Abstract
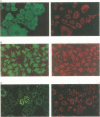
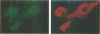
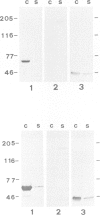
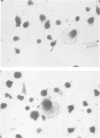
We have identified a cDNA coding for a protein of 160 kDa which is expressed in in vitro cultured human peripheral blood monocytes. The predicted amino acid sequence contains an alpha-helical rod domain possessing features characteristic of intermediate filament proteins. However, the immunocytochemical staining pattern, abundance and solubility in Triton X-100/high salt buffers suggest that this protein is probably only associated with the intermediate filament network and represents a new type of intermediate filament associated protein. In a survey of normal, inflammatory and human tumour tissue samples, this protein, which we have named restin, was found to be highly expressed in Reed-Sternberg cells, the tumoral cells diagnostic for Hodgkin's disease. We suggest that restin overexpression may be a contributing factor in the progression of Hodgkin's disease.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Albers K., Fuchs E. Expression of mutant keratin cDNAs in epithelial cells reveals possible mechanisms for initiation and assembly of intermediate filaments. J Cell Biol. 1989 Apr;108(4):1477–1493. doi: 10.1083/jcb.108.4.1477. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Asselbergs F. A., Will H., Wingfield P., Hirschi M. A recombinant Chinese hamster ovary cell line containing a 300-fold amplified tetramer of the hepatitis B genome together with a double selection marker expresses high levels of viral protein. J Mol Biol. 1986 Jun 5;189(3):401–411. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90312-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ben-Ze'ev A. Differential control of cytokeratins and vimentin synthesis by cell-cell contact and cell spreading in cultured epithelial cells. J Cell Biol. 1984 Oct;99(4 Pt 1):1424–1433. doi: 10.1083/jcb.99.4.1424. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolen J. W., McNutt M. A. Cytoskeletal intermediate filaments: practical applications of intermediate filament analysis. Ultrastruct Pathol. 1987;11(2-3):175–189. doi: 10.3109/01913128709048323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Botteri F. M., Ballmer-Hofer K., Rajput B., Nagamine Y. Disruption of cytoskeletal structures results in the induction of the urokinase-type plasminogen activator gene expression. J Biol Chem. 1990 Aug 5;265(22):13327–13334. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourne H. R. Colon cancer. Consider the coiled coil.... Nature. 1991 May 16;351(6323):188–190. doi: 10.1038/351188a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourne H. R. Colon cancer. Suppression with a difference. Nature. 1991 Oct 24;353(6346):696–697. doi: 10.1038/353696b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown K. D., Binder L. I. Identification and characterization of a novel mammalian intermediate filament-associated protein. Cell Motil Cytoskeleton. 1990;17(1):19–33. doi: 10.1002/cm.970170105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brüggen J., Sorg C. Detection of phenotypic differences on human malignant melanoma lines and their variant sublines with monoclonal antibodies. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 1983;15(3):200–205. doi: 10.1007/BF00199165. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burmeister G., Tarcsay L., Sorg C. Generation and characterization of a monoclonal antibody (1C5) to human migration inhibitory factor (MIF). Immunobiology. 1986 Jul;171(4-5):461–474. doi: 10.1016/S0171-2985(86)80077-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cabral F., Gottesman M. M., Zimmerman S. B., Steinert P. M. Intermediate filaments from Chinese hamster ovary cells contain a single protein. Comparison with more complex systems from baby hamster kidney and mouse epidermal cells. J Biol Chem. 1981 Feb 10;256(3):1428–1431. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carbone A., Gloghini A., Volpe R., Boiocchi M. Anti-vimentin antibody reactivity with Reed-Sternberg cells of Hodgkin's disease. Virchows Arch A Pathol Anat Histopathol. 1990;417(1):43–48. doi: 10.1007/BF01600108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou Y. H., Rosevear E., Goldman R. D. Phosphorylation and disassembly of intermediate filaments in mitotic cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Mar;86(6):1885–1889. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.6.1885. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coggi G., Dell'Orto P., Braidotti P., Coggi A., Viale G. Coexpression of intermediate filaments in normal and neoplastic human tissues: a reappraisal. Ultrastruct Pathol. 1989 Sep-Dec;13(5-6):501–514. doi: 10.3109/01913128909074533. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dale B. A., Gown A. M., Fleckman P., Kimball J. R., Resing K. A. Characterization of two monoclonal antibodies to human epidermal keratohyalin: reactivity with filaggrin and related proteins. J Invest Dermatol. 1987 Mar;88(3):306–313. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12466185. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dessev G., Iovcheva C., Tasheva B., Goldman R. Protein kinase activity associated with the nuclear lamina. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 May;85(9):2994–2998. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.9.2994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorsch-Häsler K., Keil G. M., Weber F., Jasin M., Schaffner W., Koszinowski U. H. A long and complex enhancer activates transcription of the gene coding for the highly abundant immediate early mRNA in murine cytomegalovirus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(24):8325–8329. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.24.8325. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrari S., Battini R., Kaczmarek L., Rittling S., Calabretta B., de Riel J. K., Philiponis V., Wei J. F., Baserga R. Coding sequence and growth regulation of the human vimentin gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Nov;6(11):3614–3620. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.11.3614. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fliegner K. H., Ching G. Y., Liem R. K. The predicted amino acid sequence of alpha-internexin is that of a novel neuronal intermediate filament protein. EMBO J. 1990 Mar;9(3):749–755. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08169.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foisner R., Wiche G. Intermediate filament-associated proteins. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1991 Feb;3(1):75–81. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(91)90168-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franke W. W., Schmid E., Osborn M., Weber K. Different intermediate-sized filaments distinguished by immunofluorescence microscopy. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Oct;75(10):5034–5038. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.10.5034. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franke W. W., Schmid E., Osborn M., Weber K. Intermediate-sized filaments of human endothelial cells. J Cell Biol. 1979 Jun;81(3):570–580. doi: 10.1083/jcb.81.3.570. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franke W. W., Weber K., Osborn M., Schmid E., Freudenstein C. Antibody to prekeratin. Decoration of tonofilament like arrays in various cells of epithelial character. Exp Cell Res. 1978 Oct 15;116(2):429–445. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(78)90466-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gabbiani G., Kapanci Y., Barazzone P., Franke W. W. Immunochemical identification of intermediate-sized filaments in human neoplastic cells. A diagnostic aid for the surgical pathologist. Am J Pathol. 1981 Sep;104(3):206–216. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gard D. L., Bell P. B., Lazarides E. Coexistence of desmin and the fibroblastic intermediate filament subunit in muscle and nonmuscle cells: identification and comparative peptide analysis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Aug;76(8):3894–3898. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.8.3894. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geisler N., Weber K. Amino acid sequence data on glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFA); implications for the subdivision of intermediate filaments into epithelial and non-epithelial members. EMBO J. 1983;2(11):2059–2063. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01700.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Georgatos S. D., Blobel G. Lamin B constitutes an intermediate filament attachment site at the nuclear envelope. J Cell Biol. 1987 Jul;105(1):117–125. doi: 10.1083/jcb.105.1.117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Georgatos S. D., Marchesi V. T. The binding of vimentin to human erythrocyte membranes: a model system for the study of intermediate filament-membrane interactions. J Cell Biol. 1985 Jun;100(6):1955–1961. doi: 10.1083/jcb.100.6.1955. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Georgatos S. D., Weaver D. C., Marchesi V. T. Site specificity in vimentin-membrane interactions: intermediate filament subunits associate with the plasma membrane via their head domains. J Cell Biol. 1985 Jun;100(6):1962–1967. doi: 10.1083/jcb.100.6.1962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldman J. E., Schaumburg H. H., Norton W. T. Isolation and characterization of glial filaments from human brain. J Cell Biol. 1978 Aug;78(2):426–440. doi: 10.1083/jcb.78.2.426. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groden J., Thliveris A., Samowitz W., Carlson M., Gelbert L., Albertsen H., Joslyn G., Stevens J., Spirio L., Robertson M. Identification and characterization of the familial adenomatous polyposis coli gene. Cell. 1991 Aug 9;66(3):589–600. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90021-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grover A., Oshima R. G., Adamson E. D. Epithelial layer formation in differentiating aggregates of F9 embryonal carcinoma cells. J Cell Biol. 1983 Jun;96(6):1690–1696. doi: 10.1083/jcb.96.6.1690. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hass R., Giese G., Meyer G., Hartmann A., Dörk T., Köhler L., Resch K., Traub P., Goppelt-Strübe M. Differentiation and retrodifferentiation of U937 cells: reversible induction and suppression of intermediate filament protein synthesis. Eur J Cell Biol. 1990 Apr;51(2):265–271. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hynes R. O., Destree A. T. 10 nm filaments in normal and transformed cells. Cell. 1978 Jan;13(1):151–163. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90146-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones D. B. The histogenesis of the Reed-Sternberg cell and its mononuclear counterparts. J Pathol. 1987 Mar;151(3):191–195. doi: 10.1002/path.1711510306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joslyn G., Carlson M., Thliveris A., Albertsen H., Gelbert L., Samowitz W., Groden J., Stevens J., Spirio L., Robertson M. Identification of deletion mutations and three new genes at the familial polyposis locus. Cell. 1991 Aug 9;66(3):601–613. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90022-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kemp B. E., Pearson R. B. Protein kinase recognition sequence motifs. Trends Biochem Sci. 1990 Sep;15(9):342–346. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(90)90073-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinzler K. W., Nilbert M. C., Su L. K., Vogelstein B., Bryan T. M., Levy D. B., Smith K. J., Preisinger A. C., Hedge P., McKechnie D. Identification of FAP locus genes from chromosome 5q21. Science. 1991 Aug 9;253(5020):661–665. doi: 10.1126/science.1651562. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Köhler G., Milstein C. Continuous cultures of fused cells secreting antibody of predefined specificity. Nature. 1975 Aug 7;256(5517):495–497. doi: 10.1038/256495a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langan T. A. Isolation of histone kinases. Methods Cell Biol. 1978;19:143–152. doi: 10.1016/s0091-679x(08)60019-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazarides E. Intermediate filaments as mechanical integrators of cellular space. Nature. 1980 Jan 17;283(5744):249–256. doi: 10.1038/283249a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehto V. P., Hovi T., Vartio T., Badley R. A., Virtanen I. Reorganization of cytoskeletal and contractile elements during transition of human monocytes into adherent macrophages. Lab Invest. 1982 Oct;47(4):391–399. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lendahl U., Zimmerman L. B., McKay R. D. CNS stem cells express a new class of intermediate filament protein. Cell. 1990 Feb 23;60(4):585–595. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90662-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy E., Liem R. K., D'Eustachio P., Cowan N. J. Structure and evolutionary origin of the gene encoding mouse NF-M, the middle-molecular-mass neurofilament protein. Eur J Biochem. 1987 Jul 1;166(1):71–77. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1987.tb13485.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis S. A., Balcarek J. M., Krek V., Shelanski M., Cowan N. J. Sequence of a cDNA clone encoding mouse glial fibrillary acidic protein: structural conservation of intermediate filaments. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 May;81(9):2743–2746. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.9.2743. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liem R. K., Yen S. H., Salomon G. D., Shelanski M. L. Intermediate filaments in nervous tissues. J Cell Biol. 1978 Dec;79(3):637–645. doi: 10.1083/jcb.79.3.637. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKeon F. D., Kirschner M. W., Caput D. Homologies in both primary and secondary structure between nuclear envelope and intermediate filament proteins. Nature. 1986 Feb 6;319(6053):463–468. doi: 10.1038/319463a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mellon P., Parker V., Gluzman Y., Maniatis T. Identification of DNA sequences required for transcription of the human alpha 1-globin gene in a new SV40 host-vector system. Cell. 1981 Dec;27(2 Pt 1):279–288. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90411-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miettinen M., Lehto V. P., Virtanen I. Antibodies to intermediate filament proteins in the diagnosis and classification of human tumors. Ultrastruct Pathol. 1984;7(2-3):83–107. doi: 10.3109/01913128409141467. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myers M. W., Lazzarini R. A., Lee V. M., Schlaepfer W. W., Nelson D. L. The human mid-size neurofilament subunit: a repeated protein sequence and the relationship of its gene to the intermediate filament gene family. EMBO J. 1987 Jun;6(6):1617–1626. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02409.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Napolitano E. W., Chin S. S., Colman D. R., Liem R. K. Complete amino acid sequence and in vitro expression of rat NF-M, the middle molecular weight neurofilament protein. J Neurosci. 1987 Aug;7(8):2590–2599. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen P. J., McMaster G. K., Trachsel H. Cloning of eukaryotic protein synthesis initiation factor genes: isolation and characterization of cDNA clones encoding factor eIF-4A. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Oct 11;13(19):6867–6880. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.19.6867. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishisho I., Nakamura Y., Miyoshi Y., Miki Y., Ando H., Horii A., Koyama K., Utsunomiya J., Baba S., Hedge P. Mutations of chromosome 5q21 genes in FAP and colorectal cancer patients. Science. 1991 Aug 9;253(5020):665–669. doi: 10.1126/science.1651563. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Odink K., Cerletti N., Brüggen J., Clerc R. G., Tarcsay L., Zwadlo G., Gerhards G., Schlegel R., Sorg C. Two calcium-binding proteins in infiltrate macrophages of rheumatoid arthritis. Nature. 