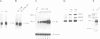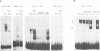Abstract
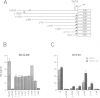
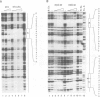
We studied the structure, regulation and expression of HOX3D, a human homeobox gene located in the HOX3 cluster on chromosome 12. HOX3D is developmentally regulated during embryogenesis and is activated by retinoic acid (RA) in cultured embryonal carcinoma (EC) cells. Transfection of HOX3D upstream genomic sequences linked to a reporter gene allowed the functional definition of its promoter, containing a canonical TATA element. This promoter directs the expression of the reporter gene in EC cells after induction with RA, and binds RA-induced nuclear factor(s) through a conserved palindromic sequence located approximately 100 bp upstream of the transcription start site. The HOX3D promoter is transactivated in both human and murine cells when cotransfected with vectors expressing the protein product of the upstream gene HOX3C and the paralogs of further upstream genes in the HOX4 cluster (i.e. HOX4D, HOX4C and the murine Hox 4.3). The HOX3D protein, and those encoded by the downstream gene HOX3E and its paralog HOX4B are instead inactive. HOX4C and HOX4D proteins synthesized in bacteria bind to the same conserved sequence located around position -120, as well as to the TATA box and immediately upstream and downstream nucleotides. These data provide evidence that cross-regulatory interactions between mammalian homeogenes take place in cultured cells, thus raising the possibility that a regulatory network may exist in vivo. The sequences on the HOX3D promoter involved in cross-regulation are different from those binding nuclear factors induced by RA.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Acampora D., D'Esposito M., Faiella A., Pannese M., Migliaccio E., Morelli F., Stornaiuolo A., Nigro V., Simeone A., Boncinelli E. The human HOX gene family. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Dec 25;17(24):10385–10402. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.24.10385. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Akam M. Hox and HOM: homologous gene clusters in insects and vertebrates. Cell. 1989 May 5;57(3):347–349. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90909-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Akam M. The molecular basis for metameric pattern in the Drosophila embryo. Development. 1987 Sep;101(1):1–22. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Angel P., Imagawa M., Chiu R., Stein B., Imbra R. J., Rahmsdorf H. J., Jonat C., Herrlich P., Karin M. Phorbol ester-inducible genes contain a common cis element recognized by a TPA-modulated trans-acting factor. Cell. 1987 Jun 19;49(6):729–739. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90611-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackwell T. K., Kretzner L., Blackwood E. M., Eisenman R. N., Weintraub H. Sequence-specific DNA binding by the c-Myc protein. Science. 1990 Nov 23;250(4984):1149–1151. doi: 10.1126/science.2251503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boncinelli E., Simeone A., Acampora D., Mavilio F. HOX gene activation by retinoic acid. Trends Genet. 1991 Oct;7(10):329–334. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(91)90423-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brockes J. P. Retinoids, homeobox genes, and limb morphogenesis. Neuron. 1989 Apr;2(4):1285–1294. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(89)90066-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carthew R. W., Chodosh L. A., Sharp P. A. An RNA polymerase II transcription factor binds to an upstream element in the adenovirus major late promoter. Cell. 1985 Dec;43(2 Pt 1):439–448. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90174-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen C., Okayama H. High-efficiency transformation of mammalian cells by plasmid DNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Aug;7(8):2745–2752. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.8.2745. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cho K. W., De Robertis E. M. Differential activation of Xenopus homeo box genes by mesoderm-inducing growth factors and retinoic acid. Genes Dev. 1990 Nov;4(11):1910–1916. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.11.1910. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cho K. W., Morita E. A., Wright C. V., De Robertis E. M. Overexpression of a homeodomain protein confers axis-forming activity to uncommitted Xenopus embryonic cells. Cell. 1991 Apr 5;65(1):55–64. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90407-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Condie B. G., Brivanlou A. H., Harland R. M. Most of the homeobox-containing Xhox 36 transcripts in early Xenopus embryos cannot encode a homeodomain protein. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jul;10(7):3376–3385. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.7.3376. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Robertis E. M., Oliver G., Wright C. V. Determination of axial polarity in the vertebrate embryo: homeodomain proteins and homeogenetic induction. Cell. 1989 Apr 21;57(2):189–191. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90954-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dearolf C. R., Topol J., Parker C. S. The caudal gene product is a direct activator of fushi tarazu transcription during Drosophila embryogenesis. Nature. 1989 Sep 28;341(6240):340–343. doi: 10.1038/341340a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Desplan C., Theis J., O'Farrell P. H. The sequence specificity of homeodomain-DNA interaction. Cell. 1988 Sep 23;54(7):1081–1090. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90123-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dignam J. D., Lebovitz R. M., Roeder R. G. Accurate transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II in a soluble extract from isolated mammalian nuclei. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 11;11(5):1475–1489. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.5.1475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dollé P., Izpisúa-Belmonte J. C., Falkenstein H., Renucci A., Duboule D. Coordinate expression of the murine Hox-5 complex homoeobox-containing genes during limb pattern formation. Nature. 1989 Dec 14;342(6251):767–772. doi: 10.1038/342767a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duboule D., Dollé P. The structural and functional organization of the murine HOX gene family resembles that of Drosophila homeotic genes. EMBO J. 1989 May;8(5):1497–1505. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03534.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fainsod A., Bogarad L. D., Ruusala T., Lubin M., Crothers D. M., Ruddle F. H. The homeo domain of a murine protein binds 5' to its own homeo box. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(24):9532–9536. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.24.9532. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gehring W. J., Hiromi Y. Homeotic genes and the homeobox. Annu Rev Genet. 1986;20:147–173. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.20.120186.001051. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gehring W. J., Müller M., Affolter M., Percival-Smith A., Billeter M., Qian Y. Q., Otting G., Wüthrich K. The structure of the homeodomain and its functional implications. Trends Genet. 1990 Oct;6(10):323–329. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(90)90253-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giampaolo A., Acampora D., Zappavigna V., Pannese M., D'Esposito M., Carè A., Faiella A., Stornaiuolo A., Russo G., Simeone A. Differential expression of human HOX-2 genes along the anterior-posterior axis in embryonic central nervous system. Differentiation. 1989 Jun;40(3):191–197. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-0436.1989.tb00598.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glass C. K., Devary O. V., Rosenfeld M. G. Multiple cell type-specific proteins differentially regulate target sequence recognition by the alpha retinoic acid receptor. Cell. 1990 Nov 16;63(4):729–738. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90139-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- González-Reyes A., Urquia N., Gehring W. J., Struhl G., Morata G. Are cross-regulatory interactions between homoeotic genes functionally significant? Nature. 1990 Mar 1;344(6261):78–80. doi: 10.1038/344078a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham A., Papalopulu N., Krumlauf R. The murine and Drosophila homeobox gene complexes have common features of organization and expression. Cell. 1989 May 5;57(3):367–378. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90912-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green S., Issemann I., Sheer E. A versatile in vivo and in vitro eukaryotic expression vector for protein engineering. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Jan 11;16(1):369–369. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.1.369. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg M. E., Ziff E. B. Stimulation of 3T3 cells induces transcription of the c-fos proto-oncogene. Nature. 1984 Oct 4;311(5985):433–438. doi: 10.1038/311433a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayashi S., Scott M. P. What determines the specificity of action of Drosophila homeodomain proteins? Cell. 1990 Nov 30;63(5):883–894. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90492-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoey T., Levine M. Divergent homeo box proteins recognize similar DNA sequences in Drosophila. Nature. 