Abstract
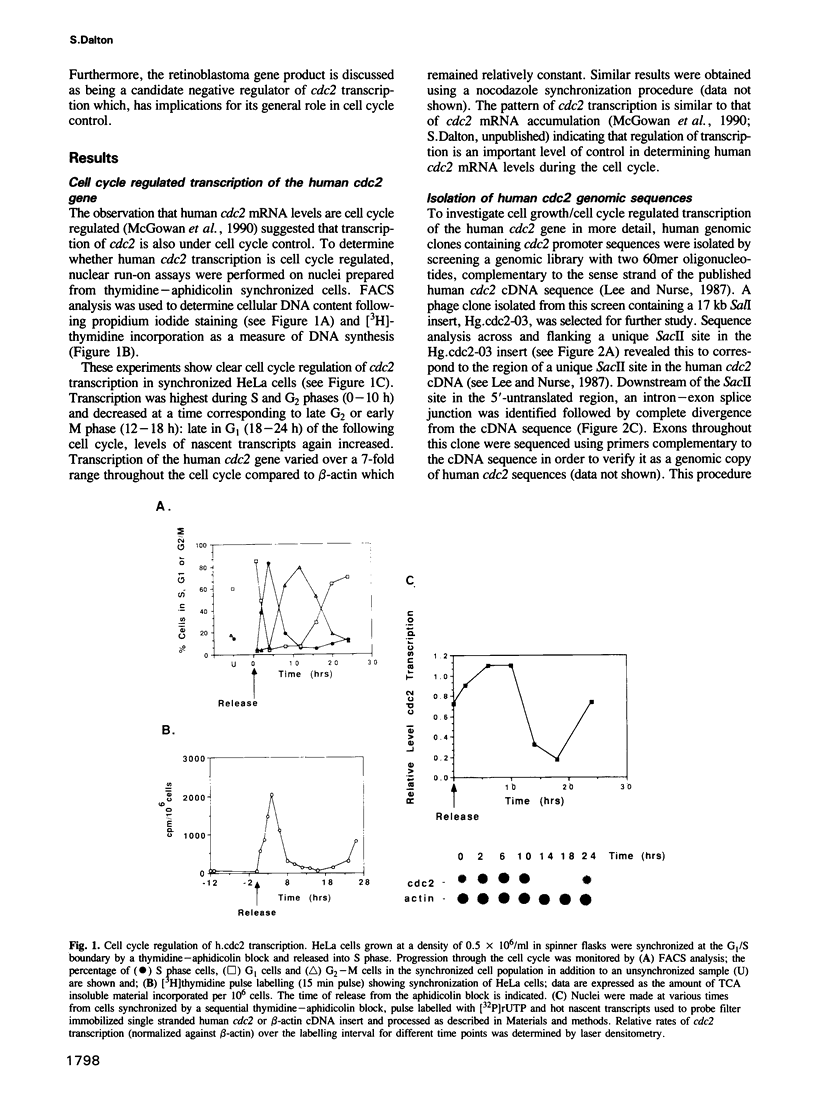
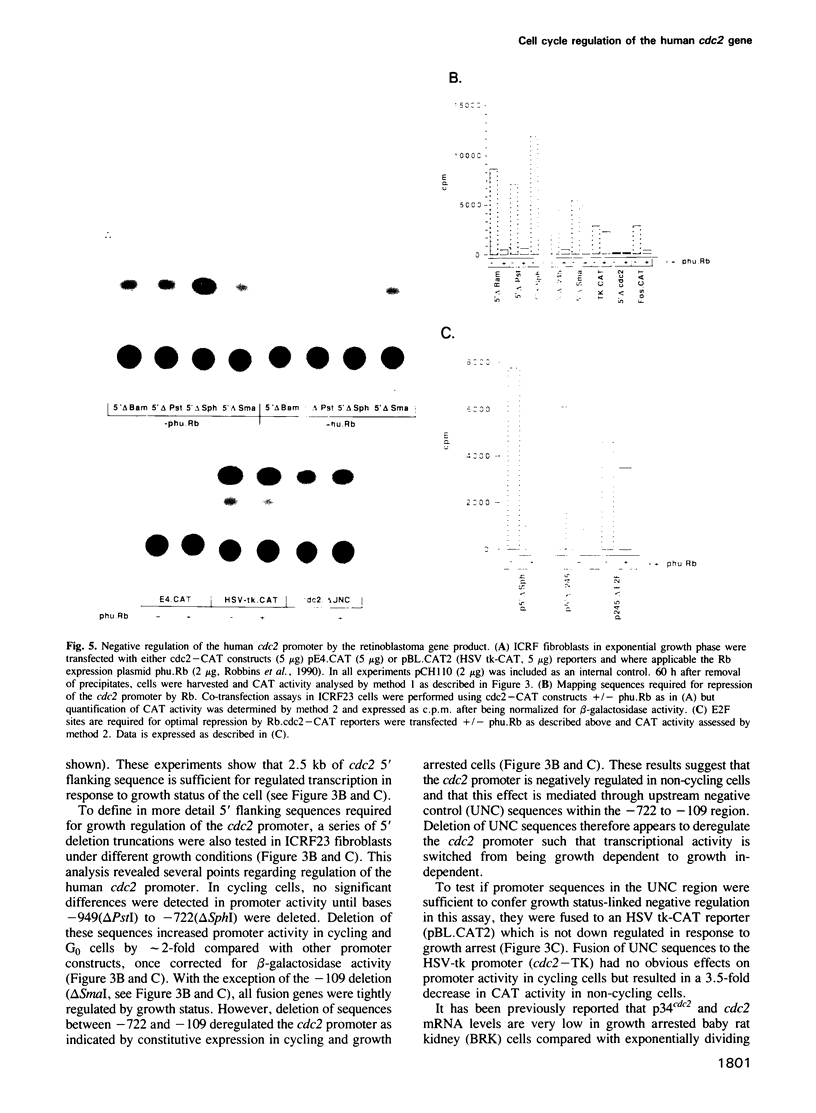
Transcription of the human cdc2 gene is cell cycle regulated and restricted to proliferating cells. Nuclear run-on assays show that cdc2 transcription is high in S and G2 phases of the cell cycle but low in G1. To investigate transcriptional control further, genomic clones of the human cdc2 gene containing 5' flanking sequences were isolated and shown to function as a growth regulated promoter in vivo when fused to a CAT reporter gene. In primary human fibroblasts, the human cdc2 promoter is negatively regulated by arrest of cell growth in a similar fashion to the endogenous gene. This requires specific 5' flanking upstream negative control (UNC) sequences which mediate repression. The retinoblastoma susceptibility gene product (Rb) specifically represses cdc2 transcription in cycling cells via 136 bp of 5' flanking sequence located between -245 and -109 within the UNC region. E2F binding sites in this region were shown to be essential for optimal repression. A model is proposed where Rb negatively regulates the cdc2 promoter in non-cycling and cycling G1 cells.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aviv H., Leder P. Purification of biologically active globin messenger RNA by chromatography on oligothymidylic acid-cellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jun;69(6):1408–1412. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.6.1408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bagchi S., Weinmann R., Raychaudhuri P. The retinoblastoma protein copurifies with E2F-I, an E1A-regulated inhibitor of the transcription factor E2F. Cell. 1991 Jun 14;65(6):1063–1072. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90558-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bandara L. R., Adamczewski J. P., Hunt T., La Thangue N. B. Cyclin A and the retinoblastoma gene product complex with a common transcription factor. Nature. 1991 Jul 18;352(6332):249–251. doi: 10.1038/352249a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bandara L. R., La Thangue N. B. Adenovirus E1a prevents the retinoblastoma gene product from complexing with a cellular transcription factor. Nature. 1991 Jun 6;351(6326):494–497. doi: 10.1038/351494a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beach D., Durkacz B., Nurse P. Functionally homologous cell cycle control genes in budding and fission yeast. Nature. 1982 Dec 23;300(5894):706–709. doi: 10.1038/300706a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blow J. J., Nurse P. A cdc2-like protein is involved in the initiation of DNA replication in Xenopus egg extracts. Cell. 1990 Sep 7;62(5):855–862. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90261-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchkovich K., Duffy L. A., Harlow E. The retinoblastoma protein is phosphorylated during specific phases of the cell cycle. Cell. 1989 Sep 22;58(6):1097–1105. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90508-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chellappan S. P., Hiebert S., Mudryj M., Horowitz J. M., Nevins J. R. The E2F transcription factor is a cellular target for the RB protein. Cell. 1991 Jun 14;65(6):1053–1061. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90557-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen P. L., Scully P., Shew J. Y., Wang J. Y., Lee W. H. Phosphorylation of the retinoblastoma gene product is modulated during the cell cycle and cellular differentiation. Cell. 1989 Sep 22;58(6):1193–1198. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90517-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chittenden T., Livingston D. M., Kaelin W. G., Jr The T/E1A-binding domain of the retinoblastoma product can interact selectively with a sequence-specific DNA-binding protein. Cell. 1991 Jun 14;65(6):1073–1082. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90559-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou Y. H., Bischoff J. R., Beach D., Goldman R. D. Intermediate filament reorganization during mitosis is mediated by p34cdc2 phosphorylation of vimentin. Cell. 1990 Sep 21;62(6):1063–1071. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90384-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'Urso G., Marraccino R. L., Marshak D. R., Roberts J. M. Cell cycle control of DNA replication by a homologue from human cells of the p34cdc2 protein kinase. Science. 1990 Nov 9;250(4982):786–791. doi: 10.1126/science.2173140. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dalton S., Coleman J. R., Wells J. R. Transcription of the histone H5 gene is not S-phase regulated. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Feb;6(2):601–606. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.2.601. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dalton S., Wells J. R. A gene-specific promoter element is required for optimal expression of the histone H1 gene in S-phase. EMBO J. 1988 Jan;7(1):49–56. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02782.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeCaprio J. A., Ludlow J. W., Lynch D., Furukawa Y., Griffin J., Piwnica-Worms H., Huang C. M., Livingston D. M. The product of the retinoblastoma susceptibility gene has properties of a cell cycle regulatory element. Cell. 1989 Sep 22;58(6):1085–1095. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90507-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Draetta G., Beach D. Activation of cdc2 protein kinase during mitosis in human cells: cell cycle-dependent phosphorylation and subunit rearrangement. Cell. 1988 Jul 1;54(1):17–26. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90175-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Draetta G., Beach D., Moran E. Synthesis of p34, the mammalian homolog of the yeast cdc2+/CDC28 protein kinase, is stimulated during adenovirus-induced proliferation of primary baby rat kidney cells. Oncogene. 1988 Jun;2(6):553–557. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Draetta G. Cell cycle control in eukaryotes: molecular mechanisms of cdc2 activation. Trends Biochem Sci. 1990 Oct;15(10):378–383. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(90)90235-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Durkacz B., Carr A., Nurse P. Transcription of the cdc2 cell cycle control gene of the fission yeast Schizosaccharomyces pombe. EMBO J. 1986 Feb;5(2):369–373. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04221.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elledge S. J., Spottswood M. R. A new human p34 protein kinase, CDK2, identified by complementation of a cdc28 mutation in Saccharomyces cerevisiae, is a homolog of Xenopus Eg1. EMBO J. 1991 Sep;10(9):2653–2659. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07808.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fang F., Newport J. W. Evidence that the G1-S and G2-M transitions are controlled by different cdc2 proteins in higher eukaryotes. Cell. 1991 Aug 23;66(4):731–742. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90117-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furukawa Y., Piwnica-Worms H., Ernst T. J., Kanakura Y., Griffin J. D. cdc2 gene expression at the G1 to S transition in human T lymphocytes. Science. 1990 Nov 9;250(4982):805–808. doi: 10.1126/science.2237430. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gautier J., Norbury C., Lohka M., Nurse P., Maller J. Purified maturation-promoting factor contains the product of a Xenopus homolog of the fission yeast cell cycle control gene cdc2+. Cell. 1988 Jul 29;54(3):433–439. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90206-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Moffat L. F., Howard B. H. Recombinant genomes which express chloramphenicol acetyltransferase in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;2(9):1044–1051. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.9.1044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayles J., Nurse P. Cell cycle regulation in yeast. J Cell Sci Suppl. 1986;4:155–170. doi: 10.1242/jcs.1986.supplement_4.10. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heintz N., Sive H. L., Roeder R. G. Regulation of human histone gene expression: kinetics of accumulation and changes in the rate of synthesis and in the half-lives of individual histone mRNAs during the HeLa cell cycle. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Apr;3(4):539–550. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.4.539. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herbomel P., Bourachot B., Yaniv M. Two distinct enhancers with different cell specificities coexist in the regulatory region of polyoma. Cell. 1984 Dec;39(3 Pt 2):653–662. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90472-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirt H., Páy A., Györgyey J., Bakó L., Németh K., Bögre L., Schweyen R. J., Heberle-Bors E., Dudits D. Complementation of a yeast cell cycle mutant by an alfalfa cDNA encoding a protein kinase homologous to p34cdc2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Mar 1;88(5):1636–1640. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.5.1636. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horowitz J. M., Park S. H., Bogenmann E., Cheng J. C., Yandell D. W., Kaye F. J., Minna J. D., Dryja T. P., Weinberg R. A. Frequent inactivation of the retinoblastoma anti-oncogene is restricted to a subset of human tumor cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Apr;87(7):2775–2779. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.7.2775. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jimenez J., Alphey L., Nurse P., Glover D. M. Complementation of fission yeast cdc2ts and cdc25ts mutants identifies two cell cycle genes from Drosophila: a cdc2 homologue and string. EMBO J. 1990 Nov;9(11):3565–3571. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07567.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krek W., Nigg E. A. Structure and developmental expression of the chicken CDC2 kinase. EMBO J. 1989 Oct;8(10):3071–3078. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08458.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labbe J. C., Picard A., Peaucellier G., Cavadore J. C., Nurse P., Doree M. Purification of MPF from starfish: identification as the H1 histone kinase p34cdc2 and a possible mechanism for its periodic activation. Cell. 1989 Apr 21;57(2):253–263. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90963-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamb N. J., Fernandez A., Watrin A., Labbé J. C., Cavadore J. C. Microinjection of p34cdc2 kinase induces marked changes in cell shape, cytoskeletal organization, and chromatin structure in mammalian fibroblasts. Cell. 1990 Jan 12;60(1):151–165. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90725-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee E. Y., To H., Shew J. Y., Bookstein R., Scully P., Lee W. H. Inactivation of the retinoblastoma susceptibility gene in human breast cancers. Science. 