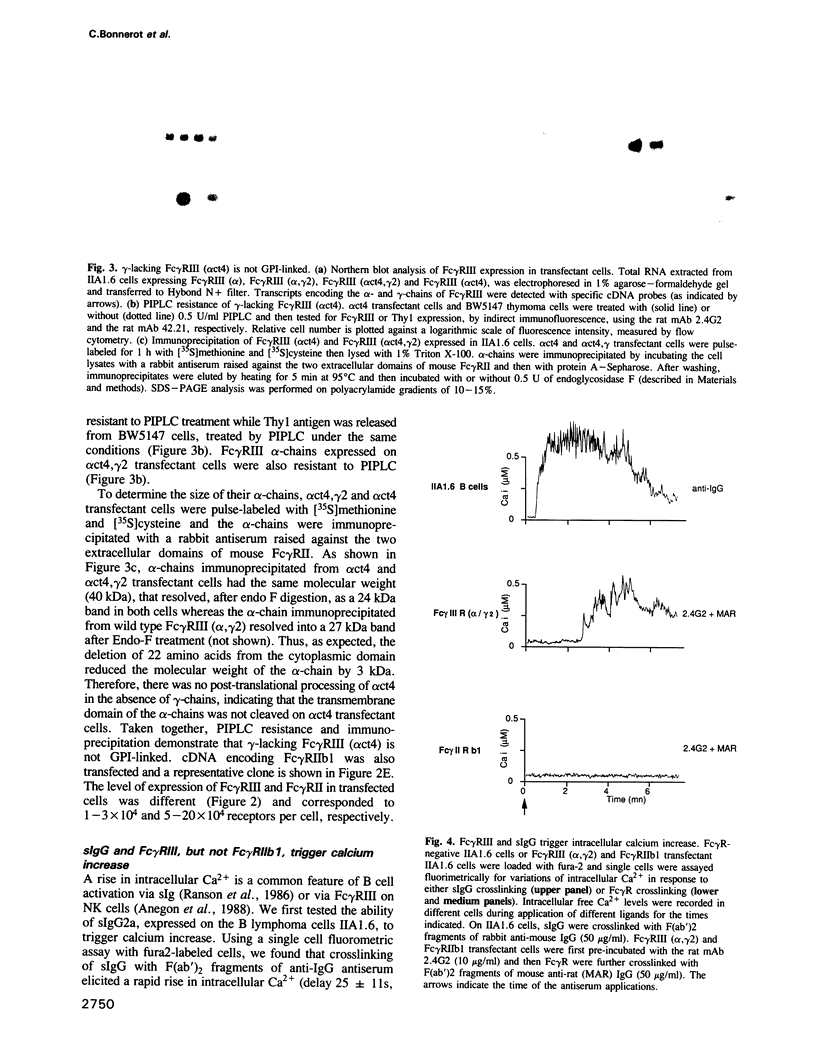
Abstract
Type III receptors for the Fc portion of IgG (Fc gamma RIII), initially characterized on macrophages and NK cells, are also expressed on several pre-B cell lines. Surface expression of Fc gamma RIII requires the association of the ligand binding alpha-chain with homodimeric gamma-chains. Type II Fc gamma R is homologous to Fc gamma RIII alpha-chain in the extracellular portion and differs in the transmembrane and cytoplasmic domains. The role of Fc gamma R in cell activation was investigated by expressing Fc gamma RIII and the lymphocyte-specific b1 isoform of Fc gamma RII (Fc gamma RIIb1) in an Fc gamma R-negative, sIgG-positive B-cell line. We found that, in contrast to Fc gamma RIIb1, Fc gamma RIII triggers the same events of cell activation as sIG i.e. Ca2+ mobilization, tyrosine phosphorylation and IL-2 secretion. By expressing cytoplasmic domain-lacking Fc gamma RIII alpha-chain in the absence or in the presence of gamma-chains, we demonstrated that cell activation via Fc gamma RIII requires the co-expression of gamma-chains, and is independent of the cytoplasmic portion of the alpha-chain. Furthermore, the cytoplasmic portion of the gamma-chain, fused to the extracellular and transmembrane domains of Fc gamma RII confers on the chimeric receptor the ability to trigger cell activation. Mutation of one tyrosine residue in the cytoplasmic domain of the gamma-chain prevented triggering of cytoplasmic signals. We therefore demonstrate that a tyrosine-containing motif, present in the cytoplasmic domain of the associated gamma-chain, is necessary and sufficient to trigger cell activation via Fc gamma RIII.
