Abstract
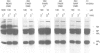
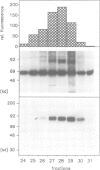
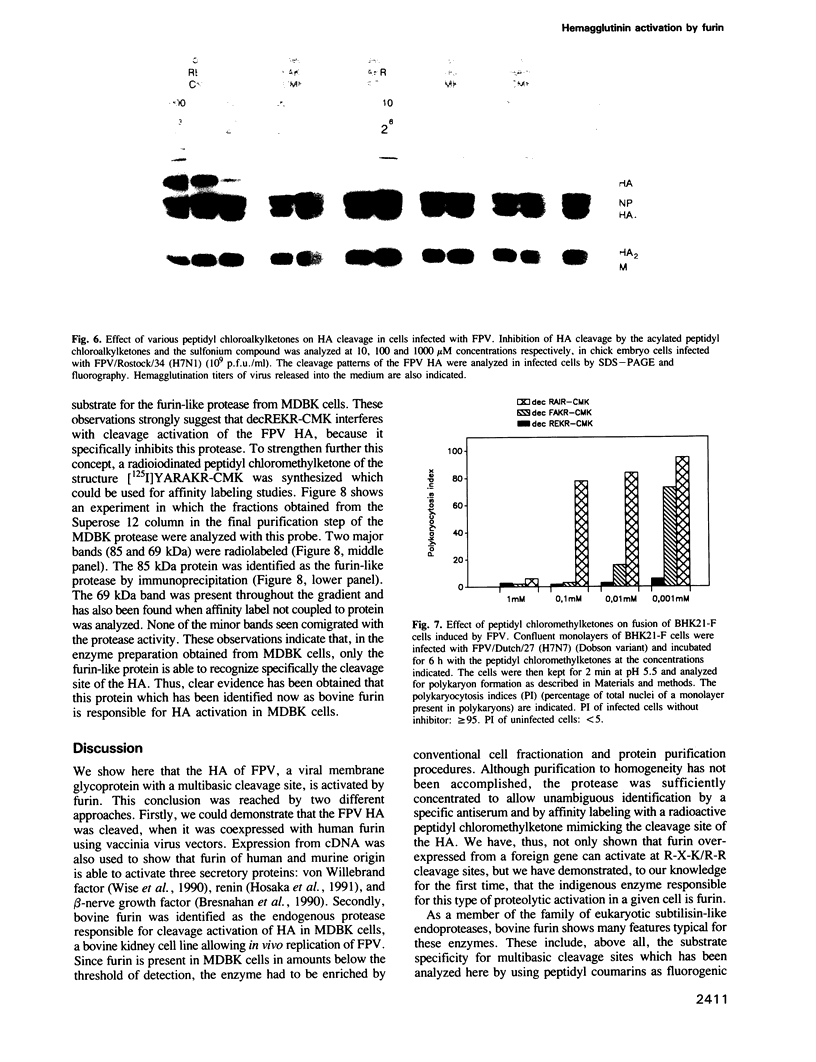
Many viruses have membrane glycoproteins that are activated at cleavage sites containing multiple arginine and lysine residues by cellular proteases so far not identified. The proteases responsible for cleavage of the hemagglutinin of fowl plague virus, a prototype of these glycoproteins, has now been isolated from Madin-Darby bovine kidney cells. The enzyme has a mol. wt of 85,000, a pH optimum ranging from 6.5 to 7.5, is calcium dependent and recognizes the consensus sequence R-X-K/R-R at the cleavage site of the hemagglutinin. Using a specific antiserum it has been identified as furin, a subtilisin-like eukaryotic protease. The fowl plague virus hemagglutinin was also cleaved after coexpression with human furin from cDNA by vaccinia virus vectors. Peptidyl chloroalkylketones containing the R-X-K/R-R motif specifically bind to the catalytic site of furin and are therefore potent inhibitors of hemagglutinin cleavage and fusion activity.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson R. G., Pathak R. K. Vesicles and cisternae in the trans Golgi apparatus of human fibroblasts are acidic compartments. Cell. 1985 Mar;40(3):635–643. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90212-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aronson N. N., Jr, Touster O. Isolation of rat liver plasma membrane fragments in isotonic sucrose. Methods Enzymol. 1974;31:90–102. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(74)31009-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barr P. J. Mammalian subtilisins: the long-sought dibasic processing endoproteases. Cell. 1991 Jul 12;66(1):1–3. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90129-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrett T., Clarke D. K., Evans S. A., Rima B. K. The nucleotide sequence of the gene encoding the F protein of canine distemper virus: a comparison of the deduced amino acid sequence with other paramyxoviruses. Virus Res. 1987 Nov;8(4):373–386. doi: 10.1016/0168-1702(87)90009-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bosch F. X., Garten W., Klenk H. D., Rott R. Proteolytic cleavage of influenza virus hemagglutinins: primary structure of the connecting peptide between HA1 and HA2 determines proteolytic cleavability and pathogenicity of Avian influenza viruses. Virology. 1981 Sep;113(2):725–735. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90201-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bresnahan P. A., Leduc R., Thomas L., Thorner J., Gibson H. L., Brake A. J., Barr P. J., Thomas G. Human fur gene encodes a yeast KEX2-like endoprotease that cleaves pro-beta-NGF in vivo. J Cell Biol. 1990 Dec;111(6 Pt 2):2851–2859. doi: 10.1083/jcb.111.6.2851. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang P. L., Rosa N. E., Davidson R. G. Differential assay of arylsulfatase A and B activities: a sensitive method for cultured human cells. Anal Biochem. 1981 Nov 1;117(2):382–389. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90795-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins P. L., Huang Y. T., Wertz G. W. Nucleotide sequence of the gene encoding the fusion (F) glycoprotein of human respiratory syncytial virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Dec;81(24):7683–7687. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.24.7683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ENGSTROM L. Studies on calf-intestinal alkaline phosphatase. I. Chromatographic purification, microheterogeneity and some other properties of the purified enzyme. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1961 Sep 2;52:36–48. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(61)90901-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elango N., Satake M., Coligan J. E., Norrby E., Camargo E., Venkatesan S. Respiratory syncytial virus fusion glycoprotein: nucleotide sequence of mRNA, identification of cleavage activation site and amino acid sequence of N-terminus of F1 subunit. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Mar 11;13(5):1559–1574. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.5.1559. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleischer B., Fleischer S., Ozawa H. Isolation and characterization of Golgi membranes from bovine liver. J Cell Biol. 1969 Oct;43(1):59–79. doi: 10.1083/jcb.43.1.59. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuller R. S., Brake A. J., Thorner J. Intracellular targeting and structural conservation of a prohormone-processing endoprotease. Science. 1989 Oct 27;246(4929):482–486. doi: 10.1126/science.2683070. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuller R. S., Sterne R. E., Thorner J. Enzymes required for yeast prohormone processing. Annu Rev Physiol. 1988;50:345–362. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.50.030188.002021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garten W., Stieneke A., Shaw E., Wikstrom P., Klenk H. D. Inhibition of proteolytic activation of influenza virus hemagglutinin by specific peptidyl chloroalkyl ketones. Virology. 1989 Sep;172(1):25–31. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90103-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gotoh B., Ogasawara T., Toyoda T., Inocencio N. M., Hamaguchi M., Nagai Y. An endoprotease homologous to the blood clotting factor X as a determinant of viral tropism in chick embryo. EMBO J. 1990 Dec;9(12):4189–4195. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07643.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffiths G., Simons K. The trans Golgi network: sorting at the exit site of the Golgi complex. Science. 1986 Oct 24;234(4775):438–443. doi: 10.1126/science.2945253. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatsuzawa K., Hosaka M., Nakagawa T., Nagase M., Shoda A., Murakami K., Nakayama K. Structure and expression of mouse furin, a yeast Kex2-related protease. Lack of processing of coexpressed prorenin in GH4C1 cells. J Biol Chem. 1990 Dec 25;265(36):22075–22078. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hosaka M., Nagahama M., Kim W. S., Watanabe T., Hatsuzawa K., Ikemizu J., Murakami K., Nakayama K. Arg-X-Lys/Arg-Arg motif as a signal for precursor cleavage catalyzed by furin within the constitutive secretory pathway. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jul 5;266(19):12127–12130. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Julius D., Brake A., Blair L., Kunisawa R., Thorner J. Isolation of the putative structural gene for the lysine-arginine-cleaving endopeptidase required for processing of yeast prepro-alpha-factor. Cell. 1984 Jul;37(3):1075–1089. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90442-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawaoka Y., Webster R. G. Sequence requirements for cleavage activation of influenza virus hemagglutinin expressed in mammalian cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jan;85(2):324–328. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.2.324. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keller P. M., Davison A. J., Lowe R. S., Bennett C. D., Ellis R. W. Identification and structure of the gene encoding gpII, a major glycoprotein of varicella-zoster virus. Virology. 1986 Jul 15;152(1):181–191. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(86)90383-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kettner C., Shaw E. Inactivation of trypsin-like enzymes with peptides of arginine chloromethyl ketone. Methods Enzymol. 1981;80(Pt 100):826–842. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(81)80065-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khatchikian D., Orlich M., Rott R. Increased viral pathogenicity after insertion of a 28S ribosomal RNA sequence into the haemagglutinin gene of an influenza virus. Nature. 1989 Jul 13;340(6229):156–157. doi: 10.1038/340156a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klenk H. D., Garten W., Rott R. Inhibition of proteolytic cleavage of the hemagglutinin of influenza virus by the calcium-specific ionophore A23187. EMBO J. 1984 Dec 1;3(12):2911–2915. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02231.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klenk H. D., Rott R. The molecular biology of influenza virus pathogenicity. Adv Virus Res. 1988;34:247–281. doi: 10.1016/S0065-3527(08)60520-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klenk H. D., Wöllert W., Rott R., Scholtissek C. Association of influenza virus proteins with cytoplasmic fractions. Virology. 1974 Jan;57(1):28–41. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(74)90105-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuroda K., Hauser C., Rott R., Klenk H. D., Doerfler W. Expression of the influenza virus haemagglutinin in insect cells by a baculovirus vector. EMBO J. 1986 Jun;5(6):1359–1365. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04367.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazarowitz S. G., Choppin P. W. Enhancement of the infectivity of influenza A and B viruses by proteolytic cleavage of the hemagglutinin polypeptide. Virology. 1975 Dec;68(2):440–454. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(75)90285-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li S. Q., Orlich M., Rott R. Generation of seal influenza virus variants pathogenic for chickens, because of hemagglutinin cleavage site changes. J Virol. 1990 Jul;64(7):3297–3303. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.7.3297-3303.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison T., Ward L. J., Semerjian A. Intracellular processing of the Newcastle disease virus fusion glycoprotein. J Virol. 1985 Mar;53(3):851–857. doi: 10.1128/jvi.53.3.851-857.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogasawara T., Gotoh B., Suzuki H., Asaka J., Shimokata K., Rott R., Nagai Y. Expression of factor X and its significance for the determination of paramyxovirus tropism in the chick embryo. EMBO J. 1992 Feb;11(2):467–472. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05076.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohuchi M., Orlich M., Ohuchi R., Simpson B. E., Garten W., Klenk H. D., Rott R. Mutations at the cleavage site of the hemagglutinin after the pathogenicity of influenza virus A/chick/Penn/83 (H5N2). Virology. 1989 Feb;168(2):274–280. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90267-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohuchi R., Ohuchi M., Garten W., Klenk H. D. Human influenza virus hemagglutinin with high sensitivity to proteolytic activation. J Virol. 1991 Jul;65(7):3530–3537. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.7.3530-3537.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perez L. G., Hunter E. Mutations within the proteolytic cleavage site of the Rous sarcoma virus glycoprotein that block processing to gp85 and gp37. J Virol. 1987 May;61(5):1609–1614. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.5.1609-1614.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Randolph V. B., Winkler G., Stollar V. Acidotropic amines inhibit proteolytic processing of flavivirus prM protein. Virology. 1990 Feb;174(2):450–458. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(90)90099-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ratner L., Haseltine W., Patarca R., Livak K. J., Starcich B., Josephs S. F., Doran E. R., Rafalski J. A., Whitehorn E. A., Baumeister K. Complete nucleotide sequence of the AIDS virus, HTLV-III. Nature. 1985 Jan 24;313(6000):277–284. doi: 10.1038/313277a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rauber P., Wikstrom P., Shaw E. Iodination of peptidyl chloromethyl ketones for protease affinity labels. Anal Biochem. 1988 Feb 1;168(2):259–264. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(88)90316-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rice C. M., Lenches E. M., Eddy S. R., Shin S. J., Sheets R. L., Strauss J. H. Nucleotide sequence of yellow fever virus: implications for flavivirus gene expression and evolution. Science. 1985 Aug 23;229(4715):726–733. doi: 10.1126/science.4023707. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richardson C., Hull D., Greer P., Hasel K., Berkovich A., Englund G., Bellini W., Rima B., Lazzarini R. The nucleotide sequence of the mRNA encoding the fusion protein of measles virus (Edmonston strain): a comparison of fusion proteins from several different paramyxoviruses. Virology. 1986 Dec;155(2):508–523. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(86)90212-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rott R., Orlich M., Klenk H. D., Wang M. L., Skehel J. J., Wiley D. C. Studies on the adaptation of influenza viruses to MDCK cells. EMBO J. 1984 Dec 20;3(13):3329–3332. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02299.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakaguchi T., Matsuda Y., Kiyokage R., Kawahara N., Kiyotani K., Katunuma N., Nagai Y., Yoshida T. Identification of endoprotease activity in the trans Golgi membranes of rat liver cells that specifically processes in vitro the fusion glycoprotein precursor of virulent Newcastle disease virus. Virology. 1991 Oct;184(2):504–512. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90420-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seidah N. G., Gaspar L., Mion P., Marcinkiewicz M., Mbikay M., Chrétien M. cDNA sequence of two distinct pituitary proteins homologous to Kex2 and furin gene products: tissue-specific mRNAs encoding candidates for pro-hormone processing proteinases. DNA Cell Biol. 1990 Jul-Aug;9(6):415–424. doi: 10.1089/dna.1990.9.415. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seidah N. G., Marcinkiewicz M., Benjannet S., Gaspar L., Beaubien G., Mattei M. G., Lazure C., Mbikay M., Chrétien M. Cloning and primary sequence of a mouse candidate prohormone convertase PC1 homologous to PC2, Furin, and Kex2: distinct chromosomal localization and messenger RNA distribution in brain and pituitary compared to PC2. Mol Endocrinol. 1991 Jan;5(1):111–122. doi: 10.1210/mend-5-1-111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw E. Peptidyl sulfonium salts. A new class of protease inhibitors. J Biol Chem. 1988 Feb 25;263(6):2768–2772. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shennan K. I., Smeekens S. P., Steiner D. F., Docherty K. Characterization of PC2, a mammalian Kex2 homologue, following expression of the cDNA in microinjected Xenopus oocytes. FEBS Lett. 1991 Jun 24;284(2):277–280. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(91)80703-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smeekens S. P., Avruch A. S., LaMendola J., Chan S. J., Steiner D. F. Identification of a cDNA encoding a second putative prohormone convertase related to PC2 in AtT20 cells and islets of Langerhans. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jan 15;88(2):340–344. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.2.340. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smeekens S. P., Steiner D. F. Identification of a human insulinoma cDNA encoding a novel mammalian protein structurally related to the yeast dibasic processing protease Kex2. J Biol Chem. 1990 Feb 25;265(6):2997–3000. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spaete R. R., Saxena A., Scott P. I., Song G. J., Probert W. S., Britt W. J., Gibson W., Rasmussen L., Pachl C. Sequence requirements for proteolytic processing of glycoprotein B of human cytomegalovirus strain Towne. J Virol. 1990 Jun;64(6):2922–2931. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.6.2922-2931.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugrue R. J., Bahadur G., Zambon M. C., Hall-Smith M., Douglas A. R., Hay A. J. Specific structural alteration of the influenza haemagglutinin by amantadine. EMBO J. 1990 Nov;9(11):3469–3476. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07555.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tashiro M., Ciborowski P., Klenk H. D., Pulverer G., Rott R. Role of Staphylococcus protease in the development of influenza pneumonia. Nature. 1987 Feb 5;325(6104):536–537. doi: 10.1038/325536a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waxham M. N., Server A. C., Goodman H. M., Wolinsky J. S. Cloning and sequencing of the mumps virus fusion protein gene. Virology. 1987 Aug;159(2):381–388. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(87)90477-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wikstrom P., Kirschke H., Stone S., Shaw E. The properties of peptidyl diazoethanes and chloroethanes as protease inactivators. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1989 Apr;270(1):286–293. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(89)90030-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wise R. J., Barr P. J., Wong P. A., Kiefer M. C., Brake A. J., Kaufman R. J. Expression of a human proprotein processing enzyme: correct cleavage of the von Willebrand factor precursor at a paired basic amino acid site. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Dec;87(23):9378–9382. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.23.9378. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamada A., Takeuchi K., Hishiyama M. Intracellular processing of mumps virus glycoproteins. Virology. 1988 Jul;165(1):268–273. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90681-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Curtis I., Simons K. Isolation of exocytic carrier vesicles from BHK cells. Cell. 1989 Aug 25;58(4):719–727. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90106-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]