Abstract
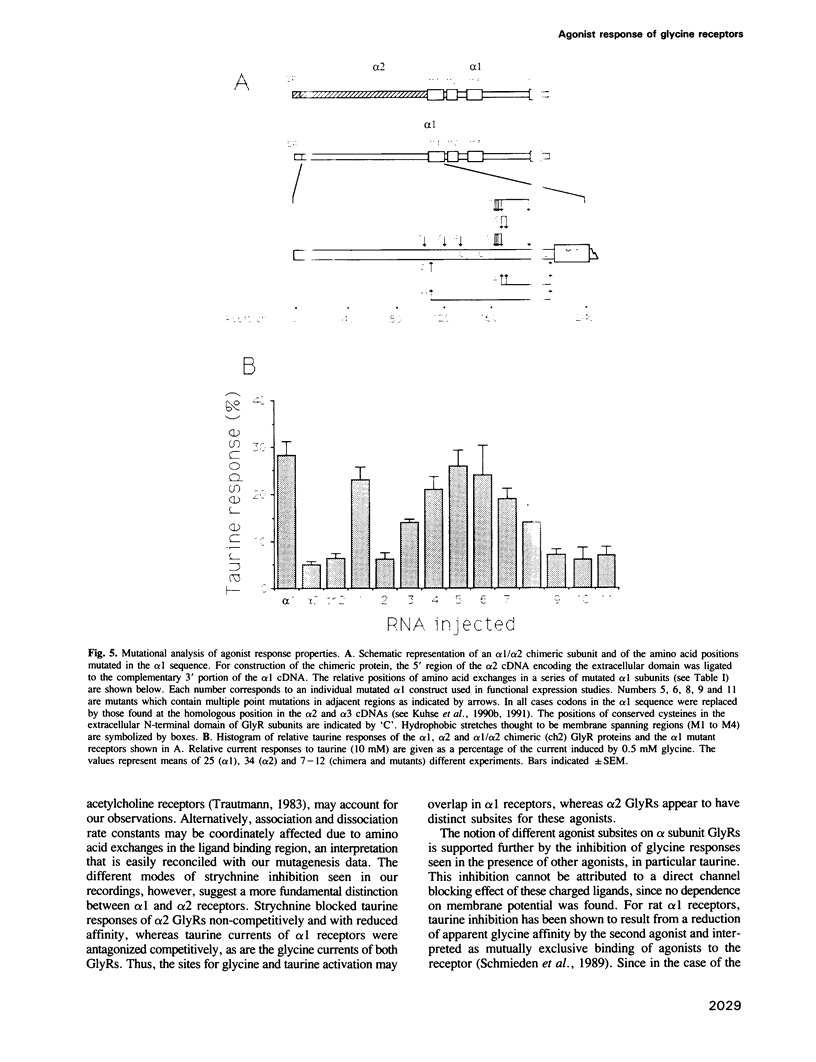
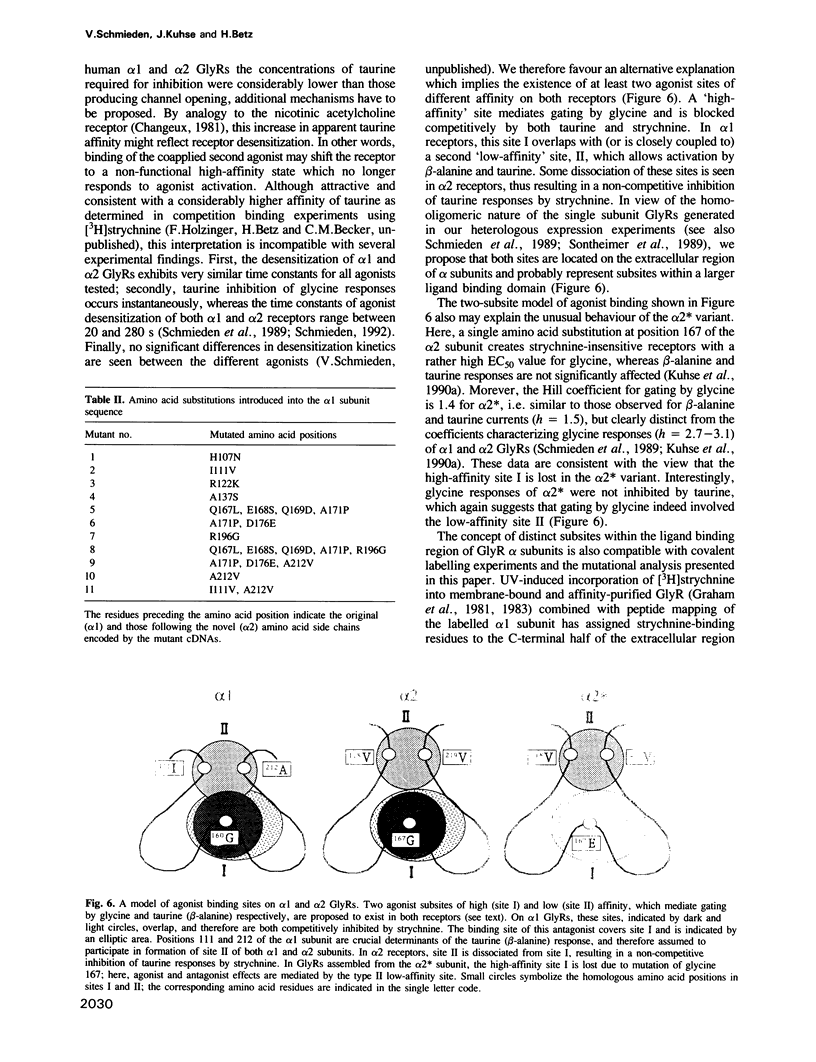
The inhibitory glycine receptor (GlyR) is a pentameric chloride channel protein which mediates postsynaptic inhibition in the mammalian central nervous system. In spinal cord, different GlyR isoforms originate from the sequential expression of developmentally regulated variants of the ligand binding alpha subunit. Here, neonatal alpha 2 and adult alpha 1 subunits are shown to generate GlyRs with distinct agonist activation profiles upon heterologous expression in Xenopus oocytes. Whereas alpha 1 receptors are efficiently gated by beta-alanine and taurine, alpha 2 GlyRs show only a low relative response to these agonists, which also display a reduced sensitivity to inhibition by the glycinergic antagonist strychnine. Construction of an alpha 2/alpha 1 subunit chimera and site-directed mutagenesis of the extracellular region of the alpha 1 sequence identified amino acid positions 111 and 212 as important determinants of taurine activation. Our results indicate the existence of distinct subsites for agonists on alpha 1 and alpha 2 GlyRs and suggest that the ligand binding pocket of these receptor proteins is formed from discontinuous domains of their extracellular region.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abramson S. N., Li Y., Culver P., Taylor P. An analog of lophotoxin reacts covalently with Tyr190 in the alpha-subunit of the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jul 25;264(21):12666–12672. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Akagi H., Hirai K., Hishinuma F. Cloning of a glycine receptor subtype expressed in rat brain and spinal cord during a specific period of neuronal development. FEBS Lett. 1991 Apr 9;281(1-2):160–166. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(91)80383-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Akagi H., Miledi R. Heterogeneity of glycine receptors and their messenger RNAs in rat brain and spinal cord. Science. 1988 Oct 14;242(4876):270–273. doi: 10.1126/science.2845580. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Akagi H., Patton D. E., Miledi R. Discrimination of heterogenous mRNAs encoding strychnine-sensitive glycine receptors in Xenopus oocytes by antisense oligonucleotides. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Oct;86(20):8103–8107. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.20.8103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Becker C. M., Hoch W., Betz H. Glycine receptor heterogeneity in rat spinal cord during postnatal development. EMBO J. 1988 Dec 1;7(12):3717–3726. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03255.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Betz H. Ligand-gated ion channels in the brain: the amino acid receptor superfamily. Neuron. 1990 Oct;5(4):383–392. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(90)90077-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Changeux J. P. The acetylcholine receptor: an "allosteric" membrane protein. Harvey Lect. 1979 1980;75:85–254. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cutler R. W., Dudzinski D. S. Regional changes in amino acid content in developing rat brain. J Neurochem. 1974 Nov;23(5):1005–1009. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1974.tb10752.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dennis M., Giraudat J., Kotzyba-Hibert F., Goeldner M., Hirth C., Chang J. Y., Lazure C., Chrétien M., Changeux J. P. Amino acids of the Torpedo marmorata acetylcholine receptor alpha subunit labeled by a photoaffinity ligand for the acetylcholine binding site. Biochemistry. 