Abstract
Superantigens are products of bacterial or viral origin which stimulate large numbers of T cells as a consequence of the interaction of particular V beta chains of the T cell receptor with class II major histocompatibility complex (MHC) molecules and superantigen on the stimulating cell. The Minor lymphocyte stimulatory (Mls) antigens, originally discovered as strong lymphocyte stimulatory determinants in vitro and subsequently shown to delete T cells expressing specific V beta chains during development, have recently been shown to be genetically linked to endogenous mouse mammary tumour viruses (MTVs). This stimulation is effectuated by an unidentified product encoded by an open reading frame (orf) present in the 3' long terminal repeat (LTR) of MTVs. Using in vitro translation in the presence of rough microsomal vesicles, we show that (i) the orf of MTV encodes a type II transmembrane glycoprotein (N-terminus intracellular, C-terminus extracytoplasmic), and (ii) a cotranslationally secreted orf protein is not produced. We have also isolated and sequenced several endogenous MTV orfs (MTV-1, MTV-6 and MTV-13) which are involved in the deletion of V beta-bearing T cells; each of these sequences are nearly identical to each other. These observations, together with sequence comparisons of several orf genes, lead to a model of action of viral superantigens.
Full text
PDF
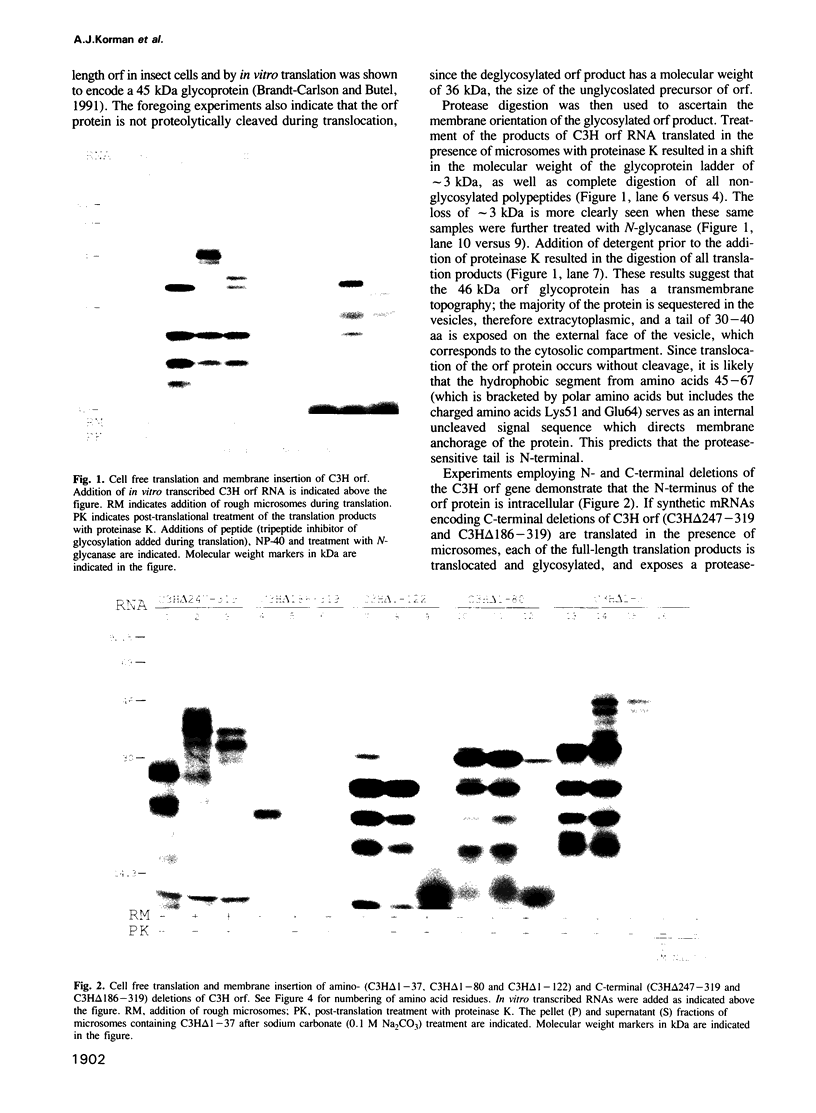



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abe R., Hodes R. J. T-cell recognition of minor lymphocyte stimulating (Mls) gene products. Annu Rev Immunol. 1989;7:683–708. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.07.040189.003343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Acha-Orbea H., Palmer E. Mls--a retrovirus exploits the immune system. Immunol Today. 1991 Oct;12(10):356–361. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(91)90066-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Acha-Orbea H., Shakhov A. N., Scarpellino L., Kolb E., Müller V., Vessaz-Shaw A., Fuchs R., Blöchlinger K., Rollini P., Billotte J. Clonal deletion of V beta 14-bearing T cells in mice transgenic for mammary tumour virus. Nature. 1991 Mar 21;350(6315):207–211. doi: 10.1038/350207a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blobel G., Dobberstein B. Transfer of proteins across membranes. II. Reconstitution of functional rough microsomes from heterologous components. J Cell Biol. 1975 Dec;67(3):852–862. doi: 10.1083/jcb.67.3.852. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brandt-Carlson C., Butel J. S. Detection and characterization of a glycoprotein encoded by the mouse mammary tumor virus long terminal repeat gene. J Virol. 1991 Nov;65(11):6051–6060. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.11.6051-6060.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cazenave P. A., Marche P. N., Jouvin-Marche E., Voegtlé D., Bonhomme F., Bandeira A., Coutinho A. V beta 17 gene polymorphism in wild-derived mouse strains: two amino acid substitutions in the V beta 17 region greatly alter T cell receptor specificity. Cell. 1990 Nov 16;63(4):717–728. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90138-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choi Y., Kappler J. W., Marrack P. A superantigen encoded in the open reading frame of the 3' long terminal repeat of mouse mammary tumour virus. Nature. 1991 Mar 21;350(6315):203–207. doi: 10.1038/350203a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crouse C. A., Pauley R. J. Molecular cloning and sequencing of the MTV-1 LTR: evidence for a LTR sequence alteration. Virus Res. 1989 Feb;12(2):123–137. doi: 10.1016/0168-1702(89)90059-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickson C., Smith R., Peters G. In vitro synthesis of polypeptides encoded by the long terminal repeat region of mouse mammary tumour virus DNA. Nature. 1981 Jun 11;291(5815):511–513. doi: 10.1038/291511a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donehower L. A., Fleurdelys B., Hager G. L. Further evidence for the protein coding potential of the mouse mammary tumor virus long terminal repeat: nucleotide sequence of an endogenous proviral long terminal repeat. J Virol. 1983 Mar;45(3):941–949. doi: 10.1128/jvi.45.3.941-949.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dyson P. J., Knight A. M., Fairchild S., Simpson E., Tomonari K. Genes encoding ligands for deletion of V beta 11 T cells cosegregate with mammary tumour virus genomes. Nature. 