Abstract
Heme-regulated inhibitor (HRI), an eukaryotic translation initiation factor 2 alpha (eIF2α) kinase, plays critical roles in cell proliferation, differentiation, adaptation to stress, and hemoglobin disorders. HRI phosphorylates eIF2α that couples cellular signals including the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress to translation. We previously identified 1,3-diarylureas and 1-((1,4-trans)-4-aryloxycyclohexyl)-3-arylureas (cHAUs) as specific activators of HRI that trigger the eIF2α phosphorylation arm of ER-stress response as molecular probes for studying HRI biology and its potential as a druggable target. To develop drug-like cHAUs needed for in vivo studies we undertook bioassay guided structure-activity relationship studies and tested them in the surrogate eIF2α phosphorylation and cell proliferation assays. We further evaluated some of these cHAUs in endogenous eIF2α phosphorylation and expression of the transcription factor CHOP protein and mRNA demonstrating significantly improved solubility and/or potencies. These cHAUs are excellent candidates for lead optimization for development of investigational new drugs that potently and specifically activate HRI.
Keywords: SAR study; 1-((1,4-trans)-4-aryloxycyclohexyl)-3-arylureas; inhibition of translation initiation; ternary complex; phosphorylation of eIF2α
TOC Graphic

Introduction
The eIF2·GTP·Met-tRNAi ternary complex, formed by the eukaryotic translation initiation factor 2 (eIF2), initiator methionine transfer RNA (Met-tRNAi) and GTP, is an essential component of the translation initiation machinery. Upon recognition of translation start codon, the first AUG, the GTP in the ternary complex is hydrolyzed to GDP and inorganic phosphate, Pi. Subsequently, dissociation of eIF2·GDP and release of Pi are coupled to initiation of translation. The eIF2 specific guanine nucleotide exchange factor, eIF2B, exchanges the GDP in the eIF2·GDP complex for GTP and thus enables the regeneration of the ternary complex and initiation of another translation cycle. Phosphorylation of the α-subunit of eIF2 (eIF2α) on Ser51 increases affinity of eIF2α for eIF2B while inhibiting eIF2B’s guanine nucleotide exchange activity thus generating an unproductive eIF2/eIF2B complex. Because the eIF2 is present in excess over eIF2B, partial phosphorylation of eIF2α results in significant depletion of eIF2·GTP·Met-tRNAi ternary complex and inhibition of translation initiation1.
The eIF2α kinases are HRI, RNA-dependent-protein-kinase/protein kinase R (PKR), pancreatic eIF2α kinase/PKR-like endoplasmic reticulum kinase (PERK), and general control non-derepressible-2 (GCN2)2. Phosphorylation of eIF2α is essential for cellular activities such as coupling protein synthesis to heme availability in red blood cells progenitors, matching the folding capacity of ER-Golgi network in secretory cells to demand for protein synthesis, and responding to nutrient and oxygen scarcity in all cells. In addition, eIF2α phosphorylation also plays a critical role in resisting viral infection3.
Defective eIF2α phosphorylation is implicated in the patho-biology of various human disorders. For example, inactivating mutations of the eIF2α kinase PERK causes Wolcott-Rallison syndrome, an autosomal recessive disease characterized by neonatal/early-onset non-autoimmune insulin-requiring diabetes4. Insufficiency of eIF2α phosphorylation in red blood cells progenitors due to HRI deficiency increases severity of hemolytic disorders such as β-thalassemia in mice5. Deregulation of eIF2α phosphorylation has also been implicated in the pathogenesis of motor-neuron disease, and neurodegenerative and proliferative disorders6. Importantly, modification of eIF2α phosphorylation is shown to be a viable approach for the treatment of proliferative and some neurodegenerative disorders in animal models6a, 6b, 7.
Based on extensive clinical and experimental data supporting the critical role of eIF2α phosphorylation in the normal- and patho-biology of human disorders7b, 8, we hypothesized that small molecule activators of eIF2α phosphorylation are important tools for studying the role of eIF2α phosphorylation in normal- and patho-biology and potential therapeutic agents for the treatment of neuro-degenerative, proliferative, and other human disorders. To meet the above-mentioned objectives, these molecules must be potent, specific, and have desirable physicochemical properties. We previously reported discovery and preliminary structure-activity relationship (SAR) studies of 1-((1,4-trans)-4-aryloxycyclohexyl)-3-arylureas (cHAUs) as potent in vitro inducers of HRI dependent eIF2α phosphorylation. In preparation for in vivo studies of this novel class of agents aiming at a new therapeutic target, we carried out further optimization of the cHAUs designated to improve their physicochemical properties and/or potencies. We now report on novel drug-like cHAUs that potently induce eIF2α phosphorylation and its downstream effector CHOP expression, and inhibit cancer cells proliferation at sub-micromolar concentrations. These compounds also have more favourable physicochemical properties (i.e. lower cLogPs). As such, we report herein on lead compounds that are promising candidates for in vivo studies aimed at understanding the role of HRI and eIF2α phosphorylation in normal- and patho-biology and further development into potential drugs for the treatment of human disorders.
Chemistry
The greater abundance of (1,4-trans)-4-aryloxycyclohexan-1-amines-derived ureas in the original hit finding library9 and the enhanced metabolic stability of the 1-((1,4-trans)- versus 1-((1,4-cis)-aryloxycyclohexyl)-3-arylurea as determined by incubation with human hepatic microsomes in the presence of NADPH10 led us to focus exclusively on the (1,4-trans)-isomers.
The (1,4-trans)-4-aryloxycyclohexan-1-amines (1a-i) were synthesized following well-established procedures (Scheme 1)9, 11. Briefly, O-alkylation of (1,4-trans)-4-hydroxycyclohexan-1-amine by fluoroaryls was carried out in DMF using sodium hydride as a base, and resulted in variable yields (25–99%) of the amines (1a-i). The resulting amines 1a-i were reacted with commercially available isocyanates 2a-d, in the presence of triethylamine in DMSO to afford moderate yields of a focused library of 1-((1,4-trans)-4-aryloxycyclohexyl)-3-arylureas, 3a-l (Scheme 1). The 3-(3-triflouromethoxy)phenyl-containing ureas 3m-q were synthesized from the crude (3-trifluoromethoxy)phenyl isocyante 2e and the corresponding (1,4-trans)-4-aryloxycyclohexan-1-amines (1a-e) in the presence of trimethylamine. Isocyante 2e was generated from the m-trifluoromethoxyaniline that was treated with 1,1′-carbonyldiimidazole (CDI) in DMSO12. A significant formation of the by-product the symmetrical 1,3-bis(3-(trifluoromethoxy)phenyl)urea in the preparation of 2e complicated the purification of the targeted ureas 3m-q and resulted in low yields (25–30%).
Scheme 1.

Synthesis of 1-((1,4-trans)-4-aryloxycyclohexyl)-3-arylureas.
The disubstituted phenylisocyanates required for the synthesis of ureas 3r-t were generated using disubstituted phenyl carbamates 4a-c as the active N-acylating components and the (1,4-trans)-4-(4-(trifluoromethyl)phenoxy)cyclohexan-1-amine 1f. The phenyl carbamates 4a-c were isolated in good to excellent yields (62–91%) following the procedure reported by Zhang and coworkers13. The N-acylating components were generated by condensing the corresponding commercially available 3-cyano-5-trifluoromethyl- and 3,4-dicyano- or the 3,5-dicyano-anilines14 with phenyl chloroformate in the presence of pyridine (Scheme 1).
1-(4-aryloxyphenyl)-3-arylureas (6a,b) were synthesized in a similar fashion by treating p-hydroxyaniline with 1-fluoro-4-(trifluoromethyl)benzene in DMF in the presence of potassium carbonate to afford 4-(4-(trifluoromethyl)phenoxy)aniline 5, which was in turn reacted with isocyanates 2a or 2e to yield the respective ureas 6a or 6b (Scheme 2).
Scheme 2.

Synthesis of 1-(4-aryloxyphenyl)-3-arylureas.
Based on reverse-phase high-performance liquid chromatography (RP-HPLC) analysis the purity of all final 1-((1,4-trans)-4-aryloxycyclohexyl)-3-arylureas submitted for biological characterization and reported herein equaled or exceeded 95%. Their structural identity and integrity were confirmed by LC–MS as well as 1H−, 13C−, and19 F-NMR.