1988 Apr 5;27(7):2346–2357. doi: 10.1021/bi00407a016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galzi J. L., Revah F., Black D., Goeldner M., Hirth C., Changeux J. P. Identification of a novel amino acid alpha-tyrosine 93 within the cholinergic ligands-binding sites of the acetylcholine receptor by photoaffinity labeling. Additional evidence for a three-loop model of the cholinergic ligands-binding sites. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jun 25;265(18):10430–10437. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham D., Pfeiffer F., Betz H. Photoaffinity-labelling of the glycine receptor of rat spinal cord. Eur J Biochem. 1983 Apr 5;131(3):519–525. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1983.tb07292.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham D., Pfeiffer F., Betz H. UV light-induced cross-linking of strychnine to the glycine receptor of rat spinal cord membranes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1981 Oct 30;102(4):1330–1335. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(81)80157-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham D., Pfeiffer F., Simler R., Betz H. Purification and characterization of the glycine receptor of pig spinal cord. Biochemistry. 1985 Feb 12;24(4):990–994. doi: 10.1021/bi00325a027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grenningloh G., Pribilla I., Prior P., Multhaup G., Beyreuther K., Taleb O., Betz H. Cloning and expression of the 58 kd beta subunit of the inhibitory glycine receptor. Neuron. 1990 Jun;4(6):963–970. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(90)90149-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grenningloh G., Rienitz A., Schmitt B., Methfessel C., Zensen M., Beyreuther K., Gundelfinger E. D., Betz H. The strychnine-binding subunit of the glycine receptor shows homology with nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. Nature. 1987 Jul 16;328(6127):215–220. doi: 10.1038/328215a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grenningloh G., Schmieden V., Schofield P. R., Seeburg P. H., Siddique T., Mohandas T. K., Becker C. M., Betz H. Alpha subunit variants of the human glycine receptor: primary structures, functional expression and chromosomal localization of the corresponding genes. EMBO J. 1990 Mar;9(3):771–776. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08172.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoch W., Betz H., Becker C. M. Primary cultures of mouse spinal cord express the neonatal isoform of the inhibitory glycine receptor. Neuron. 1989 Sep;3(3):339–348. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(89)90258-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kao P. N., Karlin A. Acetylcholine receptor binding site contains a disulfide cross-link between adjacent half-cystinyl residues. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jun 25;261(18):8085–8088. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuhse J., Kuryatov A., Maulet Y., Malosio M. L., Schmieden V., Betz H. Alternative splicing generates two isoforms of the alpha 2 subunit of the inhibitory glycine receptor. FEBS Lett. 1991 May 20;283(1):73–77. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(91)80557-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuhse J., Schmieden V., Betz H. A single amino acid exchange alters the pharmacology of neonatal rat glycine receptor subunit. Neuron. 1990 Dec;5(6):867–873. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(90)90346-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuhse J., Schmieden V., Betz H. Identification and functional expression of a novel ligand binding subunit of the inhibitory glycine receptor. J Biol Chem. 1990 Dec 25;265(36):22317–22320. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langosch D., Becker C. M., Betz H. The inhibitory glycine receptor: a ligand-gated chloride channel of the central nervous system. Eur J Biochem. 