Abstract
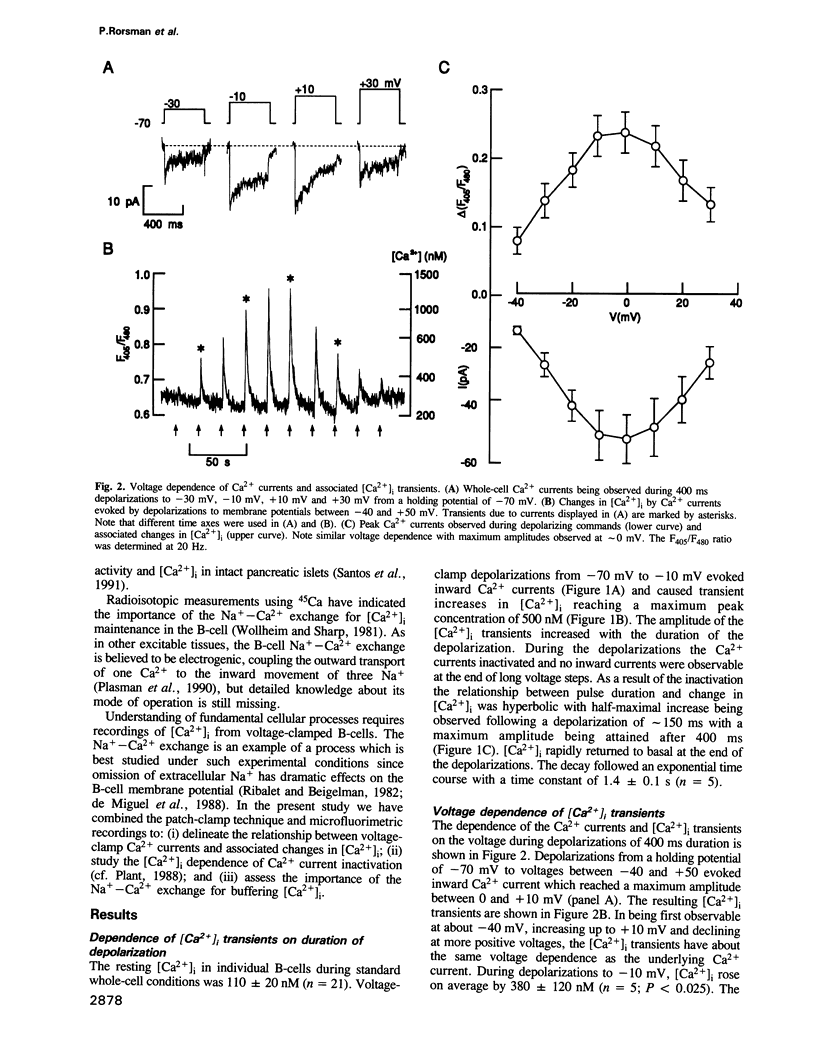
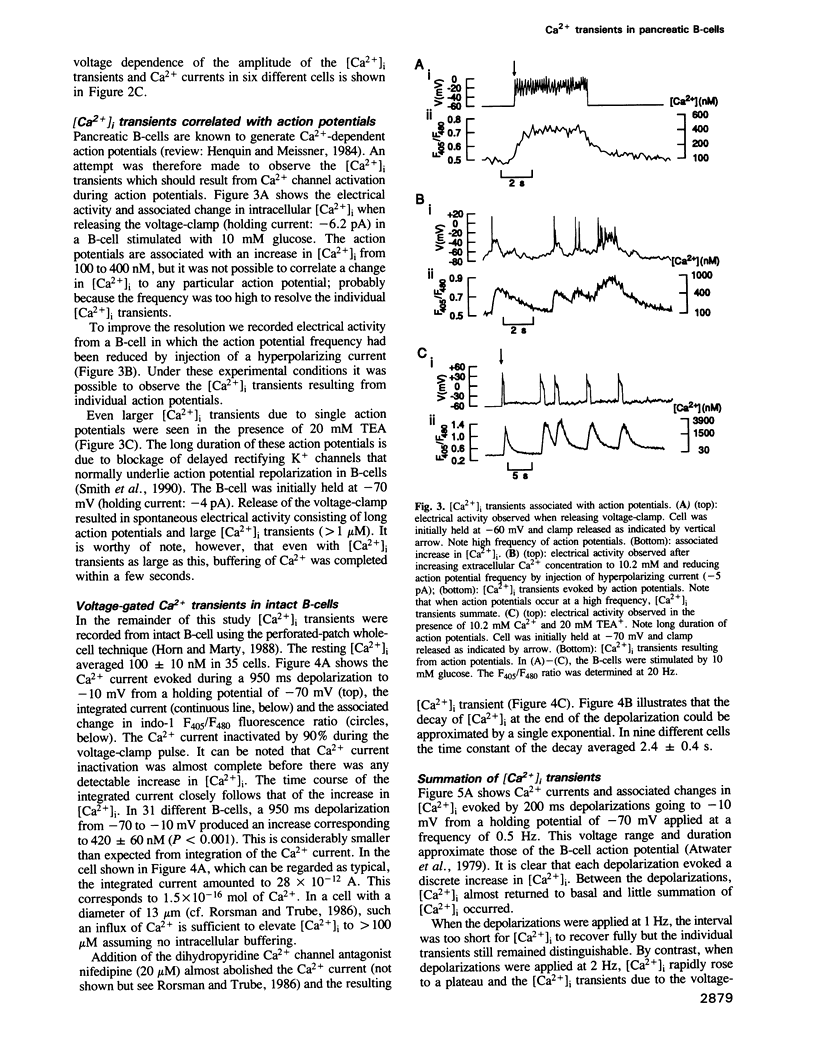
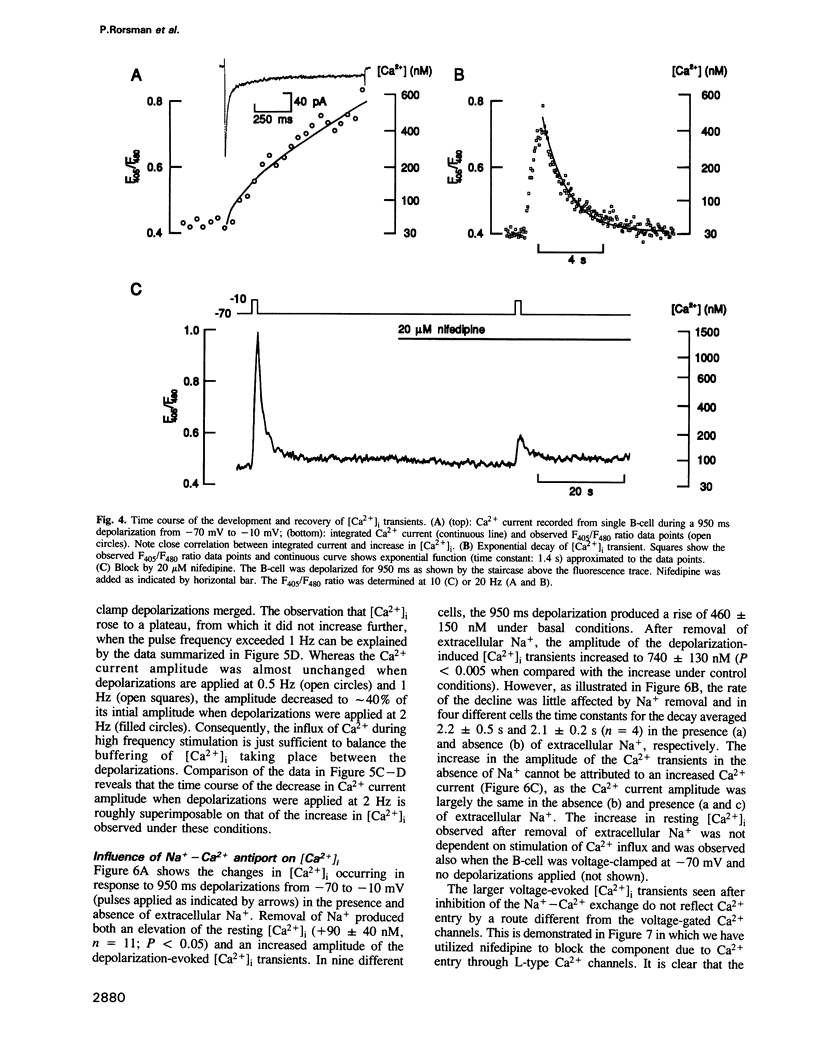
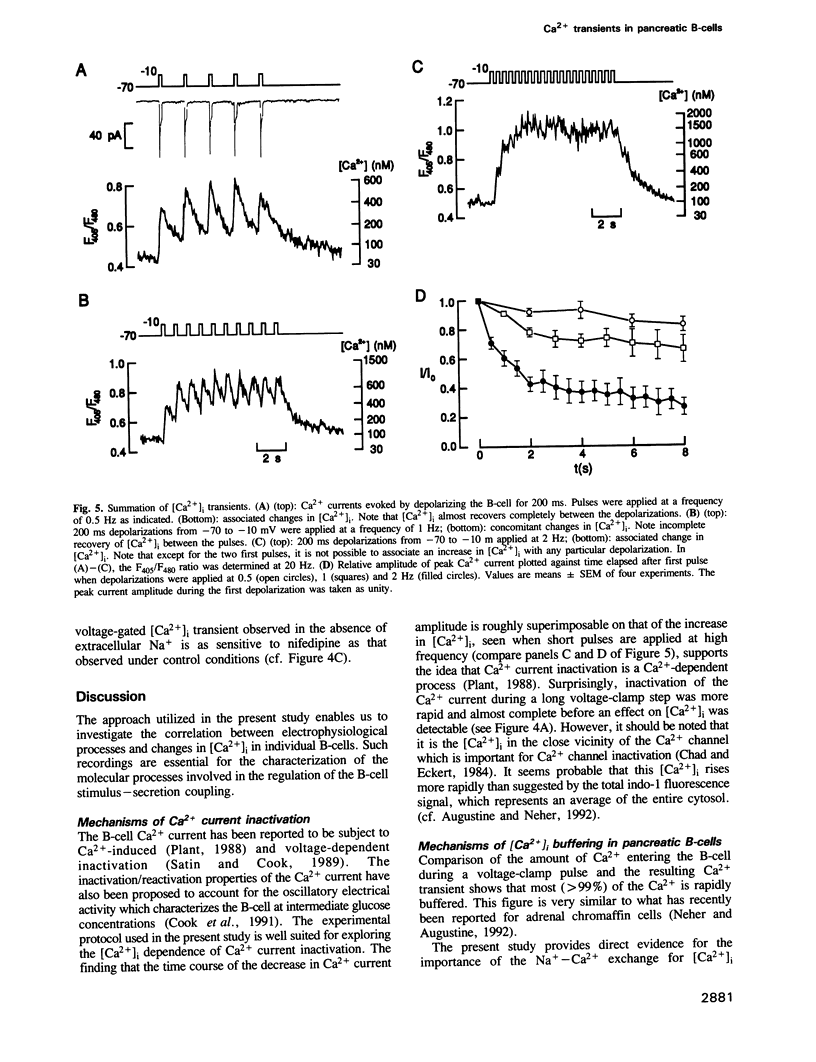
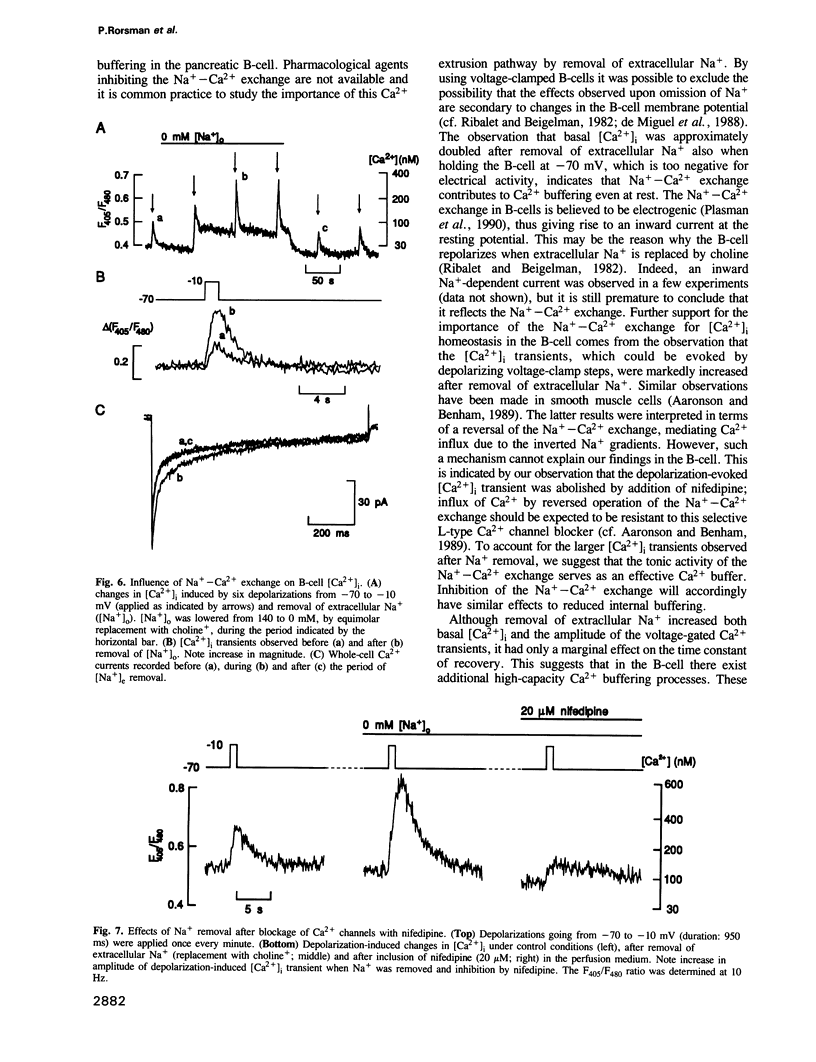
Changes in the cytoplasmic free calcium concentration ([Ca2+]i) in pancreatic B-cells play an important role in the regulation of insulin secretion. We have recorded [Ca2+]i transients evoked by single action potentials and voltage-clamp Ca2+ currents in isolated B-cells by the combination of dual wavelength emission spectrofluorimetry and the patch-clamp technique. A 500-1000 ms depolarization of the B-cell from -70 to -10 mV evoked a transient rise in [Ca2+]i from a resting value of approximately 100 nM to a peak concentration of 550 nM. Similar [Ca2+]i changes were associated with individual action potentials. The depolarization-induced [Ca2+]i transients were abolished by application of nifedipine, a blocker of L-type Ca2+ channels, indicating their dependence on influx of extracellular Ca2+. Following the voltage-clamp step, [Ca2+]i decayed with a time constant of approximately 2.5 s and summation of [Ca2+]i occurred whenever depolarizations were applied with an interval of less than 2 s. The importance of the Na(+)-Ca2+ exchange for B-cell [Ca2+]i maintenance was evidenced by the demonstration that basal [Ca2+]i rose to 200 nM and the magnitude of the depolarization-evoked [Ca2+]i transients was markedly increased after omission of extracellular Na+. However, the rate by which [Ca2+]i returned to basal was not affected, suggesting the existence of additional [Ca2+]i buffering processes.
