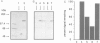
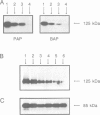
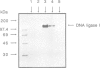
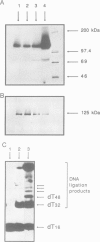
Abstract
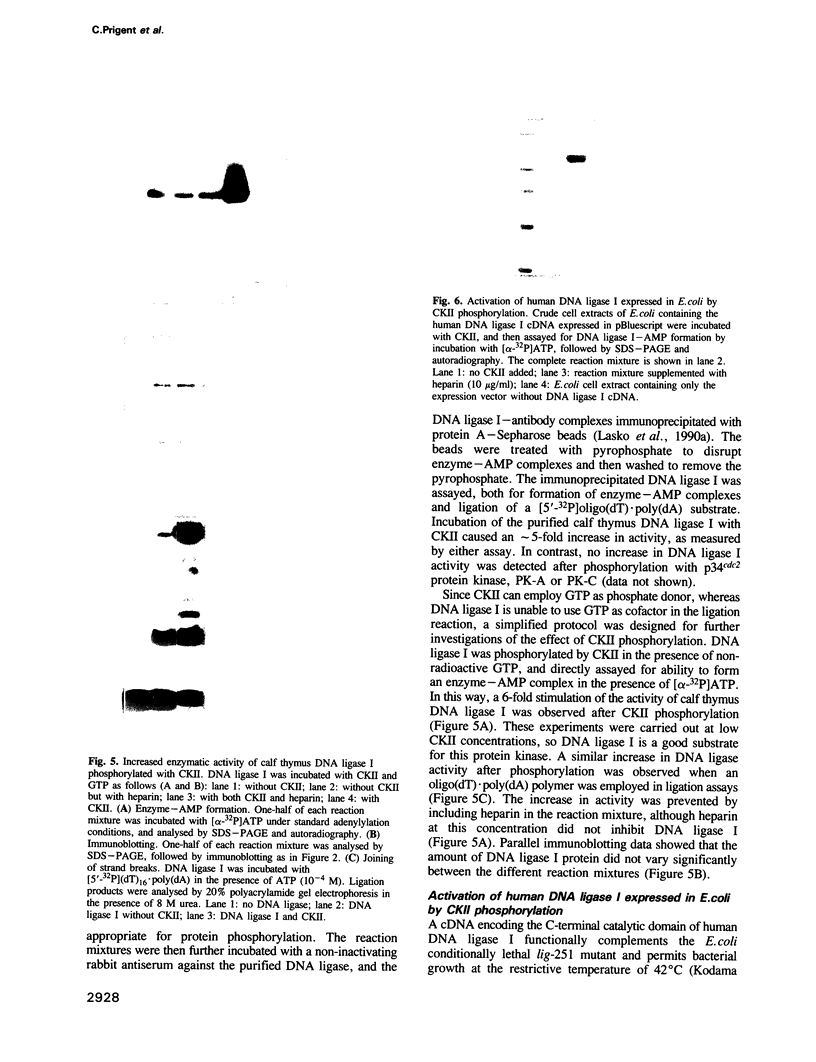
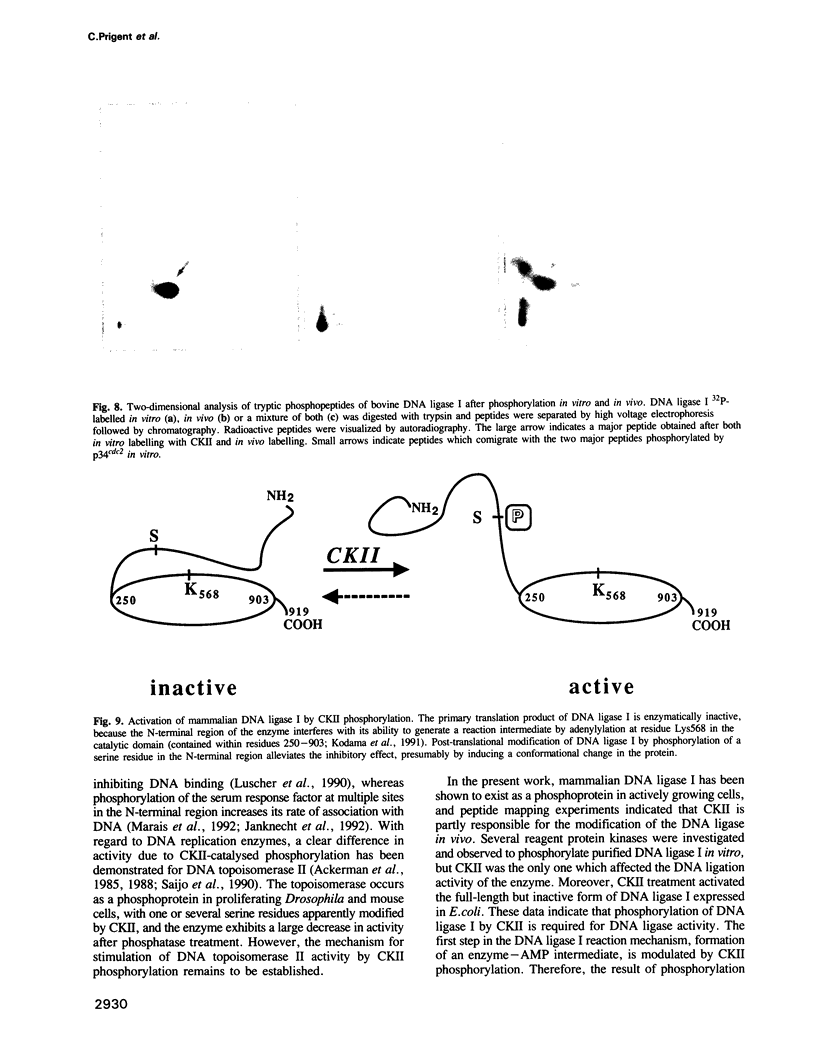
Mammalian DNA ligase I has been shown to be a phosphoprotein. Dephosphorylation of purified DNA ligase I causes inactivation, an effect dependent on the presence of the N-terminal region of the protein. Expression of full-length human DNA ligase I in Escherichia coli yielded soluble but catalytically inactive enzyme whereas an N-terminally truncated form expressed activity. Incubation of the full-length preparation from E. coli with purified casein kinase II (CKII) resulted in phosphorylation of the N-terminal region and was accompanied by activation of the DNA ligase. Of a variety of purified protein kinases tested, only CKII stimulated the activity of calf thymus DNA ligase I. Tryptic phosphopeptide analysis of DNA ligase I revealed that CKII specifically phosphorylated a major peptide also apparently phosphorylated in cells, implying that CKII is a protein kinase acting on DNA ligase I in the cell nucleus. These data suggest that DNA ligase I is negatively regulated by its N-terminal region and that this inhibition can be relieved by post-translational modification.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ackerman P., Glover C. V., Osheroff N. Phosphorylation of DNA topoisomerase II by casein kinase II: modulation of eukaryotic topoisomerase II activity in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 May;82(10):3164–3168. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.10.3164. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ackerman P., Glover C. V., Osheroff N. Phosphorylation of DNA topoisomerase II in vivo and in total homogenates of Drosophila Kc cells. The role of casein kinase II. J Biol Chem. 1988 Sep 5;263(25):12653–12660. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnes D. E., Johnston L. H., Kodama K., Tomkinson A. E., Lasko D. D., Lindahl T. Human DNA ligase I cDNA: cloning and functional expression in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Sep;87(17):6679–6683. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.17.6679. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnes D. E., Tomkinson A. E., Lehmann A. R., Webster A. D., Lindahl T. Mutations in the DNA ligase I gene of an individual with immunodeficiencies and cellular hypersensitivity to DNA-damaging agents. Cell. 1992 May 1;69(3):495–503. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90450-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyle W. J., van der Geer P., Hunter T. Phosphopeptide mapping and phosphoamino acid analysis by two-dimensional separation on thin-layer cellulose plates. Methods Enzymol. 1991;201:110–149. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)01013-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cripps-Wolfman J., Henshaw E. C., Bambara R. A. Alterations in the phosphorylation and activity of DNA polymerase alpha correlate with the change in replicative DNA synthesis as quiescent cells re-enter the cell cycle. J Biol Chem. 1989 Nov 25;264(33):19478–19486. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dermody J. J., Robinson G. T., Sternglanz R. Conditional-lethal deoxyribonucleic acid ligase mutant of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1979 Aug;139(2):701–704. doi: 10.1128/jb.139.2.701-704.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elder R. H., Rossignol J. M. DNA ligases from rat liver. Purification and partial characterization of two molecular forms. Biochemistry. 