Abstract
The integration host factor (IHF) of Escherichia coli is a small, basic protein that is required for lambda site-specific recombination and a variety of cellular processes. It is composed of two subunits, alpha and beta, that are encoded by the himA and hip (himD) genes, respectively. IHF is a sequence-specific DNA-binding protein and bends the DNA when it binds. We have used the bacteriophage P22-based challenge phage selection to isolate suppressor mutants with altered, expanded DNA binding specificities. The suppressors were isolated by selecting mutants that recognize variants of the phage lambda H'IHF recognition site. Two of the mutants recognize both the wild-type and a single variant site and contain amino acid substitutions at positions 64 (Pro to Leu) or 65 (Lys to Ser) of the alpha subunit. These substitutions are in a region of the protein that is predicted to contain a flexible arm that interacts with DNA. Three other mutants, which recognize the wild-type and a different variant site, contain amino acid substitutions at position 44 (Glu to Lys, Val or Gly) of the beta subunit. These substitutions are in the middle of a predicted beta-strand of the subunit. We discuss the possible mechanisms of suppression by the mutants in terms of a model of the IHF-DNA complex proposed by Yang and Nash [Cell, 57, 869-880 (1989)].
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Benson N., Sugiono P., Bass S., Mendelman L. V., Youderian P. General selection for specific DNA-binding activities. Genetics. 1986 Sep;114(1):1–14. doi: 10.1093/genetics/114.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craig N. L., Nash H. A. E. coli integration host factor binds to specific sites in DNA. Cell. 1984 Dec;39(3 Pt 2):707–716. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90478-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drlica K., Rouviere-Yaniv J. Histonelike proteins of bacteria. Microbiol Rev. 1987 Sep;51(3):301–319. doi: 10.1128/mr.51.3.301-319.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flamm E. L., Weisberg R. A. Primary structure of the hip gene of Escherichia coli and of its product, the beta subunit of integration host factor. J Mol Biol. 1985 May 25;183(2):117–128. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90206-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman D. I. Integration host factor: a protein for all reasons. Cell. 1988 Nov 18;55(4):545–554. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90213-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman D. I., Olson E. J., Carver D., Gellert M. Synergistic effect of himA and gyrB mutations: evidence that him functions control expression of ilv and xyl genes. J Bacteriol. 1984 Feb;157(2):484–489. doi: 10.1128/jb.157.2.484-489.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodman S. D., Nash H. A. Functional replacement of a protein-induced bend in a DNA recombination site. Nature. 1989 Sep 21;341(6239):251–254. doi: 10.1038/341251a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graña D., Gardella T., Susskind M. M. The effects of mutations in the ant promoter of phage P22 depend on context. Genetics. 1988 Oct;120(2):319–327. doi: 10.1093/genetics/120.2.319. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgins N. P., Collier D. A., Kilpatrick M. W., Krause H. M. Supercoiling and integration host factor change the DNA conformation and alter the flow of convergent transcription in phage Mu. J Biol Chem. 1989 Feb 15;264(5):3035–3042. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hong J. S., Ames B. N. Localized mutagenesis of any specific small region of the bacterial chromosome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Dec;68(12):3158–3162. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.12.3158. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kosturko L. D., Daub E., Murialdo H. The interaction of E. coli integration host factor and lambda cos DNA: multiple complex formation and protein-induced bending. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Jan 11;17(1):317–334. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.1.317. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kur J., Hasan N., Szybalski W. Physical and biological consequences of interactions between integration host factor (IHF) and coliphage lambda late p'R promoter and its mutants. Gene. 1989 Sep 1;81(1):1–15. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(89)90331-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