Biological Results and Discussion
Structure Activity relationship studies
All newly synthesized 1,3-disubstituted ureas were initially evaluated in surrogate dual-luciferase eIF2α phosphorylation reporter (DLR) assay15. Briefly, this assay takes advantage of the fact that activated HRI phosphorylates eIF2α thereby reducing the amount of the eIF2∙GTP∙Met-tRNAi ternary complex and consequently inhibits translation of most mRNAs but, paradoxically, increases translation of small subset of mRNAs that contain multiple upstream open reading frame (uORF) in their 5′ untranslated regions (5′UTRs)7, 16. In our assay, firefly (F) luciferase mRNA is fused to 5′UTR of activating transcription factor 4 (ATF-4) mRNA 5′UTR that has multiple uORFs while renilla (R) luciferase mRNA is fused to a 5′UTR lacking any uORFs. Agents that reduce the amount of the ternary complex, such as those 1,3-disubstituted ureas that activate HRI, would increase F luciferase expression while reducing the R luciferase expression, resulting in an increased F/R luciferase ratio. We calculated the activity scores as the F/R ratios for every compound-treated wells and normalized these for F/R ratio to vehicle-treated (DMSO) wells in the same plate, arbitrarily set at 1 (F/R = 1). The newly synthesized ureas were tested at 10, 5, 2.5, and 1.25 μM concentrations in 96-well assay plates15b, 17. Dose-response data obtained in the surrogate dual-luciferase eIF2α phosphorylation assay for the 1-((1,4-trans)-4-aryloxycyclohexyl)-3-arylureas are depicted in Figures 1A–D.
Figure 1.



Activity of 1-((1,4-trans)-4-aryloxycyclohexyl)-3-arylureas in the surrogate eIF2α phosphorylation assay. The activity of the compounds was measured by a DLR assay, the F/R ratio normalized to vehicle treated cells, and expressed as a function of the compounds’ concentration. The library of the 1-((1,4-trans)-4-aryloxycyclohexyl)-3-arylureas were sorted into four groups based on diversity in substitution patterns on the 4-aryloxycyclohexyl or the N-phenyl moieties: (Panel A) differ in substituents on the 4-aryloxycyclohexyl moiety; (Panel B) differ in mono-substituents on the N-phenyl; (Panel C) differ in the nature and position of di-substituents on the N-phenyl moiety; and (Panel D) replacement of the cyclohexyl ring by a phenyl ring. In each panel the parent cHAU 3 serves as a reference compound. Experiments were conducted in triplicates and each experiment was independently performed three times; data are shown as Mean±S.E.M.
Based on our preliminary structure-activity relationship studies9 we carried out a lead optimization on the cHAUs scaffold that targeted the physicochemical properties of our lead compounds9 3 and 3′ while improving their potency. In the first set of studies we have modified the substituents on the 4-aryloxycyclohexyl moiety.
Our preliminary studies indicated that substitution of the 4-aryloxycyclohexyl moiety with electron withdrawing groups is beneficial. We therefore expanded the modification at the ortho- and meta-position of the phenoxy ring to include polar electron withdrawing groups that potentially can form hydrogen bonds with the target. These substituents are NHCOCH3, CONH2, CN, and NO2 (3a-d and 3h-j with a N-(3-trifluromethyl)phenyl moiety and 3m-o with a N-(3-trifluoromethoxy)phenyl moiety. While these substitutions significantly lowered the cLogP and were less hydrophobic (as suggested by the retention time on the RP-HPLC column (Table 1)) relative to the parent ureas 3 and 3′9 they were notably less active in the surrogate eIF2α phosphorylation assay. Consistently, these analogs were also significantly less active than the parent ureas 3 and 3′ in the sulforhodamine B (SRB) cell proliferation assay: considerably higher concentrations of these compounds were needed to inhibit cell growth by 50% (IC50). These data are shown in Table 1.
Table 1.
Physicochemical properties and biological activities of the 1-((1,4-trans)-4-aryloxycyclohexyl)-3-arylureas 3 and 1-(para-aryloxyphenyl)-3-arylureas 6.
| R1 | R2 | X | R3 | R4 | R5 | R6 | Surrogate eIF2α @ μM | IC50b [μM] | cLogP | tR [min] | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.25 | 5 | |||||||||||
| 3a | H | H | C | CF3 | CF3 | H | H | 3.23±0.18 | 10.16±0.52 | 0.54±0.1 | 6.41 | 19.7 |
| 3′a | H | H | C | OCF3 | CF3 | H | H | 3.37±0.61 | 10.08±0.51 | 0.82±0.2 | 6.48 | 20.2 |
| Substitution of electron withdrawing groups on the 4-aryloxycyclohexyl moiety bearing a N-(3-trifluromethyl)phenyl ring | ||||||||||||
| 3a | CONH2 | H | C | CF3 | CF3 | H | H | 0.91±0.03 | 1.49±0.01 | 2.76±0.4 | 5.07 | 16.3 |
| 3b | H | CONH2 | C | CF3 | CF3 | H | H | 0.79±0.03 | 1.12±0.02 | 3.36±0.5 | 4.87 | 15.6 |
| 3c | NHCOCH3 | H | C | CF3 | CF3 | H | H | 0.84±0.12 | 3.9±0.02 | 1.46±0.4 | 5.17 | 17.5 |
| 3d | NO2 | H | C | CF3 | CF3 | H | H | 0.96±0.02 | 3.28±0.12 | 5.51±1.4 | 6.01 | 19.2 |
| 3h | – | H | N | CF3 | CF3 | H | H | 1.02±0.10 | 6.11±0.11 | 1.57±0.2 | 5.66 | 19.1 |
| 3i | CN | H | C | CF3 | CF3 | H | H | 1.01±0.07 | 6.3±0.18 | 1.47±0.3 | 6.00 | 18.8 |
| 3j | H | H | C | CN | CF3 | H | H | 0.92±0.06 | 3.23±0.23 | 6.06±1.0 | 4.84 | 17.4 |
| p- CF3 vs p-CN substituents on the phenylcyclohexyl moiety | ||||||||||||
| 3e | H | H | C | CF3 | CF3 | H | CF3 | 8.58±0.13 | 30.72±0.77 | 0.45±0.03 | 7.48 | 21.7 |
| 3f | H | H | C | CF3 | CN | H | H | 0.96±0.08 | 7±0.12 | 0.94±0.1 | 5.13 | 17.9 |
| 3g | H | H | C | CF3 | H | CN | H | 3.38±0.21 | 11.63±0.05 | 0.49±0.02 | 5.13 | 17.8 |
| 3k | H | H | C | CN | H | CN | H | 1.03±0.01 | 1.38±0.13 | 9.03±3.1 | 3.76 | 15.1 |
| 3l | H | H | C | CN | CN | H | H | 1.01±0.02 | 1.15±0.08 | 8.2±1.2 | 3.76 | 15.2 |
| N-phenyl ring bearing nitrile groups | ||||||||||||
| 3r | H | H | C | CF3 | CN | H | CF3 | 5.65±0.28 | 13.16±1.36 | 0.25±0.02 | 6.20 | 19.9 |
| 3s | H | H | C | CF3 | CN | CN | H | 5.54±1.34 | 7.75±1.97 | 2.01±0.7 | 4.81 | 18.3 |
| 3t | H | H | C | CF3 | CN | H | CN | 1.51±0.39 | 2.36±0.14 | 3.68±1.1 | 4.81 | 18.4 |
| Substitution of electron withdrawing groups on the 4-aryloxycyclohexyl moiety bearing a N-(3-trifluoromethoxy)phenyl ring | ||||||||||||
| 3m | CONH2 | H | C | CF3 | OCF3 | H | H | 0.88±0.09 | 5.13±0.02 | 1.53±0.4 | 3.93 | 16.6 |
| 3n | H | CONH2 | C | CF3 | OCF3 | H | H | 1.04±0.06 | 1.57±0.18 | 3.66±0.9 | 3.73 | 16.0 |
| 3o | NHCOCH3 | H | C | CF3 | OCF3 | H | H | 0.85±0.06 | 4.31±0.13 | 1.5±0.3 | 4.97 | 17.9 |
| 3p | H | H | C | OCF3 | OCF3 | H | H | 2.87±0.16 | 10.70±0.19 | 1.45±0.2 | 6.28 | 20.3 |
| 3q | H | H | C | CF3 | OCF3 | H | H | 5.2±0.08 | 13.6±0.70 | 0.92±0.1 | 6.21 | 20.1 |
| para-(4-substituted)phenoxy)phenyl-containing 1,3-diarylureas | ||||||||||||
| 6a | H | H | C | CF3 | CF3 | H | H | 3.31±0.24 | 8.99±0.1 | 0.44±0.1 | 7.40 | 20.5 |
| 6b | H | H | C | CF3 | OCF3 | H | H | 2.37±0.03 | 6.73±0.22 | 0.5±0.2 | 7.20 | 20.9 |
Reported previously in Ref. 9.