1991 Feb 7;349(6309):531–532. doi: 10.1038/349531a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fasel N., Pearson K., Buetti E., Diggelmann H. The region of mouse mammary tumor virus DNA containing the long terminal repeat includes a long coding sequence and signals for hormonally regulated transcription. EMBO J. 1982;1(1):3–7. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01115.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Festenstein H. The Mls system. Transplant Proc. 1976 Sep;8(3):339–342. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frankel W. N., Rudy C., Coffin J. M., Huber B. T. Linkage of Mls genes to endogenous mammary tumour viruses of inbred mice. Nature. 1991 Feb 7;349(6309):526–528. doi: 10.1038/349526a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fry A. M., Matis L. A. Self-tolerance alters T-cell receptor expression in an antigen-specific MHC restricted immune response. Nature. 1988 Oct 27;335(6193):830–832. doi: 10.1038/335830a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujiki Y., Hubbard A. L., Fowler S., Lazarow P. B. Isolation of intracellular membranes by means of sodium carbonate treatment: application to endoplasmic reticulum. J Cell Biol. 1982 Apr;93(1):97–102. doi: 10.1083/jcb.93.1.97. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaspar M. L., Meo T., Bourgarel P., Guenet J. L., Tosi M. A single base deletion in the Tfm androgen receptor gene creates a short-lived messenger RNA that directs internal translation initiation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Oct 1;88(19):8606–8610. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.19.8606. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herman A., Kappler J. W., Marrack P., Pullen A. M. Superantigens: mechanism of T-cell stimulation and role in immune responses. Annu Rev Immunol. 1991;9:745–772. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.09.040191.003525. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janeway C. A., Jr, Conrad P. J., Tite J., Jones B., Murphy D. B. Efficiency of antigen presentation differs in mice differing at the Mls locus. Nature. 1983 Nov 3;306(5938):80–82. doi: 10.1038/306080a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janeway C. A., Jr Self superantigens? Cell. 1990 Nov 16;63(4):659–661. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90130-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kappler J. W., Staerz U., White J., Marrack P. C. Self-tolerance eliminates T cells specific for Mls-modified products of the major histocompatibility complex. Nature. 1988 Mar 3;332(6159):35–40. doi: 10.1038/332035a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King L. B., Lund F. E., White D. A., Sharma S., Corley R. B. Molecular events in B lymphocyte differentiation. Inducible expression of the endogenous mouse mammary tumor proviral gene, Mtv-9. J Immunol. 1990 Apr 15;144(8):3218–3227. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuo W. L., Vilander L. R., Huang M., Peterson D. O. A transcriptionally defective long terminal repeat within an endogenous copy of mouse mammary tumor virus proviral DNA. J Virol. 1988 Jul;62(7):2394–2402. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.7.2394-2402.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsson-Sciard E. L., Spetz-Hagberg A. L., Casrouge A., Kourilsky P. Analysis of T cell receptor V beta gene usage in primary mixed lymphocyte reactions: evidence for directive usage by different antigen-presenting cells and Mls-like determinants on T cell blasts. Eur J Immunol. 1990 Jun;20(6):1223–1229. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830200605. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lau J. T., Welply J. K., Shenbagamurthi P., Naider F., Lennarz W. J. Substrate recognition by oligosaccharyl transferase. Inhibition of co-translational glycosylation by acceptor peptides. J Biol Chem. 1983 Dec 25;258(24):15255–15260. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipp J., Dobberstein B. The membrane-spanning segment of invariant chain (I gamma) contains a potentially cleavable signal sequence. Cell. 1986 Sep 26;46(7):1103–1112. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90710-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacDonald H. R., Schneider R., Lees R. K., Howe R. C., Acha-Orbea H., Festenstein H., Zinkernagel R. M., Hengartner H. T-cell receptor V beta use predicts reactivity and tolerance to Mlsa-encoded antigens. Nature. 