1990 Jun 26;29(25):6009–6017. doi: 10.1021/bi00477a019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardy S., Aoufouchi S., Thiebaud P., Prigent C. DNA ligase I from Xenopus laevis eggs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Feb 25;19(4):701–705. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.4.701. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hathaway G. M., Lubben T. H., Traugh J. A. Inhibition of casein kinase II by heparin. J Biol Chem. 1980 Sep 10;255(17):8038–8041. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janknecht R., Hipskind R. A., Houthaeve T., Nordheim A., Stunnenberg H. G. Identification of multiple SRF N-terminal phosphorylation sites affecting DNA binding properties. EMBO J. 1992 Mar;11(3):1045–1054. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05143.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kemp B. E., Pearson R. B. Protein kinase recognition sequence motifs. Trends Biochem Sci. 1990 Sep;15(9):342–346. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(90)90073-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kodama K., Barnes D. E., Lindahl T. In vitro mutagenesis and functional expression in Escherichia coli of a cDNA encoding the catalytic domain of human DNA ligase I. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Nov 25;19(22):6093–6099. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.22.6093. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krebs E. G., Eisenman R. N., Kuenzel E. A., Litchfield D. W., Lozeman F. J., Lüscher B., Sommercorn J. Casein kinase II as a potentially important enzyme concerned with signal transduction. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1988;53(Pt 1):77–84. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1988.053.01.012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krek W., Maridor G., Nigg E. A. Casein kinase II is a predominantly nuclear enzyme. J Cell Biol. 1992 Jan;116(1):43–55. doi: 10.1083/jcb.116.1.43. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labbé J. C., Capony J. P., Caput D., Cavadore J. C., Derancourt J., Kaghad M., Lelias J. M., Picard A., Dorée M. MPF from starfish oocytes at first meiotic metaphase is a heterodimer containing one molecule of cdc2 and one molecule of cyclin B. EMBO J. 1989 Oct;8(10):3053–3058. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08456.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lasko D. D., Tomkinson A. E., Lindahl T. Eukaryotic DNA ligases. Mutat Res. 1990 Sep-Nov;236(2-3):277–287. doi: 10.1016/0921-8777(90)90011-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lasko D. D., Tomkinson A. E., Lindahl T. Mammalian DNA ligases. Biosynthesis and intracellular localization of DNA ligase I. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jul 25;265(21):12618–12622. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leary J. J., Brigati D. J., Ward D. C. Rapid and sensitive colorimetric method for visualizing biotin-labeled DNA probes hybridized to DNA or RNA immobilized on nitrocellulose: Bio-blots. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(13):4045–4049. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.13.4045. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lüscher B., Christenson E., Litchfield D. W., Krebs E. G., Eisenman R. N. Myb DNA binding inhibited by phosphorylation at a site deleted during oncogenic activation. Nature. 1990 Apr 5;344(6266):517–522. doi: 10.1038/344517a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MADIN S. H., DARBY N. B., Jr Established kidney cell lines of normal adult bovine and ovine origin. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1958 Jul;98(3):574–576. doi: 10.3181/00379727-98-24111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malkas L. H., Hickey R. J., Li C., Pedersen N., Baril E. F. A 21S enzyme complex from HeLa cells that functions in simian virus 40 DNA replication in vitro. Biochemistry. 