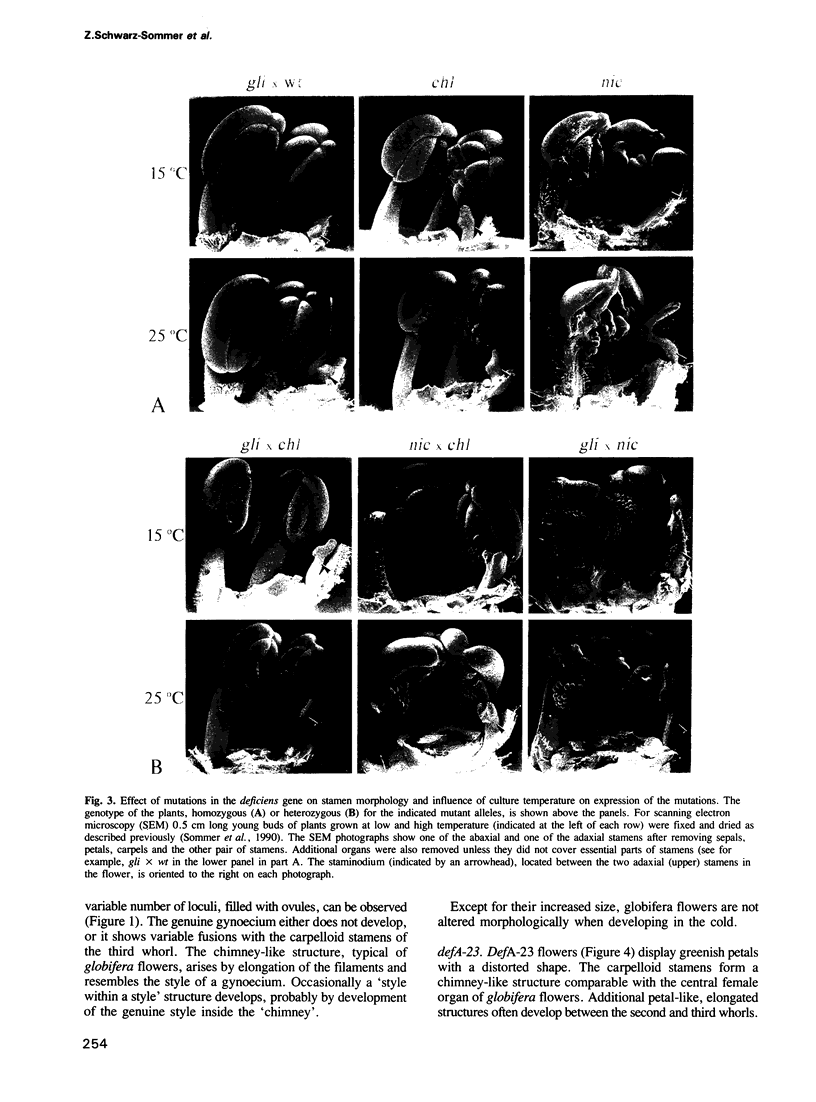
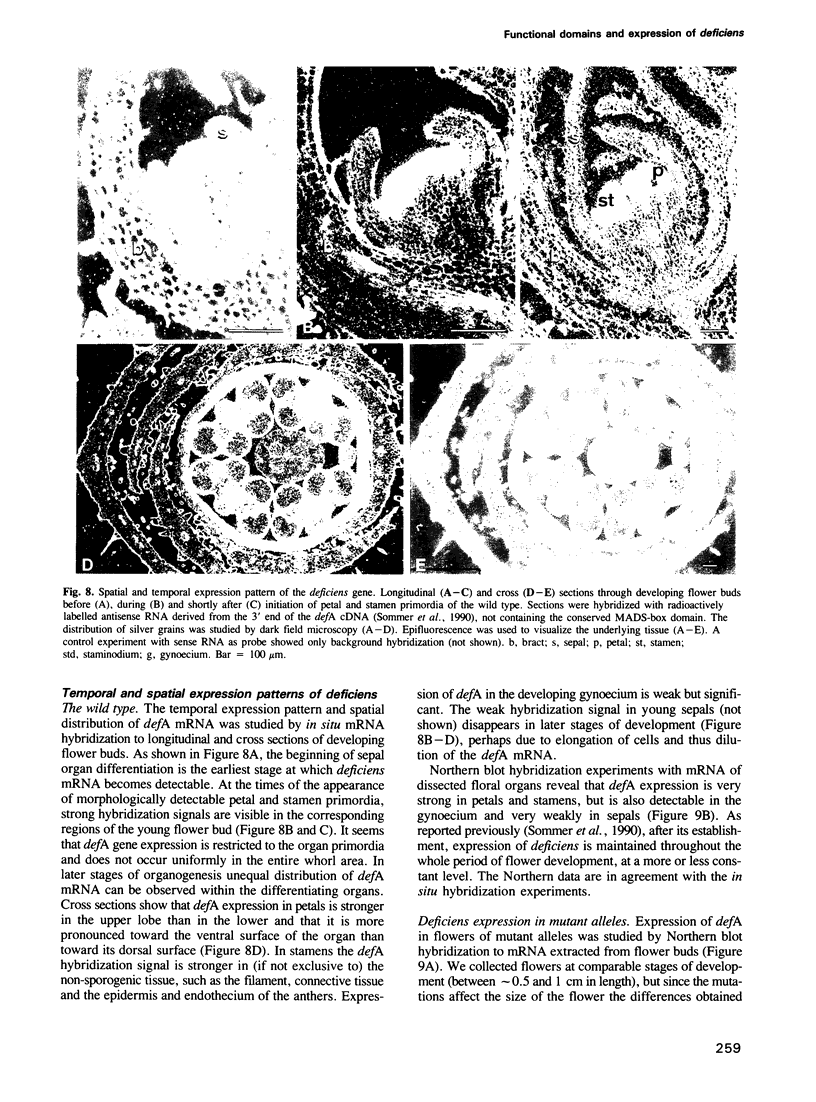
Abstract
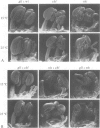
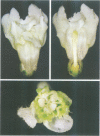
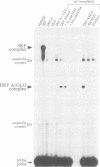
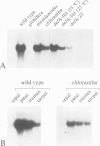
We have determined the structure of the floral homeotic deficiens (defA) gene whose mutants display sepaloid petals and carpelloid stamens, and have analysed its spatial and temporal expression pattern. In addition, several mutant alleles (morphoalleles) were studied. The results of these analyses define three functional domains of the DEF A protein and identify in the deficiens promoter a possible cis-acting binding site for a transcription factor which specifically upregulates expression of deficiens in petals and stamens. In vitro DNA binding studies show that DEF A binds to specific DNA motifs as a heterodimer, together with the protein product of the floral homeotic globosa gene, thus demonstrating that the protein encoded by deficiens is a DNA binding protein. Furthermore, Northern analysis of a temperature sensitive allele at permissive and non-permissive temperatures provides evidence for autoregulation of the persistent expression of deficiens throughout flower development. A possible mechanism of autoregulation is discussed.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bowman J. L., Smyth D. R., Meyerowitz E. M. Genetic interactions among floral homeotic genes of Arabidopsis. Development. 1991 May;112(1):1–20. doi: 10.1242/dev.112.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boxer L. M., Prywes R., Roeder R. G., Kedes L. The sarcomeric actin CArG-binding factor is indistinguishable from the c-fos serum response factor. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Feb;9(2):515–522. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.2.515. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carpenter R., Coen E. S. Floral homeotic mutations produced by transposon-mutagenesis in Antirrhinum majus. Genes Dev. 1990 Sep;4(9):1483–1493. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.9.1483. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christ C., Tye B. K. Functional domains of the yeast transcription/replication factor MCM1. Genes Dev. 1991 May;5(5):751–763. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.5.751. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coen E. S., Meyerowitz E. M. The war of the whorls: genetic interactions controlling flower development. Nature. 1991 Sep 5;353(6339):31–37. doi: 10.1038/353031a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubois E., Bercy J., Messenguy F. Characterization of two genes, ARGRI and ARGRIII required for specific regulation of arginine metabolism in yeast. Mol Gen Genet. 1987 Apr;207(1):142–148. doi: 10.1007/BF00331501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gierl A., Saedler H., Peterson P. A. Maize transposable elements. Annu Rev Genet. 1989;23:71–85. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.23.120189.000443. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gustafson T. A., Kedes L. Identification of multiple proteins that interact with functional regions of the human cardiac alpha-actin promoter. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Aug;9(8):3269–3283. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.8.3269. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayes T. E., Sengupta P., Cochran B. H. The human c-fos serum response factor and the yeast factors GRM/PRTF have related DNA-binding specificities. Genes Dev. 1988 Dec;2(12B):1713–1722. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.12b.1713. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jiang J., Hoey T., Levine M. Autoregulation of a segmentation gene in Drosophila: combinatorial interaction of the even-skipped homeo box protein with a distal enhancer element. Genes Dev. 1991 Feb;5(2):265–277. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.2.265. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joshi C. P. An inspection of the domain between putative TATA box and translation start site in 79 plant genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Aug 25;15(16):6643–6653. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.16.6643. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keleher C. A., Goutte C., Johnson A. D. The yeast cell-type-specific repressor alpha 2 acts cooperatively with a non-cell-type-specific protein. Cell. 1988 Jun 17;53(6):927–936. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(88)90449-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuziora M. A., McGinnis W. Autoregulation of a Drosophila homeotic selector gene. Cell. 1988 Nov 4;55(3):477–485. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90034-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ma H., Yanofsky M. F., Meyerowitz E. M. AGL1-AGL6, an Arabidopsis gene family with similarity to floral homeotic and transcription factor genes. Genes Dev. 1991 Mar;5(3):484–495. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.3.484. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mohun T. J., Chambers A. E., Towers N., Taylor M. V. Expression of genes encoding the transcription factor SRF during early development of Xenopus laevis: identification of a CArG box-binding activity as SRF. EMBO J. 1991 Apr;10(4):933–940. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb08027.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norman C., Runswick M., Pollock R., Treisman R. Isolation and properties of cDNA clones encoding SRF, a transcription factor that binds to the c-fos serum response element. Cell. 1988 Dec 23;55(6):989–1003. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90244-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Passmore S., Elble R., Tye B. K. A protein involved in minichromosome maintenance in yeast binds a transcriptional enhancer conserved in eukaryotes. Genes Dev. 1989 Jul;3(7):921–935. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.7.921. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Passmore S., Maine G. T., Elble R., Christ C., Tye B. K. Saccharomyces cerevisiae protein involved in plasmid maintenance is necessary for mating of MAT alpha cells. J Mol Biol. 1988 Dec 5;204(3):593–606. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90358-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pnueli L., Abu-Abeid M., Zamir D., Nacken W., Schwarz-Sommer Z., Lifschitz E. The MADS box gene family in tomato: temporal expression during floral development, conserved secondary structures and homology with homeotic genes from Antirrhinum and Arabidopsis. Plant J. 1991 Sep;1(2):255–266. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Regulski M., Dessain S., McGinnis N., McGinnis W. High-affinity binding sites for the Deformed protein are required for the function of an autoregulatory enhancer of the Deformed gene. Genes Dev. 1991 Feb;5(2):278–286. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.2.278. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sartorelli V., Webster K. A., Kedes L. Muscle-specific expression of the cardiac alpha-actin gene requires MyoD1, CArG-box binding factor, and Sp1. Genes Dev. 1990 Oct;4(10):1811–1822. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.10.1811. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schröter H., Shaw P. E., Nordheim A. Purification of intercalator-released p67, a polypeptide that interacts specifically with the c-fos serum response element. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Dec 23;15(24):10145–10158. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.24.10145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwarz-Sommer Z., Huijser P., Nacken W., Saedler H., Sommer H. Genetic Control of Flower Development by Homeotic Genes in Antirrhinum majus. Science. 1990 Nov 16;250(4983):931–936. doi: 10.1126/science.250.4983.931. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwarz-Sommer Z., Shepherd N., Tacke E., Gierl A., Rohde W., Leclercq L., Mattes M., Berndtgen R., Peterson P. A., Saedler H. Influence of transposable elements on the structure and function of the A1 gene of Zea mays. EMBO J. 1987 Feb;6(2):287–294. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04752.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Serfling E. Autoregulation--a common property of eukaryotic transcription factors? Trends Genet. 1989 May;5(5):131–133. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(89)90049-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sommer H., Beltrán J. P., Huijser P., Pape H., Lönnig W. E., Saedler H., Schwarz-Sommer Z. Deficiens, a homeotic gene involved in the control of flower morphogenesis in Antirrhinum majus: the protein shows homology to transcription factors. EMBO J. 1990 Mar;9(3):605–613. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08152.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor M., Treisman R., Garrett N., Mohun T. Muscle-specific (CArG) and serum-responsive (SRE) promoter elements are functionally interchangeable in Xenopus embryos and mouse fibroblasts. Development. 1989 May;106(1):67–78. doi: 10.1242/dev.106.1.67. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanofsky M. F., Ma H., Bowman J. L., Drews G. N., Feldmann K. A., Meyerowitz E. M. The protein encoded by the Arabidopsis homeotic gene agamous resembles transcription factors. Nature. 1990 Jul 5;346(6279):35–39. doi: 10.1038/346035a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]