Abstract
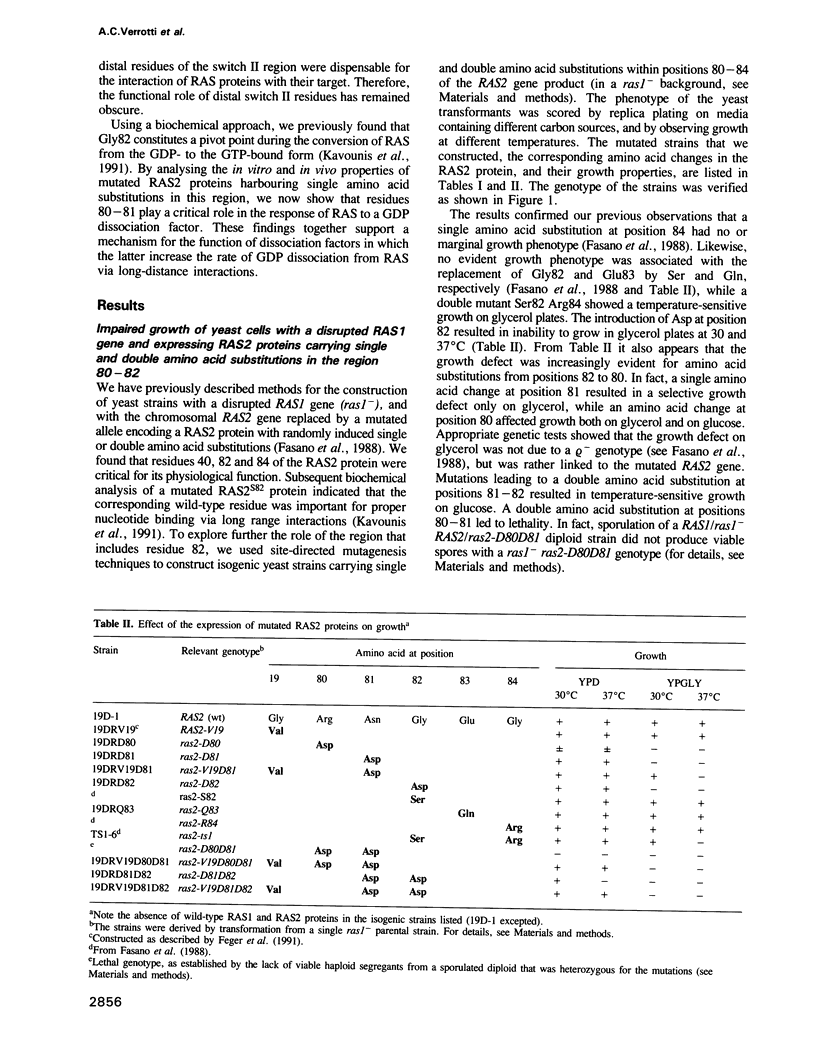
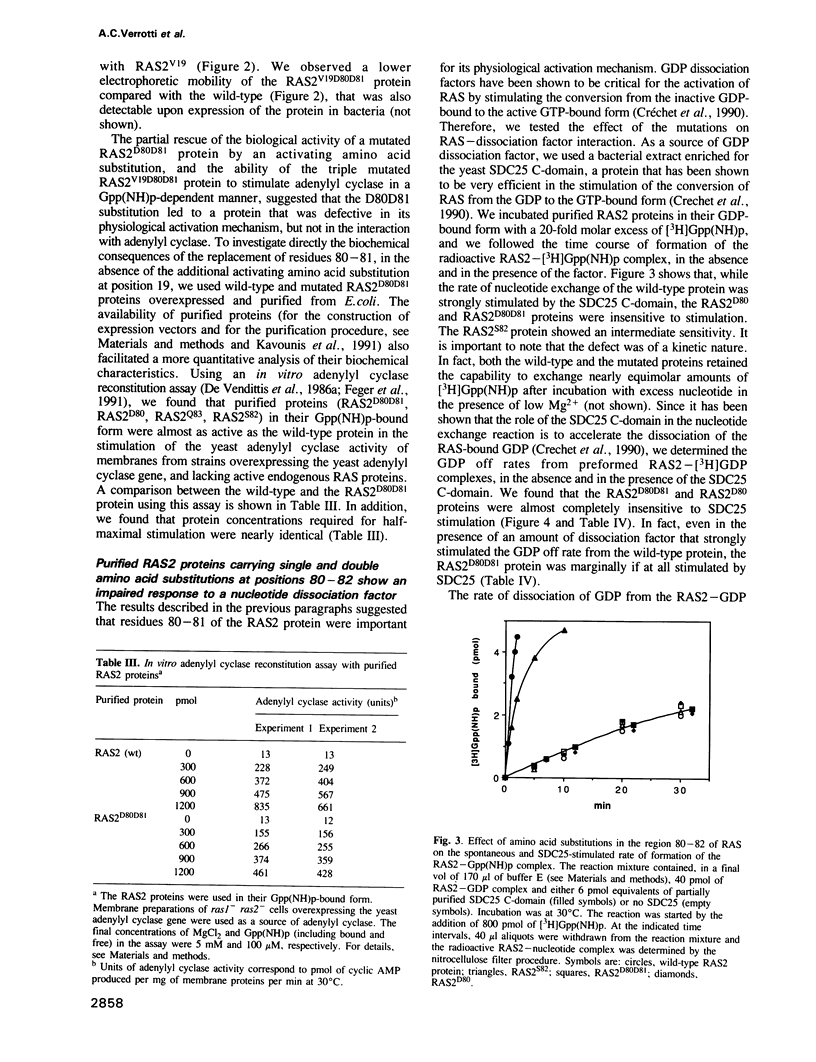
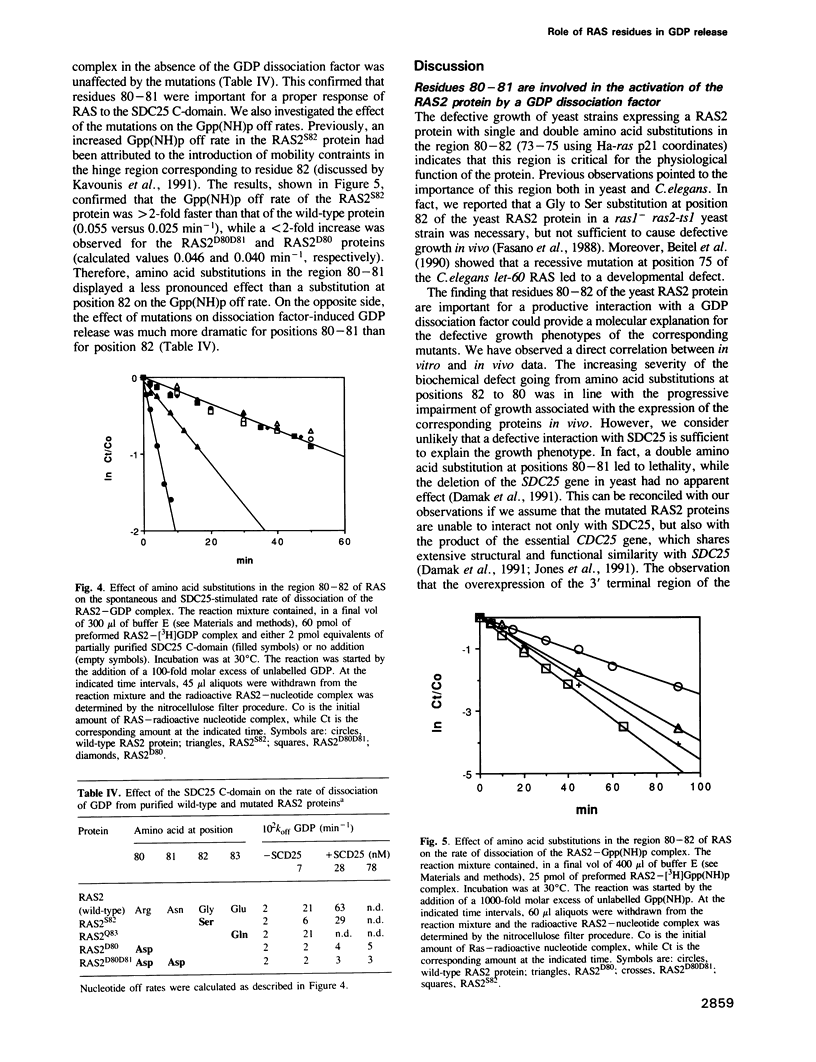
We have previously shown that a conserved glycine at position 82 of the yeast RAS2 protein is involved in the conversion of RAS proteins from the GDP- to the GTP-bound form. We have now investigated the role of glycine 82 and neighbouring amino acids of the distal switch II region in the physiological mechanism of activation of RAS. We have introduced single and double amino acid substitutions at positions 80-83 of the RAS2 gene, and we have investigated the interaction of the corresponding proteins with a yeast GDP dissociation stimulator (SDC25 C-domain). Using purified RAS proteins, we have found that the SDC25-stimulated conversion of RAS from the GDP-bound inactive state to the GTP-bound active state was severely impaired by amino acid substitutions at positions 80-81. However, the rate and the extent of conversion from the GDP- to the GTP-bound form in the absence of dissociation factor was unaffected. The insensitivity of the mutated proteins to the dissociation factor in vitro was paralleled by an inhibitory effect on growth in vivo. The mutations did not significantly affect the interaction of RAS with adenylyl cyclase. These findings point to residues 80-82 as important determinants of the response of RAS to GDP dissociation factors. This suggests a molecular model for the enhancement of nucleotide release from RAS by such factors.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Antonny B., Chardin P., Roux M., Chabre M. GTP hydrolysis mechanisms in ras p21 and in the ras-GAP complex studied by fluorescence measurements on tryptophan mutants. Biochemistry. 1991 Aug 27;30(34):8287–8295. doi: 10.1021/bi00098a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beitel G. J., Clark S. G., Horvitz H. R. Caenorhabditis elegans ras gene let-60 acts as a switch in the pathway of vulval induction. Nature. 1990 Dec 6;348(6301):503–509. doi: 10.1038/348503a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourne H. R., Sanders D. A., McCormick F. The GTPase superfamily: a conserved switch for diverse cell functions. Nature. 1990 Nov 8;348(6297):125–132. doi: 10.1038/348125a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourne H. R., Sanders D. A., McCormick F. The GTPase superfamily: conserved structure and molecular mechanism. Nature. 