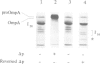Abstract
The SecY/E protein of Escherichia coli was coreconstituted with the proton pump bacteriorhodopsin and cytochrome c oxidase yielding proteoliposomes capable of sustaining a protonmotive force (delta p) of defined polarity and composition. Proteoliposomes support the ATP- and SecA-dependent translocation of proOmpA which is stimulated by a delta p, inside acid and positive. delta p of opposite polarity, inside alkaline and negative, suppresses translocation while SecA-mediated ATP hydrolysis continues unabated. delta psi and delta pH are equally effective in promoting or inhibiting translocation. Membrane-spanning translocation intermediates move backwards in the presence of a reversed delta p. These results support a model [Schiebel, E., Driessen, A.J.M., Hartl, F.-U. and Wickner, W. (1991) Cell, 64, 927-939] in which the delta p defines the direction of translocation after ATP hydrolysis has released proOmpA from its association with SecA. The polarity effect of the delta p challenges models involving delta p-dependent membrane destabilization and provides further evidence for a role of the delta p as driving force in precursor protein translocation.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akimaru J., Matsuyama S., Tokuda H., Mizushima S. Reconstitution of a protein translocation system containing purified SecY, SecE, and SecA from Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Aug 1;88(15):6545–6549. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.15.6545. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Akita M., Sasaki S., Matsuyama S., Mizushima S. SecA interacts with secretory proteins by recognizing the positive charge at the amino terminus of the signal peptide in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1990 May 15;265(14):8164–8169. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bakker E. P., Randall L. L. The requirement for energy during export of beta-lactamase in Escherichia coli is fulfilled by the total protonmotive force. EMBO J. 1984 Apr;3(4):895–900. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01902.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bieker K. L., Silhavy T. J. PrlA (SecY) and PrlG (SecE) interact directly and function sequentially during protein translocation in E. coli. Cell. 1990 Jun 1;61(5):833–842. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90193-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brundage L., Hendrick J. P., Schiebel E., Driessen A. J., Wickner W. The purified E. coli integral membrane protein SecY/E is sufficient for reconstitution of SecA-dependent precursor protein translocation. Cell. 1990 Aug 24;62(4):649–657. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90111-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang C. N., Blobel G., Model P. Detection of prokaryotic signal peptidase in an Escherichia coli membrane fraction: endoproteolytic cleavage of nascent f1 pre-coat protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jan;75(1):361–365. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.1.361. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen L. L., Tai P. C. Roles of H+-ATPase and proton motive force in ATP-dependent protein translocation in vitro. J Bacteriol. 1986 Jul;167(1):389–392. doi: 10.1128/jb.167.1.389-392.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen L., Tai P. C. ATP is essential for protein translocation into Escherichia coli membrane vesicles. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jul;82(13):4384–4388. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.13.4384. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen L., Tai P. C. Effects of nucleotides on ATP-dependent protein translocation into Escherichia coli membrane vesicles. J Bacteriol. 1986 Nov;168(2):828–832. doi: 10.1128/jb.168.2.828-832.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crooke E., Guthrie B., Lecker S., Lill R., Wickner W. ProOmpA is stabilized for membrane translocation by either purified E. coli trigger factor or canine signal recognition particle. Cell. 1988 Sep 23;54(7):1003–1011. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90115-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cunningham K., Lill R., Crooke E., Rice M., Moore K., Wickner W., Oliver D. SecA protein, a peripheral protein of the Escherichia coli plasma membrane, is essential for the functional binding and translocation of proOmpA. EMBO J. 1989 Mar;8(3):955–959. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03457.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cunningham K., Wickner W. Specific recognition of the leader region of precursor proteins is required for the activation of translocation ATPase of Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Nov;86(22):8630–8634. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.22.8630. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danon A., Stoeckenius W. Photophosphorylation in Halobacterium halobium. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Apr;71(4):1234–1238. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.4.1234. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Driessen A. J., Wickner W. Proton transfer is rate-limiting for translocation of precursor proteins by the Escherichia coli translocase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Mar 15;88(6):2471–2475. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.6.2471. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Driessen A. J., de Vrij W., Konings W. N. Incorporation of beef heart cytochrome c oxidase as a proton-motive force-generating mechanism in bacterial membrane vesicles. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Nov;82(22):7555–7559. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.22.7555. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elish M. E., Pierce J. R., Earhart C. F. Biochemical analysis of spontaneous fepA mutants of Escherichia coli. J Gen Microbiol. 1988 May;134(5):1355–1364. doi: 10.1099/00221287-134-5-1355. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fandl J. P., Cabelli R., Oliver D., Tai P. C. SecA suppresses the temperature-sensitive SecY24 defect in protein translocation in Escherichia coli membrane vesicles. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(23):8953–8957. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.23.8953. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freudl R., Schwarz H., Degen M., Henning U. The signal sequence suffices to direct export of outer membrane protein OmpA of Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1987 Jan;169(1):66–71. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.1.66-71.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freudl R., Schwarz H., Klose M., Movva N. R., Henning U. The nature of information, required for export and sorting, present within the outer membrane protein OmpA of Escherichia coli K-12. EMBO J. 1985 Dec 16;4(13A):3593–3598. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04122.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freudl R., Schwarz H., Stierhof Y. D., Gamon K., Hindennach I., Henning U. An outer membrane protein (OmpA) of Escherichia coli K-12 undergoes a conformational change during export. J Biol Chem. 1986 Aug 25;261(24):11355–11361. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardel C., Johnson K., Jacq A., Beckwith J. The secD locus of E.coli codes for two membrane proteins required for protein export. EMBO J. 1990 Oct;9(10):3209–3216. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07519.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geller B. L. Electrochemical potential releases a membrane-bound secretion intermediate of maltose-binding protein in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1990 Sep;172(9):4870–4876. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.9.4870-4876.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geller B. L., Green H. M. Translocation of pro-OmpA across inner membrane vesicles of Escherichia coli occurs in two consecutive energetically distinct steps. J Biol Chem. 1989 Oct 5;264(28):16465–16469. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geller B. L., Movva N. R., Wickner W. Both ATP and the electrochemical potential are required for optimal assembly of pro-OmpA into Escherichia coli inner membrane vesicles. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(12):4219–4222. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.12.4219. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartl F. U., Lecker S., Schiebel E., Hendrick J. P., Wickner W. The binding cascade of SecB to SecA to SecY/E mediates preprotein targeting to the E. coli plasma membrane. Cell. 1990 Oct 19;63(2):269–279. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90160-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito K. Identification of the secY (prlA) gene product involved in protein export in Escherichia coli. Mol Gen Genet. 1984;197(2):204–208. doi: 10.1007/BF00330964. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klionsky D. J., Brusilow W. S., Simoni R. D. In vivo evidence for the role of the epsilon subunit as an inhibitor of the proton-translocating ATPase of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1984 Dec;160(3):1055–1060. doi: 10.1128/jb.160.3.1055-1060.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koronakis V., Hughes C., Koronakis E. Energetically distinct early and late stages of HlyB/HlyD-dependent secretion across both Escherichia coli membranes. EMBO J. 1991 Nov;10(11):3263–3272. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb04890.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumamoto C. A. Molecular chaperones and protein translocation across the Escherichia coli inner membrane. Mol Microbiol. 1991 Jan;5(1):19–22. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1991.tb01821.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kusters R., Dowhan W., de Kruijff B. Negatively charged phospholipids restore prePhoE translocation across phosphatidylglycerol-depleted Escherichia coli inner membranes. J Biol Chem. 1991 May 15;266(14):8659–8662. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lecker S., Lill R., Ziegelhoffer T., Georgopoulos C., Bassford P. J., Jr, Kumamoto C. A., Wickner W. Three pure chaperone proteins of Escherichia coli--SecB, trigger factor and GroEL--form soluble complexes with precursor proteins in vitro. EMBO J. 1989 Sep;8(9):2703–2709. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08411.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lill R., Cunningham K., Brundage L. A., Ito K., Oliver D., Wickner W. SecA protein hydrolyzes ATP and is an essential component of the protein translocation ATPase of Escherichia coli. EMBO J. 1989 Mar;8(3):961–966. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03458.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lill R., Dowhan W., Wickner W. The ATPase activity of SecA is regulated by acidic phospholipids, SecY, and the leader and mature domains of precursor proteins. Cell. 1990 Jan 26;60(2):271–280. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90742-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lu H. M., Yamada H., Mizushima S. A proline residue near the amino terminus of the mature domain of secretory proteins lowers the level of the proton motive force required for translocation. J Biol Chem. 1991 May 25;266(15):9977–9982. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oliver D. B., Cabelli R. J., Jarosik G. P. SecA protein: autoregulated initiator of secretory precursor protein translocation across the E. coli plasma membrane. J Bioenerg Biomembr. 1990 Jun;22(3):311–336. doi: 10.1007/BF00763170. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed K. E., Cronan J. E., Jr Escherichia coli exports previously folded and biotinated protein domains. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jun 25;266(18):11425–11428. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rouser G., Fkeischer S., Yamamoto A. Two dimensional then layer chromatographic separation of polar lipids and determination of phospholipids by phosphorus analysis of spots. Lipids. 1970 May;5(5):494–496. doi: 10.1007/BF02531316. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schatz P. J., Beckwith J. Genetic analysis of protein export in Escherichia coli. Annu Rev Genet. 1990;24:215–248. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.24.120190.001243. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schatz P. J., Riggs P. D., Jacq A., Fath M. J., Beckwith J. The secE gene encodes an integral membrane protein required for protein export in Escherichia coli. Genes Dev. 1989 Jul;3(7):1035–1044. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.7.1035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiebel E., Driessen A. J., Hartl F. U., Wickner W. Delta mu H+ and ATP function at different steps of the catalytic cycle of preprotein translocase. Cell. 1991 Mar 8;64(5):927–939. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90317-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinkai A., Mei L. H., Tokuda H., Mizushima S. The conformation of SecA, as revealed by its protease sensitivity, is altered upon interaction with ATP, presecretory proteins, everted membrane vesicles, and phospholipids. J Biol Chem. 1991 Mar 25;266(9):5827–5833. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shiozuka K., Tani K., Mizushima S., Tokuda H. The proton motive force lowers the level of ATP required for the in vitro translocation of a secretory protein in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1990 Nov 5;265(31):18843–18847. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tani K., Shiozuka K., Tokuda H., Mizushima S. In vitro analysis of the process of translocation of OmpA across the Escherichia coli cytoplasmic membrane. A translocation intermediate accumulates transiently in the absence of the proton motive force. J Biol Chem. 1989 Nov 5;264(31):18582–18588. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tani K., Tokuda H., Mizushima S. Translocation of ProOmpA possessing an intramolecular disulfide bridge into membrane vesicles of Escherichia coli. Effect of membrane energization. J Biol Chem. 1990 Oct 5;265(28):17341–17347. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tokuda H., Akimaru J., Matsuyama S., Nishiyama K., Mizushima S. Purification of SecE and reconstitution of SecE-dependent protein translocation activity. FEBS Lett. 1991 Feb 25;279(2):233–236. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(91)80156-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss J. B., Ray P. H., Bassford P. J., Jr Purified secB protein of Escherichia coli retards folding and promotes membrane translocation of the maltose-binding protein in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(23):8978–8982. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.23.8978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wickner W., Driessen A. J., Hartl F. U. The enzymology of protein translocation across the Escherichia coli plasma membrane. Annu Rev Biochem. 1991;60:101–124. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.60.070191.000533. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamada H., Matsuyama S., Tokuda H., Mizushima S. A high concentration of SecA allows proton motive force-independent translocation of a model secretory protein into Escherichia coli membrane vesicles. J Biol Chem. 1989 Nov 5;264(31):18577–18581. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamada H., Tokuda H., Mizushima S. Proton motive force-dependent and -independent protein translocation revealed by an efficient in vitro assay system of Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jan 25;264(3):1723–1728. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu C., Yu L., King T. E. Studies on cytochrome oxidase. Interactions of the cytochrome oxidase protein with phospholipids and cytochrome c. J Biol Chem. 1975 Feb 25;250(4):1383–1392. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Vrij W., Driessen A. J., Hellingwerf K. J., Konings W. N. Measurements of the proton motive force generated by cytochrome c oxidase from Bacillus subtilis in proteoliposomes and membrane vesicles. Eur J Biochem. 1986 Apr 15;156(2):431–440. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1986.tb09600.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Vrije T., de Swart R. L., Dowhan W., Tommassen J., de Kruijff B. Phosphatidylglycerol is involved in protein translocation across Escherichia coli inner membranes. Nature. 1988 Jul 14;334(6178):173–175. doi: 10.1038/334173a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Heijne G. A sequence correlation between oppositely charged residues in secreted proteins. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1980 Mar 13;93(1):82–86. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(80)80248-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]