Abstract
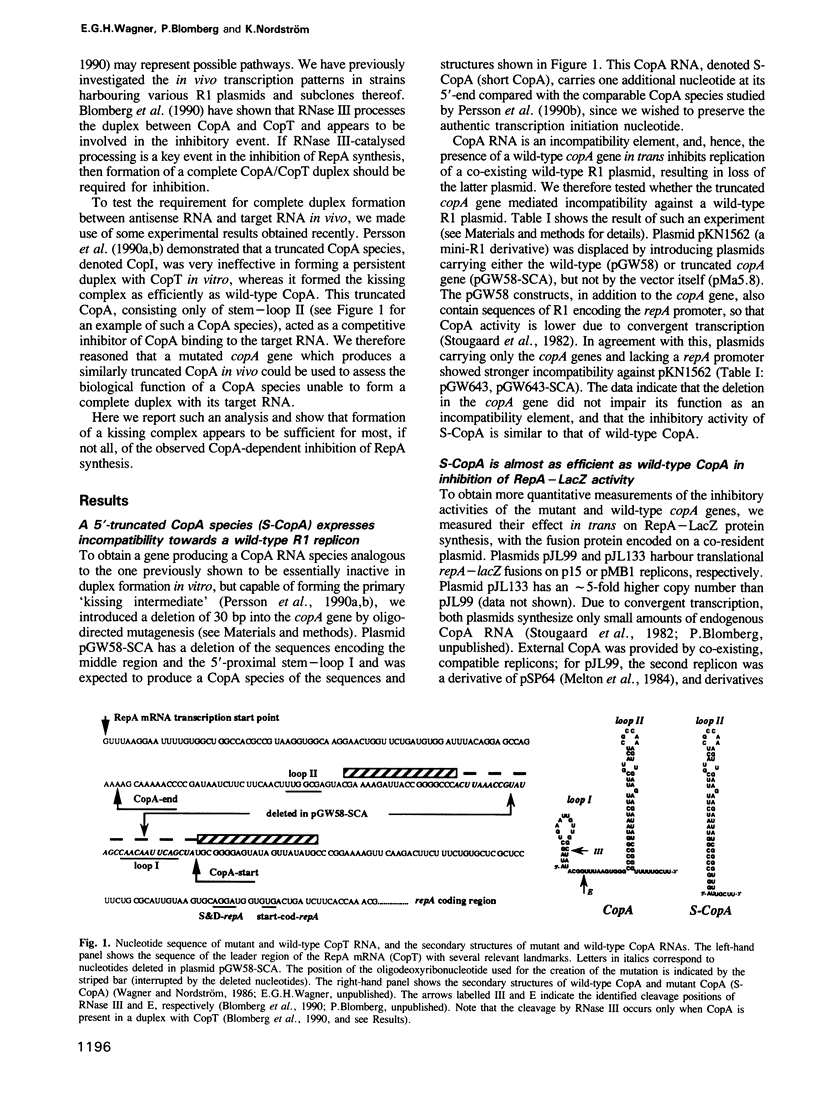
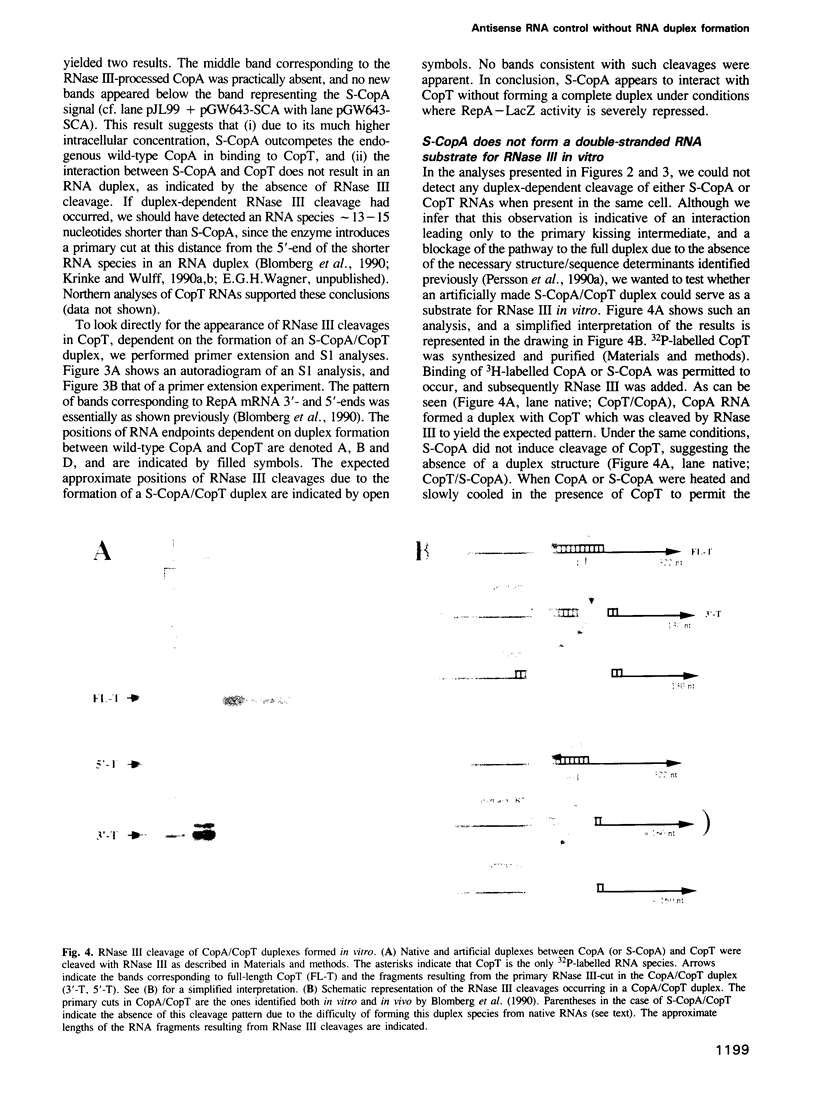
The replication frequency of plasmid R1 is regulated by an antisense RNA, CopA, which inhibits the synthesis of the rate-limiting initiator protein RepA. The inhibition requires an interaction between the antisense RNA and its target, CopT, in the leader of the RepA mRNA. This binding reaction has previously been studied in vitro, and the formation of a complete RNA duplex between the two RNAs has been demonstrated in vitro and in vivo. Here we investigate whether complete duplex formation is required for CopA-mediated inhibition in vivo. A mutated copA gene was constructed, encoding a truncated CopA which is impaired in its ability to form a complete CopA/CopT duplex, but which forms a primary binding intermediate (the 'kissing complex'). The mutated CopA species (S-CopA) mediated incompatibility against wild-type R1 plasmids and inhibited RepA-LacZ fusion protein synthesis. Northern blot, primer extension and S1 analyses indicated that S-CopA did not form a complete duplex with CopT in vivo since bands corresponding to RNase III cleavage products were missing. An in vitro analysis supported the same conclusion. These data suggest that formation of the 'kissing complex' suffices to inhibit RepA synthesis, and that complete CopA/CopT duplex formation is not required. The implications of these findings are discussed.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andersen J., Delihas N. micF RNA binds to the 5' end of ompF mRNA and to a protein from Escherichia coli. Biochemistry. 1990 Oct 2;29(39):9249–9256. doi: 10.1021/bi00491a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Asano K., Kato A., Moriwaki H., Hama C., Shiba K., Mizobuchi K. Positive and negative regulations of plasmid CoLIb-P9 repZ gene expression at the translational level. J Biol Chem. 1991 Feb 25;266(6):3774–3781. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berzal-Herranz A., Wagner E. G., Díaz-Orejas R. Control of replication of plasmid R1: the intergenic region between copA and repA modulates the level of expression of repA. Mol Microbiol. 1991 Jan;5(1):97–108. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
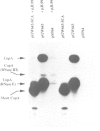
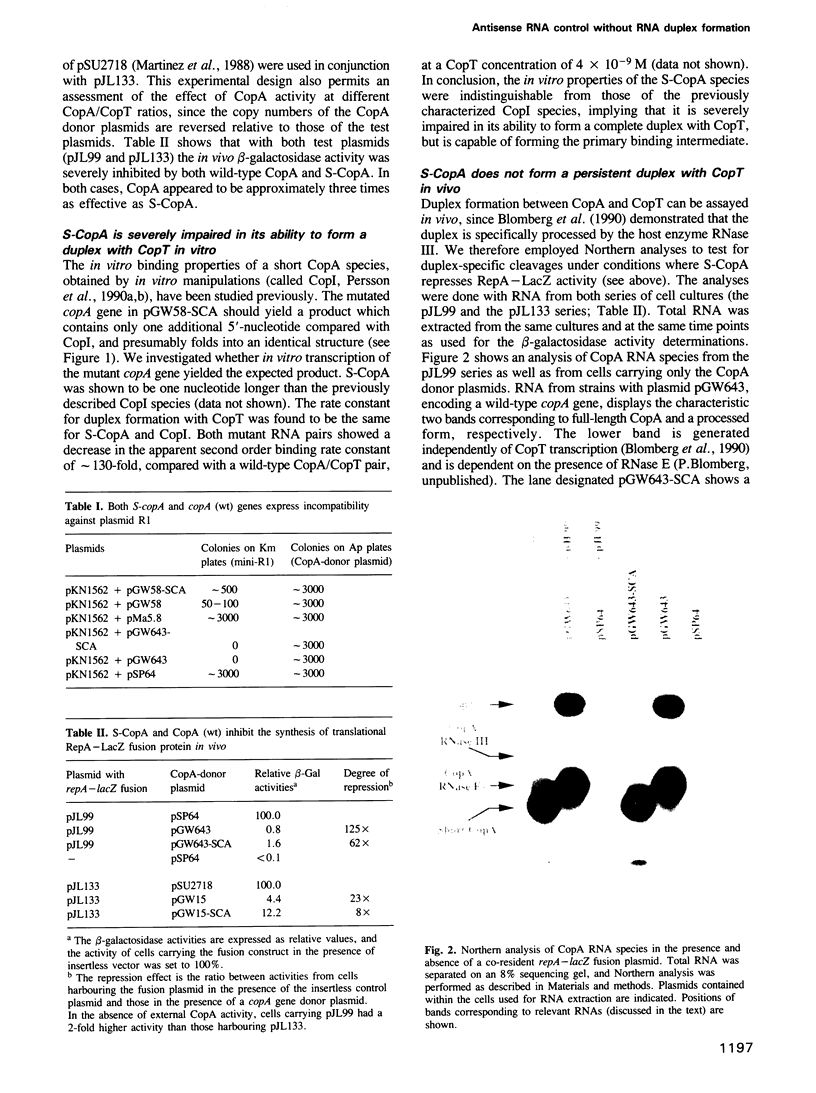
- Blomberg P., Wagner E. G., Nordström K. Control of replication of plasmid R1: the duplex between the antisense RNA, CopA, and its target, CopT, is processed specifically in vivo and in vitro by RNase III. EMBO J. 1990 Jul;9(7):2331–2340. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07405.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Case C. C., Simons E. L., Simons R. W. The IS10 transposase mRNA is destabilized during antisense RNA control. EMBO J. 1990 Apr;9(4):1259–1266. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08234.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dong X. N., Womble D. D., Rownd R. H. Transcriptional pausing in a region important for plasmid NR1 replication control. J Bacteriol. 1987 Dec;169(12):5353–5363. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.12.5353-5363.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerhart E., Wagner H., Nordström K. Structural analysis of an RNA molecule involved in replication control of plasmid R1. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Mar 25;14(6):2523–2538. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.6.2523. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kittle J. D., Simons R. W., Lee J., Kleckner N. Insertion sequence IS10 anti-sense pairing initiates by an interaction between the 5' end of the target RNA and a loop in the anti-sense RNA. J Mol Biol. 1989 Dec 5;210(3):561–572. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90132-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krinke L., Wulff D. L. RNase III-dependent hydrolysis of lambda cII-O gene mRNA mediated by lambda OOP antisense RNA. Genes Dev. 1990 Dec;4(12A):2223–2233. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.12a.2223. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krinke L., Wulff D. L. The cleavage specificity of RNase III. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Aug 25;18(16):4809–4815. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.16.4809. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Light J., Molin S. Replication control functions of plasmid R1 act as inhibitors of expression of a gene required for replication. Mol Gen Genet. 1981;184(1):56–61. doi: 10.1007/BF00271195. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin-Chao S., Cohen S. N. The rate of processing and degradation of antisense RNAI regulates the replication of ColE1-type plasmids in vivo. Cell. 1991 Jun 28;65(7):1233–1242. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90018-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ma C., Simons R. W. The IS10 antisense RNA blocks ribosome binding at the transposase translation initiation site. EMBO J. 1990 Apr;9(4):1267–1274. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08235.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martinez E., Bartolomé B., de la Cruz F. pACYC184-derived cloning vectors containing the multiple cloning site and lacZ alpha reporter gene of pUC8/9 and pUC18/19 plasmids. Gene. 1988 Aug 15;68(1):159–162. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90608-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masukata H., Tomizawa J. Control of primer formation for ColE1 plasmid replication: conformational change of the primer transcript. Cell. 1986 Jan 17;44(1):125–136. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90491-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melton D. A., Krieg P. A., Rebagliati M. R., Maniatis T., Zinn K., Green M. R. Efficient in vitro synthesis of biologically active RNA and RNA hybridization probes from plasmids containing a bacteriophage SP6 promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Sep 25;12(18):7035–7056. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.18.7035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Molin S., Stougaard P., Uhlin B. E., Gustafsson P., Nordström K. Clustering of genes involved in replication, copy number control, incompatibility, and stable maintenance of the resistance plasmid R1drd-19. J Bacteriol. 1979 Apr;138(1):70–79. doi: 10.1128/jb.138.1.70-79.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nordström K., Molin S., Aagaard-Hansen H. Partitioning of plasmid R1 in Escherichia coli. II. Incompatibility properties of the partitioning system. Plasmid. 1980 Nov;4(3):332–339. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(80)90071-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novick R. P., Iordanescu S., Projan S. J., Kornblum J., Edelman I. pT181 plasmid replication is regulated by a countertranscript-driven transcriptional attenuator. Cell. 1989 Oct 20;59(2):395–404. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90300-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohman M., Wagner E. G. Secondary structure analysis of the RepA mRNA leader transcript involved in control of replication of plasmid R1. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Apr 11;17(7):2557–2579. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.7.2557. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Persson C., Wagner E. G., Nordström K. Control of replication of plasmid R1: formation of an initial transient complex is rate-limiting for antisense RNA--target RNA pairing. EMBO J. 1990 Nov;9(11):3777–3785. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07591.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Persson C., Wagner E. G., Nordström K. Control of replication of plasmid R1: kinetics of in vitro interaction between the antisense RNA, CopA, and its target, CopT. EMBO J. 1988 Oct;7(10):3279–3288. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03195.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Persson C., Wagner E. G., Nordström K. Control of replication of plasmid R1: structures and sequences of the antisense RNA, CopA, required for its binding to the target RNA, CopT. EMBO J. 1990 Nov;9(11):3767–3775. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07590.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polisky B. ColE1 replication control circuitry: sense from antisense. Cell. 1988 Dec 23;55(6):929–932. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90235-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simons R. W., Kleckner N. Biological regulation by antisense RNA in prokaryotes. Annu Rev Genet. 1988;22:567–600. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.22.120188.003031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stougaard P., Light J., Molin S. Convergent transcription interferes with expression of the copy number control gene, copA, from plasmid R1. EMBO J. 1982;1(3):323–328. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01168.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamm J., Polisky B. Characterization of the ColE1 primer-RNA1 complex: analysis of a domain of ColE1 RNA1 necessary for its interaction with primer RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Apr;82(8):2257–2261. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.8.2257. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor J. W., Ott J., Eckstein F. The rapid generation of oligonucleotide-directed mutations at high frequency using phosphorothioate-modified DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Dec 20;13(24):8765–8785. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.24.8765. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor J. W., Schmidt W., Cosstick R., Okruszek A., Eckstein F. The use of phosphorothioate-modified DNA in restriction enzyme reactions to prepare nicked DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Dec 20;13(24):8749–8764. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.24.8749. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomizawa J. Control of ColE1 plasmid replication. Interaction of Rom protein with an unstable complex formed by RNA I and RNA II. J Mol Biol. 1990 Apr 20;212(4):695–708. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(90)90231-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomizawa J. Control of ColE1 plasmid replication: the process of binding of RNA I to the primer transcript. Cell. 1984 Oct;38(3):861–870. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90281-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner E. G., von Heijne J., Nordström K. Control of replication of plasmid R1: translation of the 7k reading frame in the RepA mRNA leader region counteracts the interaction between CopA RNA and CopT RNA. EMBO J. 1987 Feb;6(2):515–522. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04783.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]