Abstract
The physical parameters controlling the accessibility of antigen receptor loci to the V(D)J recombination activity are unknown. We have used minichromosome substrates to study the role that CpG methylation might play in controlling V(D)J recombination site accessibility. We find that CpG methylation decreases the V(D)J recombination of these substrates more than 100-fold. The decrease correlates with a considerable increase in resistance to endonuclease digestion of the methylated minichromosome DNA. The minichromosomes acquire resistance to both the intracellular V(D)J recombinase and exogenous endonuclease only after DNA replication. Therefore, CpG methylation specifies a chromatin structure that, upon DNA replication, is resistant to eukaryotic site-specific recombination. These findings are important to V(D)J recombination as well as to the chromatin assembly of methylated DNA during replication.
Full text
PDF



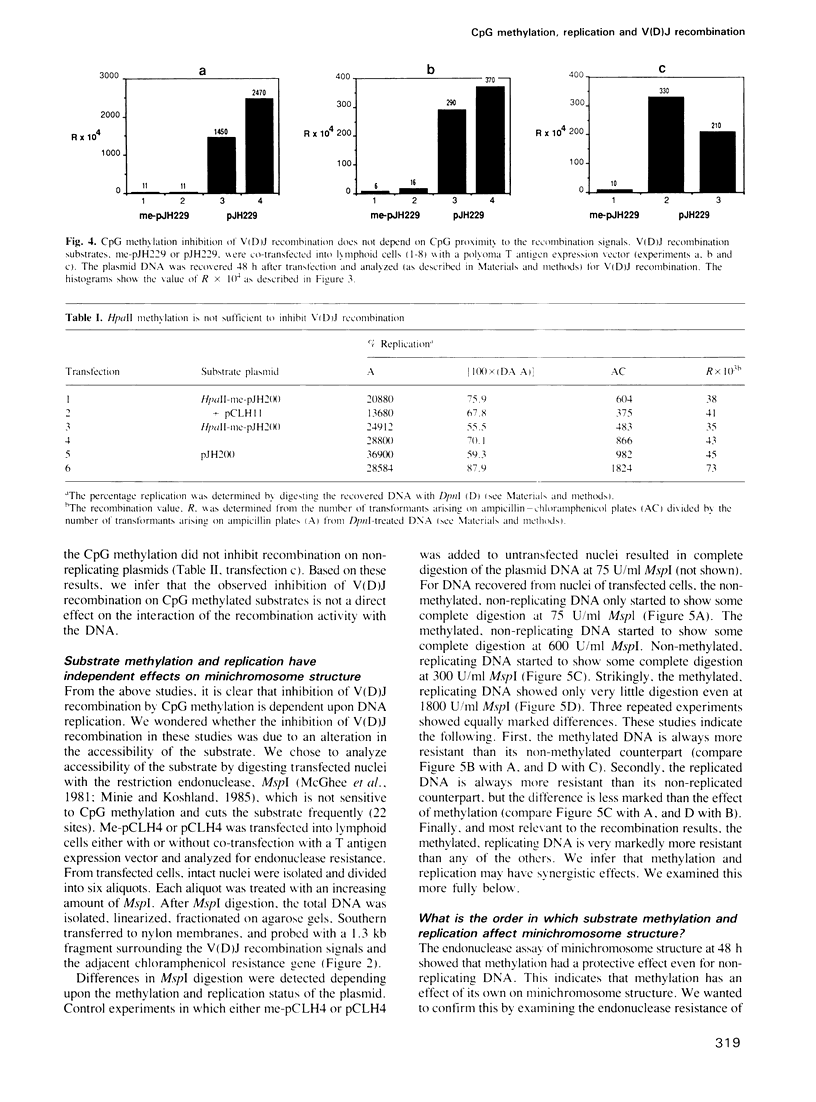






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams R. L., McKay E. L., Craig L. M., Burdon R. H. Mouse DNA methylase: methylation of native DNA. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Feb 27;561(2):345–357. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(79)90143-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alt F. W., Blackwell T. K., Yancopoulos G. D. Development of the primary antibody repertoire. Science. 1987 Nov 20;238(4830):1079–1087. doi: 10.1126/science.3317825. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Antequera F., Boyes J., Bird A. High levels of de novo methylation and altered chromatin structure at CpG islands in cell lines. Cell. 1990 Aug 10;62(3):503–514. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90015-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Antequera F., Macleod D., Bird A. P. Specific protection of methylated CpGs in mammalian nuclei. Cell. 1989 Aug 11;58(3):509–517. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90431-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Becker R. S., Zhai S. K., Currier S. J., Knight K. L. Ig VH, DH, and JH germ-line gene segments linked by overlapping cosmid clones of rabbit DNA. J Immunol. 1989 Feb 15;142(4):1351–1355. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bird A. P. CpG-rich islands and the function of DNA methylation. Nature. 1986 May 15;321(6067):209–213. doi: 10.1038/321209a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyes J., Bird A. DNA methylation inhibits transcription indirectly via a methyl-CpG binding protein. Cell. 1991 Mar 22;64(6):1123–1134. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90267-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brasier A. R., Tate J. E., Habener J. F. Optimized use of the firefly luciferase assay as a reporter gene in mammalian cell lines. Biotechniques. 1989 Nov-Dec;7(10):1116–1122. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cedar H. DNA methylation and gene activity. Cell. 1988 Apr 8;53(1):3–4. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90479-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doerfler W., Toth M., Kochanek S., Achten S., Freisem-Rabien U., Behn-Krappa A., Orend G. Eukaryotic DNA methylation: facts and problems. FEBS Lett. 1990 Aug 1;268(2):329–333. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)81280-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drahovský D., Morris N. R. Mechanism of action of rat liver DNA methylase. I. Interaction with double-stranded methyl-acceptor DNA. J Mol Biol. 1971 May 14;57(3):475–489. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90104-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engler P., Haasch D., Pinkert C. A., Doglio L., Glymour M., Brinster R., Storb U. A strain-specific modifier on mouse chromosome 4 controls the methylation of independent transgene loci. Cell. 1991 Jun 14;65(6):939–947. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90546-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engler P., Roth P., Kim J. Y., Storb U. Factors affecting the rearrangement efficiency of an Ig test gene. J Immunol. 1991 Apr 15;146(8):2826–2835. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrier P., Covey L. R., Suh H., Winoto A., Hood L., Alt F. W. T cell receptor DJ but not VDJ rearrangement within a recombination substrate introduced into a pre-B cell line. Int Immunol. 1989;1(1):66–74. doi: 10.1093/intimm/1.1.66. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hendrickson E. A., Liu V. F., Weaver D. T. Strand breaks without DNA rearrangement in V (D)J recombination. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Jun;11(6):3155–3162. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.6.3155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hesse J. E., Lieber M. R., Gellert M., Mizuuchi K. Extrachromosomal DNA substrates in pre-B cells undergo inversion or deletion at immunoglobulin V-(D)-J joining signals. Cell. 1987 Jun 19;49(6):775–783. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90615-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hesse J. E., Lieber M. R., Mizuuchi K., Gellert M. V(D)J recombination: a functional definition of the joining signals. Genes Dev. 1989 Jul;3(7):1053–1061. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.7.1053. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsieh C. L., McCloskey R. P., Radany E., Lieber M. R. V(D)J recombination: evidence that a replicative mechanism is not required. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Aug;11(8):3972–3977. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.8.3972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ichihara Y., Matsuoka H., Kurosawa Y. Organization of human immunoglobulin heavy chain diversity gene loci. EMBO J. 1988 Dec 20;7(13):4141–4150. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03309.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keshet I., Lieman-Hurwitz J., Cedar H. DNA methylation affects the formation of active chromatin. Cell. 1986 Feb 28;44(4):535–543. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90263-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knight K. L., Becker R. S. Molecular basis of the allelic inheritance of rabbit immunoglobulin VH allotypes: implications for the generation of antibody diversity. Cell. 1990 Mar 23;60(6):963–970. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90344-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis S. M., Hesse J. E., Mizuuchi K., Gellert M. Novel strand exchanges in V(D)J recombination. Cell. 1988 Dec 23;55(6):1099–1107. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90254-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lieber M. R., Hesse J. E., Lewis S., Bosma G. C., Rosenberg N., Mizuuchi K., Bosma M. J., Gellert M. The defect in murine severe combined immune deficiency: joining of signal sequences but not coding segments in V(D)J recombination. Cell. 1988 Oct 7;55(1):7–16. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90004-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lieber M. R., Hesse J. E., Mizuuchi K., Gellert M. Developmental stage specificity of the lymphoid V(D)J recombination activity. Genes Dev. 1987 Oct;1(8):751–761. doi: 10.1101/gad.1.8.751. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin D., Huang R. Q., LeBien T., Van Ness B. Induced rearrangement of kappa genes in the BLIN-1 human pre-B cell line correlates with germline J-C kappa and V kappa transcription. J Exp Med. 1991 Mar 1;173(3):639–645. doi: 10.1084/jem.173.3.639. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mather E. L., Perry R. P. Methylation status and DNase I sensitivity of immunoglobulin genes: changes associated with rearrangement. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Aug;80(15):4689–4693. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.15.4689. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCormack W. T., Carlson L. M., Tjoelker L. W., Thompson C. B. Evolutionary comparison of the avian IgL locus: combinatorial diversity plays a role in the generation of the antibody repertoire in some avian species. Int Immunol. 1989;1(4):332–341. doi: 10.1093/intimm/1.4.332. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGhee J. D., Wood W. I., Dolan M., Engel J. D., Felsenfeld G. A 200 base pair region at the 5' end of the chicken adult beta-globin gene is accessible to nuclease digestion. Cell. 1981 Nov;27(1 Pt 2):45–55. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90359-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meehan R. R., Lewis J. D., McKay S., Kleiner E. L., Bird A. P. Identification of a mammalian protein that binds specifically to DNA containing methylated CpGs. Cell. 1989 Aug 11;58(3):499–507. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90430-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minie M. E., Koshland M. E. Accessibility of the promoter sequence in the J-chain gene is regulated by chromatin changes during B-cell differentiation. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Nov;6(11):4031–4038. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.11.4031. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Persiani D. M., Selsing E. DNase I sensitivity of immunoglobulin light chain genes in Abelson murine leukemia virus transformed pre-B cell lines. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Jul 11;17(13):5339–5348. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.13.5339. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynaud C. A., Mackay C. R., Müller R. G., Weill J. C. Somatic generation of diversity in a mammalian primary lymphoid organ: the sheep ileal Peyer's patches. Cell. 1991 Mar 8;64(5):995–1005. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90323-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saragosti S., Moyne G., Yaniv M. Absence of nucleosomes in a fraction of SV40 chromatin between the origin of replication and the region coding for the late leader RNA. Cell. 1980 May;20(1):65–73. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90235-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlissel M. S., Corcoran L. M., Baltimore D. Virus-transformed pre-B cells show ordered activation but not inactivation of immunoglobulin gene rearrangement and transcription. J Exp Med. 1991 Mar 1;173(3):711–720. doi: 10.1084/jem.173.3.711. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selker E. U. DNA methylation and chromatin structure: a view from below. Trends Biochem Sci. 1990 Mar;15(3):103–107. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(90)90193-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shamblott M. J., Litman G. W. Genomic organization and sequences of immunoglobulin light chain genes in a primitive vertebrate suggest coevolution of immunoglobulin gene organization. EMBO J. 1989 Dec 1;8(12):3733–3739. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08549.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon D., Grunert F., von Acken U., Döring H. P., Kröger H. DNA-methylase from regenerating rat liver: purification and characterisation. Nucleic Acids Res. 1978 Jun;5(6):2153–2167. doi: 10.1093/nar/5.6.2153. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singer J., Roberts-Ems J., Luthardt F. W., Riggs A. D. Methylation of DNA in mouse early embryos, teratocarcinoma cells and adult tissues of mouse and rabbit. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Dec 20;7(8):2369–2385. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.8.2369. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singer J., Roberts-Ems J., Riggs A. D. Methylation of mouse liver DNA studied by means of the restriction enzymes msp I and hpa II. Science. 1979 Mar 9;203(4384):1019–1021. doi: 10.1126/science.424726. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith S., Stillman B. Purification and characterization of CAF-I, a human cell factor required for chromatin assembly during DNA replication in vitro. Cell. 1989 Jul 14;58(1):15–25. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90398-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith S., Stillman B. Stepwise assembly of chromatin during DNA replication in vitro. EMBO J. 1991 Apr;10(4):971–980. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb08031.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spratt B. G., Hedge P. J., te Heesen S., Edelman A., Broome-Smith J. K. Kanamycin-resistant vectors that are analogues of plasmids pUC8, pUC9, pEMBL8 and pEMBL9. Gene. 1986;41(2-3):337–342. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(86)90117-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Storb U., Arp B. Methylation patterns of immunoglobulin genes in lymphoid cells: correlation of expression and differentiation with undermethylation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Nov;80(21):6642–6646. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.21.6642. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Storb U., Wilson R., Selsing E., Walfield A. Rearranged and germline immunoglobulin kappa genes: different states of DNase I sensitivity of constant kappa genes in immunocompetent and nonimmune cells. Biochemistry. 1981 Feb 17;20(4):990–996. doi: 10.1021/bi00507a053. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tazi J., Bird A. Alternative chromatin structure at CpG islands. Cell. 1990 Mar 23;60(6):909–920. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90339-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yancopoulos G. D., Blackwell T. K., Suh H., Hood L., Alt F. W. Introduced T cell receptor variable region gene segments recombine in pre-B cells: evidence that B and T cells use a common recombinase. Cell. 1986 Jan 31;44(2):251–259. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90759-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yancopoulos G. D., Nolan G. P., Pollock R., Prockop S., Li S. C., Herzenberg L. A., Alt F. W. A novel fluorescence-based system for assaying and separating live cells according to VDJ recombinase activity. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Apr;10(4):1697–1704. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.4.1697. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yisraeli J., Frank D., Razin A., Cedar H. Effect of in vitro DNA methylation on beta-globin gene expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jul;85(13):4638–4642. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.13.4638. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]






