Abstract
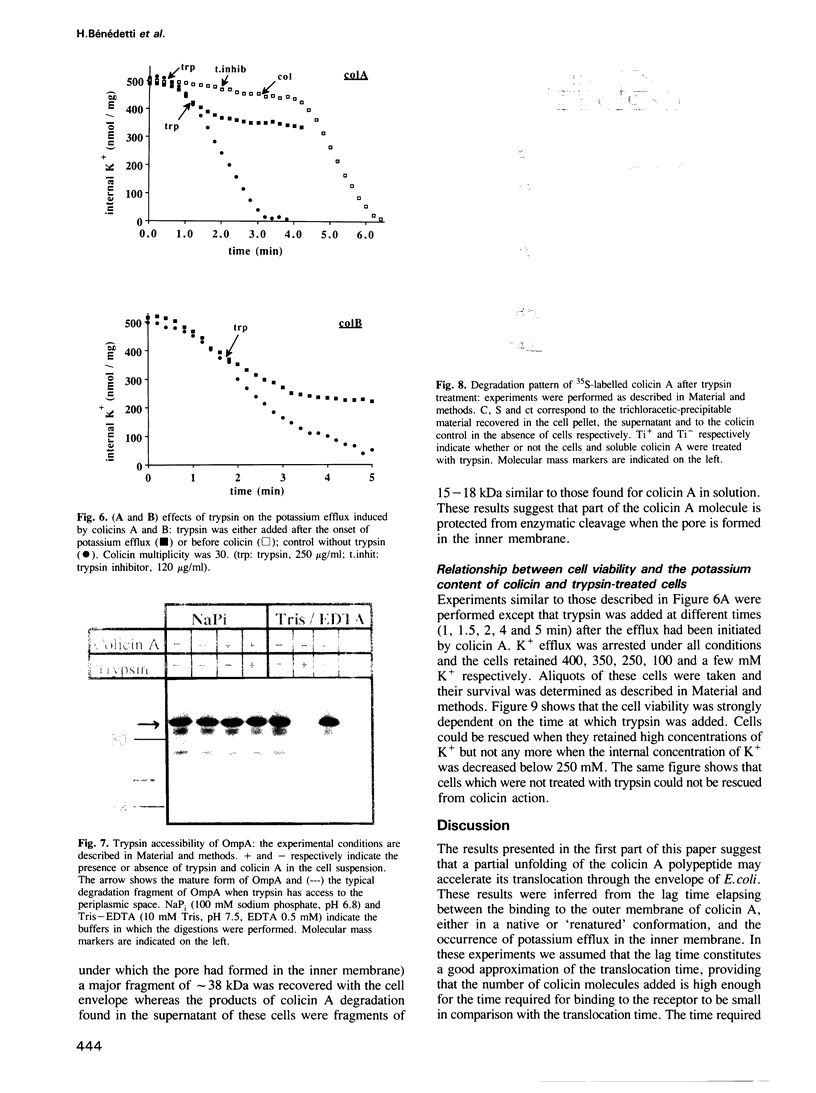
The addition of the pore forming colicin A to Escherichia coli cells results in an efflux of cytoplasmic potassium. This efflux is preceded by a lag time which is related to the time needed for the translocation of the toxin through the envelope. Denaturing the colicin A with urea, before adding it to the cells, did not affect the properties of the pore but decreased the lag time. After renaturation, the lag time was similar to that of the native colicin. This suggests that the unfolding of colicin A accelerates its translocation. The addition of trypsin, which has access neither to the periplasmic space nor to the cytoplasmic membrane, resulted in an immediate arrest of the potassium efflux induced by colicins A and B. The possibility that trypsin may act on a bacterial component required for colicin reception and/or translocation was ruled out. It is thus likely that the arrest of the efflux corresponds to a closing of the pores. This long distance effect of trypsin suggests that part of the polypeptide chain of the colicins may still be in contact with the external medium even when the pore has formed in the inner membrane.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baty D., Frenette M., Lloubès R., Geli V., Howard S. P., Pattus F., Lazdunski C. Functional domains of colicin A. Mol Microbiol. 1988 Nov;2(6):807–811. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1988.tb00092.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benedetti H., Frenette M., Baty D., Knibiehler M., Pattus F., Lazdunski C. Individual domains of colicins confer specificity in colicin uptake, in pore-properties and in immunity requirement. J Mol Biol. 1991 Feb 5;217(3):429–439. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(91)90747-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beppu T., Kawabata K., Arima K. Specific inhibition of cell division by colicin E 2 without degradation of deoxyribonucleic acid in a new colicin sensitivity mutant of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1972 May;110(2):485–493. doi: 10.1128/jb.110.2.485-493.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boulanger P., Letellier L. Characterization of ion channels involved in the penetration of phage T4 DNA into Escherichia coli cells. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jul 15;263(20):9767–9775. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourdineaud J. P., Boulanger P., Lazdunski C., Letellier L. In vivo properties of colicin A: channel activity is voltage dependent but translocation may be voltage independent. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Feb;87(3):1037–1041. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.3.1037. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cavard D., Lazdunski C. J. Purification and molecular properties of a new colicin. Eur J Biochem. 1979 Jun 1;96(3):519–524. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1979.tb13065.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cavard D., Sauve P., Heitz F., Pattus F., Martinez C., Dijkman R., Lazdunski C. Hydrodynamic properties of colicin A. Existence of a high-affinity lipid-binding site and oligomerization at acid pH. Eur J Biochem. 1988 Mar 1;172(2):507–512. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1988.tb13916.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cramer W. A., Dankert J. R., Uratani Y. The membrane channel-forming bacteriocidal protein, colicin El. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Mar 21;737(1):173–193. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(83)90016-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Creighton T. E. Protein folding. Biochem J. 1990 Aug 15;270(1):1–16. doi: 10.1042/bj2700001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dankert J., Hammond S. M., Cramer W. A. Reversal by trypsin of the inhibition of active transport by colicin E1. J Bacteriol. 1980 Aug;143(2):594–602. doi: 10.1128/jb.143.2.594-602.