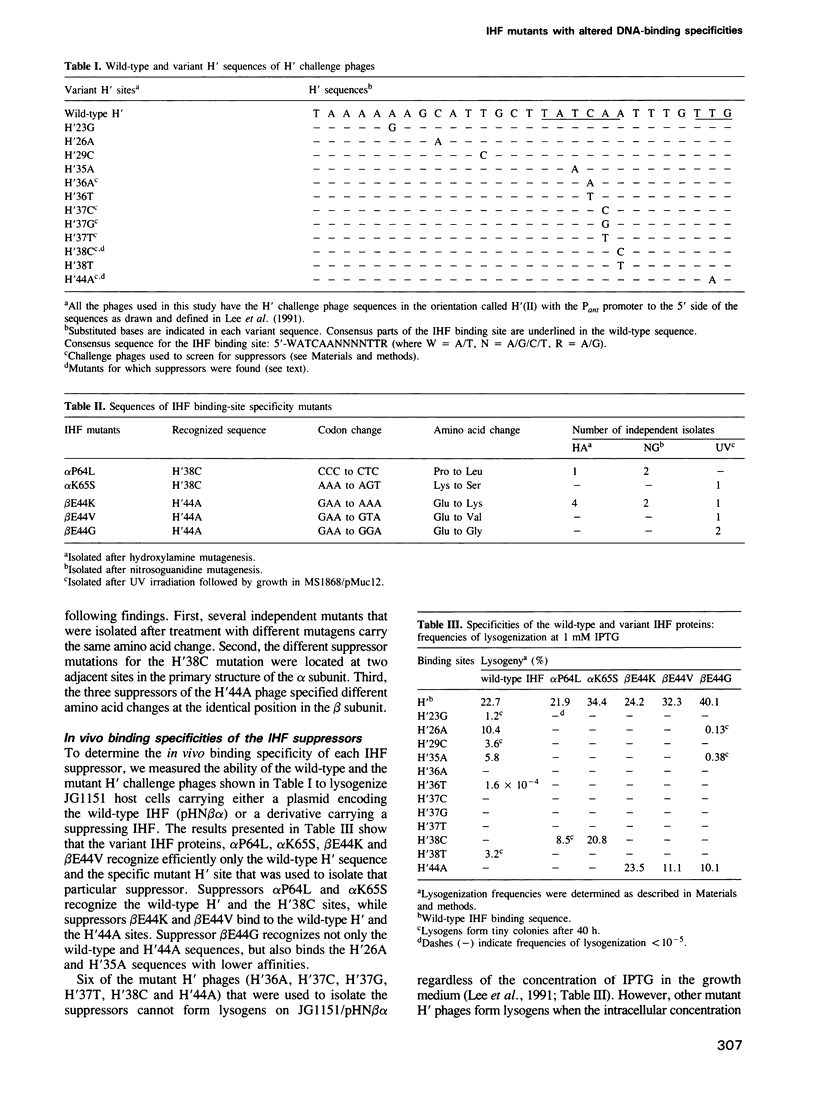
- Lee E. C., MacWilliams M. P., Gumport R. I., Gardner J. F. Genetic analysis of Escherichia coli integration host factor interactions with its bacteriophage lambda H' recognition site. J Bacteriol. 1991 Jan;173(2):609–617. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.2.609-617.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mechulam Y., Fayat G., Blanquet S. Sequence of the Escherichia coli pheST operon and identification of the himA gene. J Bacteriol. 1985 Aug;163(2):787–791. doi: 10.1128/jb.163.2.787-791.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller H. I., Friedman D. I. An E. coli gene product required for lambda site-specific recombination. Cell. 1980 Jul;20(3):711–719. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90317-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller H. I., Kikuchi A., Nash H. A., Weisberg R. A., Friedman D. I. Site-specific recombination of bacteriophage lambda: the role of host gene products. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1979;43(Pt 2):1121–1126. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1979.043.01.125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller H. I. Primary structure of the himA gene of Escherichia coli: homology with DNA-binding protein HU and association with the phenylalanyl-tRNA synthetase operon. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1984;49:691–698. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1984.049.01.078. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry K. L., Walker G. C. Identification of plasmid (pKM101)-coded proteins involved in mutagenesis and UV resistance. Nature. 1982 Nov 18;300(5889):278–281. doi: 10.1038/300278a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prentki P., Chandler M., Galas D. J. Escherichia coli integration host factor bends the DNA at the ends of IS1 and in an insertion hotspot with multiple IHF binding sites. EMBO J. 1987 Aug;6(8):2479–2487. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02529.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson C. A., Nash H. A. Bending of the bacteriophage lambda attachment site by Escherichia coli integration host factor. J Biol Chem. 1988 Mar 15;263(8):3554–3557. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmieger H. Phage P22-mutants with increased or decreased transduction abilities. Mol Gen Genet. 1972;119(1):75–88. doi: 10.1007/BF00270447. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steitz T. A. Structural studies of protein-nucleic acid interaction: the sources of sequence-specific binding. Q Rev Biophys. 1990 Aug;23(3):205–280. doi: 10.1017/s0033583500005552. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stenzel T. T., Patel P., Bastia D. The integration host factor of Escherichia coli binds to bent DNA at the origin of replication of the plasmid pSC101. Cell. 1987 Jun 5;49(5):709–717. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90547-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka I., Appelt K., Dijk J., White S. W., Wilson K. S. 3-A resolution structure of a protein with histone-like properties in prokaryotes. Nature. 1984 Aug 2;310(5976):376–381. doi: 10.1038/310376a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson J. F., Landy A. Empirical estimation of protein-induced DNA bending angles: applications to lambda site-specific recombination complexes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Oct 25;16(20):9687–9705. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.20.9687. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White S. W., Appelt K., Wilson K. S., Tanaka I. A protein structural motif that bends DNA. Proteins. 1989;5(4):281–288. doi: 10.1002/prot.340050405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang C. C., Nash H. A. The interaction of E. coli IHF protein with its specific binding sites. Cell. 1989 Jun 2;57(5):869–880. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90801-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]