1990 Nov 26;194(1):1–8. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1990.tb19419.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langosch D., Thomas L., Betz H. Conserved quaternary structure of ligand-gated ion channels: the postsynaptic glycine receptor is a pentamer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Oct;85(19):7394–7398. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.19.7394. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malosio M. L., Grenningloh G., Kuhse J., Schmieden V., Schmitt B., Prior P., Betz H. Alternative splicing generates two variants of the alpha 1 subunit of the inhibitory glycine receptor. J Biol Chem. 1991 Feb 5;266(4):2048–2053. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malosio M. L., Marquèze-Pouey B., Kuhse J., Betz H. Widespread expression of glycine receptor subunit mRNAs in the adult and developing rat brain. EMBO J. 1991 Sep;10(9):2401–2409. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07779.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfeiffer F., Graham D., Betz H. Purification by affinity chromatography of the glycine receptor of rat spinal cord. J Biol Chem. 1982 Aug 25;257(16):9389–9393. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfeiffer F., Simler R., Grenningloh G., Betz H. Monoclonal antibodies and peptide mapping reveal structural similarities between the subunits of the glycine receptor of rat spinal cord. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Nov;81(22):7224–7227. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.22.7224. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pritchett D. B., Seeburg P. H. gamma-Aminobutyric acid type A receptor point mutation increases the affinity of compounds for the benzodiazepine site. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Feb 15;88(4):1421–1425. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.4.1421. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruiz-Gómez A., Morato E., García-Calvo M., Valdivieso F., Mayor F., Jr Localization of the strychnine binding site on the 48-kilodalton subunit of the glycine receptor. Biochemistry. 1990 Jul 31;29(30):7033–7040. doi: 10.1021/bi00482a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmieden V., Grenningloh G., Schofield P. R., Betz H. Functional expression in Xenopus oocytes of the strychnine binding 48 kd subunit of the glycine receptor. EMBO J. 1989 Mar;8(3):695–700. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03428.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schröder S., Hoch W., Becker C. M., Grenningloh G., Betz H. Mapping of antigenic epitopes on the alpha 1 subunit of the inhibitory glycine receptor. Biochemistry. 1991 Jan 8;30(1):42–47. doi: 10.1021/bi00215a007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sontheimer H., Becker C. M., Pritchett D. B., Schofield P. R., Grenningloh G., Kettenmann H., Betz H., Seeburg P. H. Functional chloride channels by mammalian cell expression of rat glycine receptor subunit. Neuron. 1989 May;2(5):1491–1497. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(89)90195-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tokutomi N., Kaneda M., Akaike N. What confers specificity on glycine for its receptor site? Br J Pharmacol. 1989 Jun;97(2):353–360. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1989.tb11961.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trautmann A. A comparative study of the activation of the cholinergic receptor by various agonists. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1983 May 23;218(1211):241–251. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1983.0037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]





