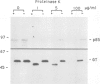
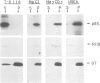
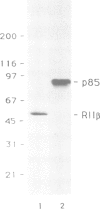
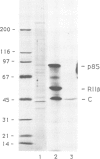
Abstract
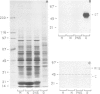
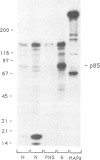
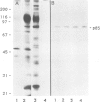
Immunocytochemical evidence of an association between the regulatory subunit RII of the cAMP-dependent protein kinase (cAMP-PK) and the Golgi apparatus in several cell types has been reported. In order to identify endogenous Golgi proteins binding RII, a fraction enriched in Golgi vesicles was isolated from human lymphoblasts. Only the RII beta isoform was detected in the Golgi-rich fraction, although RII alpha has also been found to be present in these cells. A 85 kDa RII-binding protein was identified in Golgi vesicles using a [32P]RII overlay of Western blots. The existence of an endogenous RII beta-p85 complex in isolated Golgi vesicles was demonstrated by two independent means: (i) co-immunoprecipitation of both proteins under non-denaturing conditions with an antibody against RII beta and (ii) co-purification of RII beta-p85 complexes on a cAMP-analogue affinity column. p85 was phosphorylated by both endogenous and purified catalytic subunits of cAMP-pKII. Extraction experiments and protease protection experiments indicated that p85 is an integral membrane protein although it partitioned atypically during Triton X-114 phase separation. We propose that p85 anchors RII beta to the Golgi apparatus of human lymphoblasts and thereby defines the Golgi substrate targets most accessible to phosphorylation by C subunit. This mechanism may be relevant to the regulation of processes involving the Golgi apparatus itself, such as membrane traffic and secretion, but also relevant to nearby nuclear events dependent on C subunit.
Full text
PDF

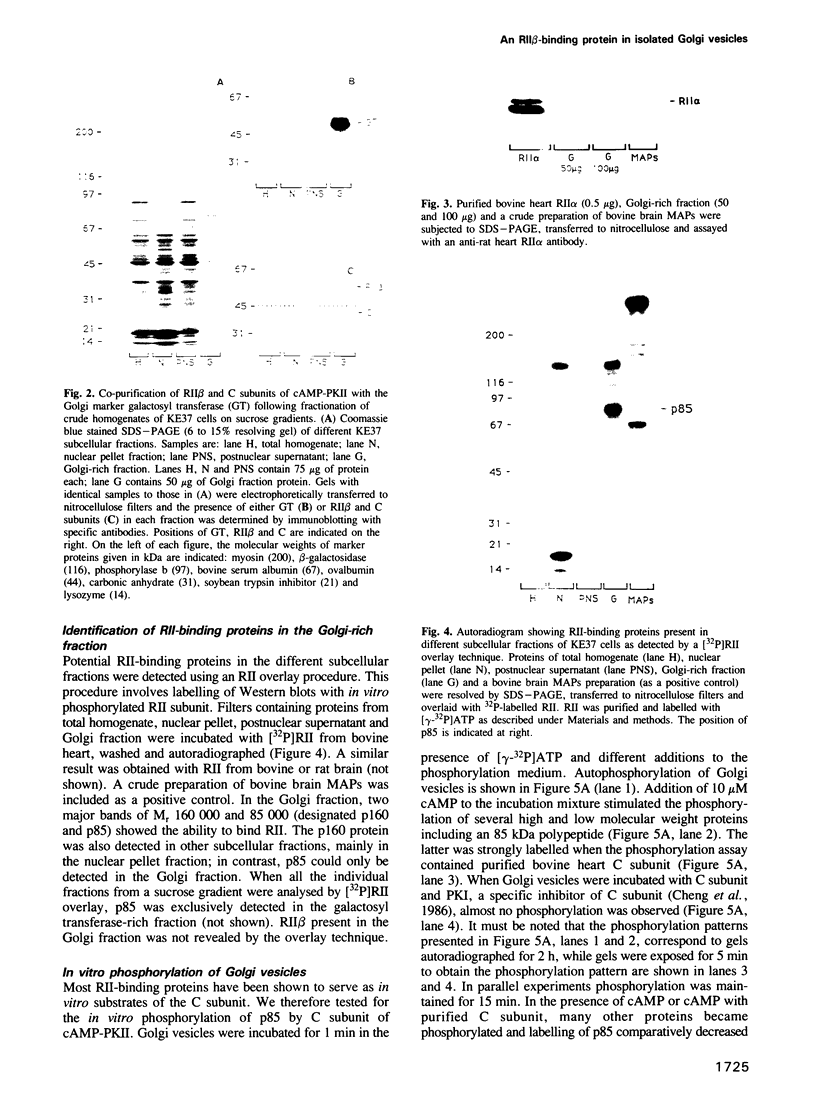
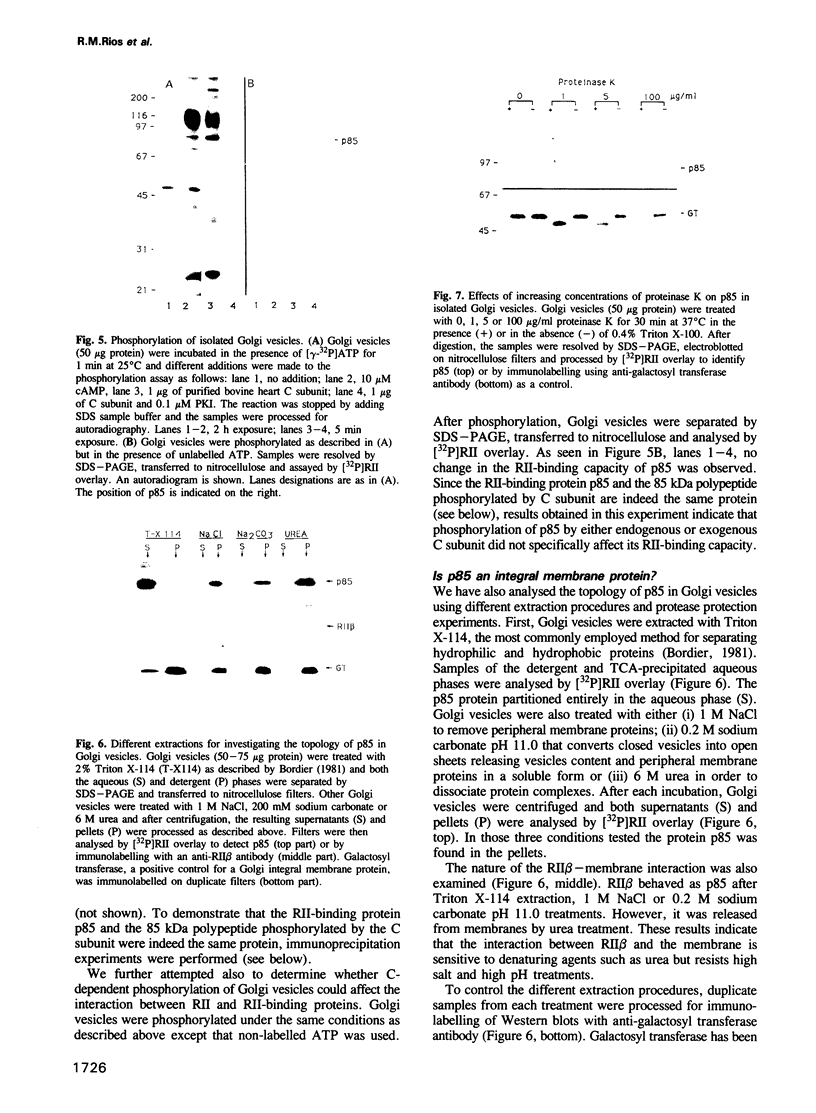





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Balch W. E., Dunphy W. G., Braell W. A., Rothman J. E. Reconstitution of the transport of protein between successive compartments of the Golgi measured by the coupled incorporation of N-acetylglucosamine. Cell. 1984 Dec;39(2 Pt 1):405–416. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90019-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beebe S. J., Oyen O., Sandberg M., Frøysa A., Hansson V., Jahnsen T. Molecular cloning of a tissue-specific protein kinase (C gamma) from human testis--representing a third isoform for the catalytic subunit of cAMP-dependent protein kinase. Mol Endocrinol. 1990 Mar;4(3):465–475. doi: 10.1210/mend-4-3-465. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berger E. G., Mandel T., Schilt U. Immunohistochemical localization of galactosyltransferase in human fibroblasts and HeLa cells. J Histochem Cytochem. 1981 Mar;29(3):364–370. doi: 10.1177/29.3.6787115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bordier C. Phase separation of integral membrane proteins in Triton X-114 solution. J Biol Chem. 1981 Feb 25;256(4):1604–1607. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bornens M., Paintrand M., Celati C. The cortical microfilament system of lymphoblasts displays a periodic oscillatory activity in the absence of microtubules: implications for cell polarity. J Cell Biol. 1989 Sep;109(3):1071–1083. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.3.1071. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bregman D. B., Bhattacharyya N., Rubin C. S. High affinity binding protein for the regulatory subunit of cAMP-dependent protein kinase II-B. Cloning, characterization, and expression of cDNAs for rat brain P150. J Biol Chem. 1989 Mar 15;264(8):4648–4656. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bregman D. B., Hirsch A. H., Rubin C. S. Molecular characterization of bovine brain P75, a high affinity binding protein for the regulatory subunit of cAMP-dependent protein kinase II beta. J Biol Chem. 1991 Apr 15;266(11):7207–7213. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Büchler W., Meinecke M., Chakraborty T., Jahnsen T., Walter U., Lohmann S. M. Regulation of gene expression by transfected subunits of cAMP-dependent protein kinase. Eur J Biochem. 1990 Mar 10;188(2):253–259. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1990.tb15397.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cadd G., McKnight G. S. Distinct patterns of cAMP-dependent protein kinase gene expression in mouse brain. Neuron. 1989 Jul;3(1):71–79. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(89)90116-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capasso J. M., Abeijon C., Hirschberg C. B. Phosphoproteins and protein kinases of the Golgi apparatus membrane. J Biol Chem. 1985 Nov 25;260(27):14879–14884. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carr D. W., Stofko-Hahn R. E., Fraser I. D., Bishop S. M., Acott T. S., Brennan R. G., Scott J. D. Interaction of the regulatory subunit (RII) of cAMP-dependent protein kinase with RII-anchoring proteins occurs through an amphipathic helix binding motif. J Biol Chem. 1991 Aug 5;266(22):14188–14192. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng H. C., Kemp B. E., Pearson R. B., Smith A. J., Misconi L., Van Patten S. M., Walsh D. A. A potent synthetic peptide inhibitor of the cAMP-dependent protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jan 25;261(3):989–992. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clegg C. H., Cadd G. G., McKnight G. S. Genetic characterization of a brain-specific form of the type I regulatory subunit of cAMP-dependent protein kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jun;85(11):3703–3707. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.11.3703. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corbin J. D., Sugden P. H., Lincoln T. M., Keely S. L. Compartmentalization of adenosine 3':5'-monophosphate and adenosine 3':5'-monophosphate-dependent protein kinase in heart tissue. J Biol Chem. 1977 Jun 10;252(11):3854–3861. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corbin J. D., Sugden P. H., West L., Flockhart D. A., Lincoln T. M., McCarthy D. Studies on the properties and mode of action of the purified regulatory subunit of bovine heart adenosine 3':5'-monophosphate-dependent protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 1978 Jun 10;253(11):3997–4003. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Camilli P., Moretti M., Donini S. D., Walter U., Lohmann S. M. Heterogeneous distribution of the cAMP receptor protein RII in the nervous system: evidence for its intracellular accumulation on microtubules, microtubule-organizing centers, and in the area of the Golgi complex. J Cell Biol. 1986 Jul;103(1):189–203. doi: 10.1083/jcb.103.1.189. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erlichman J., Sarkar D., Fleischer N., Rubin C. S. Identification of two subclasses of type II cAMP-dependent protein kinases. Neural-specific and non-neural protein kinases. J Biol Chem. 1980 Sep 10;255(17):8179–8184. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleischer B. Orientation of glycoprotein galactosyltransferase and sialyltransferase enzymes in vesicles derived from rat liver Golgi apparatus. J Cell Biol. 1981 May;89(2):246–255. doi: 10.1083/jcb.89.2.246. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujiki Y., Hubbard A. L., Fowler S., Lazarow P. B. Isolation of intracellular membranes by means of sodium carbonate treatment: application to endoplasmic reticulum. J Cell Biol. 1982 Apr;93(1):97–102. doi: 10.1083/jcb.93.1.97. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffiths G., Hollinshead R., Hemmings B. A., Nigg E. A. Ultrastructural localization of the regulatory (RII) subunit of cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase to subcellular compartments active in endocytosis and recycling of membrane receptors. J Cell Sci. 1990 Aug;96(Pt 4):691–703. doi: 10.1242/jcs.96.4.691. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horowitz J. A., Wasco W., Leiser M., Orr G. A. Interaction of the regulatory subunit of a type II cAMP-dependent protein kinase with mammalian sperm flagellum. J Biol Chem. 1988 Feb 5;263(4):2098–2104. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jahnsen T., Hedin L., Kidd V. J., Beattie W. G., Lohmann S. M., Walter U., Durica J., Schulz T. Z., Schiltz E., Browner M. Molecular cloning, cDNA structure, and regulation of the regulatory subunit of type II cAMP-dependent protein kinase from rat ovarian granulosa cells. J Biol Chem. 1986 Sep 15;261(26):12352–12361. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jahnsen T., Lohmann S. M., Walter U., Hedin L., Richards J. S. Purification and characterization of hormone-regulated isoforms of the regulatory subunit of type II cAMP-dependent protein kinase from rat ovaries. J Biol Chem. 1985 Dec 15;260(29):15980–15987. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamb N. J., Cavadore J. C., Labbe J. C., Maurer R. A., Fernandez A. Inhibition of cAMP-dependent protein kinase plays a key role in the induction of mitosis and nuclear envelope breakdown in mammalian cells. EMBO J. 1991 Jun;10(6):1523–1533. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07672.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee D. C., Carmichael D. F., Krebs E. G., McKnight G. S. Isolation of a cDNA clone for the type I regulatory subunit of bovine cAMP-dependent protein kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jun;80(12):3608–3612. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.12.3608. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lohmann S. M., De Camilli P., Walter U. Type II cAMP-dependent protein kinase regulatory subunit-binding proteins. Methods Enzymol. 1988;159:183–193. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(88)59019-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lohmann S. M., DeCamilli P., Einig I., Walter U. High-affinity binding of the regulatory subunit (RII) of cAMP-dependent protein kinase to microtubule-associated and other cellular proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Nov;81(21):6723–6727. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.21.6723. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lohmann S. M., Walter U., Greengard P. Identification of endogenous substrate proteins for cAMP-dependent protein kinase in bovine brain. J Biol Chem. 1980 Oct 25;255(20):9985–9992. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lohmann S. M., Walter U. Regulation of the cellular and subcellular concentrations and distribution of cyclic nucleotide-dependent protein kinases. Adv Cyclic Nucleotide Protein Phosphorylation Res. 1984;18:63–117. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luo Z., Shafit-Zagardo B., Erlichman J. Identification of the MAP2- and P75-binding domain in the regulatory subunit (RII beta) of type II cAMP-dependent protein kinase. Cloning and expression of the cDNA for bovine brain RII beta. J Biol Chem. 1990 Dec 15;265(35):21804–21810. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mellon P. L., Clegg C. H., Correll L. A., McKnight G. S. Regulation of transcription by cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jul;86(13):4887–4891. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.13.4887. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nigam S. K., Blobel G. Cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase in canine pancreatic rough endoplasmic reticulum. J Biol Chem. 1989 Oct 5;264(28):16927–16932. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nigg E. A., Hilz H., Eppenberger H. M., Dutly F. Rapid and reversible translocation of the catalytic subunit of cAMP-dependent protein kinase type II from the Golgi complex to the nucleus. EMBO J. 1985 Nov;4(11):2801–2806. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04006.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nigg E. A., Schäfer G., Hilz H., Eppenberger H. M. Cyclic-AMP-dependent protein kinase type II is associated with the Golgi complex and with centrosomes. Cell. 1985 Jul;41(3):1039–1051. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80084-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Obar R. A., Dingus J., Bayley H., Vallee R. B. The RII subunit of cAMP-dependent protein kinase binds to a common amino-terminal domain in microtubule-associated proteins 2A, 2B, and 2C. Neuron. 1989 Nov;3(5):639–645. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(89)90274-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pariset C., Feinberg J., Dacheux J. L., Oyen O., Jahnsen T., Weinman S. Differential expression and subcellular localization for subunits of cAMP-dependent protein kinase during ram spermatogenesis. J Cell Biol. 1989 Sep;109(3):1195–1205. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.3.1195. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin C. S., Rangel-Aldao R., Sarkar D., Erlichman J., Fleischer N. Characterization and comparison of membrane-associated and cytosolic cAMP-dependent protein kinases. Physicochemical and immunological studies on bovine cerebral cortex protein kinases. J Biol Chem. 1979 May 25;254(10):3797–3805. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubino H. M., Dammerman M., Shafit-Zagardo B., Erlichman J. Localization and characterization of the binding site for the regulatory subunit of type II cAMP-dependent protein kinase on MAP2. Neuron. 1989 Nov;3(5):631–638. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(89)90273-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarkar D., Erlichman J., Rubin C. S. Identification of a calmodulin-binding protein that co-purifies with the regulatory subunit of brain protein kinase II. J Biol Chem. 1984 Aug 10;259(15):9840–9846. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz D. A., Rubin C. S. Identification and differential expression of two forms of regulatory subunits (RII) of cAMP-dependent protein kinase II in Friend erythroleukemic cells. Differentiation and 8-bromo-cAMP elicit a large and selective increase in the rate of biosynthesis of only one type of RII. J Biol Chem. 1985 May 25;260(10):6296–6303. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott J. D., Glaccum M. B., Zoller M. J., Uhler M. D., Helfman D. M., McKnight G. S., Krebs E. G. The molecular cloning of a type II regulatory subunit of the cAMP-dependent protein kinase from rat skeletal muscle and mouse brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Aug;84(15):5192–5196. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.15.5192. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott J. D., Stofko R. E., McDonald J. R., Comer J. D., Vitalis E. A., Mangili J. A. Type II regulatory subunit dimerization determines the subcellular localization of the cAMP-dependent protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 1990 Dec 15;265(35):21561–21566. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein J. C., Farooq M., Norton W. T., Rubin C. S. Differential expression of isoforms of the regulatory subunit of type II cAMP-dependent protein kinase in rat neurons, astrocytes, and oligodendrocytes. J Biol Chem. 1987 Mar 5;262(7):3002–3006. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strous G. J., Van Kerkhof P., Willemsen R., Geuze H. J., Berger E. G. Transport and topology of galactosyltransferase in endomembranes of HeLa cells. J Cell Biol. 1983 Sep;97(3):723–727. doi: 10.1083/jcb.97.3.723. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Struthers R. S., Vale W. W., Arias C., Sawchenko P. E., Montminy M. R. Somatotroph hypoplasia and dwarfism in transgenic mice expressing a non-phosphorylatable CREB mutant. Nature. 1991 Apr 18;350(6319):622–624. doi: 10.1038/350622a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor S. S., Buechler J. A., Yonemoto W. cAMP-dependent protein kinase: framework for a diverse family of regulatory enzymes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1990;59:971–1005. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.59.070190.004543. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Theurkauf W. E., Vallee R. B. Molecular characterization of the cAMP-dependent protein kinase bound to microtubule-associated protein 2. J Biol Chem. 1982 Mar 25;257(6):3284–3290. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tournier S., Raynaud F., Gerbaud P., Lohmann S. M., Dorée M., Evain-Brion D. Association of type II cAMP-dependent protein kinase with p34cdc2 protein kinase in human fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 1991 Oct 5;266(28):19018–19022. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uhler M. D., Carmichael D. F., Lee D. C., Chrivia J. C., Krebs E. G., McKnight G. S. Isolation of cDNA clones coding for the catalytic subunit of mouse cAMP-dependent protein kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Mar;83(5):1300–1304. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.5.1300. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uhler M. D., Chrivia J. C., McKnight G. S. Evidence for a second isoform of the catalytic subunit of cAMP-dependent protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 1986 Nov 25;261(33):15360–15363. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams R. C., Jr, Lee J. C. Preparation of tubulin from brain. Methods Enzymol. 1982;85(Pt B):376–385. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(82)85038-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yuan L., Barriocanal J. G., Bonifacino J. S., Sandoval I. V. Two integral membrane proteins located in the cis-middle and trans-part of the Golgi system acquire sialylated N-linked carbohydrates and display different turnovers and sensitivity to cAMP-dependent phosphorylation. J Cell Biol. 1987 Jul;105(1):215–227. doi: 10.1083/jcb.105.1.215. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]