Abstract
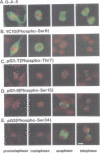
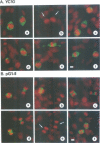
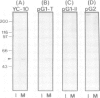
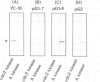
Glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) is a component of glial filaments specific to astroglia. We now report the spatial and temporal distributions of four phosphorylated sites in the GFAP molecule during mitosis of astroglial cells, determined by antibodies which can distinguish phosphorylated epitopes from non-phosphorylated-epitopes. Immunofluorescence microscopy showed that the Ser8 residues in the entire cytoplasmic glial filament system are initially phosphorylated when the cells enter mitosis. In cytokinesis, the phosphoSer8 residues become dephosphorylated, whereas Thr7, Ser13 and Ser34 in glial filaments at the cleavage furrow become the preferred sites of phosphorylation. The cdc2 kinase purified from mitotic cells can phosphorylate GFAP at Ser8 but not at Thr7, Ser13 or Ser34, in vitro. These results suggest that cdc2 kinase acts as a glial filament kinase only at the G2-M phase transition while other glial filament kinases are probably activated at the cleavage furrow before final separation of the daughter cells.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ando S., Tanabe K., Gonda Y., Sato C., Inagaki M. Domain- and sequence-specific phosphorylation of vimentin induces disassembly of the filament structure. Biochemistry. 1989 Apr 4;28(7):2974–2979. doi: 10.1021/bi00433a035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ando S., Tokui T., Yamauchi T., Sugiura H., Tanabe K., Inagaki M. Evidence that Ser-82 is a unique phosphorylation site on vimentin for Ca2(+)-calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 Mar 29;175(3):955–962. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(91)91658-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aubin J. E., Osborn M., Franke W. W., Weber K. Intermediate filaments of the vimentin-type and the cytokeratin-type are distributed differently during mitosis. Exp Cell Res. 1980 Sep;129(1):149–165. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(80)90340-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beach D., Durkacz B., Nurse P. Functionally homologous cell cycle control genes in budding and fission yeast. Nature. 1982 Dec 23;300(5894):706–709. doi: 10.1038/300706a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beavo J. A., Bechtel P. J., Krebs E. G. Preparation of homogeneous cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase(s) and its subunits from rabbit skeletal muscle. Methods Enzymol. 1974;38:299–308. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(74)38046-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blose S. H., Bushnell A. Observations on the vimentin-10-NM filaments during mitosis in BHK21 cells. Exp Cell Res. 1982 Nov;142(1):57–62. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(82)90408-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blose S. H., Chacko S. Rings of intermediate (100 A) filament bundles in the perinuclear region of vascular endothelial cells. Their mobilization by colcemid and mitosis. J Cell Biol. 1976 Aug;70(2 Pt 1):459–466. doi: 10.1083/jcb.70.2.459. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Celis J. E., Larsen P. M., Fey S. J., Celis A. Phosphorylation of keratin and vimentin polypeptides in normal and transformed mitotic human epithelial amnion cells: behavior of keratin and vimentin filaments during mitosis. J Cell Biol. 1983 Nov;97(5 Pt 1):1429–1434. doi: 10.1083/jcb.97.5.1429. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou Y. H., Bischoff J. R., Beach D., Goldman R. D. Intermediate filament reorganization during mitosis is mediated by p34cdc2 phosphorylation of vimentin. Cell. 1990 Sep 21;62(6):1063–1071. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90384-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou Y. H., Ngai K. L., Goldman R. The regulation of intermediate filament reorganization in mitosis. p34cdc2 phosphorylates vimentin at a unique N-terminal site. J Biol Chem. 1991 Apr 25;266(12):7325–7328. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou Y. H., Rosevear E., Goldman R. D. Phosphorylation and disassembly of intermediate filaments in mitotic cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Mar;86(6):1885–1889. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.6.1885. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Draetta G., Luca F., Westendorf J., Brizuela L., Ruderman J., Beach D. Cdc2 protein kinase is complexed with both cyclin A and B: evidence for proteolytic inactivation of MPF. Cell. 1989 Mar 10;56(5):829–838. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90687-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans R. M. Cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase-induced vimentin filament disassembly involves modification of the N-terminal domain of intermediate filament subunits. FEBS Lett. 1988 Jul 4;234(1):73–78. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)81306-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans R. M., Fink L. M. An alteration in the phosphorylation of vimentin-type intermediate filaments is associated with mitosis in cultured mammalian cells. Cell. 1982 May;29(1):43–52. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90088-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans R. M. Peptide mapping of phosphorylated vimentin. Evidence for a site-specific alteration in mitotic cells. J Biol Chem. 1984 May 10;259(9):5372–5375. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans R. M. Phosphorylation of vimentin in mitotically selected cells. In vitro cyclic AMP-independent kinase and calcium-stimulated phosphatase activities. J Cell Biol. 1989 Jan;108(1):67–78. doi: 10.1083/jcb.108.1.67. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans R. M. The intermediate-filament proteins vimentin and desmin are phosphorylated in specific domains. Eur J Cell Biol. 1988 Apr;46(1):152–160. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franke W. W., Schmid E., Grund C., Geiger B. Intermediate filament proteins in nonfilamentous structures: transient disintegration and inclusion of subunit proteins in granular aggregates. Cell. 1982 Aug;30(1):103–113. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90016-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gard D. L., Lazarides E. Cyclic AMP-modulated phosphorylation of intermediate filament proteins in cultured avian myogenic cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;2(9):1104–1114. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.9.1104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gautier J., Norbury C., Lohka M., Nurse P., Maller J. Purified maturation-promoting factor contains the product of a Xenopus homolog of the fission yeast cell cycle control gene cdc2+. Cell. 1988 Jul 29;54(3):433–439. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90206-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geisler N., Hatzfeld M., Weber K. Phosphorylation in vitro of vimentin by protein kinases A and C is restricted to the head domain. Identification of the phosphoserine sites and their influence on filament formation. Eur J Biochem. 1989 Aug 1;183(2):441–447. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1989.tb14947.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geisler N., Weber K. Amino acid sequence data on glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFA); implications for the subdivision of intermediate filaments into epithelial and non-epithelial members. EMBO J. 1983;2(11):2059–2063. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01700.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geisler N., Weber K. Phosphorylation of desmin in vitro inhibits formation of intermediate filaments; identification of three kinase A sites in the aminoterminal head domain. EMBO J. 1988 Jan;7(1):15–20. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02778.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonda Y., Nishizawa K., Ando S., Kitamura S., Minoura Y., Nishi Y., Inagaki M. Involvement of protein kinase C in the regulation of assembly-disassembly of neurofilaments in vitro. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 Mar 30;167(3):1316–1325. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(90)90667-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hisanaga S., Gonda Y., Inagaki M., Ikai A., Hirokawa N. Effects of phosphorylation of the neurofilament L protein on filamentous structures. Cell Regul. 1990 Jan;1(2):237–248. doi: 10.1091/mbc.1.2.237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horwitz B., Kupfer H., Eshhar Z., Geiger B. Reorganization of arrays of prekeratin filaments during mitosis. Immunofluorescence microscopy with multiclonal and monoclonal prekeratin antibodies. Exp Cell Res. 1981 Aug;134(2):281–290. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(81)90427-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inagaki M., Gonda Y., Matsuyama M., Nishizawa K., Nishi Y., Sato C. Intermediate filament reconstitution in vitro. The role of phosphorylation on the assembly-disassembly of desmin. J Biol Chem. 1988 Apr 25;263(12):5970–5978. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inagaki M., Gonda Y., Nishizawa K., Kitamura S., Sato C., Ando S., Tanabe K., Kikuchi K., Tsuiki S., Nishi Y. Phosphorylation sites linked to glial filament disassembly in vitro locate in a non-alpha-helical head domain. J Biol Chem. 1990 Mar 15;265(8):4722–4729. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inagaki M., Nishi Y., Nishizawa K., Matsuyama M., Sato C. Site-specific phosphorylation induces disassembly of vimentin filaments in vitro. Nature. 