Full text
PDF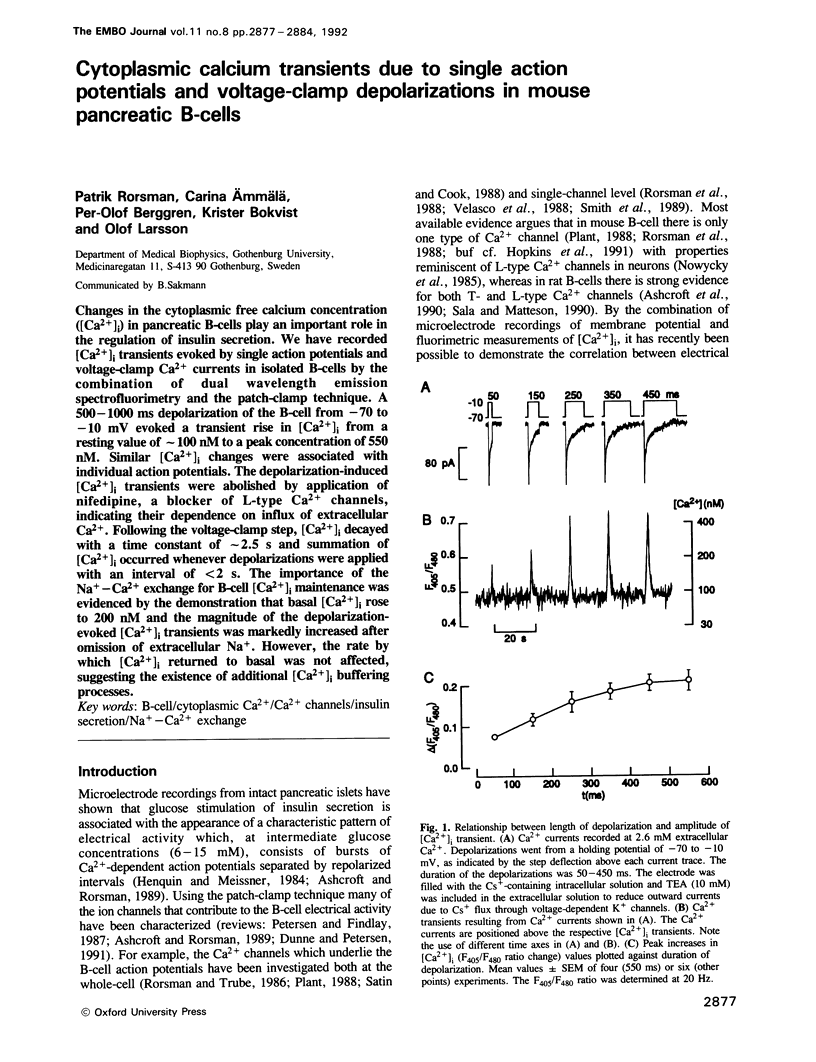


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aaronson P. I., Benham C. D. Alterations in [Ca2+]i mediated by sodium-calcium exchange in smooth muscle cells isolated from the guinea-pig ureter. J Physiol. 1989 Sep;416:1–18. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1989.sp017745. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arkhammar P., Nilsson T., Rorsman P., Berggren P. O. Inhibition of ATP-regulated K+ channels precedes depolarization-induced increase in cytoplasmic free Ca2+ concentration in pancreatic beta-cells. J Biol Chem. 1987 Apr 25;262(12):5448–5454. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashcroft F. M., Kelly R. P., Smith P. A. Two types of Ca channel in rat pancreatic beta-cells. Pflugers Arch. 1990 Jan;415(4):504–506. doi: 10.1007/BF00373633. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashcroft F. M., Rorsman P. Electrophysiology of the pancreatic beta-cell. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 1989;54(2):87–143. doi: 10.1016/0079-6107(89)90013-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atwater I., Ribalet B., Rojas E. Mouse pancreatic beta-cells: tetraethylammonium blockage of the potassium permeability increase induced by depolarization. J Physiol. 1979 Mar;288:561–574. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Augustine G. J., Neher E. Calcium requirements for secretion in bovine chromaffin cells. J Physiol. 1992 May;450:247–271. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1992.sp019126. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benham C. D. Voltage-gated and agonist-mediated rises in intracellular Ca2+ in rat clonal pituitary cells (GH3) held under voltage clamp. J Physiol. 1989 Aug;415:143–158. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1989.sp017716. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chad J. E., Eckert R. Calcium domains associated with individual channels can account for anomalous voltage relations of CA-dependent responses. Biophys J. 1984 May;45(5):993–999. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(84)84244-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cook D. L., Satin L. S., Hopkins W. F. Pancreatic B cells are bursting, but how? Trends Neurosci. 1991 Sep;14(9):411–414. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(91)90033-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunne M. J., Petersen O. H. Potassium selective ion channels in insulin-secreting cells: physiology, pharmacology and their role in stimulus-secretion coupling. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 Mar 7;1071(1):67–82. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(91)90012-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grapengiesser E., Gylfe E., Hellman B. Cyclic AMP as a determinant for glucose induction of fast Ca2+ oscillations in isolated pancreatic beta-cells. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jul 5;266(19):12207–12210. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grynkiewicz G., Poenie M., Tsien R. Y. A new generation of Ca2+ indicators with greatly improved fluorescence properties. J Biol Chem. 1985 Mar 25;260(6):3440–3450. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamill O. P., Marty A., Neher E., Sakmann B., Sigworth F. J. Improved patch-clamp techniques for high-resolution current recording from cells and cell-free membrane patches. Pflugers Arch. 1981 Aug;391(2):85–100. doi: 10.1007/BF00656997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henquin J. C., Meissner H. P. Significance of ionic fluxes and changes in membrane potential for stimulus-secretion coupling in pancreatic B-cells. Experientia. 1984 Oct 15;40(10):1043–1052. doi: 10.1007/BF01971450. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopkins W. F., Satin L. S., Cook D. L. Inactivation kinetics and pharmacology distinguish two calcium currents in mouse pancreatic B-cells. J Membr Biol. 1991 Feb;119(3):229–239. doi: 10.1007/BF01868728. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horn R., Marty A. Muscarinic activation of ionic currents measured by a new whole-cell recording method. J Gen Physiol. 1988 Aug;92(2):145–159. doi: 10.1085/jgp.92.2.145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson A. P., Timmerman M. P., Bagshaw C. R., Ashley C. C. The kinetics of calcium binding to fura-2 and indo-1. FEBS Lett. 1987 May 25;216(1):35–39. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)80752-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Juntti-Berggren L., Arkhammar P., Nilsson T., Rorsman P., Berggren P. O. Glucose-induced increase in cytoplasmic pH in pancreatic beta-cells is mediated by Na+/H+ exchange, an effect not dependent on protein kinase C. J Biol Chem. 1991 Dec 15;266(35):23537–23541. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landt M., McDaniel M. L., Bry C. G., Kotagal N., Colca J. R., Lacy P. E., McDonald J. M. Calmodulin-activated protein kinase activity in rat pancreatic islet cell membranes. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1982 Jan;213(1):148–154. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(82)90449-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lebrun P., Atwater I. Effects of the calcium channel agonist, BAY K 8644, on electrical activity in mouse pancreatic B-cells. Biophys J. 1985 Dec;48(6):919–930. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(85)83855-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neher E., Augustine G. J. Calcium gradients and buffers in bovine chromaffin cells. J Physiol. 1992 May;450:273–301. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1992.sp019127. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsson T., Arkhammar P., Hallberg A., Hellman B., Berggren P. O. Characterization of the inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate-induced Ca2+ release in pancreatic beta-cells. Biochem J. 1987 Dec 1;248(2):329–336. doi: 10.1042/bj2480329. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nowycky M. C., Fox A. P., Tsien R. W. Three types of neuronal calcium channel with different calcium agonist sensitivity. Nature. 1985 Aug 1;316(6027):440–443. doi: 10.1038/316440a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pershadsingh H. A., McDaniel M. L., Landt M., Bry C. G., Lacy P. E., McDonald J. M. Ca2+-activated ATPase and ATP-dependent calmodulin-stimulated Ca2+ transport in islet cell plasma membrane. Nature. 1980 Dec 4;288(5790):492–495. doi: 10.1038/288492a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petersen O. H., Findlay I. Electrophysiology of the pancreas. Physiol Rev. 1987 Jul;67(3):1054–1116. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1987.67.3.1054. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plant T. D. Properties and calcium-dependent inactivation of calcium currents in cultured mouse pancreatic B-cells. J Physiol. 1988 Oct;404:731–747. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp017316. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plasman P. O., Lebrun P., Herchuelz A. Characterization of the process of sodium-calcium exchange in pancreatic islet cells. Am J Physiol. 1990 Dec;259(6 Pt 1):E844–E850. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1990.259.6.E844. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pralong W. F., Bartley C., Wollheim C. B. Single islet beta-cell stimulation by nutrients: relationship between pyridine nucleotides, cytosolic Ca2+ and secretion. EMBO J. 1990 Jan;9(1):53–60. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08079.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ribalet B., Beigelman P. M. Effects of sodium on beta-cell electrical activity. Am J Physiol. 1982 May;242(5):C296–C303. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1982.242.5.C296. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rorsman P., Ashcroft F. M., Trube G. Single Ca channel currents in mouse pancreatic B-cells. Pflugers Arch. 1988 Oct;412(6):597–603. doi: 10.1007/BF00583760. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rorsman P., Trube G. Calcium and delayed potassium currents in mouse pancreatic beta-cells under voltage-clamp conditions. J Physiol. 1986 May;374:531–550. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1986.sp016096. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sala S., Matteson D. R. Single-channel recordings of two types of calcium channels in rat pancreatic beta-cells. Biophys J. 1990 Aug;58(2):567–571. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(90)82400-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Santos R. M., Rosario L. M., Nadal A., Garcia-Sancho J., Soria B., Valdeolmillos M. Widespread synchronous [Ca2+]i oscillations due to bursting electrical activity in single pancreatic islets. Pflugers Arch. 1991 May;418(4):417–422. doi: 10.1007/BF00550880. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Satin L. S., Cook D. L. Calcium current inactivation in insulin-secreting cells is mediated by calcium influx and membrane depolarization. Pflugers Arch. 1989 May;414(1):1–10. doi: 10.1007/BF00585619. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Satin L. S., Cook D. L. Evidence for two calcium currents in insulin-secreting cells. Pflugers Arch. 1988 Apr;411(4):401–409. doi: 10.1007/BF00587719. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith P. A., Bokvist K., Arkhammar P., Berggren P. O., Rorsman P. Delayed rectifying and calcium-activated K+ channels and their significance for action potential repolarization in mouse pancreatic beta-cells. J Gen Physiol. 1990 Jun;95(6):1041–1059. doi: 10.1085/jgp.95.6.1041. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith P. A., Rorsman P., Ashcroft F. M. Modulation of dihydropyridine-sensitive Ca2+ channels by glucose metabolism in mouse pancreatic beta-cells. Nature. 1989 Nov 30;342(6249):550–553. doi: 10.1038/342550a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugden M. C., Christie M. R., Ashcroft S. J. Presence and possible role of calcium-dependent regulator (calmodulin) in rat islets of Langerhans. FEBS Lett. 1979 Sep 1;105(1):95–100. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(79)80894-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tepikin A. V., Voronina S. G., Gallacher D. V., Petersen O. H. Acetylcholine-evoked increase in the cytoplasmic Ca2+ concentration and Ca2+ extrusion measured simultaneously in single mouse pancreatic acinar cells. J Biol Chem. 1992 Feb 25;267(6):3569–3572. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P., Surprenant A., Almers W. Cytosolic Ca2+, exocytosis, and endocytosis in single melanotrophs of the rat pituitary. Neuron. 1990 Nov;5(5):723–733. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(90)90226-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valverde I., Vandermeers A., Anjaneyulu R., Malaisse W. J. Calmodulin activation of adenylate cyclase in pancreatic islets. Science. 1979 Oct 12;206(4415):225–227. doi: 10.1126/science.225798. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Velasco J. M., Petersen J. U., Petersen O. H. Single-channel Ba2+ currents in insulin-secreting cells are activated by glyceraldehyde stimulation. FEBS Lett. 1988 Apr 25;231(2):366–370. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)80851-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wollheim C. B., Sharp G. W. Regulation of insulin release by calcium. Physiol Rev. 1981 Oct;61(4):914–973. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1981.61.4.914. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Miguel R., Tamagawa T., Schmeer W., Nenquin M., Henquin J. C. Effects of acute sodium omission on insulin release, ionic flux and membrane potential in mouse pancreatic B-cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1988 Apr 25;969(2):198–207. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(88)90076-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



