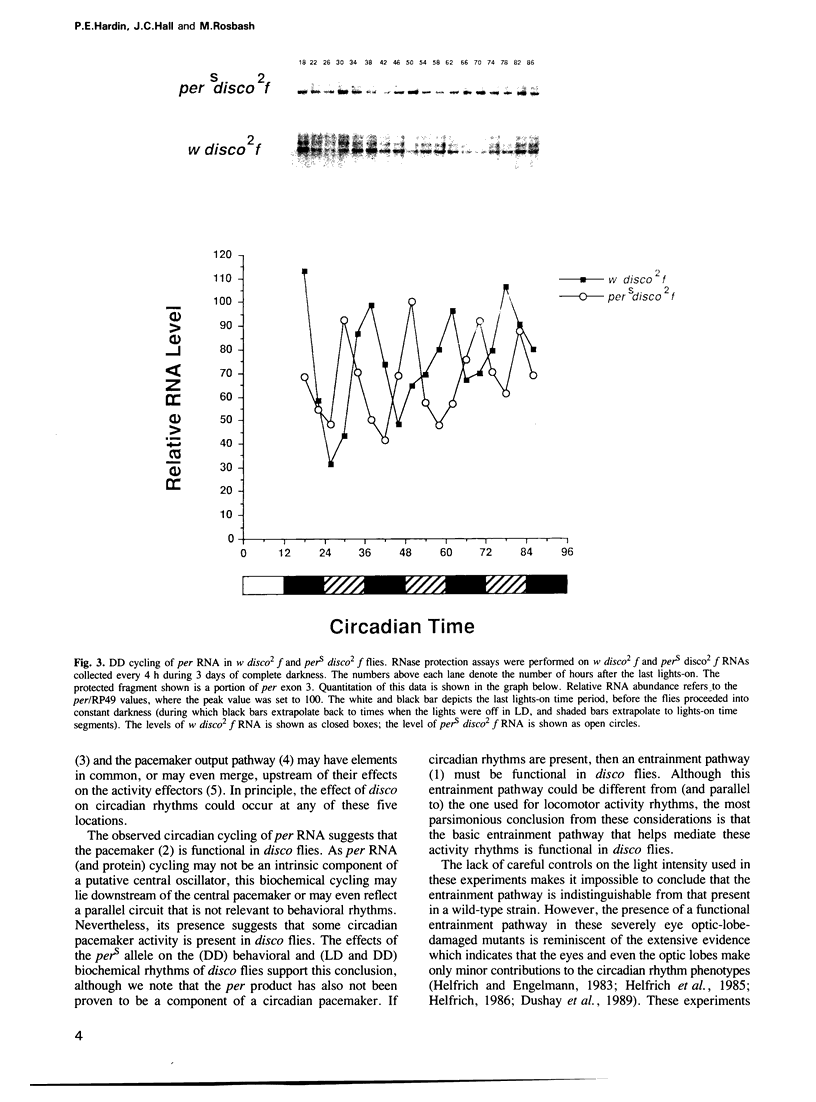
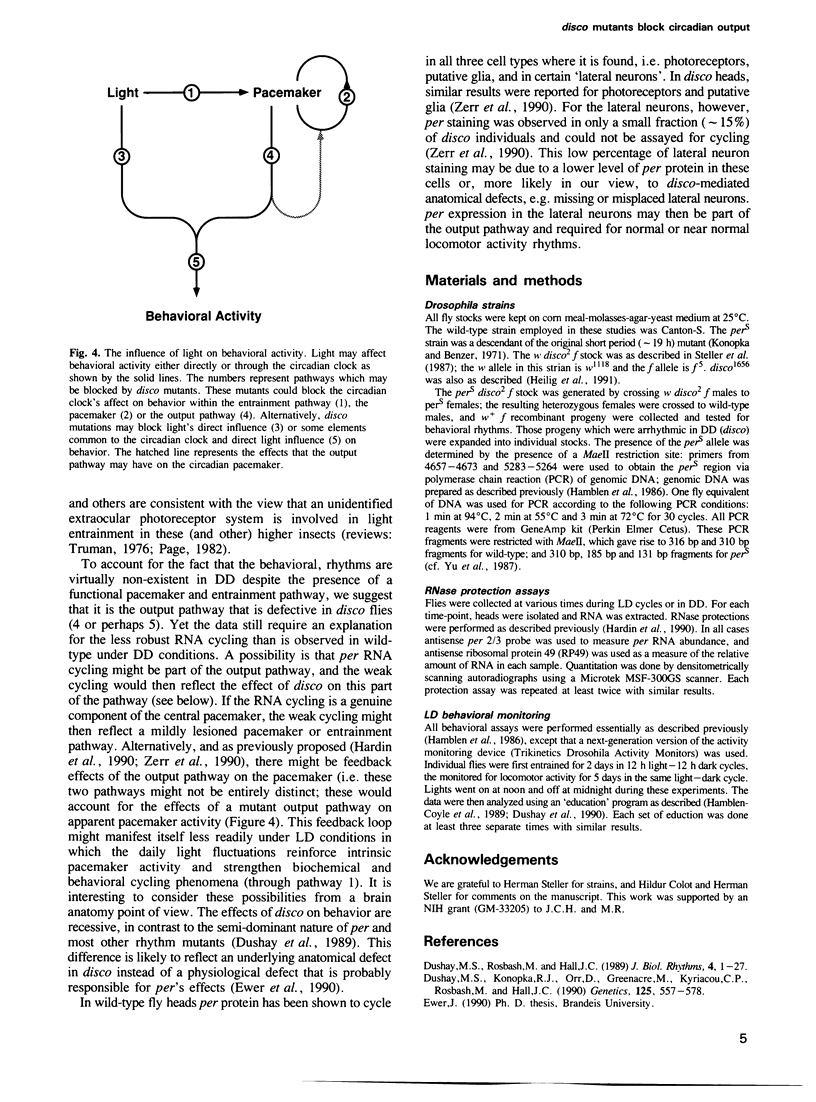
Mutations in the disconnected (disco) gene act to disrupt neural cell patterning in the Drosophila visual system. These mutations also affect adult locomotor activity rhythms, as disco flies are arrhythmic under conditions of constant darkness (DD). To determine the state of the circadian pacemaker in disco mutants, we constructed with pers double mutants (a short period allele of the period gene) and assayed their behavioral rhythms in light-dark cycles (LD), and their biochemical rhythms of period gene expression under both LD and DD conditions. The results demonstrate that disco flies are rhythmic, indicating that they have an active circadian pacemaker that can be entrained by light. They also suggest that disco mutants block or interfere with elements of the circadian system located between the central pacemaker and its outputs that mediate overt rhythms.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Dushay M. S., Konopka R. J., Orr D., Greenacre M. L., Kyriacou C. P., Rosbash M., Hall J. C. Phenotypic and genetic analysis of Clock, a new circadian rhythm mutant in Drosophila melanogaster. Genetics. 1990 Jul;125(3):557–578. doi: 10.1093/genetics/125.3.557. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dushay M. S., Rosbash M., Hall J. C. The disconnected visual system mutations in Drosophila melanogaster drastically disrupt circadian rhythms. J Biol Rhythms. 1989 Spring;4(1):1–27. doi: 10.1177/074873048900400101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ewer J., Hamblen-Coyle M., Rosbash M., Hall J. C. Requirement for period gene expression in the adult and not during development for locomotor activity rhythms of imaginal Drosophila melanogaster. J Neurogenet. 1990 Nov;7(1):31–73. doi: 10.3109/01677069009084151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall J. C., Rosbash M. Genetic and molecular analysis of biological rhythms. J Biol Rhythms. 1987 Fall;2(3):153–178. doi: 10.1177/074873048700200301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall J. C., Rosbash M. Mutations and molecules influencing biological rhythms. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1988;11:373–393. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.11.030188.002105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamblen-Coyle M., Konopka R. J., Zwiebel L. J., Colot H. V., Dowse H. B., Rosbash M., Hall J. C. A new mutation at the period locus of Drosophila melanogaster with some novel effects on circadian rhythms. J Neurogenet. 1989 Aug;5(4):229–256. doi: 10.3109/01677068909066210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamblen M., Zehring W. A., Kyriacou C. P., Reddy P., Yu Q., Wheeler D. A., Zwiebel L. J., Konopka R. J., Rosbash M., Hall J. C. Germ-line transformation involving DNA from the period locus in Drosophila melanogaster: overlapping genomic fragments that restore circadian and ultradian rhythmicity to per0 and per- mutants. J Neurogenet. 1986 Sep;3(5):249–291. doi: 10.3109/01677068609106855. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Handler A. M., Konopka R. J. Transplantation of a circadian pacemaker in Drosophila. Nature. 1979 May 17;279(5710):236–238. doi: 10.1038/279236a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardin P. E., Hall J. C., Rosbash M. Feedback of the Drosophila period gene product on circadian cycling of its messenger RNA levels. Nature. 1990 Feb 8;343(6258):536–540. doi: 10.1038/343536a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heilig J. S., Freeman M., Laverty T., Lee K. J., Campos A. R., Rubin G. M., Steller H. Isolation and characterization of the disconnected gene of Drosophila melanogaster. EMBO J. 1991 Apr;10(4):809–815. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb08013.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helfrich C., Cymborowski B., Engelmann W. Circadian activity rhythm of the house fly continues after optic tract severance and lobectomy. Chronobiol Int. 1985;2(1):19–32. doi: 10.3109/07420528509055538. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helfrich C. Role of the optic lobes in the regulation of the locomotor activity rhythm of Drosophila melanogaster: behavioral analysis of neural mutants. J Neurogenet. 1986 Nov;3(6):321–343. doi: 10.3109/01677068609106857. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konopka R. J., Benzer S. Clock mutants of Drosophila melanogaster. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Sep;68(9):2112–2116. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.9.2112. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petersen G., Hall J. C., Rosbash M. The period gene of Drosophila carries species-specific behavioral instructions. EMBO J. 1988 Dec 1;7(12):3939–3947. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03280.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosbash M., Hall J. C. The molecular biology of circadian rhythms. Neuron. 1989 Oct;3(4):387–398. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(89)90199-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siwicki K. K., Eastman C., Petersen G., Rosbash M., Hall J. C. Antibodies to the period gene product of Drosophila reveal diverse tissue distribution and rhythmic changes in the visual system. Neuron. 1988 Apr;1(2):141–150. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(88)90198-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steller H., Fischbach K. F., Rubin G. M. Disconnected: a locus required for neuronal pathway formation in the visual system of Drosophila. Cell. 1987 Sep 25;50(7):1139–1153. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90180-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Truman J. W. Extraretinal photoreception in insects. Photophysiology. 1976 Apr;23(4):215–225. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu Q., Jacquier A. C., Citri Y., Hamblen M., Hall J. C., Rosbash M. Molecular mapping of point mutations in the period gene that stop or speed up biological clocks in Drosophila melanogaster. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Feb;84(3):784–788. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.3.784. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zerr D. M., Hall J. C., Rosbash M., Siwicki K. K. Circadian fluctuations of period protein immunoreactivity in the CNS and the visual system of Drosophila. J Neurosci. 1990 Aug;10(8):2749–2762. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.10-08-02749.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zwiebel L. J., Hardin P. E., Liu X., Hall J. C., Rosbash M. A post-transcriptional mechanism contributes to circadian cycling of a per-beta-galactosidase fusion protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 May 1;88(9):3882–3886. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.9.3882. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]