Concentration that inhibits 50% of human CRL-2813 melanoma cell growth.
Replacement of the 4-(trifluoromethyl)phenoxy moiety in the parent cHAUs 3 with (5-(trifluoromethyl)pyridin-2-yl)oxy as in 3h reduced the hydrophobicity and led to lower cLogP values and shorter retention time (tR) on the RP-HPLC column (cLogP = 6.41 vs 5.66 and tR = 19.7 vs 19.1 min, respectively). However, this improvement in physicochemical properties was not accompanied by gains in potency. In fact, 3h was significantly less potent than the parent 3 in both the surrogate eIF2α phosphorylation and the cell proliferation assays (Table 1). Consistently, the heteroatom in the (pyridine-2-yl)oxy moiety plays a similar role to the ortho-R1 electron withdrawing substituents such as CONH2, NHCOCH3, NO2, and CN in the respective 3a,c,d,i and results in similar loss of biological potency.
Based on the above findings that the 4-aryloxycyclohexyl ring does not tolerate such polar electron withdrawing substituents, we turned our attention to modifications of the N-phenyl moiety, 3e-g, 3k,l, and 3r-t (Fig. 1 panels B–C and Table 1). Replacement of m-CF3 (as in 3) with m-OCF3 or m-CN (3q and 3f, respectively) resulted in quite distinct outcomes. While m-OCF3 maintained the activity of the 3q it did not improve its cLogP or the retention time on RP-HPLC. In 3f, on the other hand, presence of the m-CN group led to lower hydrophobicity than that of the parent urea 3 (cLogP 5.13 vs 6.41 and tR in the RP-HPLC 17.8 min vs 19.7 min, Table 1), but at the same time resulted in somewhat reduced activity compared to the parent urea 3, especially at low concentrations. Interestingly, switching the nitrile from the meta- to the para-position as in 3g not only maintained the physicochemical properties of 3f, but also recovered the potency almost to the same level as the parent urea 3 (activity in the surrogate phosphorylation eIF2α assay at 1.25 μM 3.38 vs 3.23, and IC50 0.49 vs 0.54 μM for 3g and 3, respectively, Table 1). Indeed, substitution with p-CN on the N-phenyl ring proved to be advantageous.
Following our previous observations with a closely related chemotype the 1,3-diarylureas that, in general, identified ureas containing phenyl substituted with two electron withdrawing groups were more potent than those containing phenyl substituted with one electron withdrawing group15b, 18 we synthesized -(3,4-di-substituted)- or -(3,5-di-substituted)-phenyl-containing ureas (3s and 3e,r,t, respectively). Indeed, the 3,5-diCF3-substituted 3e was more potent in the surrogate eIF2α phosphorylation assay than the parent mono-CF3-substituted 3 (activity in the surrogate phosphorylation eIF2α assay at 1.25 μM 8.58 vs 3.23 for 3e and 3, respectively, Table 1). However, the 3,5-diCF3-substituted analog 3e was also the most hydrophobic analog in this series (cLogP = 7.48 and tR = 21.7 min, Table 1). In an effort to take advantage of the high potency displayed by N-phenyl ring substituted by two electron withdrawing groups and ameliorate the high hydrophobicity associated with the two CF3 groups, as the (3,5-diCF3)phenyl moiety in 3e, we replaced either one or two CF3 substituents with CN, a relatively polar and quite substantial electron withdrawing group, obtaining (3-CN,5-CF3)phenyl, 3r and the respective (3,4-diCN)- and (3,5-diCN)phenyl, 3s and 3t, respectively). Stepwise replacement of the CF3 groups by CN reduced the compound’s hydrophobicity as evidenced by the decrease in the cLogP values and tR in the analytical RP-HPLC (cLogP = 7.48, 6.20, and 4.81; tR = 21.7, 19.9, and 18.3 min for 3,5-diCF3 3e, 3-CN,5-CF3 3r, and 3,4-diCN 3s, respectively, Table 1). Consequently, replacement of one of the two CF3 substituents on the -(3,5-diCF3)phenyl moiety in 3e by a CN substituent to yield a -(3-CN,5-CF3)phenyl moiety as in 3r, that was less hydrophobic and less potent than the 3,5-diCF3 containing 3e. Moreover, while improvement in the physicochemical properties of 3r compared with our parent cHAU 3 are modest (cLogP = 6.20 vs 6.41 and tR = 19.9 vs 19.7, respectively) there is marked improvement in the potency in both the surrogate eIF2α phosphorylation and the cell proliferation assays (activity at 1.25 and 5 μM in the surrogate eIF2α phosphorylation assay = 5.65 and 13.16 vs 3.23 and 10.16, and IC50 = 0.25 vs 0.54 μM for 3r and 3, respectively, Table 1). Disappointingly, both (3,4-diCN)- and (3,5-diCN)phenyl-containing cHAUs 3s and 3t, respectively, were less potent than the (3,5-diCF3)phenyl-containing urea 3e.
The para-(4-substituted)phenoxy)phenyl-containing 1,3-diarylureas 6a and 6b, which are the respective homologs of the 1-((1,4-trans)-4-substituted-phenoxy)-3-cyclohexyl ureas 3 and 3q, were prepared to reaffirm the advantageous role of the cyclohexyl ring in the putative pharmacophore of the cHAUs. As anticipated, both 6a and 6b were more hydrophobic and less potent than the cyclohexyl-containing homologs 3 and 3q (Table 1).

Activities in Secondary Mechanistic Assays
To validate the newly synthesized 1-((1,4-trans)-4-aryloxycyclohexyl)-3-arylureas 3a-t and 1-(para-aryloxyphenyl)-3-arylureas 6a,b as activators of HRI, and thereby inducers of phosphorylation of eIF2α, we selected representative compounds from Table 1 and tested them in secondary mechanistic assays, namely phosphorylation of endogenous eIF2α and expression of the transcription factor C/EBP homologous protein (CHOP) and its mRNA. While phosphorylation of endogenous eIF2α is the immediate target of HRI, which is upstream regulator of the ternary complex abundance, expression of CHOP is a downstream effector. The active cHAUs, 3e, 3g, and 3q-s, selected for these secondary mechanistic studies share a common 1-((1,4-trans)-4-(4-trifluoromethyl)phenoxy)cyclohexyl sub-structure and differ in the nature and position of substituents on the N-phenyl moiety. We first determined the effect of these compounds on the phosphorylation of endogenous eIF2α in adherent human melanoma CRL-2813 cells by Western blot analysis in which expression of the total- (T-eIF2α) and the phosphorylated-eIF2α (P-eIF2α) was determined using anti-[phosphoserine-51]eIF2α (PhoS-eIF2α) and anti-T-eIF2α-specific antibodies (Figure 2). CHOP protein expression and CHOP mRNA levels in CRL-2813 cells were measured by the Western blot analysis of cell lysates and real-time PCR, respectively19. Similarly, we studied the expression of cyclin D1 protein, an oncogenic protein whose expression is reduced in response to eIF2α phosphorylation16, 20. As anticipated, all selected compounds caused phosphorylation of endogenous eIF2α (Figure 2) and increased the expression of CHOP protein and mRNA (Figure 3 and Table 2). Consistently, these compounds also reduced the expression of cyclin D1 protein and affected minimally the expression of housekeeping protein such as β-actin (Figure 3), most likely due to their specific effects on translation initiation. The ability of these representative cHAUs to induce phosphorylation of endogenous eIF2α, expression of CHOP protein and mRNA, and inhibit expression of oncogenic proteins is in full agreement with the data from the surrogate eIF2α phosphorylation report assay.
Figure 2. Phosphorylation of endogenous eIF2α by selected cHAUs.