1988 Mar 3;332(6159):40–45. doi: 10.1038/332040a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Majors J. E., Varmus H. E. Nucleotide sequencing of an apparent proviral copy of env mRNA defines determinants of expression of the mouse mammary tumor virus env gene. J Virol. 1983 Sep;47(3):495–504. doi: 10.1128/jvi.47.3.495-504.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marrack P., Kappler J. The staphylococcal enterotoxins and their relatives. Science. 1990 May 11;248(4956):705–711. doi: 10.1126/science.2185544. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marrack P., Kushnir E., Kappler J. A maternally inherited superantigen encoded by a mammary tumour virus. Nature. 1991 Feb 7;349(6309):524–526. doi: 10.1038/349524a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mecheri S., Edidin M., Dannecker G., Mittler R. S., Hoffmann M. K. Immunogenic Ia-binding peptides immobilize the Ia molecule and facilitate its aggregation on the B cell membrane. Control by the M1s-1 gene. J Immunol. 1990 Feb 15;144(4):1361–1368. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore R., Dixon M., Smith R., Peters G., Dickson C. Complete nucleotide sequence of a milk-transmitted mouse mammary tumor virus: two frameshift suppression events are required for translation of gag and pol. J Virol. 1987 Feb;61(2):480–490. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.2.480-490.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pullen A. M., Bill J., Kubo R. T., Marrack P., Kappler J. W. Analysis of the interaction site for the self superantigen Mls-1a on T cell receptor V beta. J Exp Med. 1991 May 1;173(5):1183–1192. doi: 10.1084/jem.173.5.1183. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pullen A. M., Marrack P., Kappler J. W. Evidence that Mls-2 antigens which delete V beta 3+ T cells are controlled by multiple genes. J Immunol. 1989 May 1;142(9):3033–3037. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pullen A. M., Marrack P., Kappler J. W. The T-cell repertoire is heavily influenced by tolerance to polymorphic self-antigens. Nature. 1988 Oct 27;335(6193):796–801. doi: 10.1038/335796a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Racevskis J. Expression of the protein product of the mouse mammary tumor virus long terminal repeat gene in phorbol ester-treated mouse T-cell-leukemia cells. J Virol. 1986 May;58(2):441–449. doi: 10.1128/jvi.58.2.441-449.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Racevskis J., Prakash O. Proteins encoded by the long terminal repeat region of mouse mammary tumor virus: identification by hybrid-selected translation. J Virol. 1984 Sep;51(3):604–610. doi: 10.1128/jvi.51.3.604-610.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Speiser D. E., Schneider R., Hengartner H., MacDonald H. R., Zinkernagel R. M. Clonal deletion of self-reactive T cells in irradiation bone marrow chimeras and neonatally tolerant mice. Evidence for intercellular transfer of Mlsa. J Exp Med. 1989 Aug 1;170(2):595–600. doi: 10.1084/jem.170.2.595. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webb S. R., Okamoto A., Ron Y., Sprent J. Restricted tissue distribution of Mlsa determinants. Stimulation of Mlsa-reactive T cells by B cells but not by dendritic cells or macrophages. J Exp Med. 1989 Jan 1;169(1):1–12. doi: 10.1084/jem.169.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webb S. R., Sprent J. Induction of neonatal tolerance to Mlsa antigens by CD8+ T cells. Science. 1990 Jun 29;248(4963):1643–1646. doi: 10.1126/science.1973003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webb S., Morris C., Sprent J. Extrathymic tolerance of mature T cells: clonal elimination as a consequence of immunity. Cell. 1990 Dec 21;63(6):1249–1256. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90420-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodland D. L., Happ M. P., Gollob K. J., Palmer E. An endogenous retrovirus mediating deletion of alpha beta T cells? Nature. 1991 Feb 7;349(6309):529–530. doi: 10.1038/349529a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodland D., Happ M. P., Bill J., Palmer E. Requirement for cotolerogenic gene products in the clonal deletion of I-E reactive T cells. Science. 1990 Feb 23;247(4945):964–967. doi: 10.1126/science.1968289. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]