1987 Nov 5;330(6143):80–82. doi: 10.1038/330080a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osborn M., Weber K. Tumor diagnosis by intermediate filament typing: a novel tool for surgical pathology. Lab Invest. 1983 Apr;48(4):372–394. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oshima R. G., Millán J. L., Ceceña G. Comparison of mouse and human keratin 18: a component of intermediate filaments expressed prior to implantation. Differentiation. 1986;33(1):61–68. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-0436.1986.tb00411.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramaekers F. C., Puts J. J., Kant A., Moesker O., Jap P. H., Vooijs G. P. Use of antibodies to intermediate filaments in the characterization of human tumors. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1982;46(Pt 1):331–339. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1982.046.01.034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raphael K. A., Marshall R. C., Pennycuik P. R. Protein and amino acid composition of hair from mice carrying the naked (N) gene. Genet Res. 1984 Aug;44(1):29–38. doi: 10.1017/s0016672300026227. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robson R. M. Intermediate filaments. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1989 Feb;1(1):36–43. doi: 10.1016/s0955-0674(89)80034-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinert P. M., Liem R. K. Intermediate filament dynamics. Cell. 1990 Feb 23;60(4):521–523. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90651-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinert P. M., Parry D. A., Idler W. W., Johnson L. D., Steven A. C., Roop D. R. Amino acid sequences of mouse and human epidermal type II keratins of Mr 67,000 provide a systematic basis for the structural and functional diversity of the end domains of keratin intermediate filament subunits. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jun 10;260(11):7142–7149. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinert P. M., Roop D. R. Molecular and cellular biology of intermediate filaments. Annu Rev Biochem. 1988;57:593–625. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.57.070188.003113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suter L., Bröcker E. B., Brüggen J., Ruiter D. J., Sorg C. Heterogeneity of primary and metastatic human malignant melanoma as detected with monoclonal antibodies in cryostat sections of biopsies. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 1983;16(1):53–58. doi: 10.1007/BF00199906. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sémat A., Duprey P., Vasseur M., Darmon M. Mesenchymal-epithelial conversions induced by 5-azacytidine: appearance of cytokeratin Endo-A messenger RNA. Differentiation. 1986;31(1):61–66. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-0436.1986.tb00384.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson M. A., Ziff E. B. Structure of the gene encoding peripherin, an NGF-regulated neuronal-specific type III intermediate filament protein. Neuron. 1989 Jan;2(1):1043–1053. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(89)90228-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urlaub G., Chasin L. A. Isolation of Chinese hamster cell mutants deficient in dihydrofolate reductase activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jul;77(7):4216–4220. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.7.4216. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vorburger K., Lehner C. F., Kitten G. T., Eppenberger H. M., Nigg E. A. A second higher vertebrate B-type lamin. cDNA sequence determination and in vitro processing of chicken lamin B2. J Mol Biol. 1989 Aug 5;208(3):405–415. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90505-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber F., Schaffner W. Simian virus 40 enhancer increases RNA polymerase density within the linked gene. Nature. 1985 May 2;315(6014):75–77. doi: 10.1038/315075a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White J. R., Naccache P. H., Sha'afi R. I. The synthetic chemotactic peptide formyl-methionyl-leucyl-phenylalanine causes an increase in actin associated with the cytoskeleton in rabbit neutrophils. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1982 Oct 15;108(3):1144–1149. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(82)92120-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiche G., Becker B., Luber K., Weitzer G., Castañon M. J., Hauptmann R., Stratowa C., Stewart M. Cloning and sequencing of rat plectin indicates a 466-kD polypeptide chain with a three-domain structure based on a central alpha-helical coiled coil. J Cell Biol. 1991 Jul;114(1):83–99. doi: 10.1083/jcb.114.1.83. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood L., Theriault N., Vogeli G. Vimentin cDNA clones covering the complete intermediate-filament protein are found in an EHS tumor cDNA library. Gene. 1989 Mar 15;76(1):171–175. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(89)90020-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Koskull H., Virtanen I. Induction of cytokeratin expression in human mesenchymal cells. J Cell Physiol. 1987 Nov;133(2):321–329. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041330216. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]