CRL-2813 cells were incubated with a 5 μM dose of the indicated compounds for two hours and cell lysates were probed with antibodies specific to total or phosphorylated eIF2α by Western blot analysis. The gels shown are representative from three independent experiments.
Figure 3. Activity of selected cHAUs in secondary and tertiary mechanistic assays.
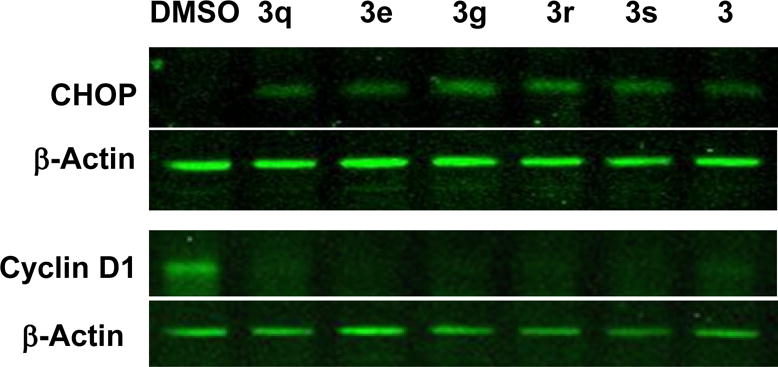
CRL-2813 cells were incubated with 5 μM dose of the indicated compounds for 8 hours and cell lysates were probed with antibodies specific to CHOP, Cyclin D1 and β-Actin by Western blot analysis. The gels shown are representative from three independent experiments.
Table 2.
Induction (fold increase) of CHOP mRNA by selected cHAUs at 5μM concentration (normalized to 18S RNA)
| DMSO | 3 | 3q | 3e | 3g | 3r | 3s |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1±0.68 | 4.72±1.26 | 11.86±2.5 | 14.47±1.9 | 12.78±0.53 | 9.87±0.65 | 6.21±0.59 |
The experiment was conducted in triplicate and each experiment was independently performed three times; data are shown as Mean ± SEM.
In vivo efficacy studies
To evaluate the in vivo potency of the lead cCAU 3r to inhibit tumor growth we evaluated this compound in the xenograft model of human melanoma cancer. We measured animal weight twice weekly and tumor size weekly using electronic calipers. In all the groups, body weight changes were less than 10%, (Figure 5 A). Rewardingly, 3r inhibited tumor growth significantly and dose dependently; ~90% in 150 mg/kg and ~50% in 37.5 mg/kg groups Figure 5B). Importantly 3r also induced phosphorylation of eIf2α in the tumors compared to vehicle treatment (Figure 5C). To rule out the possibility that 3r may be rapidly metabolized and that its metabolite (s) may be responsible for the observed in vivo activity we determined the pharmacokinetic profile of 3r after intra peritoneal (i.p.) injection. Mice were bled before or 0.5, 1, 2, 4, 6, 24, 48, and 72 hours after single injection and compound concentrations in the blood were determined by liquid chromatography mass spectrometry (LC-MS) using a standard curve. Details of analytical methods are described in Experimental Section. As shown in Figure 5D, compound 3r reaches peak blood concentrations between 6–24 hours after i.p. injection. This compounds shows remarkable in vivo stability with apparent half-life of ~40 hours. Furthermore we did not observe any other peaks in the LC-MS spectra indicating that this compound is not metabolized fast. Finally, as shown in Figure 6, histologic examination of mouse tissue indicates that r3 does not show apparent organ toxicity. Taken together, these data demonstrate that cHAUs inhibit tumor growth at non-toxic doses, providing impetus for further development of this chemotype and lead candidate for IND enabling studies.
Figure 5.
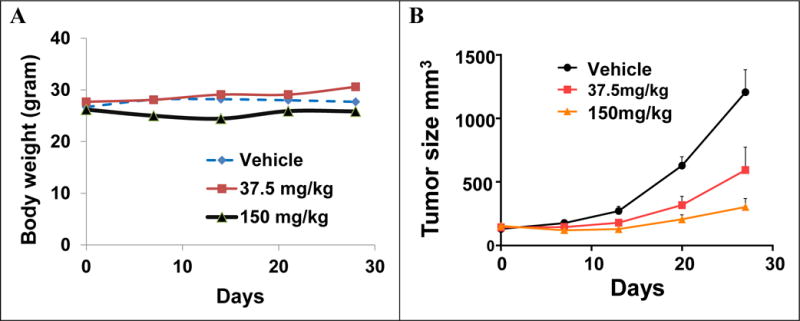

In vivo studies of lead compound 3r. A and B. Mice bearing human melanoma xenografts were treated with vehicle or the indicated doses of 3r as described in the experimental section. Animals were weighed twice a week and tumor dimensions were measured weekly. Panel A shows mice weight while panel B shows tumor volume in each group throughout the treatment period (nine animals per group). Data are shown as Mean±S.E.M. C. Mice were treated with single injection of 40 mg/kg of 3r, 20 μl blood was collected at indicated time points, compound concentrations in the whole blood was measured by LC-MS and quantified using a standard curve. Data is average of at least three mice per group. Data are shown as Mean±S.E.M. and error bars denote standard error of mean. D. Melanoma xenograft (~200 mg) bearing mice were treated with the vehicle or the indicated doses of lead compound 3r for 3 days and tumor lysates were immunoblotted with antibodies against the phosphorylated and total eIF2α.
Figure 6.
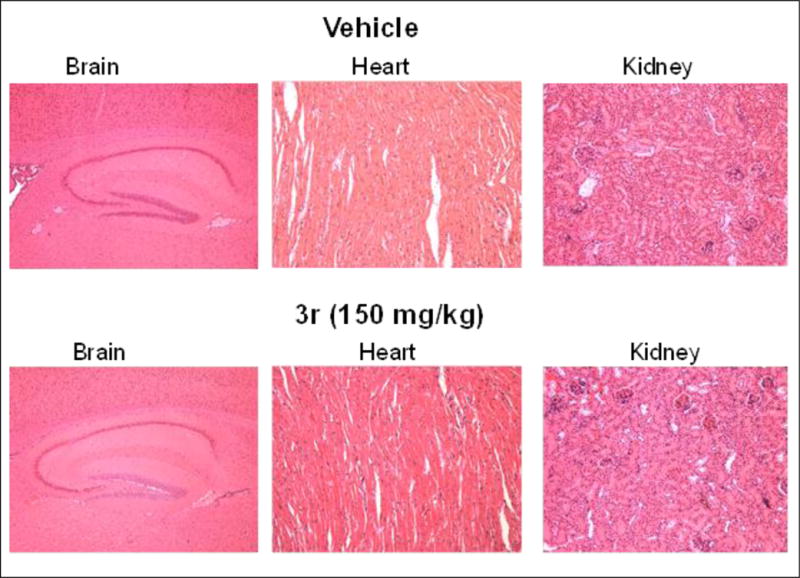
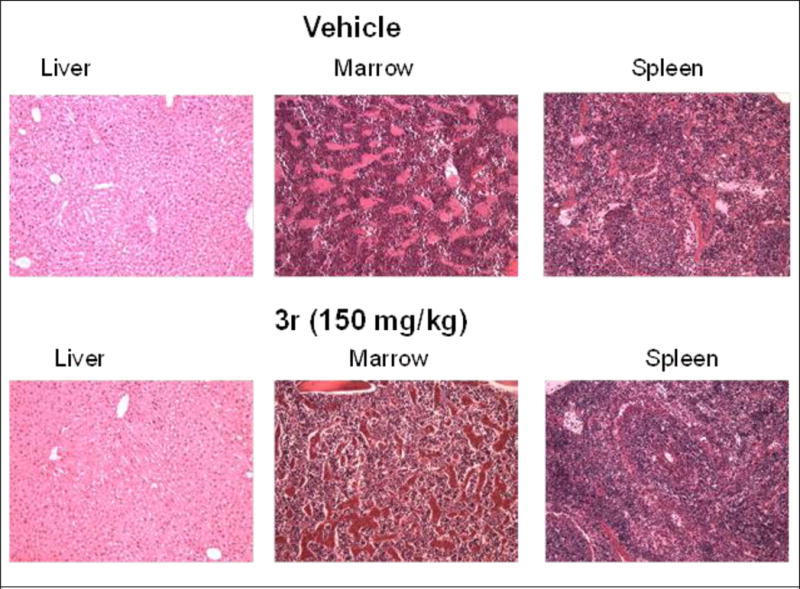
Tumor bearing mice treated with the lead compound 3r as described in Figure 5A and B were euthanized at the end of the 28 days treatment period, organs were harvested, fixed and subjected to histopathologic examination.