1988 Apr 28;332(6167):858–861. doi: 10.1038/332858a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holland P. W., Hogan B. L. Spatially restricted patterns of expression of the homeobox-containing gene Hox 2.1. during mouse embryogenesis. Development. 1988 Jan;102(1):159–174. doi: 10.1242/dev.102.1.159. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ingham P. W. The molecular genetics of embryonic pattern formation in Drosophila. Nature. 1988 Sep 1;335(6185):25–34. doi: 10.1038/335025a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Izpisúa-Belmonte J. C., Tickle C., Dollé P., Wolpert L., Duboule D. Expression of the homeobox Hox-4 genes and the specification of position in chick wing development. Nature. 1991 Apr 18;350(6319):585–589. doi: 10.1038/350585a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kessel M., Balling R., Gruss P. Variations of cervical vertebrae after expression of a Hox-1.1 transgene in mice. Cell. 1990 Apr 20;61(2):301–308. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90810-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kessel M., Gruss P. Murine developmental control genes. Science. 1990 Jul 27;249(4967):374–379. doi: 10.1126/science.1974085. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krumlauf R., Holland P. W., McVey J. H., Hogan B. L. Developmental and spatial patterns of expression of the mouse homeobox gene, Hox 2.1. Development. 1987 Apr;99(4):603–617. doi: 10.1242/dev.99.4.603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee W., Mitchell P., Tjian R. Purified transcription factor AP-1 interacts with TPA-inducible enhancer elements. Cell. 1987 Jun 19;49(6):741–752. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90612-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malicki J., Schughart K., McGinnis W. Mouse Hox-2.2 specifies thoracic segmental identity in Drosophila embryos and larvae. Cell. 1990 Nov 30;63(5):961–967. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90499-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mavilio F., Simeone A., Giampaolo A., Faiella A., Zappavigna V., Acampora D., Poiana G., Russo G., Peschle C., Boncinelli E. Differential and stage-related expression in embryonic tissues of a new human homoeobox gene. Nature. 1986 Dec 18;324(6098):664–668. doi: 10.1038/324664a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGinnis N., Kuziora M. A., McGinnis W. Human Hox-4.2 and Drosophila deformed encode similar regulatory specificities in Drosophila embryos and larvae. Cell. 1990 Nov 30;63(5):969–976. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90500-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melton D. A. Pattern formation during animal development. Science. 1991 Apr 12;252(5003):234–241. doi: 10.1126/science.1672778. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicholson R. C., Mader S., Nagpal S., Leid M., Rochette-Egly C., Chambon P. Negative regulation of the rat stromelysin gene promoter by retinoic acid is mediated by an AP1 binding site. EMBO J. 1990 Dec;9(13):4443–4454. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07895.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nohno T., Noji S., Koyama E., Ohyama K., Myokai F., Kuroiwa A., Saito T., Taniguchi S. Involvement of the Chox-4 chicken homeobox genes in determination of anteroposterior axial polarity during limb development. Cell. 1991 Mar 22;64(6):1197–1205. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90274-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Odenwald W. F., Garbern J., Arnheiter H., Tournier-Lasserve E., Lazzarini R. A. The Hox-1.3 homeo box protein is a sequence-specific DNA-binding phosphoprotein. Genes Dev. 1989 Feb;3(2):158–172. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.2.158. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Odenwald W. F., Taylor C. F., Palmer-Hill F. J., Friedrich V., Jr, Tani M., Lazzarini R. A. Expression of a homeo domain protein in noncontact-inhibited cultured cells and postmitotic neurons. Genes Dev. 1987 Jul;1(5):482–496. doi: 10.1101/gad.1.5.482. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohkuma Y., Horikoshi M., Roeder R. G., Desplan C. Engrailed, a homeodomain protein, can repress in vitro transcription by competition with the TATA box-binding protein transcription factor IID. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Mar;87(6):2289–2293. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.6.2289. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oliver G., De Robertis E. M., Wolpert L., Tickle C. Expression of a homeobox gene in the chick wing bud following application of retinoic acid and grafts of polarizing region tissue. EMBO J. 1990 Oct;9(10):3093–3099. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07506.