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies J. K., Reeves P. Genetics of resistance to colicins in Escherichia coli K-12: cross-resistance among colicins of group A. J Bacteriol. 1975 Jul;123(1):102–117. doi: 10.1128/jb.123.1.102-117.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies J. K., Reeves P. Genetics of resistance to colicins in Escherichia coli K-12: cross-resistance among colicins of group B. J Bacteriol. 1975 Jul;123(1):96–101. doi: 10.1128/jb.123.1.96-101.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eilers M., Hwang S., Schatz G. Unfolding and refolding of a purified precursor protein during import into isolated mitochondria. EMBO J. 1988 Apr;7(4):1139–1145. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02923.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feucht A., Schmid A., Benz R., Schwarz H., Heller K. J. Pore formation associated with the tail-tip protein pb2 of bacteriophage T5. J Biol Chem. 1990 Oct 25;265(30):18561–18567. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fields K. L., Luria S. E. Effects of colicins E1 and K on cellular metabolism. J Bacteriol. 1969 Jan;97(1):64–77. doi: 10.1128/jb.97.1.64-77.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fourel D., Hikita C., Bolla J. M., Mizushima S., Pagès J. M. Characterization of ompF domains involved in Escherichia coli K-12 sensitivity to colicins A and N. J Bacteriol. 1990 Jul;172(7):3675–3680. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.7.3675-3680.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gould J. M., Cramer W. A. Studies on the depolarization of the Escherichia coli cell membrane by colicin E1. J Biol Chem. 1977 Aug 10;252(15):5491–5497. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granger-Schnarr M., Lloubes R., de Murcia G., Schnarr M. Specific protein-DNA complexes: immunodetection of the protein component after gel electrophoresis and Western blotting. Anal Biochem. 1988 Oct;174(1):235–238. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(88)90540-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartl F. U., Pfanner N., Nicholson D. W., Neupert W. Mitochondrial protein import. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989 Jan 18;988(1):1–45. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(89)90002-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishidate K., Creeger E. S., Zrike J., Deb S., Glauner B., MacAlister T. J., Rothfield L. I. Isolation of differentiated membrane domains from Escherichia coli and Salmonella typhimurium, including a fraction containing attachment sites between the inner and outer membranes and the murein skeleton of the cell envelope. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jan 5;261(1):428–443. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konisky J. Colicins and other bacteriocins with established modes of action. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1982;36:125–144. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.36.100182.001013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazdunski C. J., Baty D., Geli V., Cavard D., Morlon J., Lloubes R., Howard S. P., Knibiehler M., Chartier M., Varenne S. The membrane channel-forming colicin A: synthesis, secretion, structure, action and immunity. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1988 Oct 11;947(3):445–464. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(88)90003-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levengood S. K., Beyer W. F., Jr, Webster R. E. TolA: a membrane protein involved in colicin uptake contains an extended helical region. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jul 15;88(14):5939–5943. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.14.5939. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levengood S. K., Webster R. E. Nucleotide sequences of the tolA and tolB genes and localization of their products, components of a multistep translocation system in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1989 Dec;171(12):6600–6609. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.12.6600-6609.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levisohn R., Konisky J., Nomura M. Interaction of colicins with bacterial cells. IV. Immunity breakdown studied with colicins Ia and Ib. J Bacteriol. 1968 Sep;96(3):811–821. doi: 10.1128/jb.96.3.811-821.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meury J., Robin A., Monnier-Champeix P. Turgor-controlled K+ fluxes and their pathways in Escherichia coli. Eur J Biochem. 1985 Sep 16;151(3):613–619. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1985.tb09148.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer D. I. Preprotein conformation: the year's major theme in translocation studies. Trends Biochem Sci. 1988 Dec;13(12):471–474. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(88)90233-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NOMURA M., NAKAMURA M. Reversibility of inhibition of nucleic acids and protein synthesis by colicin K. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1962 May 4;7:306–309. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(62)90196-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nose K., Mizuno D. Degradation of ribosomes in Escherichia coli cells treated with colicin E2. J Biochem. 1968 Jul;64(1):1–6. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a128853. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pattus F., Massotte D., Wilmsen H. U., Lakey J., Tsernoglou D., Tucker A., Parker M. W. Colicins: prokaryotic killer-pores. Experientia. 1990 Feb 15;46(2):180–192. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Randall L. L., Hardy S. J. Correlation of competence for export with lack of tertiary structure of the mature species: a study in vivo of maltose-binding protein in E. coli. Cell. 1986 Sep 12;46(6):921–928. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90074-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roos U., Harkness R. E., Braun V. Assembly of colicin genes from a few DNA fragments. Nucleotide sequence of colicin D. Mol Microbiol. 1989 Jul;3(7):891–902. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1989.tb00238.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saier M. H., Jr, Werner P. K., Müller M. Insertion of proteins into bacterial membranes: mechanism, characteristics, and comparisons with the eucaryotic process. Microbiol Rev. 1989 Sep;53(3):333–366. doi: 10.1128/mr.53.3.333-366.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schein S. J., Kagan B. L., Finkelstein A. Colicin K acts by forming voltage-dependent channels in phospholipid bilayer membranes. Nature. 1978 Nov 9;276(5684):159–163. doi: 10.1038/276159a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schleyer M., Neupert W. Transport of proteins into mitochondria: translocational intermediates spanning contact sites between outer and inner membranes. Cell. 1985 Nov;43(1):339–350. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90039-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schramm E., Mende J., Braun V., Kamp R. M. Nucleotide sequence of the colicin B activity gene cba: consensus pentapeptide among TonB-dependent colicins and receptors. J Bacteriol. 1987 Jul;169(7):3350–3357. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.7.3350-3357.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun T. P., Webster R. E. fii, a bacterial locus required for filamentous phage infection and its relation to colicin-tolerant tolA and tolB. J Bacteriol. 1986 Jan;165(1):107–115. doi: 10.1128/jb.165.1.107-115.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tommassen J., Lugtenberg B. Amino terminus of outer membrane PhoE protein: localization by use of a bla-phoE hybrid gene. J Bacteriol. 1984 Jan;157(1):327–329. doi: 10.1128/jb.157.1.327-329.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verner K., Schatz G. Protein translocation across membranes. Science. 1988 Sep 9;241(4871):1307–1313. doi: 10.1126/science.2842866. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]