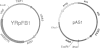Abstract
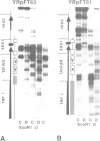
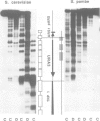
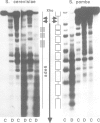
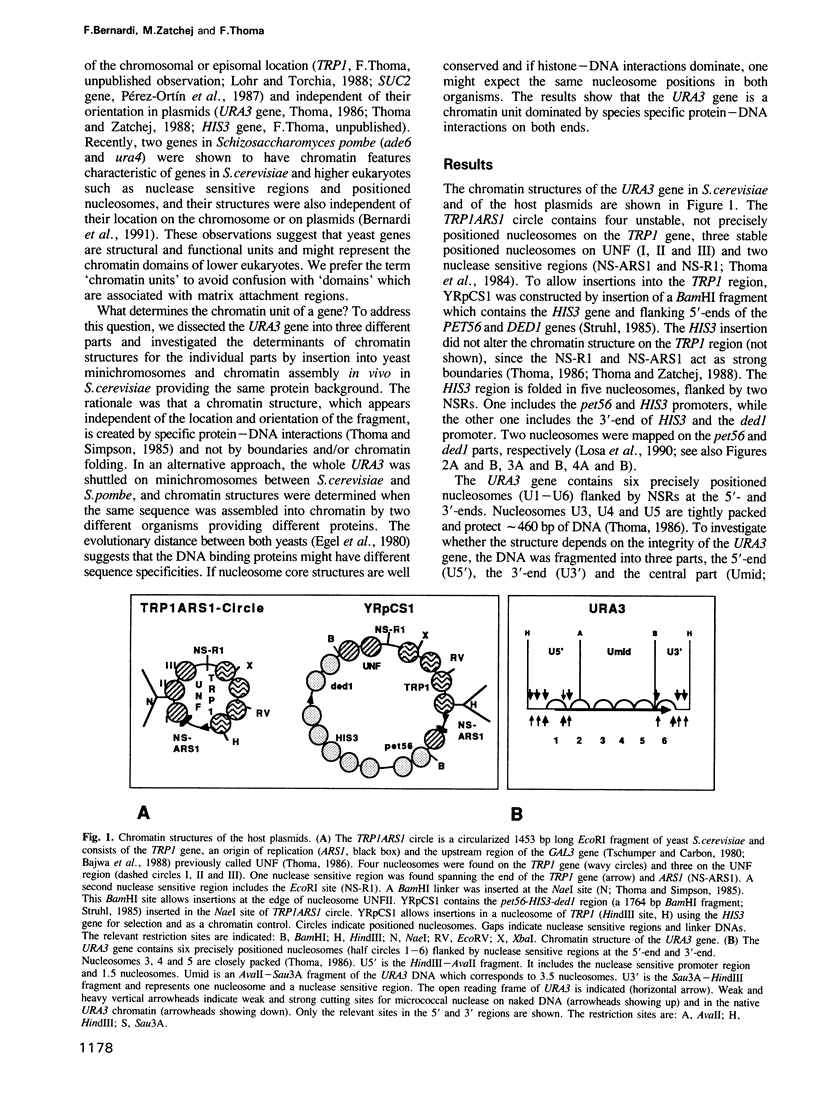
Yeast genes, such as URA3, are chromatin units characterized by positioned nucleosomes and flanking nuclease sensitive regions (NSRs). To investigate the structural determinants at the chromatin level in vivo, the URA3 gene was dissected into three parts (U5', Umid and U3'), and the chromatin structures of the individual parts were analysed after insertion into minichromosomes and after chromatin assembly in vivo in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. While nucleosome positions were altered on Umid, the 5'-end and the 3'-end of URA3 maintained their native structures (a positioned nucleosome and a NSR each) independent of the site or orientation of insertion. This suggests that the chromatin unit of the native URA3 gene is dominated by strong protein boundaries at the 5'- and 3'-ends. In an alternative approach, we investigated whether nucleosome positions or NSRs were maintained when the whole URA3 gene was placed on a shuttle vector and assembled into chromatin by Schizosaccharomyces pombe providing different proteins, but the same nucleosomal spacing. In a complementary exchange experiment, the ade6 gene of S.pombe was shuttled to S.cerevisiae. In spite of a general conservation of histone proteins and nucleosome core structures, neither nucleosome positions nor NSRs were maintained in the heterologous background. The results demonstrate that chromatin structures are species specific and that the structural boundaries of yeast genes may be dominated by strong species specific protein-DNA interactions.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bajwa W., Torchia T. E., Hopper J. E. Yeast regulatory gene GAL3: carbon regulation; UASGal elements in common with GAL1, GAL2, GAL7, GAL10, GAL80, and MEL1; encoded protein strikingly similar to yeast and Escherichia coli galactokinases. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Aug;8(8):3439–3447. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.8.3439. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernardi F., Koller T., Thoma F. The ade6 gene of the fission yeast Schizosaccharomyces pombe has the same chromatin structure in the chromosome and in plasmids. Yeast. 1991 Aug-Sep;7(6):547–558. doi: 10.1002/yea.320070603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choe J., Schuster T., Grunstein M. Organization, primary structure, and evolution of histone H2A and H2B genes of the fission yeast Schizosaccharomyces pombe. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Nov;5(11):3261–3269. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.11.3261. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Egel R., Kohli J., Thuriaux P., Wolf K. Genetics of the fission yeast Schizosaccharomyces pombe. Annu Rev Genet. 1980;14:77–108. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.14.120180.000453. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fedor M. J., Kornberg R. D. Upstream activation sequence-dependent alteration of chromatin structure and transcription activation of the yeast GAL1-GAL10 genes. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Apr;9(4):1721–1732. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.4.1721. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fedor M. J., Lue N. F., Kornberg R. D. Statistical positioning of nucleosomes by specific protein-binding to an upstream activating sequence in yeast. J Mol Biol. 1988 Nov 5;204(1):109–127. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90603-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grimm C., Kohli J., Murray J., Maundrell K. Genetic engineering of Schizosaccharomyces pombe: a system for gene disruption and replacement using the ura4 gene as a selectable marker. Mol Gen Genet. 1988 Dec;215(1):81–86. doi: 10.1007/BF00331307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross D. S., Garrard W. T. Nuclease hypersensitive sites in chromatin. Annu Rev Biochem. 1988;57:159–197. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.57.070188.001111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grunstein M. Histone function in transcription. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1990;6:643–678. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.06.110190.003235. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito H., Fukuda Y., Murata K., Kimura A. Transformation of intact yeast cells treated with alkali cations. J Bacteriol. 1983 Jan;153(1):163–168. doi: 10.1128/jb.153.1.163-168.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornberg R. D., Stryer L. Statistical distributions of nucleosomes: nonrandom locations by a stochastic mechanism. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Jul 25;16(14A):6677–6690. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.14.6677. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee M. S., Garrard W. T. Transcription-induced nucleosome 'splitting': an underlying structure for DNase I sensitive chromatin. EMBO J. 1991 Mar;10(3):607–615. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07988.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lohr D., Torchia T. Structure of the chromosomal copy of yeast ARS1. Biochemistry. 1988 May 31;27(11):3961–3965. doi: 10.1021/bi00411a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Losa R., Omari S., Thoma F. Poly(dA).poly(dT) rich sequences are not sufficient to exclude nucleosome formation in a constitutive yeast promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Jun 25;18(12):3495–3502. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.12.3495. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Losson R., Fuchs R. P., Lacroute F. Yeast promoters URA1 and URA3. Examples of positive control. J Mol Biol. 1985 Sep 5;185(1):65–81. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90183-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Losson R., Lacroute F. Plasmids carrying the yeast OMP decarboxylase structural and regulatory genes: transcription regulation in a foreign environment. Cell. 1983 Feb;32(2):371–377. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90456-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsumoto S., Yanagida M. Histone gene organization of fission yeast: a common upstream sequence. EMBO J. 1985 Dec 16;4(13A):3531–3538. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04113.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maundrell K., Hutchison A., Shall S. Sequence analysis of ARS elements in fission yeast. EMBO J. 1988 Jul;7(7):2203–2209. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03059.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morse R. H., Pederson D. S., Dean A., Simpson R. T. Yeast nucleosomes allow thermal untwisting of DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Dec 23;15(24):10311–10330. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.24.10311. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pederson D. S., Thoma F., Simpson R. T. Core particle, fiber, and transcriptionally active chromatin structure. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1986;2:117–147. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.02.110186.001001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piñeiro M., Puerta C., Palacián E. Yeast nucleosomal particles: structural and transcriptional properties. Biochemistry. 1991 Jun 11;30(23):5805–5810. doi: 10.1021/bi00237a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pérez-Ortin J. E., Matallana E., Franco L. Chromatin structure of yeast genes. Yeast. 1989 Jul-Aug;5(4):219–238. doi: 10.1002/yea.320050404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pérez-Ortín J. E., Estruch F., Matallana E., Franco L. Fine analysis of the chromatin structure of the yeast SUC2 gene and of its changes upon derepression. Comparison between the chromosomal and plasmid-inserted genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Sep 11;15(17):6937–6956. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.17.6937. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richmond T. J., Finch J. T., Rushton B., Rhodes D., Klug A. Structure of the nucleosome core particle at 7 A resolution. Nature. 