1988 Jul 8;241(4862):218–221. doi: 10.1126/science.3388033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee M. G., Norbury C. J., Spurr N. K., Nurse P. Regulated expression and phosphorylation of a possible mammalian cell-cycle control protein. Nature. 1988 Jun 16;333(6174):676–679. doi: 10.1038/333676a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee M. G., Nurse P. Complementation used to clone a human homologue of the fission yeast cell cycle control gene cdc2. Nature. 1987 May 7;327(6117):31–35. doi: 10.1038/327031a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehner C. F., O'Farrell P. H. Drosophila cdc2 homologs: a functional homolog is coexpressed with a cognate variant. EMBO J. 1990 Nov;9(11):3573–3581. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07568.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luckow B., Schütz G. CAT constructions with multiple unique restriction sites for the functional analysis of eukaryotic promoters and regulatory elements. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Jul 10;15(13):5490–5490. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.13.5490. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGowan C. H., Russell P., Reed S. I. Periodic biosynthesis of the human M-phase promoting factor catalytic subunit p34 during the cell cycle. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jul;10(7):3847–3851. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.7.3847. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKnight S. L., Gavis E. R., Kingsbury R., Axel R. Analysis of transcriptional regulatory signals of the HSV thymidine kinase gene: identification of an upstream control region. Cell. 1981 Aug;25(2):385–398. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90057-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moran E., Mathews M. B. Multiple functional domains in the adenovirus E1A gene. Cell. 1987 Jan 30;48(2):177–178. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90418-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mudryj M., Devoto S. H., Hiebert S. W., Hunter T., Pines J., Nevins J. R. Cell cycle regulation of the E2F transcription factor involves an interaction with cyclin A. Cell. 1991 Jun 28;65(7):1243–1253. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90019-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nurse P. Universal control mechanism regulating onset of M-phase. Nature. 1990 Apr 5;344(6266):503–508. doi: 10.1038/344503a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peter M., Nakagawa J., Dorée M., Labbé J. C., Nigg E. A. In vitro disassembly of the nuclear lamina and M phase-specific phosphorylation of lamins by cdc2 kinase. Cell. 1990 May 18;61(4):591–602. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90471-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pines J., Hunter T. Isolation of a human cyclin cDNA: evidence for cyclin mRNA and protein regulation in the cell cycle and for interaction with p34cdc2. Cell. 1989 Sep 8;58(5):833–846. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90936-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riabowol K., Draetta G., Brizuela L., Vandre D., Beach D. The cdc2 kinase is a nuclear protein that is essential for mitosis in mammalian cells. Cell. 1989 May 5;57(3):393–401. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90914-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robbins P. D., Horowitz J. M., Mulligan R. C. Negative regulation of human c-fos expression by the retinoblastoma gene product. Nature. 1990 Aug 16;346(6285):668–671. doi: 10.1038/346668a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Santhanam U., Ray A., Sehgal P. B. Repression of the interleukin 6 gene promoter by p53 and the retinoblastoma susceptibility gene product. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Sep 1;88(17):7605–7609. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.17.7605. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider J. F., Fisher F., Goding C. R., Jones N. C. Mutational analysis of the adenovirus E1a gene: the role of transcriptional regulation in transformation. EMBO J. 1987 Jul;6(7):2053–2060. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02470.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shirodkar S., Ewen M., DeCaprio J. A., Morgan J., Livingston D. M., Chittenden T. The transcription factor E2F interacts with the retinoblastoma product and a p107-cyclin A complex in a cell cycle-regulated manner. Cell. 1992 Jan 10;68(1):157–166. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90214-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simanis V., Nurse P. The cell cycle control gene cdc2+ of fission yeast encodes a protein kinase potentially regulated by phosphorylation. Cell. 1986 Apr 25;45(2):261–268. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90390-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sleigh M. J. A nonchromatographic assay for expression of the chloramphenicol acetyltransferase gene in eucaryotic cells. Anal Biochem. 1986 Jul;156(1):251–256. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(86)90180-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein G. H., Beeson M., Gordon L. Failure to phosphorylate the retinoblastoma gene product in senescent human fibroblasts. Science. 1990 Aug 10;249(4969):666–669. doi: 10.1126/science.2166342. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Th'ng J. P., Wright P. S., Hamaguchi J., Lee M. G., Norbury C. J., Nurse P., Bradbury E. M. The FT210 cell line is a mouse G2 phase mutant with a temperature-sensitive CDC2 gene product. Cell. 1990 Oct 19;63(2):313–324. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90164-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas N. S., Burke L. C., Bybee A., Linch D. C. The phosphorylation state of the retinoblastoma (RB) protein in G0/G1 is dependent on growth status. Oncogene. 1991 Feb;6(2):317–322. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Treisman R. Transient accumulation of c-fos RNA following serum stimulation requires a conserved 5' element and c-fos 3' sequences. Cell. 1985 Oct;42(3):889–902. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90285-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai L. H., Harlow E., Meyerson M. Isolation of the human cdk2 gene that encodes the cyclin A- and adenovirus E1A-associated p33 kinase. Nature. 1991 Sep 12;353(6340):174–177. doi: 10.1038/353174a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner S., Green M. R. Retinoblastoma. A transcriptional tryst. Nature. 1991 Jul 18;352(6332):189–190. doi: 10.1038/352189a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang H. G., Draetta G., Moran E. E1A induces phosphorylation of the retinoblastoma protein independently of direct physical association between the E1A and retinoblastoma products. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Aug;11(8):4253–4265. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.8.4253. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinberg R. A. The retinoblastoma gene and cell growth control. Trends Biochem Sci. 1990 May;15(5):199–202. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(90)90162-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whyte P., Williamson N. M., Harlow E. Cellular targets for transformation by the adenovirus E1A proteins. Cell. 1989 Jan 13;56(1):67–75. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90984-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]