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruiz i Altaba A., Melton D. A. Interaction between peptide growth factors and homoeobox genes in the establishment of antero-posterior polarity in frog embryos. Nature. 1989 Sep 7;341(6237):33–38. doi: 10.1038/341033a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawadogo M., Roeder R. G. Interaction of a gene-specific transcription factor with the adenovirus major late promoter upstream of the TATA box region. Cell. 1985 Nov;43(1):165–175. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90021-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott M. P., Tamkun J. W., Hartzell G. W., 3rd The structure and function of the homeodomain. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989 Jul 28;989(1):25–48. doi: 10.1016/0304-419x(89)90033-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selden R. F., Howie K. B., Rowe M. E., Goodman H. M., Moore D. D. Human growth hormone as a reporter gene in regulation studies employing transient gene expression. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Sep;6(9):3173–3179. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.9.3173. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simeone A., Acampora D., Arcioni L., Andrews P. W., Boncinelli E., Mavilio F. Sequential activation of HOX2 homeobox genes by retinoic acid in human embryonal carcinoma cells. Nature. 1990 Aug 23;346(6286):763–766. doi: 10.1038/346763a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simeone A., Acampora D., Nigro V., Faiella A., D'Esposito M., Stornaiuolo A., Mavilio F., Boncinelli E. Differential regulation by retinoic acid of the homeobox genes of the four HOX loci in human embryonal carcinoma cells. Mech Dev. 1991 Mar;33(3):215–227. doi: 10.1016/0925-4773(91)90029-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simeone A., Mavilio F., Acampora D., Giampaolo A., Faiella A., Zappavigna V., D'Esposito M., Pannese M., Russo G., Boncinelli E. Two human homeobox genes, c1 and c8: structure analysis and expression in embryonic development. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jul;84(14):4914–4918. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.14.4914. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simeone A., Mavilio F., Bottero L., Giampaolo A., Russo G., Faiella A., Boncinelli E., Peschle C. A human homoeo box gene specifically expressed in spinal cord during embryonic development. Nature. 1986 Apr 24;320(6064):763–765. doi: 10.1038/320763a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simeone A., Pannese M., Acampora D., D'Esposito M., Boncinelli E. At least three human homeoboxes on chromosome 12 belong to the same transcription unit. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Jun 24;16(12):5379–5390. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.12.5379. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Studier F. W., Rosenberg A. H., Dunn J. J., Dubendorff J. W. Use of T7 RNA polymerase to direct expression of cloned genes. Methods Enzymol. 1990;185:60–89. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(90)85008-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thali M., Müller M. M., DeLorenzi M., Matthias P., Bienz M. Drosophila homoeotic genes encode transcriptional activators similar to mammalian OTF-2. Nature. 1988 Dec 8;336(6199):598–601. doi: 10.1038/336598a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P. S. Hybridization of denatured RNA and small DNA fragments transferred to nitrocellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5201–5205. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright C. V., Cho K. W., Hardwicke J., Collins R. H., De Robertis E. M. Interference with function of a homeobox gene in Xenopus embryos produces malformations of the anterior spinal cord. Cell. 1989 Oct 6;59(1):81–93. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90871-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright C. V., Cho K. W., Oliver G., De Robertis E. M. Vertebrate homeodomain proteins: families of region-specific transcription factors. Trends Biochem Sci. 1989 Feb;14(2):52–56. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(89)90043-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zappavigna V., Renucci A., Izpisúa-Belmonte J. C., Urier G., Peschle C., Duboule D. HOX4 genes encode transcription factors with potential auto- and cross-regulatory capacities. EMBO J. 1991 Dec;10(13):4177–4187. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb04996.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zwartkruis F., Hoeijmakers T., Deschamps J., Meijlink F. Characterization of the murine Hox-2.3 promoter: involvement of the transcription factor USF (MLTF). Mech Dev. 1991 Mar;33(3):179–190. doi: 10.1016/0925-4773(91)90026-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]