Abstract
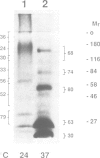
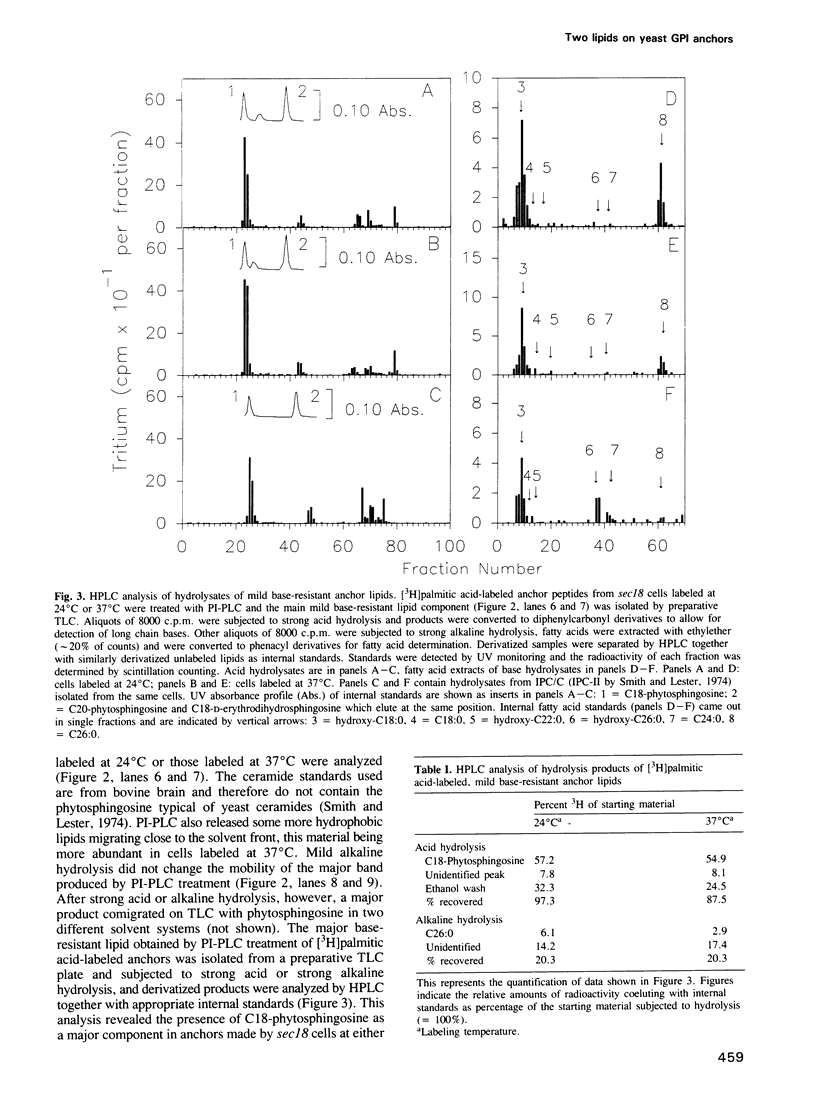
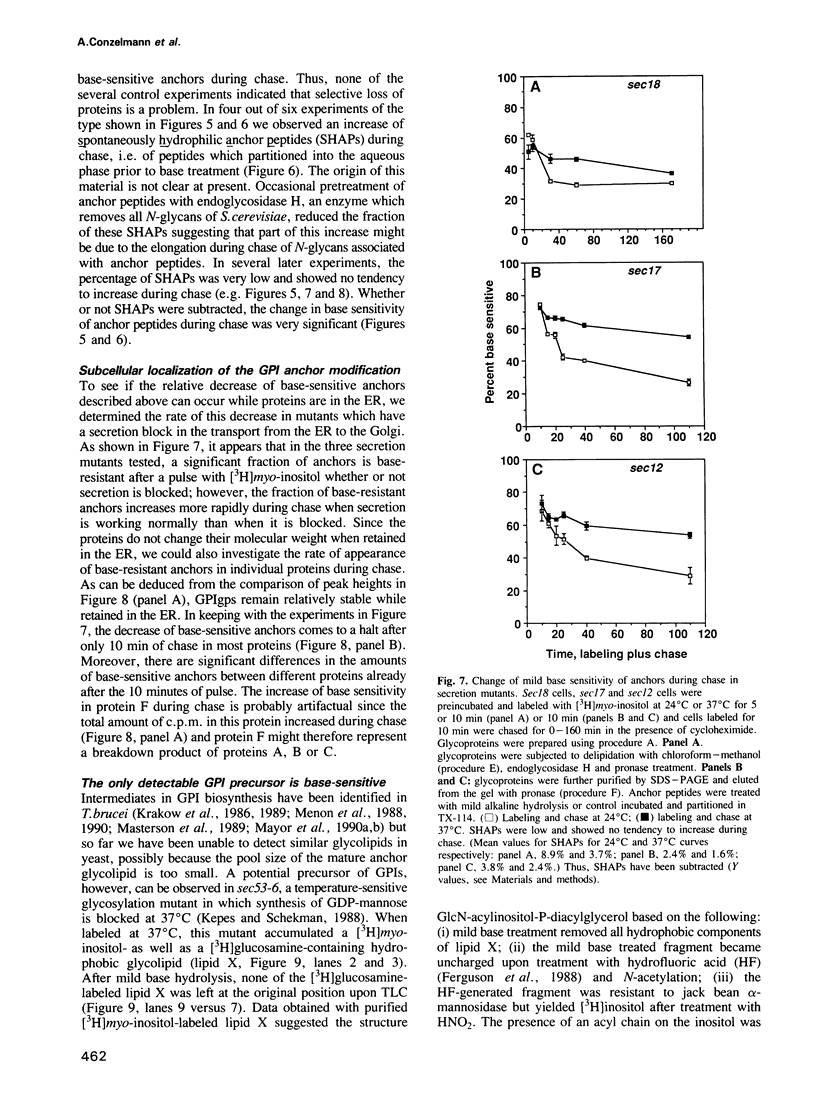
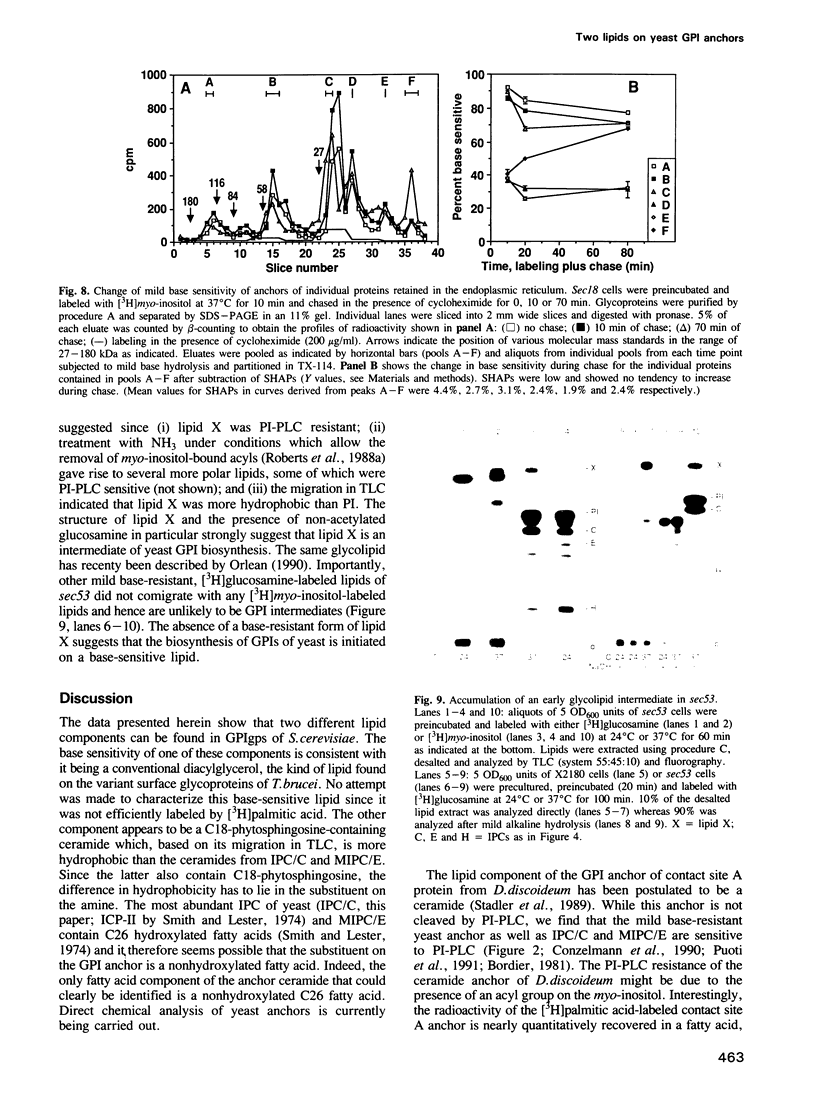
Numerous glycoproteins of Saccharomyces cerevisiae are anchored in the lipid bilayer by a glycophosphatidylinositol (GPI) anchor. Mild alkaline hydrolysis reveals that the lipid components of these anchors are heterogeneous in that both base-sensitive and base-resistant lipid moieties can be found on most proteins. The relative abundance of base-resistant lipid moieties is different for different proteins. Strong alkaline or acid hydrolysis of the mild base-resistant lipid component liberates C18-phytosphingosine indicating the presence of a ceramide. Two lines of evidence suggest that proteins are first attached to a base-sensitive GPI anchor, the lipid moiety of which subsequently gets exchanged for a base-resistant ceramide: (i) an early glycolipid intermediate of GPI biosynthesis only contains base-sensitive lipid moieties; (ii) after a pulse with [3H]myo-inositol the relative abundance of base-sensitive GPI anchors decreases significantly during chase. This decrease does not take place if GPI-anchored proteins are retained in the ER.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bangs J. D., Hereld D., Krakow J. L., Hart G. W., Englund P. T. Rapid processing of the carboxyl terminus of a trypanosome variant surface glycoprotein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 May;82(10):3207–3211. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.10.3207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Becker G. W., Lester R. L. Biosynthesis of phosphoinositol-containing sphingolipids from phosphatidylinositol by a membrane preparation from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Bacteriol. 1980 Jun;142(3):747–754. doi: 10.1128/jb.142.3.747-754.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhown A. S., Mole J. E., Hunter F., Bennett J. C. High-sensitivity sequence determination of proteins quantitatively recovered from sodium dodecyl sulfate gels using an improved electrodialysis procedure. Anal Biochem. 1980 Mar 15;103(1):184–190. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90254-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bleasdale J. E., Wallis P. Phosphatidylinositol-inositol exchange in a rabbit lung. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 May 22;664(2):428–440. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(81)90065-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bordier C. Phase separation of integral membrane proteins in Triton X-114 solution. J Biol Chem. 1981 Feb 25;256(4):1604–1607. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conzelmann A., Fankhauser C., Desponds C. Myoinositol gets incorporated into numerous membrane glycoproteins of Saccharomyces cerevisiae; incorporation is dependent on phosphomannomutase (sec53). EMBO J. 1990 Mar;9(3):653–661. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08157.