Abstract
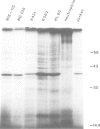
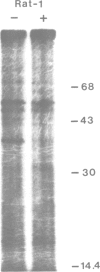
Lysophosphatidic acid (LPA) is a naturally occurring phospholipid with hormone- and growth factor-like activities. Exogenous LPA stimulates GTP-dependent phosphoinositide hydrolysis and inhibits adenylate cyclase in its target cells, but the site of action of LPA is unknown. We now report the identification by photoaffinity labeling of a putative LPA membrane receptor in various LPA-responsive cell types. A 32P-labeled LPA analogue containing a photoreactive fatty acid, [32P]diazirine-LPA, labels a membrane protein of apparent molecular mass of 38-40 kDa in various cell types, including neuronal cells, brain homogenates, carcinoma cells, leukemic cells and normal fibroblasts. Labeling of the 38-40 kDa protein is competitively inhibited by unlabeled 1-oleoyl-LPA (IC50 approximately 10 nM), but not by other phospholipids. Specific labeling is not detected in rat liver membranes or in human neutrophils, which are physiologically unresponsive to LPA. Suramin, an inhibitor of both early and late events in the action of LPA, completely inhibits the binding of photoreactive LPA. We suggest that the 38-40 kDa protein represents a specific LPA cell surface receptor mediating at least part of the multiple cellular responses to LPA.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BLIGH E. G., DYER W. J. A rapid method of total lipid extraction and purification. Can J Biochem Physiol. 1959 Aug;37(8):911–917. doi: 10.1139/o59-099. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benton A. M., Gerrard J. M., Michiel T., Kindom S. E. Are lysophosphatidic acids or phosphatidic acids involved in stimulus activation coupling in platelets? Blood. 1982 Sep;60(3):642–649. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brunner J. Photochemical labeling of apolar phase of membranes. Methods Enzymol. 1989;172:628–687. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(89)72037-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chowdhry V., Westheimer F. H. Photoaffinity labeling of biological systems. Annu Rev Biochem. 1979;48:293–325. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.48.070179.001453. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emmelot P., Bos C. J., van Hoeven R. P., van Blitterswijk W. J. Isolation of plasma membranes from rat and mouse livers and hepatomas. Methods Enzymol. 1974;31:75–90. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(74)31008-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerrard J. M., Robinson P. Identification of the molecular species of lysophosphatidic acid produced when platelets are stimulated by thrombin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989 Feb 20;1001(3):282–285. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(89)90112-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harter C., Bächi T., Semenza G., Brunner J. Hydrophobic photolabeling identifies BHA2 as the subunit mediating the interaction of bromelain-solubilized influenza virus hemagglutinin with liposomes at low pH. Biochemistry. 1988 Mar 22;27(6):1856–1864. doi: 10.1021/bi00406a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirata M., Hayashi Y., Ushikubi F., Yokota Y., Kageyama R., Nakanishi S., Narumiya S. Cloning and expression of cDNA for a human thromboxane A2 receptor. Nature. 1991 Feb 14;349(6310):617–620. doi: 10.1038/349617a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honda Z., Nakamura M., Miki I., Minami M., Watanabe T., Seyama Y., Okado H., Toh H., Ito K., Miyamoto T. Cloning by functional expression of platelet-activating factor receptor from guinea-pig lung. Nature. 1991 Jan 24;349(6307):342–346. doi: 10.1038/349342a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jalink K., van Corven E. J., Moolenaar W. H. Lysophosphatidic acid, but not phosphatidic acid, is a potent Ca2(+)-mobilizing stimulus for fibroblasts. Evidence for an extracellular site of action. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jul 25;265(21):12232–12239. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kramer I. M., van der Bend R. L., Tool A. T., van Blitterswijk W. J., Roos D., Verhoeven A. J. 1-O-hexadecyl-2-Q-methylglycerol, a novel inhibitor of protein kinase C, inhibits the respiratory burst in human neutrophils. J Biol Chem. 1989 Apr 5;264(10):5876–5884. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michalak M., Wandler E. L., Strynadka K., Lopaschuk G. L., Njue W. M., Liu H. J., Olley P. M. Photolabelling of the prostaglandin E2 receptor in cardiac sarcolemmal vesicles. FEBS Lett. 1990 Jun 4;265(1-2):117–120. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)80898-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moolenaar W. H., Aerts R. J., Tertoolen L. G., de Laat S. W. The epidermal growth factor-induced calcium signal in A431 cells. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jan 5;261(1):279–284. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moolenaar W. H. Mitogenic action of lysophosphatidic acid. Adv Cancer Res. 1991;57:87–102. doi: 10.1016/s0065-230x(08)60996-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niggli V., Sommer L., Brunner J., Burger M. M. Interaction in situ of the cytoskeletal protein vinculin with bilayers studied by introducing a photoactivatable fatty acid into living chicken embryo fibroblasts. Eur J Biochem. 1990 Jan 12;187(1):111–117. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1990.tb15283.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plevin R., MacNulty E. E., Palmer S., Wakelam M. J. Differences in the regulation of endothelin-1- and lysophosphatidic-acid-stimulated Ins(1,4,5)P3 formation in rat-1 fibroblasts. Biochem J. 1991 Dec 15;280(Pt 3):609–615. doi: 10.1042/bj2800609. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prescott S. M., Zimmerman G. A., McIntyre T. M. Platelet-activating factor. J Biol Chem. 1990 Oct 15;265(29):17381–17384. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaap D., de Widt J., van der Wal J., Vandekerckhove J., van Damme J., Gussow D., Ploegh H. L., van Blitterswijk W. J., van der Bend R. L. Purification, cDNA-cloning and expression of human diacylglycerol kinase. FEBS Lett. 1990 Nov 26;275(1-2):151–158. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)81461-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tokumura A., Fukuzawa K., Yamada S., Tsukatani H. Stimulatory effect of lysophosphatidic acids on uterine smooth muscles of non-pregant rats. Arch Int Pharmacodyn Ther. 1980 May;245(1):74–83. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson S. P., McConnell R. T., Lapetina E. G. Decanoyl lysophosphatidic acid induces platelet aggregation through an extracellular action. Evidence against a second messenger role for lysophosphatidic acid. Biochem J. 1985 Nov 15;232(1):61–66. doi: 10.1042/bj2320061. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Corven E. J., Groenink A., Jalink K., Eichholtz T., Moolenaar W. H. Lysophosphatidate-induced cell proliferation: identification and dissection of signaling pathways mediated by G proteins. Cell. 1989 Oct 6;59(1):45–54. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90868-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Corven E. J., van Rijswijk A., Jalink K., van der Bend R. L., van Blitterswijk W. J., Moolenaar W. H. Mitogenic action of lysophosphatidic acid and phosphatidic acid on fibroblasts. Dependence on acyl-chain length and inhibition by suramin. Biochem J. 1992 Jan 1;281(Pt 1):163–169. doi: 10.1042/bj2810163. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Bend R. L., de Widt J., van Corven E. J., Moolenaar W. H., van Blitterswijk W. J. Metabolic conversion of the biologically active phospholipid, lysophosphatidic acid, in fibroblasts. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1992 Apr 8;1125(1):110–112. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(92)90163-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]