Abstract
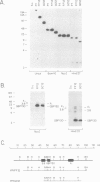
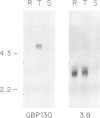
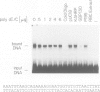
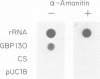
We have mapped Plasmodium falciparum erythrocytic stage transcription units on chromosome 10 in the vicinity of the gene encoding the glycophorin binding protein (GBP130) using yeast artificial chromosomes (YACs). Three erythrocytic stage transcription units are clustered in a 40 kb region. Two of these genes are closely linked, separated by less than 2 kb. Nuclear run-on data demonstrate that transcription of these two genes, though unidirectional, is monocistronic. Within this intergenic region are the sites at which transcription of the upstream gene terminates and the GBP130 gene initiates. These studies represent the first description of the minimal and necessary cis-acting elements for transcription termination and initiation in this protozoan parasite.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Burke D. T., Carle G. F., Olson M. V. Cloning of large segments of exogenous DNA into yeast by means of artificial chromosome vectors. Science. 1987 May 15;236(4803):806–812. doi: 10.1126/science.3033825. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Enea V., Ellis J., Zavala F., Arnot D. E., Asavanich A., Masuda A., Quakyi I., Nussenzweig R. S. DNA cloning of Plasmodium falciparum circumsporozoite gene: amino acid sequence of repetitive epitope. Science. 1984 Aug 10;225(4662):628–630. doi: 10.1126/science.6204384. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goman M., Langsley G., Hyde J. E., Yankovsky N. K., Zolg J. W., Scaife J. G. The establishment of genomic DNA libraries for the human malaria parasite Plasmodium falciparum and identification of individual clones by hybridisation. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1982 Jun;5(6):391–400. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(82)90012-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green E. D., Olson M. V. Systematic screening of yeast artificial-chromosome libraries by use of the polymerase chain reaction. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Feb;87(3):1213–1217. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.3.1213. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall R., Osland A., Hyde J. E., Simmons D. L., Hope I. A., Scaife J. G. Processing, polymorphism, and biological significance of P190, a major surface antigen of the erythrocytic forms of Plasmodium falciparum. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1984 Apr;11:61–80. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(84)90055-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kemp D. J., Cowman A. F., Walliker D. Genetic diversity in Plasmodium falciparum. Adv Parasitol. 1990;29:75–149. doi: 10.1016/s0065-308x(08)60105-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kochan J., Perkins M., Ravetch J. V. A tandemly repeated sequence determines the binding domain for an erythrocyte receptor binding protein of P. falciparum. Cell. 1986 Mar 14;44(5):689–696. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90834-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kutner S., Breuer W. V., Ginsburg H., Aley S. B., Cabantchik Z. I. Characterization of permeation pathways in the plasma membrane of human erythrocytes infected with early stages of Plasmodium falciparum: association with parasite development. J Cell Physiol. 1985 Dec;125(3):521–527. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041250323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langsley G., Hyde J. E., Goman M., Scaife J. G. Cloning and characterisation of the rRNA genes from the human malaria parasite Plasmodium falciparum. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Dec 20;11(24):8703–8717. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.24.8703. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis A. P. Sequence analysis upstream of the gene encoding the precursor to the major merozoite surface antigens of Plasmodium yoelii. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1990 Mar;39(2):285–288. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(90)90068-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loh E. Y., Elliott J. F., Cwirla S., Lanier L. L., Davis M. M. Polymerase chain reaction with single-sided specificity: analysis of T cell receptor delta chain. Science. 1989 Jan 13;243(4888):217–220. doi: 10.1126/science.2463672. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCormick M. K., Shero J. H., Cheung M. C., Kan Y. W., Hieter P. A., Antonarakis S. E. Construction of human chromosome 21-specific yeast artificial chromosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Dec;86(24):9991–9995. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.24.9991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nevins J. R. Isolation and analysis of nuclear RNA. Methods Enzymol. 1987;152:234–241. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)52025-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perkins M. Stage-dependent processing and localization of a Plasmodium falciparum protein of 130,000 molecular weight. Exp Parasitol. 1988 Feb;65(1):61–68. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(88)90107-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollack Y., Katzen A. L., Spira D. T., Golenser J. The genome of Plasmodium falciparum. I: DNA base composition. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Jan 22;10(2):539–546. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.2.539. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pologe L. G., Ravetch J. V. A chromosomal rearrangement in a P. falciparum histidine-rich protein gene is associated with the knobless phenotype. 1986 Jul 31-Aug 6Nature. 322(6078):474–477. doi: 10.1038/322474a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ravetch J. V., Kochan J., Perkins M. Isolation of the gene for a glycophorin-binding protein implicated in erythrocyte invasion by a malaria parasite. Science. 1985 Mar 29;227(4694):1593–1597. doi: 10.1126/science.3883491. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robson K. J., Jennings M. W. The structure of the calmodulin gene of Plasmodium falciparum. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1991 May;46(1):19–34. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(91)90195-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruiz i Altaba A., Ozaki L. S., Gwadz R. W., Godson G. N. Organization and expression of the Plasmodium knowlesi circumsporozoite antigen gene. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1987 Apr;23(3):233–245. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(87)90030-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreiber E., Matthias P., Müller M. M., Schaffner W. Rapid detection of octamer binding proteins with 'mini-extracts', prepared from a small number of cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Aug 11;17(15):6419–6419. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.15.6419. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz D. C., Cantor C. R. Separation of yeast chromosome-sized DNAs by pulsed field gradient gel electrophoresis. Cell. 1984 May;37(1):67–75. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90301-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trager W., Jensen J. B. Human malaria parasites in continuous culture. Science. 1976 Aug 20;193(4254):673–675. doi: 10.1126/science.781840. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trager W., Tershakovec M., Lyandvert L., Stanley H., Lanners N., Gubert E. Clones of the malaria parasite Plasmodium falciparum obtained by microscopic selection: their characterization with regard to knobs, chloroquine sensitivity, and formation of gametocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Oct;78(10):6527–6530. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.10.6527. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Triglia T., Kemp D. J. Large fragments of Plasmodium falciparum DNA can be stable when cloned in yeast artificial chromosomes. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1991 Feb;44(2):207–211. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(91)90006-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallach M. Efficient extraction and translation of Plasmodium falciparum messenger RNA. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1982 Dec;6(6):335–342. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(82)90023-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waters A. P., Syin C., McCutchan T. F. Developmental regulation of stage-specific ribosome populations in Plasmodium. Nature. 1989 Nov 23;342(6248):438–440. doi: 10.1038/342438a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber J. L. Molecular biology of malaria parasites. Exp Parasitol. 1988 Aug;66(2):143–170. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(88)90087-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiher H., König M., Gruss P. Multiple point mutations affecting the simian virus 40 enhancer. Science. 1983 Feb 11;219(4585):626–631. doi: 10.1126/science.6297005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wellems T. E., Howard R. J. Homologous genes encode two distinct histidine-rich proteins in a cloned isolate of Plasmodium falciparum. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Aug;83(16):6065–6069. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.16.6065. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wesseling J. G., Snijders P. J., van Someren P., Jansen J., Smits M. A., Schoenmakers J. G. Stage-specific expression and genomic organization of the actin genes of the malaria parasite Plasmodium falciparum. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1989 Jun 15;35(2):167–176. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(89)90119-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]