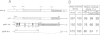Abstract
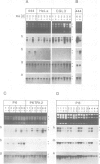
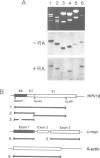
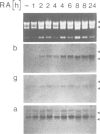
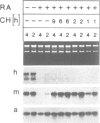
Human papillomavirus type 18 (HPV18) belongs to the group of genital papillomaviruses involved in the development of cervical carcinomas. Since retinoic acid (RA) is a key regulator of epithelial cell differentiation and a growth inhibitor in vitro of HPV18-positive HeLa cervical carcinoma cells, we have used HeLa and HeLa hybrid cells in order to analyse the effects of RA on expression of the HPV18 E6 and E7 oncogenes and of the cellular RA receptor genes RAR-beta and -gamma. We show here that RA down-regulates HPV18 mRNA levels apparently due to transcriptional repression. Transient cotransfection assays indicated that RARs negatively regulate the HPV18 upstream regulatory region and that the central enhancer can confer RA-dependent repression on a heterologous promoter. RA treatment resulted in induction of RAR-beta mRNA levels in non-tumorigenic HeLa hybrid cells, but not in tumorigenic hybrid segregants nor in HeLa cells. No alterations of the RAR-beta gene or of the HeLa RAR-beta promoter could be revealed by Southern and DNA sequence analysis, respectively. As determined by transient transfection assays, however, the RAR-beta control region was activated by RA more strongly in non-tumorigenic hybrid cells than in HeLa cells, thus indicating differences in trans-acting regulatory factors. Our data suggest that the RARs are potential negative regulators of HPV18 E6 and E7 gene expression, and that dysregulation of the RAR-beta gene either causatively contributes to or is an indicator of tumorigenicity in HeLa and HeLa hybrid cells.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baker C. C., Phelps W. C., Lindgren V., Braun M. J., Gonda M. A., Howley P. M. Structural and transcriptional analysis of human papillomavirus type 16 sequences in cervical carcinoma cell lines. J Virol. 1987 Apr;61(4):962–971. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.4.962-971.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbosa M. S., Schlegel R. The E6 and E7 genes of HPV-18 are sufficient for inducing two-stage in vitro transformation of human keratinocytes. Oncogene. 1989 Dec;4(12):1529–1532. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bosch F. X., Schwarz E., Boukamp P., Fusenig N. E., Bartsch D., zur Hausen H. Suppression in vivo of human papillomavirus type 18 E6-E7 gene expression in nontumorigenic HeLa X fibroblast hybrid cells. J Virol. 1990 Oct;64(10):4743–4754. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.10.4743-4754.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boshart M., Gissmann L., Ikenberg H., Kleinheinz A., Scheurlen W., zur Hausen H. A new type of papillomavirus DNA, its presence in genital cancer biopsies and in cell lines derived from cervical cancer. EMBO J. 1984 May;3(5):1151–1157. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01944.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brand N., Petkovich M., Krust A., Chambon P., de Thé H., Marchio A., Tiollais P., Dejean A. Identification of a second human retinoic acid receptor. Nature. 1988 Apr 28;332(6167):850–853. doi: 10.1038/332850a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brand N., Petkovich M., Krust A., Chambon P., de Thé H., Marchio A., Tiollais P., Dejean A. Identification of a second human retinoic acid receptor. Nature. 1988 Apr 28;332(6167):850–853. doi: 10.1038/332850a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brasier A. R., Tate J. E., Habener J. F. Optimized use of the firefly luciferase assay as a reporter gene in mammalian cell lines. Biotechniques. 1989 Nov-Dec;7(10):1116–1122. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bugge T. H., Pohl J., Lonnoy O., Stunnenberg H. G. RXR alpha, a promiscuous partner of retinoic acid and thyroid hormone receptors. EMBO J. 1992 Apr;11(4):1409–1418. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05186.