1984 Oct 11;311(5986):532–537. doi: 10.1038/311532a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose M., Botstein D. Structure and function of the yeast URA3 gene. Differentially regulated expression of hybrid beta-galactosidase from overlapping coding sequences in yeast. J Mol Biol. 1983 Nov 15;170(4):883–904. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80193-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth S. Y., Dean A., Simpson R. T. Yeast alpha 2 repressor positions nucleosomes in TRP1/ARS1 chromatin. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 May;10(5):2247–2260. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.5.2247. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roy A., Exinger F., Losson R. cis- and trans-acting regulatory elements of the yeast URA3 promoter. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Oct;10(10):5257–5270. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.10.5257. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell P. R. Evolutionary divergence of the mRNA transcription initiation mechanism in yeast. Nature. 1983 Jan 13;301(5896):167–169. doi: 10.1038/301167a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Satchwell S. C., Drew H. R., Travers A. A. Sequence periodicities in chicken nucleosome core DNA. J Mol Biol. 1986 Oct 20;191(4):659–675. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90452-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shrader T. E., Crothers D. M. Artificial nucleosome positioning sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Oct;86(19):7418–7422. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.19.7418. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson R. T. Nucleosome positioning can affect the function of a cis-acting DNA element in vivo. Nature. 1990 Jan 25;343(6256):387–389. doi: 10.1038/343387a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson R. T. Nucleosome positioning: occurrence, mechanisms, and functional consequences. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1991;40:143–184. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6603(08)60841-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snyder M., Sapolsky R. J., Davis R. W. Transcription interferes with elements important for chromosome maintenance in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 May;8(5):2184–2194. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.5.2184. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stief A., Winter D. M., Strätling W. H., Sippel A. E. A nuclear DNA attachment element mediates elevated and position-independent gene activity. Nature. 1989 Sep 28;341(6240):343–345. doi: 10.1038/341343a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Straka C., Hörz W. A functional role for nucleosomes in the repression of a yeast promoter. EMBO J. 1991 Feb;10(2):361–368. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07957.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Struhl K. Nucleotide sequence and transcriptional mapping of the yeast pet56-his3-ded1 gene region. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Dec 9;13(23):8587–8601. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.23.8587. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szankasi P., Heyer W. D., Schuchert P., Kohli J. DNA sequence analysis of the ade6 gene of Schizosaccharomyces pombe. Wild-type and mutant alleles including the recombination host spot allele ade6-M26. J Mol Biol. 1988 Dec 20;204(4):917–925. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90051-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szent-Györgyi C., Finkelstein D. B., Garrard W. T. Sharp boundaries demarcate the chromatin structure of a yeast heat-shock gene. J Mol Biol. 1987 Jan 5;193(1):71–80. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90628-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
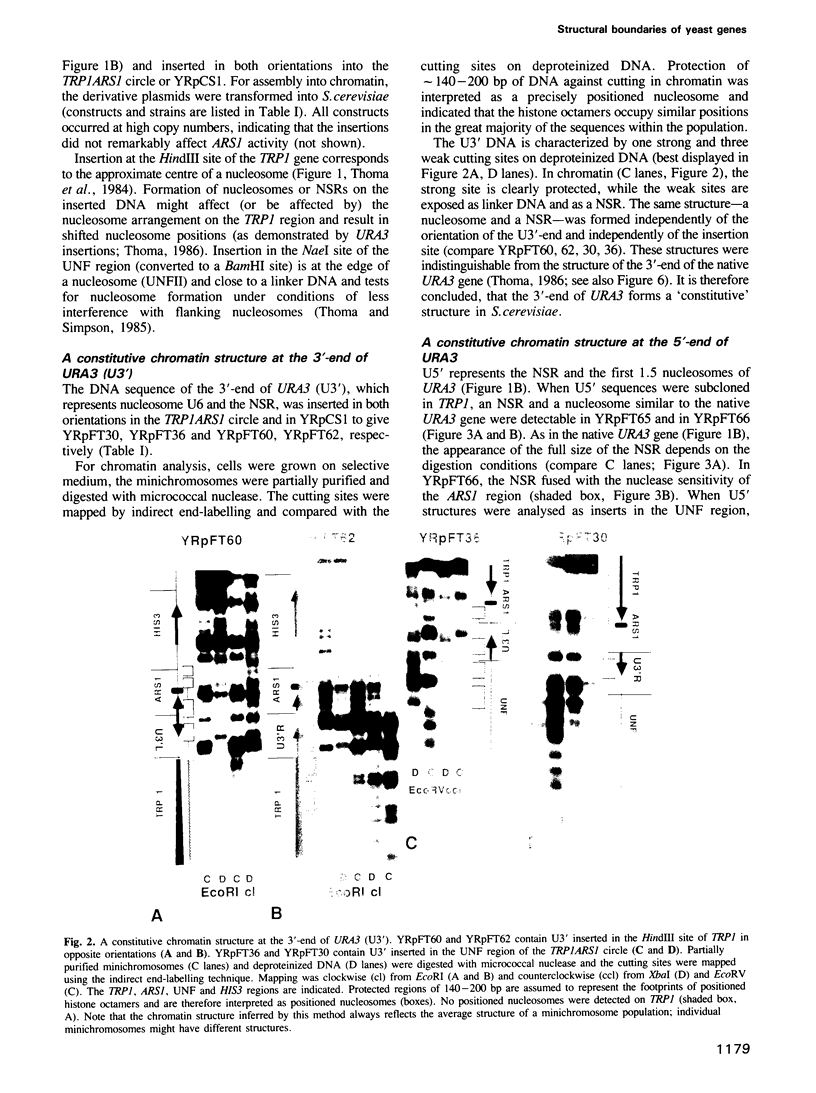
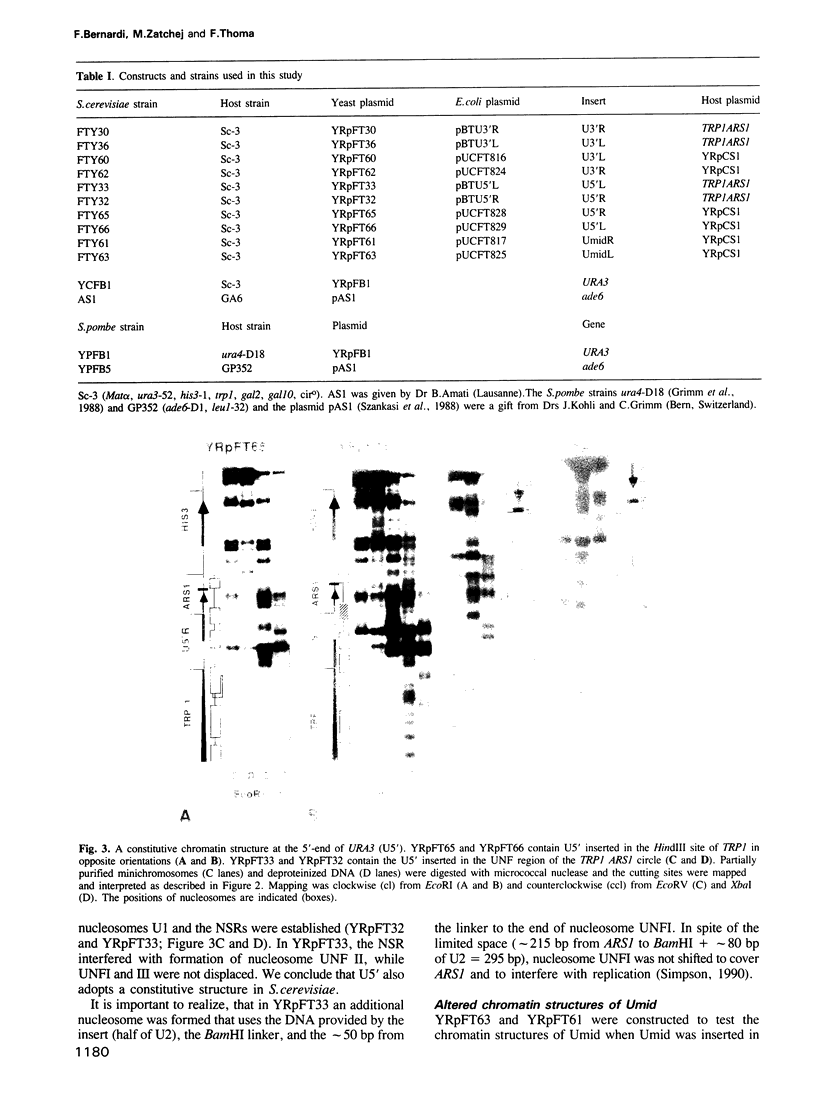
- Thoma F., Bergman L. W., Simpson R. T. Nuclease digestion of circular TRP1ARS1 chromatin reveals positioned nucleosomes separated by nuclease-sensitive regions. J Mol Biol. 1984 Aug 25;177(4):715–733. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90046-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thoma F. Protein-DNA interactions and nuclease-sensitive regions determine nucleosome positions on yeast plasmid chromatin. J Mol Biol. 1986 Jul 20;190(2):177–190. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90291-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thoma F., Simpson R. T. Local protein-DNA interactions may determine nucleosome positions on yeast plasmids. Nature. 1985 May 16;315(6016):250–252. doi: 10.1038/315250a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thoma F., Zatchej M. Chromatin folding modulates nucleosome positioning in yeast minichromosomes. Cell. 1988 Dec 23;55(6):945–953. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90240-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Travers A. A., Klug A. The bending of DNA in nucleosomes and its wider implications. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1987 Dec 15;317(1187):537–561. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1987.0080. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tschumper G., Carbon J. Sequence of a yeast DNA fragment containing a chromosomal replicator and the TRP1 gene. Gene. 1980 Jul;10(2):157–166. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(80)90133-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]