Conclusions
At the mechanistic level, similar to the previous series of cHAUs, the newly synthesized 1-((1,4-trans)-4-aryloxycyclohexyl)-3-arylureas induce phosphorylation of eIF2α and expression of its downstream effector, CHOP protein and mRNA. These 1,3-disubstituted-ureas also inhibit expression of oncogenic proteins and cell proliferation. Consistently, there is a very good correlation between the activity of these agents in the mechanistic assays and their potency in inhibiting cancer cell proliferation.
Structure-activity relationship analysis of the focused library of 1-((1,4-trans)-4-aryloxycyclohexyl)-3-arylureas 3a-t confirms that substitution of the N-phenyl moiety with strong electron withdrawing groups is essential for their activity in both the mechanistic surrogate eIF2α phosphorylation and cell proliferation assays. Our current study demonstrates that the presence of two electron withdrawing substituents on the N-phenyl moiety is a viable approach to generate more potent and/or less hydrophobic cHAUs. On the other hand, introduction of a second electron withdrawing substituent on the 4-aryloxycyclohexyl moiety was deleterious for the activity. As such, relative to the N-phenyl moiety, the 4-aryloxycyclohexyl moiety is much less tolerant to structural modification. In the future, elucidation of the structure of cHAUs bound to their macromolecular target will provide insights that will guide further structural optimization. Toward this end we are directing efforts to obtain atomic structure of HRI and study its interaction with cHAUs at the molecular level. Availability of high resolution structures of other eIF2α kinases in absence or presence of their cognate inhibitors should help accelerate these studies21. The 1-((1,4-trans)-4-(4-trifluoromethyl)phenoxy)cyclohexyl-3-(3-cyano,5-trifluoromethyl)phenylurea (3r), which combines one CF3 and one CN substituents on the N-phenyl ring, achieves a favorable combination of reduced hydrophobicity and good bioactivity. This compound also displays a remarkable in vivo stability and significant anti-tumor activity. As such 3r emerges as a lead for studying the role of HRI and eIF2α phosphorylation in normal- and patho-biology in vivo. It also becomes a good candidate for lead optimization in efforts to develop drug candidates for the treatment of various human ailments such as cancer, neurodegenerative disorders, and α– and β-thalassemia.
Experimentals
Chemistry
All reagents and solvents were purchased from commercial sources and used without further purification. Reactions were monitored by LC–MS analysis on a reverse-phase column (Waters Symmetry C18, 2.1 × 100 mm, 3.5 μm particle size) using a Waters Alliance 2695/Micromass ZQ or Agilent 1200 series system with UV detector (214 and 254 nm) and an Agilent 6130 quadrupole mass detector, with the binary system of water/acetonitrile containing 0.1% formic acid as eluent. The purity of all final compounds was ≥95% as determined by analytical HPLC on a reverse-phase column (XBridge BEH130 C18, 4.6 × 100 mm, 5 μm particle size) using a Waters Alliance 2695 with the binary system water/acetonitrile containing 0.1% trifluoracetic acid (TFA) as eluent. Unless otherwise mentioned for a specific compound, purifications by flash chromatography were performed on Biotage SP1 using silica gel prepacked columns (200−400 mesh) or reverse phase columns using a gradient of methanol water containing 0.1% formic acid, and were monitored by UV at 254 and 280 nm. Melting points were determined using a Mel-Temp Electrothermal melting point apparatus and were uncorrected. Proton, carbon, and fluorine NMR analyses were performed on Varian Inova 500 MHz or 400 MHz spectrometers, as indicated for each compound, using DMSO-d6 as solvent. Chemical shifts (δ) are reported in ppm relative to TMS as the internal standard. HR–MS analyses were analyzed initially in EI mode GCMS using a Waters GCT MS, and Agilent 6890 GC. Then the samples were analyzed on the same instrument in EI mode using a direct probe which was heated to ~350° C. ESI+ analysis was performed on a Waters Ultima MS. Samples were prepared in a 3:1 (methanol/water) sodium acetate solution.
General Procedure A for the Synthesis of (1,4-trans)-4-aryloxycyclohexan-1-amines (1a-h)
NaH (60% in mineral oil, 240 mg, 6 mmol) was added to a solution of (1,4-trans)-4-aminocyclohexanol (230 mg, 2 mmol) in dry DMF (10 mL) at 0 °C. The reaction mixture was stirred at room temperature for 1 h, and the appropriate aryl fluoride (2.4 mmol) was added. The mixture was heated to 60 °C for 2 h and then stirred overnight at room temperature. The reaction mixture was diluted with ethyl acetate and washed with 10 mL of water (×3) and brine. The organic layer was dried (MgSO4), filtered, and concentrated under vacuum. The residue was purified using reverse phase column chromatography using a linear gradient of methanol in water (containing 0.1% formic acid). Products were eluted at 53% methanol.
2-(((1,4-trans)-4-Aminocyclohexyl)oxy)-5-(trifluoromethyl)benzamide (1a)
Prepared according to general procedure A. Off-white solid, 63% yield; mp 186 °C; 1H NMR (500 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 8.45 (s, 1H), 8.02 (s, 1H), 7.79 (s, 1H), 7.76 (d, J = 8.4 Hz, 1 H), 7.57 (s, 1H), 7.46 (d, J = 8.8 Hz, 1H), 4.60–4.55 (m, 1H), 3.04–2.98 (m, 1H), 2.15–2.13 (m, 2H), 2.00–1.98 (m, 2H), 1.59–1.49 (m, 4H); 13C NMR (125 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 166.0, 165.2, 157.9, 129.1, 127.8, (q, J = 4.4 Hz), 124.4, 124.2 (q, J = 270.5 Hz), 121.0 (q, J = 33.3 Hz), 115.2, 75.9, 47.9, 28.8, 28.5; LC-MS (ESI+): m/z calcd for C14H17F3N2O2: 302.12; found: 303.00 [M+H]+; AHPLC (RP): tR = 8.8 min, 100%.
5-(((1,4-trans)-Aminocyclohexyl)oxy)-2-(trifluoromethyl)benzamide (1b)
Prepared according to general procedure A. Light yellow oil, 35% yield; 1H NMR (500 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 8.45 (s, 1H), 7.92 (s, 1H), 7.63 (d, J = 8.8 Hz, 1H), 7.57 (s, 1H), 7.15 (d, J = 8.4 Hz, 1H), 7.02 (s, 1H), 4.49–4.44 (m, 1H), 3.54 (s, 1H), 3.01–2.95 (m, 1H), 2.11–2.09 (m, 2H), 1.98–1.96 (m, 2H), 1.52–1.41 (m, 4H); LC-MS (ESI+): m/z calcd for C14H17F3N2O2: 302.12; found: 303.00 [M+H]+; AHPLC (RP): tR = 7.7 min, 95.0%.
N-(2-(((1,4-trans)-4-Aminocyclohexyl)oxy)-5-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)acetamide (1c)
Prepared according to general procedure A. White powder, 40% yield; mp 172 °C; 1H NMR (500 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 9.12 (s, 1H), 8.45 (s, 1H), 8.35 (s, 1H), 7.36 (d, J = 8.4 Hz, 1H), 7.31 (d, J = 8.8 Hz, 1H), 4.46–4.42 (m, H), 2.98–2.94 (m, 1H), 2.13–2.08 (m, 5H), 1.99–1.97 (m, 2H), 1.59–1.53 (m, 2H), 1.48–1.41 (m, 2H); 13C NMR (100 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 169.0, 165.9, 149.9, 128.7, 124.4, (q, J = 270.9 Hz), 121.0 (m), 120.6 (q, J = 31.9 Hz), 118.2 (m), 113.7, 75.5, 48.2, 28.9, 28.7, 24.0; 19F NMR (376 MHz, DMSO-d6) −60.1 ; LC-MS (ESI+): m/z calcd for C15H19F3N2O2: 316.14; found: 317.03 [M+H]+; AHPLC (RP): tR = 9.8 min, 100%.