1991 Jan 10;349(6305):117–127. doi: 10.1038/349117a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broach J. R., Deschenes R. J. The function of ras genes in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Adv Cancer Res. 1990;54:79–139. doi: 10.1016/s0065-230x(08)60809-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broek D., Samiy N., Fasano O., Fujiyama A., Tamanoi F., Northup J., Wigler M. Differential activation of yeast adenylate cyclase by wild-type and mutant RAS proteins. Cell. 1985 Jul;41(3):763–769. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80057-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broek D., Toda T., Michaeli T., Levin L., Birchmeier C., Zoller M., Powers S., Wigler M. The S. cerevisiae CDC25 gene product regulates the RAS/adenylate cyclase pathway. Cell. 1987 Mar 13;48(5):789–799. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90076-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Créchet J. B., Poullet P., Mistou M. Y., Parmeggiani A., Camonis J., Boy-Marcotte E., Damak F., Jacquet M. Enhancement of the GDP-GTP exchange of RAS proteins by the carboxyl-terminal domain of SCD25. Science. 1990 May 18;248(4957):866–868. doi: 10.1126/science.2188363. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Damak F., Boy-Marcotte E., Le-Roscouet D., Guilbaud R., Jacquet M. SDC25, a CDC25-like gene which contains a RAS-activating domain and is a dispensable gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Jan;11(1):202–212. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.1.202. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Vendittis E., Vitelli A., Zahn R., Fasano O. Suppression of defective RAS1 and RAS2 functions in yeast by an adenylate cyclase activated by a single amino acid change. EMBO J. 1986 Dec 20;5(13):3657–3663. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04696.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Vendittis E., Zahn R., Fasano O. Regeneration of the GTP-bound from the GDP-bound form of human and yeast ras proteins by nucleotide exchange. Stimulatory effect of organic and inorganic polyphosphates. Eur J Biochem. 1986 Dec 1;161(2):473–478. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1986.tb10468.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fasano O., Crechet J. B., De Vendittis E., Zahn R., Feger G., Vitelli A., Parmeggiani A. Yeast mutants temperature-sensitive for growth after random mutagenesis of the chromosomal RAS2 gene and deletion of the RAS1 gene. EMBO J. 1988 Nov;7(11):3375–3383. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03210.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feger G., De Vendittis E., Vitelli A., Masturzo P., Zahn R., Verrotti A. C., Kavounis C., Pal G. P., Fasano O. Identification of regulatory residues of the yeast adenylyl cyclase. EMBO J. 1991 Feb;10(2):349–359. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07956.