Abstract
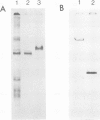
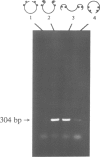
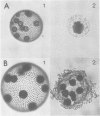
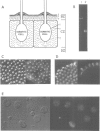
ISG is a sulphated, extracellular glycoprotein synthesized for only a few minutes in inverting Volvox embryos and inverting sperm cell packets. This control operates at the level of transcription. ISG has been characterized by studies of protein chemistry and electron microscopy. The primary structure of ISG has been derived from genomic DNA and cDNA. ISG is composed of a globular and a rod-shaped domain. The rod-shaped domain represents a member of the extensin family with numerous repeats of Ser-(Hyp)4-6 motifs. A synthetic decapeptide matching the C-terminal sequence is able to disaggregate the organism into individual cells. Immunofluorescence microscopy localizes ISG within the boundary zone of the ECM.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adair W. S., Steinmetz S. A., Mattson D. M., Goodenough U. W., Heuser J. E. Nucleated assembly of Chlamydomonas and Volvox cell walls. J Cell Biol. 1987 Nov;105(5):2373–2382. doi: 10.1083/jcb.105.5.2373. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ertl H., Mengele R., Wenzl S., Engel J., Sumper M. The extracellular matrix of Volvox carteri: molecular structure of the cellular compartment. J Cell Biol. 1989 Dec;109(6 Pt 2):3493–3501. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.6.3493. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frischauf A. M., Lehrach H., Poustka A., Murray N. Lambda replacement vectors carrying polylinker sequences. J Mol Biol. 1983 Nov 15;170(4):827–842. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80190-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green K. J., Viamontes G. I., Kirk D. L. Mechanism of formation, ultrastructure, and function of the cytoplasmic bridge system during morphogenesis in Volvox. J Cell Biol. 1981 Dec;91(3 Pt 1):756–769. doi: 10.1083/jcb.91.3.756. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirk D. L., Birchem R., King N. The extracellular matrix of Volvox: a comparative study and proposed system of nomenclature. J Cell Sci. 1986 Feb;80:207–231. doi: 10.1242/jcs.80.1.207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirk M. M., Kirk D. L. Translational regulation of protein synthesis, in response to light, at a critical stage of Volvox development. Cell. 1985 Jun;41(2):419–428. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80015-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mort A. J., Lamport D. T. Anhydrous hydrogen fluoride deglycosylates glycoproteins. Anal Biochem. 1977 Oct;82(2):289–309. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(77)90165-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mörgelin M., Paulsson M., Hardingham T. E., Heinegård D., Engel J. Cartilage proteoglycans. Assembly with hyaluronate and link protein as studied by electron microscopy. Biochem J. 1988 Jul 1;253(1):175–185. doi: 10.1042/bj2530175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts K., Grief C., Hills G. J., Shaw P. J. Cell wall glycoproteins: structure and function. J Cell Sci Suppl. 1985;2:105–127. doi: 10.1242/jcs.1985.supplement_2.6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Showalter A. M., Bell J. N., Cramer C. L., Bailey J. A., Varner J. E., Lamb C. J. Accumulation of hydroxyproline-rich glycoprotein mRNAs in response to fungal elicitor and infection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Oct;82(19):6551–6555. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.19.6551. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starr R. C. Control of differentiation in Volvox. Symp Soc Dev Biol. 1970;29:59–100. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-395534-0.50009-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starr R. C., Jaenicke L. Purification and characterization of the hormone initiating sexual morphogenesis in Volvox carteri f. nagariensis Iyengar. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Apr;71(4):1050–1054. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.4.1050. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Studier F. W., Rosenberg A. H., Dunn J. J., Dubendorff J. W. Use of T7 RNA polymerase to direct expression of cloned genes. Methods Enzymol. 1990;185:60–89. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(90)85008-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tschochner H., Lottspeich F., Sumper M. The sexual inducer of Volvox carteri: purification, chemical characterization and identification of its gene. EMBO J. 1987 Aug;6(8):2203–2207. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02491.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Viamontes G. I., Fochtmann L. J., Kirk D. L. Morphogenesis in Volvox: analysis of critical variables. Cell. 1979 Jul;17(3):537–550. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90262-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Viamontes G. I., Kirk D. L. Cell shape changes and the mechanism of inversion in Volvox. J Cell Biol. 1977 Dec;75(3):719–730. doi: 10.1083/jcb.75.3.719. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wenzl S., Sumper M. A novel glycosphingolipid that may participate in embryo inversion in Volvox carteri. Cell. 1986 Aug 15;46(4):633–639. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90889-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woessner J. P., Goodenough U. W. Molecular characterization of a zygote wall protein: an extensin-like molecule in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Plant Cell. 1989 Sep;1(9):901–911. doi: 10.1105/tpc.1.9.901. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]