(1,4-trans)-4-(2-Nitro-4-(trifluoromethyl)phenoxy)cyclohexan-1-amine (1d)
Was used without further purification. LC-MS (ESI+): m/z calcd for C13H15F3N2O3: 304.10; found: 305.05 [M+H]+.
(1,4-trans)-4-(4-(Trifluoromethoxy)phenoxy)cyclohexan-1-amine (1e)
Prepared according to general procedure A. White powder, 25% yield; mp 146 °C; 1H NMR (500 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 8.46 (s, 1H), 7.25 (d, J = 8.8 Hz, 2H), 7.04 (d, J = 8.8 Hz, 2H), 4.4.30–4.26 (m, 1H), 2.98–2.94, (m, 1H), 2.09–2.06 (m, 2H), 1.98–1.96 (m, 2H), 1.50–1.38 (m, 4H) ; 13C NMR (125 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 165.9, 156.10, 141.6, 122.5, 120.2 (q, J = 255.0 Hz), 116.8, 74.5, 48.1, 29.1, 28.7 ; LC-MS (ESI+): m/z calcd for C13H16F3NO2: 275.11; found: 275.93 [M+H]+; AHPLC (RP): tR = 11.8 min, 94.6%.
(1,4-trans)-4-(4-(Trifluoromethyl)phenoxy)cyclohexan-1-amine (1f)
Prepared according to general procedure A. White powder, 95% yield; mp 158 °C; 1H NMR (500 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 8.47 (s, 1H), 7.61 (d, J = 8.4 Hz, 2H), 7.13 (d, J = 8.4 Hz, 2H), 4.42–4.40 (m, 1H), 3.00–2.96 (m, 1H), 2.11–2.09 (m, 2H), 1.99–1.97 (m, 2H), 1.53–1.41 (m, 4H); 13C NMR (125 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 166.0, 160.2, 127.1 (q, J = 3.6 Hz), 124.8 (q, J = 270.8 Hz), 121.1 (q, J = 32.1 Hz), 115.8, 74.2, 48.1, 29.0, 28.6 ; LC-MS (ESI+): m/z calcd for C13H16F3NO: 259.12; found: 259.92 [M+H]+; AHPLC (RP): tR = 11.2 min, 94.6%.
(1,4-trans)-4-((5-(Trifluoromethyl)pyridin-2-yl)oxy)cyclohexan-1-amine (1g)
Prepared according to general procedure A. Yellow solid, 99% yield; mp 150 °C; 1H NMR (500 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 8.56 (s, 1H), 8.45 (s, 1H), 8.03 (d, J = 8.8 Hz, 1 H), 6.95 (d, J = 8.4 Hz, 1H), 5.01–4.97 (m, 1H), 3.00–2.95 (m, 1H), 2.12–2.10 (m, 2H), 1.99–1.97 (m, 2H), 1.53–1.42 (m, 4H); 13C NMR (100 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 165.9, 165.0, 144.9 (q, J = 4.7 Hz), 136.5 (q, J = 3.1 Hz), 124.1 (q, J = 270.9 Hz), 118.6 (q, J = 32.7 Hz), 111.7, 73.1, 48.0, 29.0; 19F NMR (376 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ −60.0 ; LC-MS (ESI+): m/z calcd for C12H15F3N2O: 260.11; found: 260.91 [M+H]+; AHPLC (RP): tR = 9.6 min, 100%.
2-(((1,4-trans)-4-Aminocyclohexyl)oxy)-5-(trifluoromethyl)benzonitrile (1h)
Prepared according to general procedure A. Off-white solid, 50% yield; mp 190 °C; 8.44 (s, 1H), 8.21 (s, 1H), 7.97 (d, J = 9.2 Hz, 1 H), 7.58 (d, J = 8.8 Hz, 1H), 4.64 (m, 1H), 3.00 (m, 1H), 2.12 (m, 2H), 1.97 (m, 2H), 1.50 (m, 4H); LC-MS (ESI+): m/z calcd for C20H19F6N3O2: 284.11; found: 285.00 [M+H]+; AHPLC (RP): tR = 10.9 min, 89%.
4-(((1,4-trans)-4-Aminocyclohexyl)oxy)benzonitrile (1i)
Prepared according to general procedure A. Off-white powder, 96% yield; mp 197 °C; 1H NMR (500 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 8.45 (s, 1H), 7.73 (d, J = 8.1 Hz, 2H), 7.12 (d, J = 8.1 Hz, 2H), 4.43 (m, 1H), 2.96 (m, 1H), 2.08 (m, 2H), 1.96 (m, 2H), 1.45 (m, 4H); LC-MS (ESI+): m/z calcd for C13H16F6N2O: 216.13; found: 216.83 [M+H]+; AHPLC (RP): tR = 1.44 min, 100%.
General Procedure B for the Synthesis of 1-((1,4-trans)-4-aryloxy)cyclohexyl)-3-(trifluoromethyl)phenylureas (3a-l)
The arylisocyanate (1.22 mmol, 1eq) was added to a solution of the appropriate trans-4-aryloxycyclohexylamine (1 eq) in dry DMSO (2 mL) in the presence of triethylamine (2eq). The mixture was stirred overnight at rt. LCMS showed the formation of the desired urea and the consumption of the trans-4-aryloxycyclohexylamine. Water (3 mL) was added and the product was extracted with ethyl acetate (10 mL), dried (MgSO4) and the residue obtained after the evaporation of the solvent was purified by reverse phase chromatography using a gradient of methanol in water (containing 0.1% formic acid). The product was eluted at 80% methanol.
5-(Trifluoromethyl)-2-(((1,4-trans)-4-(3-(3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)ureido)cyclohexyl)oxy)benzamide (3a)
Prepared according to general procedure B. White powder, 58% yield; mp 135 °C; 1H NMR (500 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 8.69 (s, 1H), 8.05 (s, 1H), 7.98 (s, 1H), 7.79 (d, J = 6.9 Hz, 1H), 7.60 (s, 1H), 7.47–7.43 (m, 3H), 7.22 (d, J = 6.6 Hz, 1H), 6.32 (d, J = 7.7 Hz, 1H), 4.68–4.64 (m, 1H), 3.60–3.55 (m, 1H), 2.12–2.10 (m, 2H), 1.96–1.94 (m, 2H), 1.68–1.61 (m, 2H), 1.44–1.38 (m, 2H); 13C NMR (125 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 165.2, 158.0, 154.4, 141.3, 129.7, 129.4 (q, J = 31.1 Hz), 129.0 (q, J = 2.9 Hz), 127.8 (q, J=3.4 Hz), 124.4, 124.3 (q, J = 272.0 Hz), 124.2 (q, J = 271.0 Hz), 121.1, 120.8 (q, J = 32.6 Hz), 117.2 (q, J = 3.4 Hz), 115.0, 113.4 (q, J = 3.8 Hz), 76.1, 47.0, 29.7, 29.2; LC-MS (ESI+): m/z calcd for C22H21F6N3O3: 489.15; found: 490.15 [M+H]+; HR-MS (ESI+):m/z calcd for C22H21F6N3NaO3: 512.1385; found: 512.1366 [M+Na]+; AHPLC (RP): tR = 16.2 min, 98.8%.
2-(Trifluoromethyl)-5-(((1,4-trans)-4-(3-(3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)ureido)cyclohexyl)oxy)benzamide (3b)
Prepared according to general procedure B. White powder, 41% yield; mp 197 °C; 1H NMR (500 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 8.69 (s, 1H), 7.98 (s, 1H), 7.91 (m, 1H), 7.64 (d, J = 8.8 Hz, 1H), 7.56 (s, 1H), 4.47–7.72 (m, 2H), 7.22 (d, J = 6.6 Hz, 1H), 7.15 (d, J = 8.4 Hz, 1H), 6.29 (d, J = 7.3 Hz, 1H), 4.54–4.51 (m, 1H), 3.58–3.54 (m, 1H), 2.2.08–2.06 (m, 2H), 1.96–1.94 (m, 2H), 1.54–1.48 (m, 2H), 1.44–1.37 (m, 2H); 13C NMR (125 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 168.6, 159.7, 154.4, 141.3, 138.7, 129.7, 129.4 (q, J = 31.4 Hz), 128.1 (q, J = 2 Hz), 124.3 (q, J = 272.5 Hz), 124.0 (q, J = 272.0 Hz), 121.0, 117.5 (q, J = 32.1 Hz), 115.5, 115.0, 74.5, 47.2, 29.8, 29.5; LC-MS (ESI+): m/z calcd for C22H21F6N3O3: 489.15; found: 490.15 [M+H]+; HR-MS (ESI+):m/z calcd for C22H21F6N3NaO3: 512.1385; found: 512.1362 [M+Na]+; AHPLC (RP): tR = 15.6 min, 96.7%.