1990 Jul 10;29(27):6362–6374. doi: 10.1021/bi00479a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marais R. M., Hsuan J. J., McGuigan C., Wynne J., Treisman R. Casein kinase II phosphorylation increases the rate of serum response factor-binding site exchange. EMBO J. 1992 Jan;11(1):97–105. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05032.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marais R. M., Parker P. J. Purification and characterisation of bovine brain protein kinase C isotypes alpha, beta and gamma. Eur J Biochem. 1989 Jun 1;182(1):129–137. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1989.tb14809.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nasheuer H. P., Moore A., Wahl A. F., Wang T. S. Cell cycle-dependent phosphorylation of human DNA polymerase alpha. J Biol Chem. 1991 Apr 25;266(12):7893–7903. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Padmanabha R., Chen-Wu J. L., Hanna D. E., Glover C. V. Isolation, sequencing, and disruption of the yeast CKA2 gene: casein kinase II is essential for viability in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Aug;10(8):4089–4099. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.8.4089. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saijo M., Enomoto T., Hanaoka F., Ui M. Purification and characterization of type II DNA topoisomerase from mouse FM3A cells: phosphorylation of topoisomerase II and modification of its activity. Biochemistry. 1990 Jan 16;29(2):583–590. doi: 10.1021/bi00454a036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Söderhäll S. DNA ligases during rat liver regeneration. Nature. 1976 Apr 15;260(5552):640–642. doi: 10.1038/260640a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Söderhäll S., Lindahl T. Mammalian deoxyribonucleic acid ligase. Isolation of an active enzyme-adenylate complex. J Biol Chem. 1973 Jan 25;248(2):672–675. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teitz T., Eli D., Penner M., Bakhanashvili M., Naiman T., Timme T. L., Wood C. M., Moses R. E., Canaani D. Expression of the cDNA for the beta subunit of human casein kinase II confers partial UV resistance on xeroderma pigmentosum cells. Mutat Res. 1990 Jul;236(1):85–97. doi: 10.1016/0921-8777(90)90036-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teraoka H., Tsukada K. Eukaryotic DNA ligase. Purification and properties of the enzyme from bovine thymus, and immunochemical studies of the enzyme from animal tissues. J Biol Chem. 1982 May 10;257(9):4758–4763. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomkinson A. E., Lasko D. D., Daly G., Lindahl T. Mammalian DNA ligases. Catalytic domain and size of DNA ligase I. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jul 25;265(21):12611–12617. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomkinson A. E., Roberts E., Daly G., Totty N. F., Lindahl T. Three distinct DNA ligases in mammalian cells. J Biol Chem. 1991 Nov 15;266(32):21728–21735. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomkinson A. E., Totty N. F., Ginsburg M., Lindahl T. Location of the active site for enzyme-adenylate formation in DNA ligases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jan 15;88(2):400–404. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.2.400. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodgett J. R. Use of synthetic peptides mimicking phosphorylation sites for affinity purification of protein-serine kinases. Methods Enzymol. 1991;200:169–178. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)00137-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]