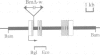Abstract
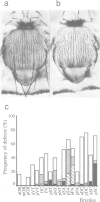
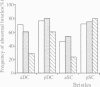
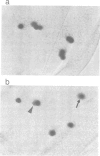
Cyclin proteins are one of the important components of the mechanism regulating mitosis in eukaryotic cells. We isolated a Drosophila Cyclin-A mutant in which the progenitor cells of the peripheral nervous system (the sensory mother cells) do not divide properly, causing the loss and other abnormalities of mechanosensory organs in the adult fly. Sequence analysis of the mutant genome reveals that a P element is inserted into the first intron of the Cyclin-A gene. A 13 kb wild-type genomic DNA containing the Cyclin-A transcription units rescued the mutant phenotype when introduced into the mutant fly. The regulation of cell type specific expression of the Cyclin-A gene is discussed.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alonso M. C., Cabrera C. V. The achaete-scute gene complex of Drosophila melanogaster comprises four homologous genes. EMBO J. 1988 Aug;7(8):2585–2591. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03108.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackwell T. K., Kretzner L., Blackwood E. M., Eisenman R. N., Weintraub H. Sequence-specific DNA binding by the c-Myc protein. Science. 1990 Nov 23;250(4984):1149–1151. doi: 10.1126/science.2251503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackwell T. K., Weintraub H. Differences and similarities in DNA-binding preferences of MyoD and E2A protein complexes revealed by binding site selection. Science. 1990 Nov 23;250(4984):1104–1110. doi: 10.1126/science.2174572. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cabrera C. V., Alonso M. C. Transcriptional activation by heterodimers of the achaete-scute and daughterless gene products of Drosophila. EMBO J. 1991 Oct;10(10):2965–2973. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07847.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caudy M., Vässin H., Brand M., Tuma R., Jan L. Y., Jan Y. N. daughterless, a Drosophila gene essential for both neurogenesis and sex determination, has sequence similarities to myc and the achaete-scute complex. Cell. 1988 Dec 23;55(6):1061–1067. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90250-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cubas P., de Celis J. F., Campuzano S., Modolell J. Proneural clusters of achaete-scute expression and the generation of sensory organs in the Drosophila imaginal wing disc. Genes Dev. 1991 Jun;5(6):996–1008. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.6.996. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellis H. M., Spann D. R., Posakony J. W. extramacrochaetae, a negative regulator of sensory organ development in Drosophila, defines a new class of helix-loop-helix proteins. Cell. 1990 Apr 6;61(1):27–38. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90212-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans T., Rosenthal E. T., Youngblom J., Distel D., Hunt T. Cyclin: a protein specified by maternal mRNA in sea urchin eggs that is destroyed at each cleavage division. Cell. 1983 Jun;33(2):389–396. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90420-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garrell J., Campuzano S. The helix-loop-helix domain: a common motif for bristles, muscles and sex. Bioessays. 1991 Oct;13(10):493–498. doi: 10.1002/bies.950131002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garrell J., Modolell J. The Drosophila extramacrochaetae locus, an antagonist of proneural genes that, like these genes, encodes a helix-loop-helix protein. Cell. 1990 Apr 6;61(1):39–48. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90213-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gasch A., Hinz U., Renkawitz-Pohl R. Intron and upstream sequences regulate expression of the Drosophila beta 3-tubulin gene in the visceral and somatic musculature, respectively. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 May;86(9):3215–3218. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.9.3215. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghysen A., Dambly-Chaudiere C. Genesis of the Drosophila peripheral nervous system. Trends Genet. 1989 Aug;5(8):251–255. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(89)90097-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghysen A., O'Kane C. Neural enhancer-like elements as specific cell markers in Drosophila. Development. 1989 Jan;105(1):35–52. doi: 10.1242/dev.105.1.35. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- González F., Romani S., Cubas P., Modolell J., Campuzano S. Molecular analysis of the asense gene, a member of the achaete-scute complex of Drosophila melanogaster, and its novel role in optic lobe development. EMBO J. 1989 Dec 1;8(12):3553–3562. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08527.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoogwerf A. M., Akam M., Roberts D. A genetic analysis of the rose-gespleten region (68C8-69B5) of Drosophila melanogaster. Genetics. 1988 Apr;118(4):665–670. doi: 10.1093/genetics/118.4.665. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang F., Dambly-Chaudière C., Ghysen A. The emergence of sense organs in the wing disc of Drosophila. Development. 1991 Apr;111(4):1087–1095. doi: 10.1242/dev.111.4.1087. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kassis J. A. Spatial and temporal control elements of the Drosophila engrailed gene. Genes Dev. 1990 Mar;4(3):433–443. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.3.433. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehner C. F., O'Farrell P. H. Expression and function of Drosophila cyclin A during embryonic cell cycle progression. Cell. 1989 Mar 24;56(6):957–968. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90629-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehner C. F., O'Farrell P. H. The roles of Drosophila cyclins A and B in mitotic control. Cell. 1990 May 4;61(3):535–547. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90535-m. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murre C., McCaw P. S., Baltimore D. A new DNA binding and dimerization motif in immunoglobulin enhancer binding, daughterless, MyoD, and myc proteins. Cell. 1989 Mar 10;56(5):777–783. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90682-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pirrotta V., Steller H., Bozzetti M. P. Multiple upstream regulatory elements control the expression of the Drosophila white gene. EMBO J. 1985 Dec 16;4(13A):3501–3508. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04109.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romani S., Campuzano S., Macagno E. R., Modolell J. Expression of achaete and scute genes in Drosophila imaginal discs and their function in sensory organ development. Genes Dev. 1989 Jul;3(7):997–1007. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.7.997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rushlow C. A., Hogan A., Pinchin S. M., Howe K. M., Lardelli M., Ish-Horowicz D. The Drosophila hairy protein acts in both segmentation and bristle patterning and shows homology to N-myc. EMBO J. 1989 Oct;8(10):3095–3103. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08461.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schultz J. R., Tansey T., Gremke L., Storti R. V. A muscle-specific intron enhancer required for rescue of indirect flight muscle and jump muscle function regulates Drosophila tropomyosin I gene expression. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Apr;11(4):1901–1911. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.4.1901. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Standart N., Minshull J., Pines J., Hunt T. Cyclin synthesis, modification and destruction during meiotic maturation of the starfish oocyte. Dev Biol. 1987 Nov;124(1):248–258. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(87)90476-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steller H., Pirrotta V. A transposable P vector that confers selectable G418 resistance to Drosophila larvae. EMBO J. 1985 Jan;4(1):167–171. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb02332.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swenson K. I., Farrell K. M., Ruderman J. V. The clam embryo protein cyclin A induces entry into M phase and the resumption of meiosis in Xenopus oocytes. Cell. 1986 Dec 26;47(6):861–870. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90801-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitfield W. G., Gonzalez C., Maldonado-Codina G., Glover D. M. The A- and B-type cyclins of Drosophila are accumulated and destroyed in temporally distinct events that define separable phases of the G2-M transition. EMBO J. 1990 Aug;9(8):2563–2572. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07437.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitfield W. G., González C., Sánchez-Herrero E., Glover D. M. Transcripts of one of two Drosophila cyclin genes become localized in pole cells during embryogenesis. Nature. 1989 Mar 23;338(6213):337–340. doi: 10.1038/338337a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]