N-(5-(Trifluoromethyl)-2-(((1,4-trans)-4-(3-(3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)ureido)cyclohexyl)oxy)phenyl)acetamide (3c)
Prepared according to general procedure B. White powder, 53% yield; mp 204 °C; 1H NMR (500 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 9.11 (s, 1H), 8.71 (s, 1H), 8.38 (s, 1H), 7.99 (s, 1H), 7.–7.41 (m, 2H), 7.38 (d, J = 8.4 Hz, 1H), 7.30 (d, J = 8.4 Hz, 1H), 7.21 (d, J = 6.2 Hz, 1H), 6.32 (d, J = 7.3 Hz, 1H), 4.52–4.48 (m, 1H), 3.57–52 (m, 1H), 2.15 (s, 3H), 2.07–2.05 (m, 2H), 1.97–1.95 (m, 2H), 1.65–1.59 (m, 2H), 1.40–1.34 (m, 2H); 13C NMR (125 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 169.1, 154.4, 150.0, 141.3, 129.7, 129.4 (q, J = 31.1 Hz), 128.8, 124.4 (q, J = 271.3 Hz), 124.3 (q, J = 272.3 Hz), 121.1, 120.4 (q, J = 32.1 Hz), 118.2 (m), 117.4 (m), 113.6, 113.4 (q, J = 4.1 Hz), 75.7, 47.3, 29.9, 29.4, 24.0; LC-MS (ESI+): m/z calcd for C23H23F6N3O3: 503.16; found: 504.17 [M+H]+; HR-MS (ESI+):m/z calcd for C23H23F6N3NaO3: 526.1541; found: 526.1556 [M+Na]+; AHPLC (RP): tR = 17.5 min, 95.6%.
1-(1,4-trans)-4-((2-Nitro-4-(trifluoromethyl)phenoxy)cyclohexyl)-3-(3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)urea (3d)
Prepared according to general procedure B. White powder, 61% yield; mp 162 °C; 1H NMR (500 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 8.68 (s, 1H), 8.28 (s, 1H), 7.98–7.96 (m, 2H), 7.67 (d, J = 8.4 Hz, 1H), 7.45–7.44 (m, 2H), 7.21 (d, 1H), 6.35 (d, J = 5.9 Hz, 1H), 4.77–4.74 (m, 1H), 3.60–3.55 (m, 1H), 2.06–2.04 (m, 2H), 1.95–1.92 (m, 2H), 1.59–1.53 (m, 2H), 1.45–1.38 (m, 2H); 13C NMR (125 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 154.4, 152.6, 141.3, 140.1, 130.7 (q, J = 3.8 Hz), 129.7, 129.4 (q, J = 31.6 Hz), 124.2 (q, J = 271.8 Hz), 123.3 (q, J = 271.8 Hz), 122.5 (q, J = 4.5 Hz), 121.0, 120.7 (q, J = 33.5 Hz), 117.2 (q, J = 2.6 Hz), 117.0, 113.4 (q, J = 3.4 Hz), 76.7, 46.7, 29.1, 28.7; LC-MS (ESI+): m/z calcd for C21H19F6N3O4: 491.13; found: 492.07 [M+H]+; HR-MS (ESI+):m/z calcd for C22H19F6N3NaO4: 514.1177; found: 514.1160 [M+Na]+; AHPLC (RP): tR = 19.2 min, 95.4%.
1-(3,5-Bis(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)-3-((1,4-trans)-4-(4-(trifluoromethyl)phenoxy)cyclohexyl)urea (3e)
Prepared according to general procedure B. White powder, 68% yield; mp 221 °C; 1H NMR (500 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 9.09 (s, 1H), 8.07 (s, 2H), 7.63 (d, J = 8.4 Hz, 2H), 7.54 (s, 1H), 7.14 (d, J = 8.4 Hz, 2H), 6.56 (d, J = 7.7 Hz, 1H), 4.49–4.46 (m, 1H), 3.57–3.55 (m, 1H), 2.09–2.07 (m, 2H), 1.96–1.94 (m, 2H), 1.54–1.40 (m, 4H); 13C NMR (125 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 160.3, 154.2, 142.5, 130.6 (J = 32.3 Hz), 126.9 (m), 124.6 (q, J = 270.6 Hz), 123.3 (q, J = 272.5 Hz), 120.8 (q, J = 31.9 Hz), 117.2 (m), 115.8, 113.4 (m), 74.4, 47.4, 29.7, 29.6; 19F NMR (376 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ −59.8, 61.7; LC-MS (ESI+): m/z calcd for C22H19F9N2O2: 514.13; found: 515.08 [M+H]+; HR-MS (ESI+): m/z called for C22H20F9N2O2: 515.1381; found: 515.1394 [M+H]+; AHPLC (RP): tR = 21.7 min, 98.7%.
1-(3-Cyanophenyl)-3-((1,4-trans)-4-(4-(trifluoromethyl)phenoxy)cyclohexyl)urea (3f)
Prepared according to general procedure B. White powder, 49% yield; mp 220 °C; 1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 8.67 (s, 1H), 7.93 (s, 1H), 7.61 (d, J = 8.6 Hz, 2H), 7.58 (d, J = 8.6 Hz, 1H), 7.42 (t, J = 7.8 Hz, 1H), 7.32 (d, J = 7.4 Hz, 1H), 7.13 (d, J = 8.6 Hz, 2H), 7.35 (d, J = 7.4 Hz, 1H), 4.49–4.43 (m, 1H), 3.58–3.52 (m, 1H), 2.08–2.05 (m, 2H), 1.96–1.93 (m, 2H), 1.55–1.46 (m, 2H), 1.43–1.34 (m, 2H); 13C NMR (100 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 160.3, 154.3, 141.3, 130.0, 126.9, (q, J = 3.9 Hz), 124.5 (q, J = 270.9 Hz), 124.4, 122.1, 120.8 (q, J = 31.9 Hz), 120.0, 119.0, 115.8, 112.1, 111.5, 74.4, 47.2, 29.8, 29.5; 19F NMR (376 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ −59.8; LC-MS (ESI+): m/z calcd for C21H20F3N3O2: 403.15; found: 404.23 [M+H]+; HR-MS (ESI+): m/z calcd for C21H20F3N3NaO2: 426.1405; found: 426.1402 [M+Na]+; AHPLC (RP): tR = 17.9 min, 98.2%.
1-(4-Cyanophenyl)-3-((1,4-trans)-4-(4-(trifluoromethyl)phenoxy)cyclohexyl)urea (3g)
Prepared according to general procedure B. White powder, 39% yield; mp 213 °C; 1H NMR (500 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 8.84 (s, 1H), 7.66 (d, J = 8.8 Hz, 2 H), 7.62 (d, J = 8.8 Hz, 2H), 7.55 (d, J = 8.8 Hz, 2H), 7.13 (d, J = 8.8 Hz, 2H), 6.38 (d, J = 7.3 Hz, 1H), 4.49–4.45 (m, 1H), 3.57–3.53 (m, 1H), 2.07–2.05 (m, 2H), 1.95–1.93 (m, 2H), 1.54–1.47 (m, 2H), 1.42–1.35 (m, 2H); 13C NMR (100 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 160.3, 153.9, 144.9, 133.2, 126.9 (q, J = 3.6 Hz), 124.6 (q, J = 270.6 Hz), 120.8 (q, J = 32.1 Hz), 119.4, 117.3, 115.8, 102.3, 74.4, 47.2, 29.8, 29.5 ; LC-MS (ESI+): m/z calcd for C21H20F3N3O2: 403.15; found: 404.16 [M+H]+; HR-MS (ESI+): m/z calcd for C21H20F3N3O2: 403.1508; found: 403.1516 [M]+; AHPLC (RP): tR = 17.8 min, 98.8%.
