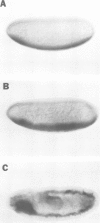
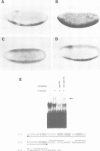
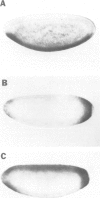
Abstract
Like many DNA binding transcription factors, the Drosophila morphogen encoded by dorsal can both stimulate and repress promoter activity. In particular, this factor activates twist and represses zerknüllt on the ventral side of the early embryo. We find that when multiple copies of a dorsal binding site from the zerknüllt ventral repressor element are fused to a heterologous basal promoter, the resulting construct is activated by dorsal to give a ventral specific expression pattern. Thus, the ability of a dorsal binding site to mediate repression rather than activation is not an intrinsic property of the site, but depends upon its context. We also show that a hybrid promoter containing both the zerknüllt ventral repressor element and the twist ventral activator region is not ventrally active in the early embryo, demonstrating that repression is dominant over activation. Thus, the default mode of action of the dorsal protein is transcriptional activation. Additional factors may modify dorsal activity to bring about repression.
Full text
PDF

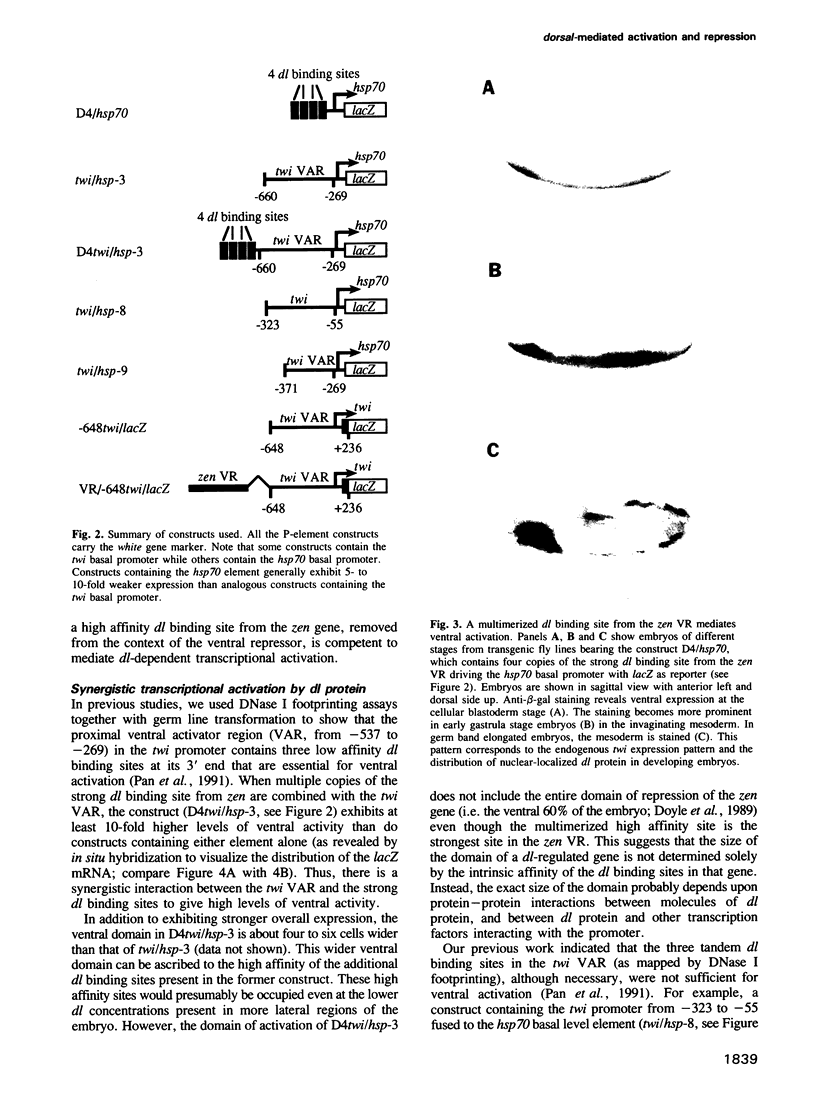


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blackwell T. K., Weintraub H. Differences and similarities in DNA-binding preferences of MyoD and E2A protein complexes revealed by binding site selection. Science. 1990 Nov 23;250(4984):1104–1110. doi: 10.1126/science.2174572. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamond M. I., Miner J. N., Yoshinaga S. K., Yamamoto K. R. Transcription factor interactions: selectors of positive or negative regulation from a single DNA element. Science. 1990 Sep 14;249(4974):1266–1272. doi: 10.1126/science.2119054. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doyle H. J., Kraut R., Levine M. Spatial regulation of zerknüllt: a dorsal-ventral patterning gene in Drosophila. Genes Dev. 1989 Oct;3(10):1518–1533. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.10.1518. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh S., Gifford A. M., Riviere L. R., Tempst P., Nolan G. P., Baltimore D. Cloning of the p50 DNA binding subunit of NF-kappa B: homology to rel and dorsal. Cell. 1990 Sep 7;62(5):1019–1029. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90276-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Govind S., Steward R. Dorsoventral pattern formation in Drosophila: signal transduction and nuclear targeting. Trends Genet. 1991 Apr;7(4):119–125. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(91)90456-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ip Y. T., Kraut R., Levine M., Rushlow C. A. The dorsal morphogen is a sequence-specific DNA-binding protein that interacts with a long-range repression element in Drosophila. Cell. 1991 Jan 25;64(2):439–446. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90651-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jiang J., Kosman D., Ip Y. T., Levine M. The dorsal morphogen gradient regulates the mesoderm determinant twist in early Drosophila embryos. Genes Dev. 1991 Oct;5(10):1881–1891. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.10.1881. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamens J., Brent R. A yeast transcription assay defines distinct rel and dorsal DNA recognition sequences. New Biol. 1991 Oct;3(10):1005–1013. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kieran M., Blank V., Logeat F., Vandekerckhove J., Lottspeich F., Le Bail O., Urban M. B., Kourilsky P., Baeuerle P. A., Israël A. The DNA binding subunit of NF-kappa B is identical to factor KBF1 and homologous to the rel oncogene product. Cell. 1990 Sep 7;62(5):1007–1018. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90275-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pan D. J., Huang J. D., Courey A. J. Functional analysis of the Drosophila twist promoter reveals a dorsal-binding ventral activator region. Genes Dev. 1991 Oct;5(10):1892–1901. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.10.1892. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patel N. H., Martin-Blanco E., Coleman K. G., Poole S. J., Ellis M. C., Kornberg T. B., Goodman C. S. Expression of engrailed proteins in arthropods, annelids, and chordates. Cell. 1989 Sep 8;58(5):955–968. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90947-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ray R. P., Arora K., Nüsslein-Volhard C., Gelbart W. M. The control of cell fate along the dorsal-ventral axis of the Drosophila embryo. Development. 1991 Sep;113(1):35–54. doi: 10.1242/dev.113.1.35. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth S., Hiromi Y., Godt D., Nüsslein-Volhard C. cactus, a maternal gene required for proper formation of the dorsoventral morphogen gradient in Drosophila embryos. Development. 1991 Jun;112(2):371–388. doi: 10.1242/dev.112.2.371. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth S., Stein D., Nüsslein-Volhard C. A gradient of nuclear localization of the dorsal protein determines dorsoventral pattern in the Drosophila embryo. Cell. 1989 Dec 22;59(6):1189–1202. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90774-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin G. M., Spradling A. C. Genetic transformation of Drosophila with transposable element vectors. Science. 1982 Oct 22;218(4570):348–353. doi: 10.1126/science.6289436. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rushlow C. A., Han K., Manley J. L., Levine M. The graded distribution of the dorsal morphogen is initiated by selective nuclear transport in Drosophila. Cell. 1989 Dec 22;59(6):1165–1177. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90772-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rushlow C., Doyle H., Hoey T., Levine M. Molecular characterization of the zerknüllt region of the Antennapedia gene complex in Drosophila. Genes Dev. 1987 Dec;1(10):1268–1279. doi: 10.1101/gad.1.10.1268. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sauer F., Jäckle H. Concentration-dependent transcriptional activation or repression by Krüppel from a single binding site. Nature. 1991 Oct 10;353(6344):563–566. doi: 10.1038/353563a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt M. C., Zhou Q., Berk A. J. Sp1 activates transcription without enhancing DNA-binding activity of the TATA box factor. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Aug;9(8):3299–3307. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.8.3299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson P. Maternal-Zygotic Gene Interactions during Formation of the Dorsoventral Pattern in Drosophila Embryos. Genetics. 1983 Nov;105(3):615–632. doi: 10.1093/genetics/105.3.615. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- St Johnston R. D., Gelbart W. M. Decapentaplegic transcripts are localized along the dorsal-ventral axis of the Drosophila embryo. EMBO J. 1987 Sep;6(9):2785–2791. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02574.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steward R. Dorsal, an embryonic polarity gene in Drosophila, is homologous to the vertebrate proto-oncogene, c-rel. Science. 1987 Oct 30;238(4827):692–694. doi: 10.1126/science.3118464. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steward R. Relocalization of the dorsal protein from the cytoplasm to the nucleus correlates with its function. Cell. 1989 Dec 22;59(6):1179–1188. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90773-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun X. H., Baltimore D. An inhibitory domain of E12 transcription factor prevents DNA binding in E12 homodimers but not in E12 heterodimers. Cell. 1991 Jan 25;64(2):459–470. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90653-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tautz D., Pfeifle C. A non-radioactive in situ hybridization method for the localization of specific RNAs in Drosophila embryos reveals translational control of the segmentation gene hunchback. Chromosoma. 1989 Aug;98(2):81–85. doi: 10.1007/BF00291041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thisse C., Perrin-Schmitt F., Stoetzel C., Thisse B. Sequence-specific transactivation of the Drosophila twist gene by the dorsal gene product. Cell. 1991 Jun 28;65(7):1191–1201. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90014-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urban M. B., Baeuerle P. A. The role of the p50 and p65 subunits of NF-kappa B in the recognition of cognate sequences. New Biol. 1991 Mar;3(3):279–288. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]