Abstract
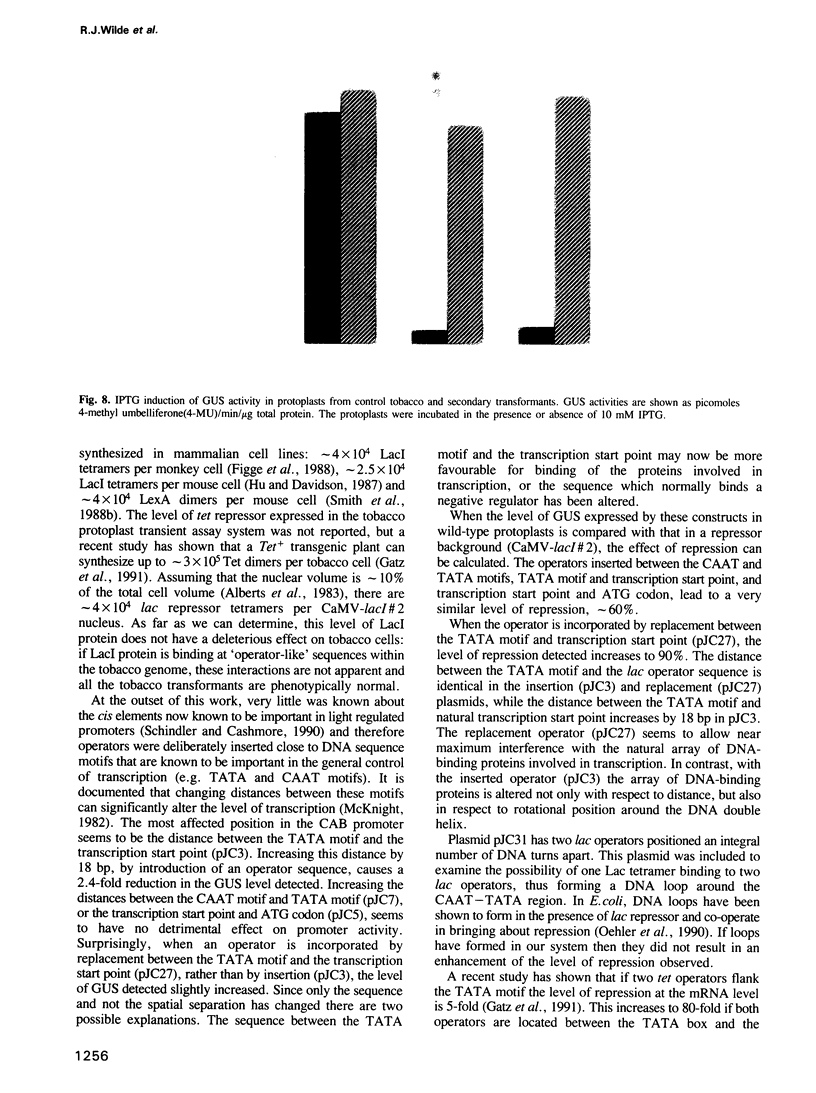
We have investigated the efficacy of using the Escherichia coli lac operator-repressor system to control plant gene expression. The lacI gene was modified to allow optimal expression in plant cells and then placed downstream of the cauliflower mosaic virus (CaMV) 35S RNA promoter. This construct was introduced into tobacco plants by leaf disc transformation. Transgenic tobacco plants synthesized significant quantities of LacI protein (up to 0.06% of total soluble protein). We have used the E.coli beta-glucuronidase gene (gus) as the reporter gene by placing it downstream of the maize chlorophyll a/b binding protein (CAB) gene promoter. Lac operators were introduced into several positions within the CAB promoter and operator-free plasmid was used as control. Repression was assessed by comparing the transient expression from CAB-operator-gus reporter constructs in protoplasts expressing lac protein, with that in control cells not expressing the repressor. Repression varied between 10 and 90% with different operator positions. Transient assays were also performed in the presence of the inducer, isopropyl-beta-D-thiogalactoside (IPTG). In lacI protoplasts the presence of IPTG manifested itself in a 4.2-fold relief of repression. The study was extended to show regulation of expression in stable transformants. Tobacco transformants harbouring a CAB-operator-gus reporter construct and the lacI gene were shown to have repressed GUS levels, but in the presence of IPTG, repression was relieved 15-fold. We conclude that the lac repressor can enter the plant cell nucleus, find its cognate operator sequence in the chromatin to form a repressor--operator complex and effectively block transcription of a downstream gene.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bevan M. Binary Agrobacterium vectors for plant transformation. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Nov 26;12(22):8711–8721. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.22.8711. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brent R., Ptashne M. A bacterial repressor protein or a yeast transcriptional terminator can block upstream activation of a yeast gene. Nature. 1984 Dec 13;312(5995):612–615. doi: 10.1038/312612a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown M., Figge J., Hansen U., Wright C., Jeang K. T., Khoury G., Livingston D. M., Roberts T. M. lac repressor can regulate expression from a hybrid SV40 early promoter containing a lac operator in animal cells. Cell. 1987 Jun 5;49(5):603–612. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90536-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deuschle U., Pepperkok R., Wang F. B., Giordano T. J., McAllister W. T., Ansorge W., Bujard H. Regulated expression of foreign genes in mammalian cells under the control of coliphage T3 RNA polymerase and lac repressor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jul;86(14):5400–5404. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.14.5400. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dynan W. S., Tjian R. Control of eukaryotic messenger RNA synthesis by sequence-specific DNA-binding proteins. 1985 Aug 29-Sep 4Nature. 316(6031):774–778. doi: 10.1038/316774a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Figge J., Wright C., Collins C. J., Roberts T. M., Livingston D. M. Stringent regulation of stably integrated chloramphenicol acetyl transferase genes by E. coli lac repressor in monkey cells. Cell. 1988 Mar 11;52(5):713–722. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90409-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuerst T. R., Fernandez M. P., Moss B. Transfer of the inducible lac repressor/operator system from Escherichia coli to a vaccinia virus expression vector. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Apr;86(8):2549–2553. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.8.2549. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gatz C., Kaiser A., Wendenburg R. Regulation of a modified CaMV 35S promoter by the Tn10-encoded Tet repressor in transgenic tobacco. Mol Gen Genet. 1991 Jun;227(2):229–237. doi: 10.1007/BF00259675. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gatz C., Quail P. H. Tn10-encoded tet repressor can regulate an operator-containing plant promoter. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Mar;85(5):1394–1397. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.5.1394. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horsch R. B., Fraley R. T., Rogers S. G., Sanders P. R., Lloyd A., Hoffmann N. Inheritance of functional foreign genes in plants. Science. 1984 Feb 3;223(4635):496–498. doi: 10.1126/science.223.4635.496. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu M. C., Davidson N. The inducible lac operator-repressor system is functional in mammalian cells. Cell. 1987 Feb 27;48(4):555–566. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90234-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jefferson R. A., Kavanagh T. A., Bevan M. W. GUS fusions: beta-glucuronidase as a sensitive and versatile gene fusion marker in higher plants. EMBO J. 1987 Dec 20;6(13):3901–3907. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02730.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joshi C. P. An inspection of the domain between putative TATA box and translation start site in 79 plant genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Aug 25;15(16):6643–6653. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.16.6643. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalderon D., Roberts B. L., Richardson W. D., Smith A. E. A short amino acid sequence able to specify nuclear location. Cell. 1984 Dec;39(3 Pt 2):499–509. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90457-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lang I., Scholz M., Peters R. Molecular mobility and nucleocytoplasmic flux in hepatoma cells. J Cell Biol. 1986 Apr;102(4):1183–1190. doi: 10.1083/jcb.102.4.1183. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu H. S., Feliciano E. S., Stambrook P. J. Cytochemical observation of regulated bacterial beta-galactosidase gene expression in mammalian cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Dec;86(24):9951–9955. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.24.9951. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKnight S. L. Functional relationships between transcriptional control signals of the thymidine kinase gene of herpes simplex virus. Cell. 1982 Dec;31(2 Pt 1):355–365. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90129-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKnight S., Tjian R. Transcriptional selectivity of viral genes in mammalian cells. Cell. 1986 Sep 12;46(6):795–805. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90061-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oehler S., Eismann E. R., Krämer H., Müller-Hill B. The three operators of the lac operon cooperate in repression. EMBO J. 1990 Apr;9(4):973–979. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08199.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paine P. L., Moore L. C., Horowitz S. B. Nuclear envelope permeability. Nature. 1975 Mar 13;254(5496):109–114. doi: 10.1038/254109a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ptashne M. Gene regulation by proteins acting nearby and at a distance. Nature. 1986 Aug 21;322(6081):697–701. doi: 10.1038/322697a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riggs A. D., Suzuki H., Bourgeois S. Lac repressor-operator interaction. I. Equilibrium studies. J Mol Biol. 1970 Feb 28;48(1):67–83. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90219-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schindler U., Cashmore A. R. Photoregulated gene expression may involve ubiquitous DNA binding proteins. EMBO J. 1990 Nov;9(11):3415–3427. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07549.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simons A., Tils D., von Wilcken-Bergmann B., Müller-Hill B. Possible ideal lac operator: Escherichia coli lac operator-like sequences from eukaryotic genomes lack the central G X C pair. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Mar;81(6):1624–1628. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.6.1624. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith G. M., Mileham K. A., Cooke S. E., Woolston S. J., George H. K., Charles A. D., Brammar W. J. The Escherichia coli LexA repressor-operator system works in mammalian cells. EMBO J. 1988 Dec 1;7(12):3975–3982. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03285.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stark M. J. Multicopy expression vectors carrying the lac repressor gene for regulated high-level expression of genes in Escherichia coli. Gene. 1987;51(2-3):255–267. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(87)90314-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]






