Abstract
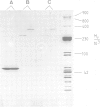
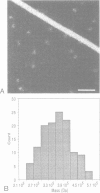
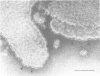
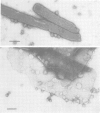
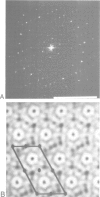
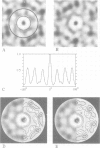
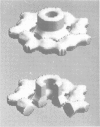
The cytolytic toxin aerolysin has been found to form heptameric oligomers by SDS-PAGE electrophoresis, STEM mass measurements of single oligomers and image analysis of two-dimensional membrane crystals. Two types of crystal, flat sheets and long regular tubes, have been obtained by reconstitution of purified protein and Escherichia coli phospholipids. A noise-filtered image of the best crystalline sheets reveals a structure with 7-fold symmetry containing a central strongly stain-excluding ring that encircles a dark stain-filled channel 17 A in diameter. The ring is surrounded by seven arms each made up of two unequal sized domains. By combining projected views and side-views, a simplified model of the aerolysin channel complex has been constructed. The relevance of this structure to the mode of action of aerolysin is discussed.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Buckley J. T., Howard S. P. Aerolysin from Aeromonas hydrophila. Methods Enzymol. 1988;165:193–199. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(88)65030-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chakraborty T., Schmid A., Notermans S., Benz R. Aerolysin of Aeromonas sobria: evidence for formation of ion-permeable channels and comparison with alpha-toxin of Staphylococcus aureus. Infect Immun. 1990 Jul;58(7):2127–2132. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.7.2127-2132.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freeman R., Leonard K. R. Comparative mass measurement of biological macromolecules by scanning transmission electron microscopy. J Microsc. 1981 Jun;122(Pt 3):275–286. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2818.1981.tb01267.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freer J. H., Arbuthnott J. P., Billcliffe B. Effects of staphylococcal -toxin on the structure of erythrocyte membranes: a biochemical and freeze-etching study. J Gen Microbiol. 1973 Apr;75(2):321–332. doi: 10.1099/00221287-75-2-321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freer J. H., Arbuthnott J. P. Toxins of Staphylococcus aureus. Pharmacol Ther. 1982;19(1):55–106. doi: 10.1016/0163-7258(82)90042-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garland W. J., Buckley J. T. The cytolytic toxin aerolysin must aggregate to disrupt erythrocytes, and aggregation is stimulated by human glycophorin. Infect Immun. 1988 May;56(5):1249–1253. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.5.1249-1253.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green M. J., Buckley J. T. Site-directed mutagenesis of the hole-forming toxin aerolysin: studies on the roles of histidines in receptor binding and oligomerization of the monomer. Biochemistry. 1990 Feb 27;29(8):2177–2180. doi: 10.1021/bi00460a031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard S. P., Buckley J. T. Membrane glycoprotein receptor and hole-forming properties of a cytolytic protein toxin. Biochemistry. 1982 Mar 30;21(7):1662–1667. doi: 10.1021/bi00536a029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hutchinson E. G., Tichelaar W., Hofhaus G., Weiss H., Leonard K. R. Identification and electron microscopic analysis of a chaperonin oligomer from Neurospora crassa mitochondria. EMBO J. 1989 May;8(5):1485–1490. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03532.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lakey A., Ferguson C., Labeit S., Reedy M., Larkins A., Butcher G., Leonard K., Bullard B. Identification and localization of high molecular weight proteins in insect flight and leg muscle. EMBO J. 1990 Nov;9(11):3459–3467. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07554.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Menestrina G. Ionic channels formed by Staphylococcus aureus alpha-toxin: voltage-dependent inhibition by divalent and trivalent cations. J Membr Biol. 1986;90(2):177–190. doi: 10.1007/BF01869935. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olofsson A., Kavéus U., Hacksell I., Thelestam M., Hebert H. Crystalline layers and three-dimensional structure of Staphylococcus aureus alpha-toxin. J Mol Biol. 1990 Jul 5;214(1):299–306. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(90)90162-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenbusch J. P. Structural and functional properties of porin channels in E. coli outer membranes. Experientia. 1990 Feb 15;46(2):167–173. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thelestam M., Olofsson A., Blomqvist L., Hebert H. Oligomerisation of cell-bound staphylococcal alpha-toxin in relation to membrane permeabilisation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 Feb 25;1062(2):245–254. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(91)90399-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tobkes N., Wallace B. A., Bayley H. Secondary structure and assembly mechanism of an oligomeric channel protein. Biochemistry. 1985 Apr 9;24(8):1915–1920. doi: 10.1021/bi00329a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tucker A. D., Parker M. W., Tsernoglou D., Buckley J. T. Crystallization of a proform of aerolysin, a hole-forming toxin from Aeromonas hydrophila. J Mol Biol. 1990 Apr 20;212(4):561–562. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(90)90222-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilmsen H. U., Buckley J. T., Pattus F. Site-directed mutagenesis at histidines of aerolysin from Aeromonas hydrophila: a lipid planar bilayer study. Mol Microbiol. 1991 Nov;5(11):2745–2751. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1991.tb01983.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilmsen H. U., Pattus F., Buckley J. T. Aerolysin, a hemolysin from Aeromonas hydrophila, forms voltage-gated channels in planar lipid bilayers. J Membr Biol. 1990 Apr;115(1):71–81. doi: 10.1007/BF01869107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]