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan W. K., Chong T., Bernard H. U., Klock G. Transcription of the transforming genes of the oncogenic human papillomavirus-16 is stimulated by tumor promotors through AP1 binding sites. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Feb 25;18(4):763–769. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.4.763. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen C., Okayama H. High-efficiency transformation of mammalian cells by plasmid DNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Aug;7(8):2745–2752. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.8.2745. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chong T., Apt D., Gloss B., Isa M., Bernard H. U. The enhancer of human papillomavirus type 16: binding sites for the ubiquitous transcription factors oct-1, NFA, TEF-2, NF1, and AP-1 participate in epithelial cell-specific transcription. J Virol. 1991 Nov;65(11):5933–5943. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.11.5933-5943.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chong T., Chan W. K., Bernard H. U. Transcriptional activation of human papillomavirus 16 by nuclear factor I, AP1, steroid receptors and a possibly novel transcription factor, PVF: a model for the composition of genital papillomavirus enhancers. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Feb 11;18(3):465–470. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.3.465. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choo K. B., Pan C. C., Han S. H. Integration of human papillomavirus type 16 into cellular DNA of cervical carcinoma: preferential deletion of the E2 gene and invariable retention of the long control region and the E6/E7 open reading frames. Virology. 1987 Nov;161(1):259–261. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(87)90195-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole S. T., Danos O. Nucleotide sequence and comparative analysis of the human papillomavirus type 18 genome. Phylogeny of papillomaviruses and repeated structure of the E6 and E7 gene products. J Mol Biol. 1987 Feb 20;193(4):599–608. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90343-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cripe T. P., Alderborn A., Anderson R. D., Parkkinen S., Bergman P., Haugen T. H., Pettersson U., Turek L. P. Transcriptional activation of the human papillomavirus-16 P97 promoter by an 88-nucleotide enhancer containing distinct cell-dependent and AP-1-responsive modules. New Biol. 1990 May;2(5):450–463. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cripe T. P., Haugen T. H., Turk J. P., Tabatabai F., Schmid P. G., 3rd, Dürst M., Gissmann L., Roman A., Turek L. P. Transcriptional regulation of the human papillomavirus-16 E6-E7 promoter by a keratinocyte-dependent enhancer, and by viral E2 trans-activator and repressor gene products: implications for cervical carcinogenesis. EMBO J. 1987 Dec 1;6(12):3745–3753. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02709.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crum C. P., Nuovo G., Friedman D., Silverstein S. J. Accumulation of RNA homologous to human papillomavirus type 16 open reading frames in genital precancers. J Virol. 1988 Jan;62(1):84–90. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.1.84-90.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crum C. P., Symbula M., Ward B. E. Topography of early HPV 16 transcription in high-grade genital precancers. Am J Pathol. 1989 Jun;134(6):1183–1188. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dani C., Blanchard J. M., Piechaczyk M., El Sabouty S., Marty L., Jeanteur P. Extreme instability of myc mRNA in normal and transformed human cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Nov;81(22):7046–7050. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.22.7046. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dion L. D., Gifford G. E. Retinoic acid induces a G1 cell cycle block in HeLa cells. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1980 Apr;163(4):510–514. doi: 10.3181/00379727-163-40806. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dürst M., Bosch F. X., Glitz D., Schneider A., zur Hausen H. Inverse relationship between human papillomavirus (HPV) type 16 early gene expression and cell differentiation in nude mouse epithelial cysts and tumors induced by HPV-positive human cell lines. J Virol. 1991 Feb;65(2):796–804. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.2.796-804.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eick D., Bornkamm G. W. Transcriptional arrest within the first exon is a fast control mechanism in c-myc gene expression. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Nov 11;14(21):8331–8346. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.21.8331. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elder J. T., Fisher G. J., Zhang Q. Y., Eisen D., Krust A., Kastner P., Chambon P., Voorhees J. J. Retinoic acid receptor gene expression in human skin. J Invest Dermatol. 1991 Apr;96(4):425–433. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12469889. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans R. M. The steroid and thyroid hormone receptor superfamily. Science. 1988 May 13;240(4854):889–895. doi: 10.1126/science.3283939. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garcia-Carranca A., Thierry F., Yaniv M. Interplay of viral and cellular proteins along the long control region of human papillomavirus type 18. J Virol. 1988 Nov;62(11):4321–4330. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.11.4321-4330.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gebert J. F., Moghal N., Frangioni J. V., Sugarbaker D. J., Neel B. G. High frequency of retinoic acid receptor beta abnormalities in human lung cancer. Oncogene. 1991 Oct;6(10):1859–1868. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giguere V., Ong E. S., Segui P., Evans R. M. Identification of a receptor for the morphogen retinoic acid. Nature. 1987 Dec 17;330(6149):624–629. doi: 10.1038/330624a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gius D., Grossman S., Bedell M. A., Laimins L. A. Inducible and constitutive enhancer domains in the noncoding region of human papillomavirus type 18. J Virol. 1988 Mar;62(3):665–672. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.3.665-672.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gloss B., Bernard H. U., Seedorf K., Klock G. The upstream regulatory region of the human papilloma virus-16 contains an E2 protein-independent enhancer which is specific for cervical carcinoma cells and regulated by glucocorticoid hormones. EMBO J. 1987 Dec 1;6(12):3735–3743. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02708.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawley-Nelson P., Vousden K. H., Hubbert N. L., Lowy D. R., Schiller J. T. HPV16 E6 and E7 proteins cooperate to immortalize human foreskin keratinocytes. EMBO J. 1989 Dec 1;8(12):3905–3910. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08570.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffmann B., Lehmann J. M., Zhang X. K., Hermann T., Husmann M., Graupner G., Pfahl M. A retinoic acid receptor-specific element controls the retinoic acid receptor-beta promoter. Mol Endocrinol. 1990 Nov;4(11):1727–1736. doi: 10.1210/mend-4-11-1727. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoppe-Seyler F., Butz K., zur Hausen H. Repression of the human papillomavirus type 18 enhancer by the cellular transcription factor Oct-1. J Virol. 1991 Oct;65(10):5613–5618. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.10.5613-5618.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houle B., Leduc F., Bradley W. E. Implication of RARB in epidermoid (Squamous) lung cancer. Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 1991 Sep;3(5):358–366. doi: 10.1002/gcc.2870030506. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howley P. M. Role of the human papillomaviruses in human cancer. Cancer Res. 1991 Sep 15;51(18 Suppl):5019s–5022s. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu L., Crowe D. L., Rheinwald J. G., Chambon P., Gudas L. J. Abnormal expression of retinoic acid receptors and keratin 19 by human oral and epidermal squamous cell carcinoma cell lines. Cancer Res. 1991 Aug 1;51(15):3972–3981. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hudson J. B., Bedell M. A., McCance D. J., Laiminis L. A. Immortalization and altered differentiation of human keratinocytes in vitro by the E6 and E7 open reading frames of human papillomavirus type 18. J Virol. 1990 Feb;64(2):519–526. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.2.519-526.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khandjian E. W., Méric C. A procedure for Northern blot analysis of native RNA. Anal Biochem. 1986 Nov 15;159(1):227–232. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(86)90332-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
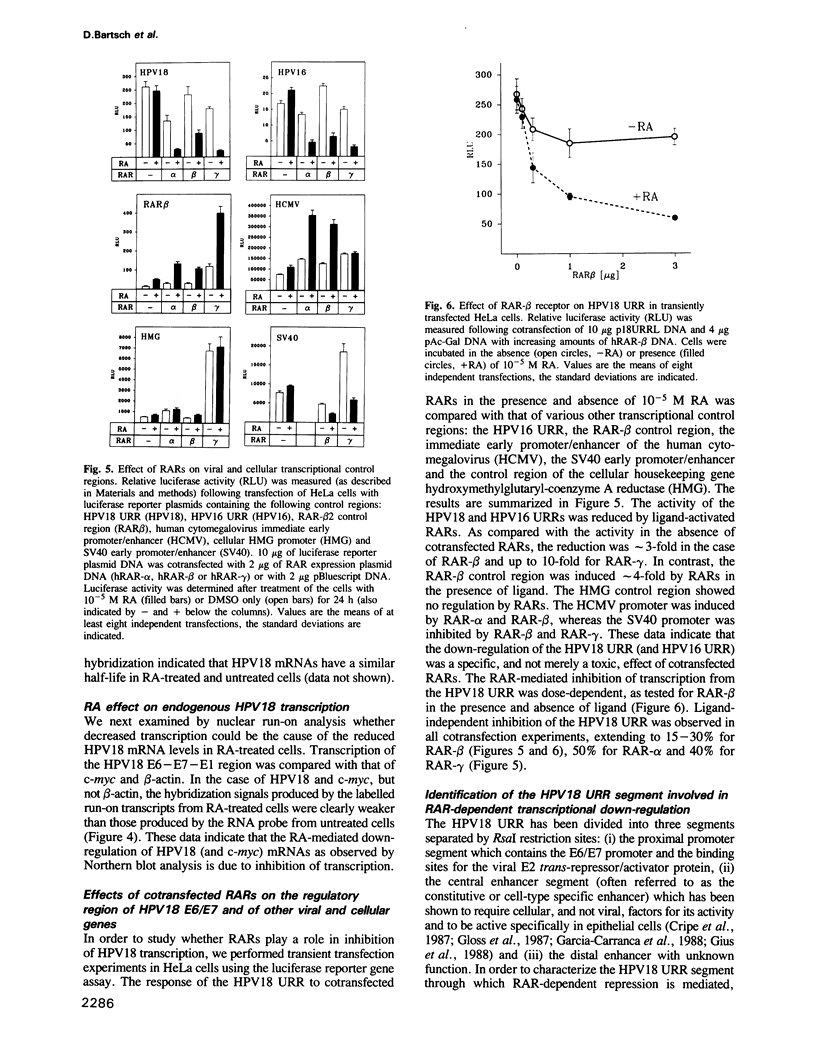
- Kliewer S. A., Umesono K., Mangelsdorf D. J., Evans R. M. Retinoid X receptor interacts with nuclear receptors in retinoic acid, thyroid hormone and vitamin D3 signalling. Nature. 1992 Jan 30;355(6359):446–449. doi: 10.1038/355446a0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koi M., Morita H., Yamada H., Satoh H., Barrett J. C., Oshimura M. Normal human chromosome 11 suppresses tumorigenicity of human cervical tumor cell line SiHa. Mol Carcinog. 1989;2(1):12–21. doi: 10.1002/mc.2940020103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kovacs G., Erlandsson R., Boldog F., Ingvarsson S., Müller-Brechlin R., Klein G., Sümegi J. Consistent chromosome 3p deletion and loss of heterozygosity in renal cell carcinoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Mar;85(5):1571–1575. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.5.1571. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krust A., Kastner P., Petkovich M., Zelent A., Chambon P. A third human retinoic acid receptor, hRAR-gamma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jul;86(14):5310–5314. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.14.5310. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leid M., Kastner P., Lyons R., Nakshatri H., Saunders M., Zacharewski T., Chen J. Y., Staub A., Garnier J. M., Mader S. Purification, cloning, and RXR identity of the HeLa cell factor with which RAR or TR heterodimerizes to bind target sequences efficiently. Cell. 1992 Jan 24;68(2):377–395. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90478-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
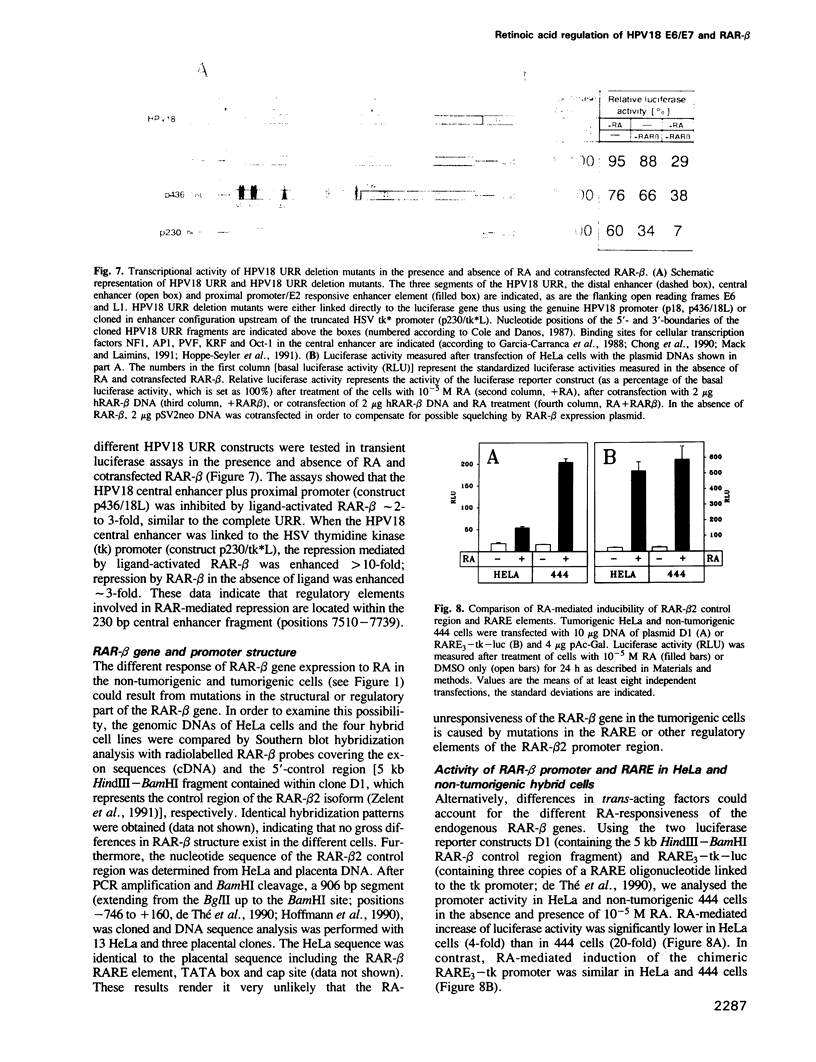
- Lippman S. M., Kessler J. F., Meyskens F. L., Jr Retinoids as preventive and therapeutic anticancer agents (Part I). Cancer Treat Rep. 1987 Apr;71(4):391–405. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lotan R. Effects of vitamin A and its analogs (retinoids) on normal and neoplastic cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Mar 12;605(1):33–91. doi: 10.1016/0304-419x(80)90021-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lotan R., Kramer R. H., Neumann G., Lotan D., Nicolson G. L. Retinoic acid-induced modifications in the growth and cell surface components of a human carcinoma (HeLa) cell line. Exp Cell Res. 1980 Dec;130(2):401–414. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(80)90018-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mack D. H., Laimins L. A. A keratinocyte-specific transcription factor, KRF-1, interacts with AP-1 to activate expression of human papillomavirus type 18 in squamous epithelial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Oct 15;88(20):9102–9106. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.20.9102. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mangelsdorf D. J., Ong E. S., Dyck J. A., Evans R. M. Nuclear receptor that identifies a novel retinoic acid response pathway. Nature. 1990 May 17;345(6272):224–229. doi: 10.1038/345224a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meinkoth J., Wahl G. Hybridization of nucleic acids immobilized on solid supports. Anal Biochem. 1984 May 1;138(2):267–284. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90808-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miner J. N., Yamamoto K. R. Regulatory crosstalk at composite response elements. Trends Biochem Sci. 1991 Nov;16(11):423–426. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(91)90168-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Münger K., Phelps W. C., Bubb V., Howley P. M., Schlegel R. The E6 and E7 genes of the human papillomavirus type 16 together are necessary and sufficient for transformation of primary human keratinocytes. J Virol. 1989 Oct;63(10):4417–4421. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.10.4417-4421.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naylor S. L., Johnson B. E., Minna J. D., Sakaguchi A. Y. Loss of heterozygosity of chromosome 3p markers in small-cell lung cancer. Nature. 1987 Oct 1;329(6138):451–454. doi: 10.1038/329451a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicholson R. C., Mader S., Nagpal S., Leid M., Rochette-Egly C., Chambon P. Negative regulation of the rat stromelysin gene promoter by retinoic acid is mediated by an AP1 binding site. EMBO J. 1990 Dec;9(13):4443–4454. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07895.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peehl D. M., Stanbridge E. J. The role of differentiation in the suppression of tumorigenicity in human cell hybrids. Int J Cancer. 1982 Jul 15;30(1):113–120. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910300119. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petkovich M., Brand N. J., Krust A., Chambon P. A human retinoic acid receptor which belongs to the family of nuclear receptors. Nature. 1987 Dec 3;330(6147):444–450. doi: 10.1038/330444a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saxon P. J., Srivatsan E. S., Stanbridge E. J. Introduction of human chromosome 11 via microcell transfer controls tumorigenic expression of HeLa cells. EMBO J. 1986 Dec 20;5(13):3461–3466. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04670.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider-Gädicke A., Schwarz E. Different human cervical carcinoma cell lines show similar transcription patterns of human papillomavirus type 18 early genes. EMBO J. 1986 Sep;5(9):2285–2292. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04496.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwarz E., Freese U. K., Gissmann L., Mayer W., Roggenbuck B., Stremlau A., zur Hausen H. Structure and transcription of human papillomavirus sequences in cervical carcinoma cells. Nature. 1985 Mar 7;314(6006):111–114. doi: 10.1038/314111a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schüle R., Evans R. M. Cross-coupling of signal transduction pathways: zinc finger meets leucine zipper. Trends Genet. 1991 Nov-Dec;7(11-12):377–381. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(91)90259-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schüle R., Rangarajan P., Yang N., Kliewer S., Ransone L. J., Bolado J., Verma I. M., Evans R. M. Retinoic acid is a negative regulator of AP-1-responsive genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jul 15;88(14):6092–6096. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.14.6092. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schüle R., Umesono K., Mangelsdorf D. J., Bolado J., Pike J. W., Evans R. M. Jun-Fos and receptors for vitamins A and D recognize a common response element in the human osteocalcin gene. Cell. 1990 May 4;61(3):497–504. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90531-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smotkin D., Wettstein F. O. Transcription of human papillomavirus type 16 early genes in a cervical cancer and a cancer-derived cell line and identification of the E7 protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jul;83(13):4680–4684. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.13.4680. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern P. J., Berg P. Transformation of mammalian cells to antibiotic resistance with a bacterial gene under control of the SV40 early region promoter. J Mol Appl Genet. 1982;1(4):327–341. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Srivatsan E. S., Benedict W. F., Stanbridge E. J. Implication of chromosome 11 in the suppression of neoplastic expression in human cell hybrids. Cancer Res. 1986 Dec;46(12 Pt 1):6174–6179. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanbridge E. J., Der C. J., Doersen C. J., Nishimi R. Y., Peehl D. M., Weissman B. E., Wilkinson J. E. Human cell hybrids: analysis of transformation and tumorigenicity. Science. 1982 Jan 15;215(4530):252–259. doi: 10.1126/science.7053574. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanbridge E. J. Suppression of malignancy in human cells. Nature. 1976 Mar 4;260(5546):17–20. doi: 10.1038/260017a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vasios G. W., Gold J. D., Petkovich M., Chambon P., Gudas L. J. A retinoic acid-responsive element is present in the 5' flanking region of the laminin B1 gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Dec;86(23):9099–9103. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.23.9099. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yokota J., Tsukada Y., Nakajima T., Gotoh M., Shimosato Y., Mori N., Tsunokawa Y., Sugimura T., Terada M. Loss of heterozygosity on the short arm of chromosome 3 in carcinoma of the uterine cervix. Cancer Res. 1989 Jul 1;49(13):3598–3601. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu V. C., Delsert C., Andersen B., Holloway J. M., Devary O. V., När A. M., Kim S. Y., Boutin J. M., Glass C. K., Rosenfeld M. G. RXR beta: a coregulator that enhances binding of retinoic acid, thyroid hormone, and vitamin D receptors to their cognate response elements. Cell. 1991 Dec 20;67(6):1251–1266. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90301-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zbar B., Brauch H., Talmadge C., Linehan M. Loss of alleles of loci on the short arm of chromosome 3 in renal cell carcinoma. 1987 Jun 25-Jul 1Nature. 327(6124):721–724. doi: 10.1038/327721a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zelent A., Mendelsohn C., Kastner P., Krust A., Garnier J. M., Ruffenach F., Leroy P., Chambon P. Differentially expressed isoforms of the mouse retinoic acid receptor beta generated by usage of two promoters and alternative splicing. EMBO J. 1991 Jan;10(1):71–81. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07922.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang X. K., Hoffmann B., Tran P. B., Graupner G., Pfahl M. Retinoid X receptor is an auxiliary protein for thyroid hormone and retinoic acid receptors. Nature. 1992 Jan 30;355(6359):441–446. doi: 10.1038/355441a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de The H., Marchio A., Tiollais P., Dejean A. Differential expression and ligand regulation of the retinoic acid receptor alpha and beta genes. EMBO J. 1989 Feb;8(2):429–433. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03394.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Thé H., Marchio A., Tiollais P., Dejean A. A novel steroid thyroid hormone receptor-related gene inappropriately expressed in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Nature. 1987 Dec 17;330(6149):667–670. doi: 10.1038/330667a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Thé H., Vivanco-Ruiz M. M., Tiollais P., Stunnenberg H., Dejean A. Identification of a retinoic acid responsive element in the retinoic acid receptor beta gene. Nature. 1990 Jan 11;343(6254):177–180. doi: 10.1038/343177a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Knebel Doeberitz M., Oltersdorf T., Schwarz E., Gissmann L. Correlation of modified human papilloma virus early gene expression with altered growth properties in C4-1 cervical carcinoma cells. Cancer Res. 1988 Jul 1;48(13):3780–3786. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- zur Hausen H. Intracellular surveillance of persisting viral infections. Human genital cancer results from deficient cellular control of papillomavirus gene expression. Lancet. 1986 Aug 30;2(8505):489–491. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(86)90360-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- zur Hausen H. Viruses in human cancers. Science. 1991 Nov 22;254(5035):1167–1173. doi: 10.1126/science.1659743. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]