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frascotti G., Coccetti P., Vanoni M. A., Alberghina L., Martegani E. The overexpression of the 3' terminal region of the CDC25 gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae causes growth inhibition and alteration of purine nucleotides pools. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 Jun 13;1089(2):206–212. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(91)90009-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furth M. E., Davis L. J., Fleurdelys B., Scolnick E. M. Monoclonal antibodies to the p21 products of the transforming gene of Harvey murine sarcoma virus and of the cellular ras gene family. J Virol. 1982 Jul;43(1):294–304. doi: 10.1128/jvi.43.1.294-304.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbs J. B., Marshall M. S. The ras oncogene--an important regulatory element in lower eucaryotic organisms. Microbiol Rev. 1989 Jun;53(2):171–185. doi: 10.1128/mr.53.2.171-185.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hart M. J., Eva A., Evans T., Aaronson S. A., Cerione R. A. Catalysis of guanine nucleotide exchange on the CDC42Hs protein by the dbl oncogene product. Nature. 1991 Nov 28;354(6351):311–314. doi: 10.1038/354311a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hattori S., Clanton D. J., Satoh T., Nakamura S., Kaziro Y., Kawakita M., Shih T. Y. Neutralizing monoclonal antibody against ras oncogene product p21 which impairs guanine nucleotide exchange. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 May;7(5):1999–2002. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.5.1999. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hiroyoshi M., Kaibuchi K., Kawamura S., Hata Y., Takai Y. Role of the C-terminal region of smg p21, a ras p21-like small GTP-binding protein, in membrane and smg p21 GDP/GTP exchange protein interactions. J Biol Chem. 1991 Feb 15;266(5):2962–2969. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones S., Vignais M. L., Broach J. R. The CDC25 protein of Saccharomyces cerevisiae promotes exchange of guanine nucleotides bound to ras. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 May;11(5):2641–2646. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.5.2641. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kataoka T., Powers S., McGill C., Fasano O., Strathern J., Broach J., Wigler M. Genetic analysis of yeast RAS1 and RAS2 genes. Cell. 1984 Jun;37(2):437–445. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90374-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kavounis C., Verrotti A. C., De Vendittis E., Bozopoulos A., Di Blasi F., Zahn R., Crechet J. B., Parmeggiani A., Tsernoglou D., Fasano O. Role of glycine-82 as a pivot point during the transition from the inactive to the active form of the yeast Ras2 protein. FEBS Lett. 1991 Apr 9;281(1-2):235–239. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(91)80401-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaziro Y., Itoh H., Kozasa T., Nakafuku M., Satoh T. Structure and function of signal-transducing GTP-binding proteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1991;60:349–400. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.60.070191.002025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowy D. R., Zhang K., DeClue J. E., Willumsen B. M. Regulation of p21ras activity. Trends Genet. 1991 Nov-Dec;7(11-12):346–351. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(91)90253-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pai E. F., Kabsch W., Krengel U., Holmes K. C., John J., Wittinghofer A. Structure of the guanine-nucleotide-binding domain of the Ha-ras oncogene product p21 in the triphosphate conformation. Nature. 1989 Sep 21;341(6239):209–214. doi: 10.1038/341209a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powers S., Kataoka T., Fasano O., Goldfarb M., Strathern J., Broach J., Wigler M. Genes in S. cerevisiae encoding proteins with domains homologous to the mammalian ras proteins. Cell. 1984 Mar;36(3):607–612. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90340-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powers S., O'Neill K., Wigler M. Dominant yeast and mammalian RAS mutants that interfere with the CDC25-dependent activation of wild-type RAS in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Feb;9(2):390–395. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.2.390. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson L. C., Gibbs J. B., Marshall M. S., Sigal I. S., Tatchell K. CDC25: a component of the RAS-adenylate cyclase pathway in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Science. 1987 Mar 6;235(4793):1218–1221. doi: 10.1126/science.3547648. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ron D., Zannini M., Lewis M., Wickner R. B., Hunt L. T., Graziani G., Tronick S. R., Aaronson S. A., Eva A. A region of proto-dbl essential for its transforming activity shows sequence similarity to a yeast cell cycle gene, CDC24, and the human breakpoint cluster gene, bcr. New Biol. 1991 Apr;3(4):372–379. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salomon Y., Londos C., Rodbell M. A highly sensitive adenylate cyclase assay. Anal Biochem. 1974 Apr;58(2):541–548. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(74)90222-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlichting I., Almo S. C., Rapp G., Wilson K., Petratos K., Lentfer A., Wittinghofer A., Kabsch W., Pai E. F., Petsko G. A. Time-resolved X-ray crystallographic study of the conformational change in Ha-Ras p21 protein on GTP hydrolysis. Nature. 1990 May 24;345(6273):309–315. doi: 10.1038/345309a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sigal I. S., Gibbs J. B., D'Alonzo J. S., Scolnick E. M. Identification of effector residues and a neutralizing epitope of Ha-ras-encoded p21. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jul;83(13):4725–4729. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.13.4725. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamanoi F. Yeast RAS genes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1988 Aug 3;948(1):1–15. doi: 10.1016/0304-419x(88)90002-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tong L. A., de Vos A. M., Milburn M. V., Kim S. H. Crystal structures at 2.2 A resolution of the catalytic domains of normal ras protein and an oncogenic mutant complexed with GDP. J Mol Biol. 1991 Feb 5;217(3):503–516. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(91)90753-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valencia A., Chardin P., Wittinghofer A., Sander C. The ras protein family: evolutionary tree and role of conserved amino acids. Biochemistry. 1991 May 14;30(19):4637–4648. doi: 10.1021/bi00233a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valencia A., Kjeldgaard M., Pai E. F., Sander C. GTPase domains of ras p21 oncogene protein and elongation factor Tu: analysis of three-dimensional structures, sequence families, and functional sites. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jun 15;88(12):5443–5447. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.12.5443. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willumsen B. M., Papageorge A. G., Kung H. F., Bekesi E., Robins T., Johnsen M., Vass W. C., Lowy D. R. Mutational analysis of a ras catalytic domain. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jul;6(7):2646–2654. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.7.2646. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willumsen B. M., Vass W. C., Velu T. J., Papageorge A. G., Schiller J. T., Lowy D. R. The bovine papillomavirus E5 oncogene can cooperate with ras: identification of p21 amino acids critical for transformation by c-rasH but not v-rasH. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Dec;11(12):6026–6033. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.12.6026. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]