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conzelmann A., Kornfeld S. Beta-linked N-acetylgalactosamine residues present at the nonreducing termini of O-linked oligosaccharides of a cloned murine cytotoxic T lymphocyte line are absent in a Vicia villosa lectin-resistant mutant cell line. J Biol Chem. 1984 Oct 25;259(20):12528–12535. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conzelmann A., Riezman H., Desponds C., Bron C. A major 125-kd membrane glycoprotein of Saccharomyces cerevisiae is attached to the lipid bilayer through an inositol-containing phospholipid. EMBO J. 1988 Jul;7(7):2233–2240. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03063.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conzelmann A., Spiazzi A., Bron C. Glycolipid anchors are attached to Thy-1 glycoprotein rapidly after translation. Biochem J. 1987 Sep 15;246(3):605–610. doi: 10.1042/bj2460605. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cross G. A. Glycolipid anchoring of plasma membrane proteins. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1990;6:1–39. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.06.110190.000245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickson R. C., Wells G. B., Schmidt A., Lester R. L. Isolation of mutant Saccharomyces cerevisiae strains that survive without sphingolipids. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 May;10(5):2176–2181. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.5.2176. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doering T. L., Masterson W. J., Hart G. W., Englund P. T. Biosynthesis of glycosyl phosphatidylinositol membrane anchors. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jan 15;265(2):611–614. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esmon B., Novick P., Schekman R. Compartmentalized assembly of oligosaccharides on exported glycoproteins in yeast. Cell. 1981 Aug;25(2):451–460. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90063-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferguson M. A., Duszenko M., Lamont G. S., Overath P., Cross G. A. Biosynthesis of Trypanosoma brucei variant surface glycoproteins. N-glycosylation and addition of a phosphatidylinositol membrane anchor. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jan 5;261(1):356–362. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferguson M. A., Homans S. W., Dwek R. A., Rademacher T. W. Glycosyl-phosphatidylinositol moiety that anchors Trypanosoma brucei variant surface glycoprotein to the membrane. Science. 1988 Feb 12;239(4841 Pt 1):753–759. doi: 10.1126/science.3340856. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferguson M. A., Low M. G., Cross G. A. Glycosyl-sn-1,2-dimyristylphosphatidylinositol is covalently linked to Trypanosoma brucei variant surface glycoprotein. J Biol Chem. 1985 Nov 25;260(27):14547–14555. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferguson M. A., Williams A. F. Cell-surface anchoring of proteins via glycosyl-phosphatidylinositol structures. Annu Rev Biochem. 1988;57:285–320. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.57.070188.001441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Field M. C., Menon A. K., Cross G. A. Developmental variation of glycosylphosphatidylinositol membrane anchors in Trypanosoma brucei. Identification of a candidate biosynthetic precursor of the glycosylphosphatidylinositol anchor of the major procyclic stage surface glycoprotein. J Biol Chem. 1991 May 5;266(13):8392–8400. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gopal P. K., Ballou C. E. Regulation of the protein glycosylation pathway in yeast: structural control of N-linked oligosaccharide elongation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(24):8824–8828. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.24.8824. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Homans S. W., Ferguson M. A., Dwek R. A., Rademacher T. W., Anand R., Williams A. F. Complete structure of the glycosyl phosphatidylinositol membrane anchor of rat brain Thy-1 glycoprotein. Nature. 1988 May 19;333(6170):269–272. doi: 10.1038/333269a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kepes F., Schekman R. The yeast SEC53 gene encodes phosphomannomutase. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jul 5;263(19):9155–9161. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krakow J. L., Doering T. L., Masterson W. J., Hart G. W., Englund P. T. A glycolipid from Trypanosoma brucei related to the variant surface glycoprotein membrane anchor. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1989 Oct;36(3):263–270. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(89)90174-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krakow J. L., Hereld D., Bangs J. D., Hart G. W., Englund P. T. Identification of a glycolipid precursor of the Trypanosoma brucei variant surface glycoprotein. J Biol Chem. 1986 Sep 15;261(26):12147–12153. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Low M. G., Saltiel A. R. Structural and functional roles of glycosyl-phosphatidylinositol in membranes. Science. 1988 Jan 15;239(4837):268–275. doi: 10.1126/science.3276003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luhrs C. A., Slomiany B. L. A human membrane-associated folate binding protein is anchored by a glycosyl-phosphatidylinositol tail. J Biol Chem. 1989 Dec 25;264(36):21446–21449. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masterson W. J., Doering T. L., Hart G. W., Englund P. T. A novel pathway for glycan assembly: biosynthesis of the glycosyl-phosphatidylinositol anchor of the trypanosome variant surface glycoprotein. Cell. 1989 Mar 10;56(5):793–800. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90684-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masterson W. J., Raper J., Doering T. L., Hart G. W., Englund P. T. Fatty acid remodeling: a novel reaction sequence in the biosynthesis of trypanosome glycosyl phosphatidylinositol membrane anchors. Cell. 1990 Jul 13;62(1):73–80. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90241-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayor S., Menon A. K., Cross G. A., Ferguson M. A., Dwek R. A., Rademacher T. W. Glycolipid precursors for the membrane anchor of Trypanosoma brucei variant surface glycoproteins. I. Can structure of the phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase C sensitive and resistant glycolipids. J Biol Chem. 1990 Apr 15;265(11):6164–6173. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayor S., Menon A. K., Cross G. A. Glycolipid precursors for the membrane anchor of Trypanosoma brucei variant surface glycoproteins. II. Lipid structures of phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase C sensitive and resistant glycolipids. J Biol Chem. 1990 Apr 15;265(11):6174–6181. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Menon A. K., Mayor S., Ferguson M. A., Duszenko M., Cross G. A. Candidate glycophospholipid precursor for the glycosylphosphatidylinositol membrane anchor of Trypanosoma brucei variant surface glycoproteins. J Biol Chem. 1988 Feb 5;263(4):1970–1977. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Menon A. K., Schwarz R. T., Mayor S., Cross G. A. Cell-free synthesis of glycosyl-phosphatidylinositol precursors for the glycolipid membrane anchor of Trypanosoma brucei variant surface glycoproteins. Structural characterization of putative biosynthetic intermediates. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jun 5;265(16):9033–9042. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novick P., Ferro S., Schekman R. Order of events in the yeast secretory pathway. Cell. 1981 Aug;25(2):461–469. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90064-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novick P., Field C., Schekman R. Identification of 23 complementation groups required for post-translational events in the yeast secretory pathway. Cell. 1980 Aug;21(1):205–215. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90128-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orlean P. Dolichol phosphate mannose synthase is required in vivo for glycosyl phosphatidylinositol membrane anchoring, O mannosylation, and N glycosylation of protein in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Nov;10(11):5796–5805. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.11.5796. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owen M. J., Kissonerghis A. M., Lodish H. F., Crumpton M. J. Biosynthesis and maturation of HLA-DR antigens in vivo. J Biol Chem. 1981 Sep 10;256(17):8987–8993. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Puoti A., Desponds C., Conzelmann A. Biosynthesis of mannosylinositolphosphoceramide in Saccharomyces cerevisiae is dependent on genes controlling the flow of secretory vesicles from the endoplasmic reticulum to the Golgi. J Cell Biol. 1991 May;113(3):515–525. doi: 10.1083/jcb.113.3.515. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts W. L., Kim B. H., Rosenberry T. L. Differences in the glycolipid membrane anchors of bovine and human erythrocyte acetylcholinesterases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Nov;84(22):7817–7821. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.22.7817. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts W. L., Myher J. J., Kuksis A., Low M. G., Rosenberry T. L. Lipid analysis of the glycoinositol phospholipid membrane anchor of human erythrocyte acetylcholinesterase. Palmitoylation of inositol results in resistance to phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase C. J Biol Chem. 1988 Dec 15;263(35):18766–18775. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts W. L., Santikarn S., Reinhold V. N., Rosenberry T. L. Structural characterization of the glycoinositol phospholipid membrane anchor of human erythrocyte acetylcholinesterase by fast atom bombardment mass spectrometry. J Biol Chem. 1988 Dec 15;263(35):18776–18784. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider P., Ferguson M. A., McConville M. J., Mehlert A., Homans S. W., Bordier C. Structure of the glycosyl-phosphatidylinositol membrane anchor of the Leishmania major promastigote surface protease. J Biol Chem. 1990 Oct 5;265(28):16955–16964. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith S. W., Lester R. L. Inositol phosphorylceramide, a novel substance and the chief member of a major group of yeast sphingolipids containing a single inositol phosphate. J Biol Chem. 1974 Jun 10;249(11):3395–3405. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stadler J., Keenan T. W., Bauer G., Gerisch G. The contact site A glycoprotein of Dictyostelium discoideum carries a phospholipid anchor of a novel type. EMBO J. 1989 Feb;8(2):371–377. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03387.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steiner S., Smith S., Waechter C. J., Lester R. L. Isolation and partial characterization of a major inositol-containing lipid in baker's yeast, mannosyl-diinositol, diphosphoryl-ceramide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Nov;64(3):1042–1048. doi: 10.1073/pnas.64.3.1042. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takenawa T., Egawa K. Phosphatidyl inositol: myo-inositol exchange enzyme from rat liver: partial purification and characterization. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1980 Jul;202(2):601–607. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(80)90467-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas J. R., Dwek R. A., Rademacher T. W. Structure, biosynthesis, and function of glycosylphosphatidylinositols. Biochemistry. 1990 Jun 12;29(23):5413–5422. doi: 10.1021/bi00475a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai P. K., Frevert J., Ballou C. E. Carbohydrate structure of Saccharomyces cerevisiae mnn9 mannoprotein. J Biol Chem. 1984 Mar 25;259(6):3805–3811. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wickerham L. J. A Critical Evaluation of the Nitrogen Assimilation Tests Commonly Used in the Classification of Yeasts. J Bacteriol. 1946 Sep;52(3):293–301. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]