Full text
PDF









Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amigorena S., Bonnerot C., Choquet D., Fridman W. H., Teillaud J. L. Fc gamma RII expression in resting and activated B lymphocytes. Eur J Immunol. 1989 Aug;19(8):1379–1385. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830190805. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anegón I., Cuturi M. C., Trinchieri G., Perussia B. Interaction of Fc receptor (CD16) ligands induces transcription of interleukin 2 receptor (CD25) and lymphokine genes and expression of their products in human natural killer cells. J Exp Med. 1988 Feb 1;167(2):452–472. doi: 10.1084/jem.167.2.452. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baniyash M., Garcia-Morales P., Luong E., Samelson L. E., Klausner R. D. The T cell antigen receptor zeta chain is tyrosine phosphorylated upon activation. J Biol Chem. 1988 Dec 5;263(34):18225–18230. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benhamou M., Gutkind J. S., Robbins K. C., Siraganian R. P. Tyrosine phosphorylation coupled to IgE receptor-mediated signal transduction and histamine release. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jul;87(14):5327–5330. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.14.5327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blank U., Ra C., Miller L., White K., Metzger H., Kinet J. P. Complete structure and expression in transfected cells of high affinity IgE receptor. Nature. 1989 Jan 12;337(6203):187–189. doi: 10.1038/337187a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonifacino J. S., Chen C., Lippincott-Schwartz J., Ashwell J. D., Klausner R. D. Subunit interactions within the T-cell antigen receptor: clues from the study of partial complexes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Sep;85(18):6929–6933. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.18.6929. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonifacino J. S., Suzuki C. K., Klausner R. D. A peptide sequence confers retention and rapid degradation in the endoplasmic reticulum. Science. 1990 Jan 5;247(4938):79–82. doi: 10.1126/science.2294595. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonnerot C., Amigorena S., Fridman W. H., Even J., Daëron M. Unmethylation of specific sites in the 5' region is critical for the expression of murine alpha Fc gamma R gene. J Immunol. 1990 Jan 1;144(1):323–328. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braun J., Sha'afi R. I., Unanue E. R. Crosslinking by ligands to surface immunoglobulin triggers mobilization of intracellular 45Ca2+ in B lymphocytes. J Cell Biol. 1979 Sep;82(3):755–766. doi: 10.1083/jcb.82.3.755. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burkhardt A. L., Brunswick M., Bolen J. B., Mond J. J. Anti-immunoglobulin stimulation of B lymphocytes activates src-related protein-tyrosine kinases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Aug 15;88(16):7410–7414. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.16.7410. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cassatella M. A., Anegón I., Cuturi M. C., Griskey P., Trinchieri G., Perussia B. Fc gamma R(CD16) interaction with ligand induces Ca2+ mobilization and phosphoinositide turnover in human natural killer cells. Role of Ca2+ in Fc gamma R(CD16)-induced transcription and expression of lymphokine genes. J Exp Med. 1989 Feb 1;169(2):549–567. doi: 10.1084/jem.169.2.549. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan A. C., Irving B. A., Fraser J. D., Weiss A. The zeta chain is associated with a tyrosine kinase and upon T-cell antigen receptor stimulation associates with ZAP-70, a 70-kDa tyrosine phosphoprotein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Oct 15;88(20):9166–9170. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.20.9166. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chu G., Hayakawa H., Berg P. Electroporation for the efficient transfection of mammalian cells with DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Feb 11;15(3):1311–1326. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.3.1311. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cosson P., Lankford S. P., Bonifacino J. S., Klausner R. D. Membrane protein association by potential intramembrane charge pairs. Nature. 1991 May 30;351(6325):414–416. doi: 10.1038/351414a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eiseman E., Bolen J. B. Engagement of the high-affinity IgE receptor activates src protein-related tyrosine kinases. Nature. 1992 Jan 2;355(6355):78–80. doi: 10.1038/355078a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frank S. J., Niklinska B. B., Orloff D. G., Merćep M., Ashwell J. D., Klausner R. D. Structural mutations of the T cell receptor zeta chain and its role in T cell activation. Science. 1990 Jul 13;249(4965):174–177. doi: 10.1126/science.2371564. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fridman W. H., Bonnerot C., Daeron M., Amigorena S., Teillaud J. L., Sautes C. Structural bases of Fc gamma receptor functions. Immunol Rev. 1992 Feb;125:49–76. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1992.tb00625.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hogarth P. M., Hibbs M. L., Bonadonna L., Scott B. M., Witort E., Pietersz G. A., McKenzie I. F. The mouse Fc receptor for IgG (Ly-17): molecular cloning and specificity. Immunogenetics. 1987;26(3):161–168. doi: 10.1007/BF00365906. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hombach J., Tsubata T., Leclercq L., Stappert H., Reth M. Molecular components of the B-cell antigen receptor complex of the IgM class. Nature. 1990 Feb 22;343(6260):760–762. doi: 10.1038/343760a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irving B. A., Weiss A. The cytoplasmic domain of the T cell receptor zeta chain is sufficient to couple to receptor-associated signal transduction pathways. Cell. 1991 Mar 8;64(5):891–901. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90314-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones B., Tite J. P., Janeway C. A., Jr Different phenotypic variants of the mouse B cell tumor A20/2J are selected by antigen- and mitogen-triggered cytotoxicity of L3T4-positive, I-A-restricted T cell clones. J Immunol. 1986 Jan;136(1):348–356. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Justement L. B., Campbell K. S., Chien N. C., Cambier J. C. Regulation of B cell antigen receptor signal transduction and phosphorylation by CD45. Science. 1991 Jun 28;252(5014):1839–1842. doi: 10.1126/science.1648262. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Justement L. B., Kreiger J., Cambier J. C. Production of multiple lymphokines by the A20.1 B cell lymphoma after cross-linking of membrane Ig by immobilized anti-Ig. J Immunol. 1989 Aug 1;143(3):881–889. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinet J. P. Antibody-cell interactions: Fc receptors. Cell. 1989 May 5;57(3):351–354. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90910-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klausner R. D., Samelson L. E. T cell antigen receptor activation pathways: the tyrosine kinase connection. Cell. 1991 Mar 8;64(5):875–878. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90310-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koyasu S., D'Adamio L., Arulanandam A. R., Abraham S., Clayton L. K., Reinherz E. L. T cell receptor complexes containing Fc epsilon RI gamma homodimers in lieu of CD3 zeta and CD3 eta components: a novel isoform expressed on large granular lymphocytes. J Exp Med. 1992 Jan 1;175(1):203–209. doi: 10.1084/jem.175.1.203. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurosaki T., Ravetch J. V. A single amino acid in the glycosyl phosphatidylinositol attachment domain determines the membrane topology of Fc gamma RIII. Nature. 1989 Dec 14;342(6251):805–807. doi: 10.1038/342805a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lane P. J., Ledbetter J. A., McConnell F. M., Draves K., Deans J., Schieven G. L., Clark E. A. The role of tyrosine phosphorylation in signal transduction through surface Ig in human B cells. Inhibition of tyrosine phosphorylation prevents intracellular calcium release. J Immunol. 1991 Jan 15;146(2):715–722. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanier L. L., Yu G., Phillips J. H. Co-association of CD3 zeta with a receptor (CD16) for IgG Fc on human natural killer cells. Nature. 1989 Dec 14;342(6251):803–805. doi: 10.1038/342803a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Letourneur F., Klausner R. D. Activation of T cells by a tyrosine kinase activation domain in the cytoplasmic tail of CD3 epsilon. Science. 1992 Jan 3;255(5040):79–82. doi: 10.1126/science.1532456. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Letourneur F., Klausner R. D. T-cell and basophil activation through the cytoplasmic tail of T-cell-receptor zeta family proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Oct 15;88(20):8905–8909. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.20.8905. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis V. A., Koch T., Plutner H., Mellman I. A complementary DNA clone for a macrophage-lymphocyte Fc receptor. 1986 Nov 27-Dec 3Nature. 324(6095):372–375. doi: 10.1038/324372a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miettinen H. M., Rose J. K., Mellman I. Fc receptor isoforms exhibit distinct abilities for coated pit localization as a result of cytoplasmic domain heterogeneity. Cell. 1989 Jul 28;58(2):317–327. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90846-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mustelin T., Coggeshall K. M., Isakov N., Altman A. T cell antigen receptor-mediated activation of phospholipase C requires tyrosine phosphorylation. Science. 1990 Mar 30;247(4950):1584–1587. doi: 10.1126/science.2138816. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nomura J., Matsuo T., Kubota E., Kimoto M., Sakaguchi N. Signal transmission through the B cell-specific MB-1 molecule at the pre-B cell stage. Int Immunol. 1991 Feb;3(2):117–126. doi: 10.1093/intimm/3.2.117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orloff D. G., Ra C. S., Frank S. J., Klausner R. D., Kinet J. P. Family of disulphide-linked dimers containing the zeta and eta chains of the T-cell receptor and the gamma chain of Fc receptors. Nature. 1990 Sep 13;347(6289):189–191. doi: 10.1038/347189a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paolini R., Jouvin M. H., Kinet J. P. Phosphorylation and dephosphorylation of the high-affinity receptor for immunoglobulin E immediately after receptor engagement and disengagement. Nature. 1991 Oct 31;353(6347):855–858. doi: 10.1038/353855a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Park D. J., Rho H. W., Rhee S. G. CD3 stimulation causes phosphorylation of phospholipase C-gamma 1 on serine and tyrosine residues in a human T-cell line. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jun 15;88(12):5453–5456. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.12.5453. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perussia B., Tutt M. M., Qiu W. Q., Kuziel W. A., Tucker P. W., Trinchieri G., Bennett M., Ravetch J. V., Kumar V. Murine natural killer cells express functional Fc gamma receptor II encoded by the Fc gamma R alpha gene. J Exp Med. 1989 Jul 1;170(1):73–86. doi: 10.1084/jem.170.1.73. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips N. E., Parker D. C. Cross-linking of B lymphocyte Fc gamma receptors and membrane immunoglobulin inhibits anti-immunoglobulin-induced blastogenesis. J Immunol. 1984 Feb;132(2):627–632. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ra C., Jouvin M. H., Blank U., Kinet J. P. A macrophage Fc gamma receptor and the mast cell receptor for IgE share an identical subunit. Nature. 1989 Oct 26;341(6244):752–754. doi: 10.1038/341752a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ransom J. T., Harris L. K., Cambier J. C. Anti-Ig induces release of inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate, which mediates mobilization of intracellular Ca++ stores in B lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1986 Jul 15;137(2):708–714. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ravetch J. V., Luster A. D., Weinshank R., Kochan J., Pavlovec A., Portnoy D. A., Hulmes J., Pan Y. C., Unkeless J. C. Structural heterogeneity and functional domains of murine immunoglobulin G Fc receptors. Science. 1986 Nov 7;234(4777):718–725. doi: 10.1126/science.2946078. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ravetch J. V., Perussia B. Alternative membrane forms of Fc gamma RIII(CD16) on human natural killer cells and neutrophils. Cell type-specific expression of two genes that differ in single nucleotide substitutions. J Exp Med. 1989 Aug 1;170(2):481–497. doi: 10.1084/jem.170.2.481. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romeo C., Seed B. Cellular immunity to HIV activated by CD4 fused to T cell or Fc receptor polypeptides. Cell. 1991 Mar 8;64(5):1037–1046. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90327-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakaguchi N., Berger C. N., Melchers F. Isolation of a cDNA copy of an RNA species expressed in murine pre-B cells. EMBO J. 1986 Sep;5(9):2139–2147. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04477.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unkeless J. C. Characterization of a monoclonal antibody directed against mouse macrophage and lymphocyte Fc receptors. J Exp Med. 1979 Sep 19;150(3):580–596. doi: 10.1084/jem.150.3.580. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vivier E., Morin P., O'Brien C., Druker B., Schlossman S. F., Anderson P. Tyrosine phosphorylation of the Fc gamma RIII(CD16): zeta complex in human natural killer cells. Induction by antibody-dependent cytotoxicity but not by natural killing. J Immunol. 1991 Jan 1;146(1):206–210. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wegener A. M., Letourneur F., Hoeveler A., Brocker T., Luton F., Malissen B. The T cell receptor/CD3 complex is composed of at least two autonomous transduction modules. Cell. 1992 Jan 10;68(1):83–95. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90208-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weissman A. M., Baniyash M., Hou D., Samelson L. E., Burgess W. H., Klausner R. D. Molecular cloning of the zeta chain of the T cell antigen receptor. Science. 1988 Feb 26;239(4843):1018–1021. doi: 10.1126/science.3278377. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamanashi Y., Kakiuchi T., Mizuguchi J., Yamamoto T., Toyoshima K. Association of B cell antigen receptor with protein tyrosine kinase Lyn. Science. 1991 Jan 11;251(4990):192–194. doi: 10.1126/science.1702903. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]