1987 Aug 13;328(6131):649–652. doi: 10.1038/328649a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones J. C., Goldman A. E., Yang H. Y., Goldman R. D. The organizational fate of intermediate filament networks in two epithelial cell types during mitosis. J Cell Biol. 1985 Jan;100(1):93–102. doi: 10.1083/jcb.100.1.93. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitamura S., Ando S., Shibata M., Tanabe K., Sato C., Inagaki M. Protein kinase C phosphorylation of desmin at four serine residues within the non-alpha-helical head domain. J Biol Chem. 1989 Apr 5;264(10):5674–5678. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labbe J. C., Lee M. G., Nurse P., Picard A., Doree M. Activation at M-phase of a protein kinase encoded by a starfish homologue of the cell cycle control gene cdc2+. Nature. 1988 Sep 15;335(6187):251–254. doi: 10.1038/335251a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lane E. B., Goodman S. L., Trejdosiewicz L. K. Disruption of the keratin filament network during epithelial cell division. EMBO J. 1982;1(11):1365–1372. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01324.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer H. E., Hoffmann-Posorske E., Korte H., Heilmeyer L. M., Jr Sequence analysis of phosphoserine-containing peptides. Modification for picomolar sensitivity. FEBS Lett. 1986 Aug 11;204(1):61–66. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)81388-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishizawa K., Yano T., Shibata M., Ando S., Saga S., Takahashi T., Inagaki M. Specific localization of phosphointermediate filament protein in the constricted area of dividing cells. J Biol Chem. 1991 Feb 15;266(5):3074–3079. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nurse P., Bissett Y. Gene required in G1 for commitment to cell cycle and in G2 for control of mitosis in fission yeast. Nature. 1981 Aug 6;292(5823):558–560. doi: 10.1038/292558a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nurse P., Thuriaux P., Nasmyth K. Genetic control of the cell division cycle in the fission yeast Schizosaccharomyces pombe. Mol Gen Genet. 1976 Jul 23;146(2):167–178. doi: 10.1007/BF00268085. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Connor C. M., Gard D. L., Lazarides E. Phosphorylation of intermediate filament proteins by cAMP-dependent protein kinases. Cell. 1981 Jan;23(1):135–143. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90278-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reeves S. A., Helman L. J., Allison A., Israel M. A. Molecular cloning and primary structure of human glial fibrillary acidic protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jul;86(13):5178–5182. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.13.5178. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinert P. M., Roop D. R. Molecular and cellular biology of intermediate filaments. Annu Rev Biochem. 1988;57:593–625. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.57.070188.003113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stull J. T., Buss J. E. Phosphorylation of cardiac troponin by cyclic adenosine 3':5'-monophosphate-dependent protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 1977 Feb 10;252(3):851–857. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tokui T., Yamauchi T., Yano T., Nishi Y., Kusagawa M., Yatani R., Inagaki M. Ca2(+)-calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II phosphorylates various types of non-epithelial intermediate filament proteins. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 Jun 29;169(3):896–904. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(90)91977-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tölle H. G., Weber K., Osborn M. Keratin filament disruption in interphase and mitotic cells--how is it induced? Eur J Cell Biol. 1987 Feb;43(1):35–47. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westwood J. T., Church R. B., Wagenaar E. B. Changes in protein phosphorylation during the cell cycle of Chinese hamster ovary cells. J Biol Chem. 1985 Aug 25;260(18):10308–10313. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yano T., Taura C., Shibata M., Hirono Y., Ando S., Kusubata M., Takahashi T., Inagaki M. A monoclonal antibody to the phosphorylated form of glial fibrillary acidic protein: application to a non-radioactive method for measuring protein kinase activities. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 Mar 29;175(3):1144–1151. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(91)91685-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zieve G. W., Turnbull D., Mullins J. M., McIntosh J. R. Production of large numbers of mitotic mammalian cells by use of the reversible microtubule inhibitor nocodazole. Nocodazole accumulated mitotic cells. Exp Cell Res. 1980 Apr;126(2):397–405. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(80)90279-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]