1-(3-(Trifluoromethyl)phenyl)-3-((1,4-trans)-4-((5-(trifluoromethyl)pyridin-2-yl)oxy)cyclohexyl)urea (3h)
Prepared according to general procedure B. White solid, 47% yield; mp 192 °C; 1H NMR (500 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 8.72 (s, 1H), 8.56 (s, 1H), 8.04 (d, J = 8.5, Hz, 1H), 7.97 (s, 1H), 7.47–7.42 (m, 2H), 7.21 (d, J = 6.9 Hz, 1H), 6.97 (d, J = 8.4 Hz, 1H), 6.26 (d, J = 7.3 Hz, 1H), 5.08–5.04 (m, 1H), 3.58–3.54 (m, 1H), 2.10–2.08 (m, 2H), 1.97–1.95 (m, 2H), 1.58–1.51 (m, 2H), 1.42–1.35 (m, 2H); 13C NMR (125 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 165.1, 154.4, 144.9, 141.3, 136.4, 129.7, 129.4 (q, J = 31.1 Hz), 124.2 (q, J = 272.2 Hz), 124.15 (q, J = 271.1 Hz), 121.0 (m), 118.5 (q, J = 32.3 Hz), 117.1 (q, J = 2.4 Hz), 113.4 (q, J = 4.1 Hz), 111.8, 73.4, 47.2, 30.0, 29.6; LC-MS (ESI+): m/z called for C20H19F6N3O2: 447.14; found: 448.02 [M+H]+; HR-MS (ESI+): m/z calcd for C20H19F6N3O2: 447.1381; found: 447.1385 [M]+; AHPLC (RP): tR = 19.2 min, 97.6%.
1-((1,4-trans)-4-(3-(Trifluoromethyl)phenoxy)cyclohexyl)-3-(3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)urea (3i)
Prepared according to general procedure B. White powder, 32% yield; mp 195 °C; 1H NMR (500 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 8.66 (s, 1H), 8.22 (s, 1H), 7.997.98 (m, 2H), 7.56 (d, J = 9.2 Hz, 1H), 7.47–7.43 (m, 2H), 7.22 (d, J = 6.6 Hz, 2 H), 6.33 (d, J = 7.3 Hz, 1H), 4.73–4.70 (m, 1H), 3.61–3.56 (m, 1H), 2.09–2.07 (m, 2H), 1.97–1.95 (m, 2H), 1.63–1.56, (m, 2H), 1.46–1.39 (m, 2H); 13C NMR (125 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 161.8, 154.4, 141.3, 131.9 (m), 131.5 (m), 129.7, 129.4 (q, J = 31.3 Hz), 124.3 (q, J = 272.5 Hz), 123.5 (q, J = 271.5 Hz), 121.4 (q, J = 33.7 Hz), 121.0, 117.2 (m), 115.1, 114.9, 113.4 (m), 102.1, 76.3, 46.8, 29.4, 29.0; LC-MS (ESI+): m/z calcd for C22H19F6N3O2: 471.14; found: 472.22 [M+H]+; HR-MS (ESI+): m/z calcd for C22H19F6N3O2: 471.1381; found: 471.1378 [M]+; AHPLC (RP): tR = 18.8 min, 98.8%.
1-((1,4-trans)-4-(4-Cyanophenoxy)cyclohexyl)-3-(3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)urea (3j)
Prepared according to general procedure B. off-white powder, 68% yield; mp 168 °C; 1H NMR (500 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 8.66 (s, 1H), 7.98 (s, 1H), 7.74 (d, J = 8.4 Hz, 2H), 7.46–7.42 (m, 2H), 7.22 (d, J = 6.3 Hz, 1H), 7.13 (d, J = 8.5 Hz), 6.29 (d, J = 7.3 Hz, 1H), 4.52–4.48 (m, 1H), 3.56–3.52 (m, 1H), 2.06–2.04 (m, 2H), 1.95–1.93 (m, 2H), 1.53–1.47 (m, 2H), 1.42–1.36 (m, 2H); 13C NMR (125 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 160.9, 154.4, 141.3, 134.2, 133.6 (J = 34.7 Hz), 129.7, 129.4 (J = 31.1 Hz), 124.2 (q, J = 272.3 Hz), 121.3, 119.2, 117.2 (J = 4.6 Hz), 116.3, 113.4 (J = 3.8 Hz), 102.4, 74.6, 47.2, 29.8, 29.5; LC-MS (ESI+): m/z calcd for C21H20F3N3O2: 403.15; found: 404.09 [M+H]+; HR-MS (ESI+): m/z calcd for C21H20F3N3O2: 404.1586; found: 404.1578 [M+H]+; AHPLC (RP): tR = 17.4 min, 99.5%.
1-((1,4-trans)-4-(4-Cyanophenoxy)cyclohexyl)-3-(4-cyanophenyl)urea (3k)
Prepared according to general procedure B. White solid, 36% yield; mp 246 °C; 1H NMR (500 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 8.83 (s, 1H), 7.74 (d, J = 8.8 Hz, 2H), 7.66 (d, J = 8.4 Hz, 1H), 7.55 (d, J = 8.4 Hz, 2H), 7.12 (d, J = 8.8 Hz, 2H), 6.38 (d, J = 7.3 Hz, 1H), 4.50–4.47 (m, 1H), 3.55–3.53 (m, 1H), 2.06–2.04 (m, 2H), 1.94–1.92 (m, 2H), 1.53–1.47 (m, 2H), 1.42–1.35 (m, 2H); 13C NMR (125 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 160.9, 153.9, 144.9, 134.2, 133.2, 119.4, 119.2, 117.3, 116.3, 102.4, 102.3, 74.5, 47.1, 29.8, 29.4 ; LC-MS (ESI+): m/z calcd for C21H20N4O2: 360.16; found: 360.96 [M+H]+; HR-MS (ESI+): m/z calcd for C21H21N4O2: 361.1665; found: 361.1675 [M+H]+; AHPLC (RP): tR = 15.1 min, 98.8%.
1-((1,4-trans)-4-(4-Cyanophenoxy)cyclohexyl)-3-(3-cyanophenyl)urea (3l)
Prepared according to general procedure B. White solid, 48% yield; mp 197 °C; 1H NMR (500 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 8.67 (s, 1H), 7.92 (s, 1H), 7.74 (d, J = 8.8 Hz, 2 H), 7.56 (d, J = 8.1 Hz, 1H), 7.42 (t, J = 8.1 Hz, 1H), 7.33 (d, J = 7.3 Hz, 1H), 7.12 (d, J = 8.4 Hz, 1H), 6.36 (d, J = 7.3 Hz, 1H), 4.49 (s, 1H), 3.54 (m, 1H), 2.05 (m, 2H), 1.93 (m, 2H), 1.50 (m, 2H), 1.38 (m, 2H); 13C NMR (125 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 160.9, 154.3, 141.3, 134.2, 130.0, 124.42, 122.1, 120.0, 119.2, 119.0, 116.3, 111.4, 102.4, 74.5, 47.2, 29.8, 29.5 ; LC-MS (ESI+): m/z calcd for C21H20N4O2: 360.16; found: 361.03 [M+H]+; HR-MS (ESI+): m/z calcd for C21H20N4NaO2: 383.1484; found: 383.1492 [M+Na]+; AHPLC (RP): tR = 15.2 min, 98.9%.
General Procedure C for the Synthesis of 1-((1,4-trans)-4-aryloxycyclohexyl)-3-((2-(trifluoromethoxy))phenylureas (3m-q)
A fresh solution of 1-isocyanato-3-(trifluoromethoxy)benzene (2e) in dry DMSO (0.2 M solution, 2eq, prepared according to reference12 was added to the appropriate trans-4-aryloxycyclohexylamine (1eq) under N2 atm. Addition of triethylamine (2eq) followed immediately. The mixture was stirred overnight at rt. LCMS showed the formation of the desired urea and the consumption of the phenoxycyclohexylamine. Water (5 mL) was added and the product was extracted with ethyl acetate (20 mL), dried (MgSO4) and the residue obtained after the evaporation of the solvent was purified by reverse phase chromatography using a gradient of methanol in water (containing 0.1% formic acid). The product was eluted at 80% methanol.
2-(((1,4-trans)-4-(3-(3-(Trifluoromethoxy)phenyl)ureido)cyclohexyl)oxy)-5-(trifluoromethyl)benzamide (3m)
Prepared according to general procedure C. White powder, 30% yield; mp 197 °C; 1H NMR (500 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 8.63 (s, 1H), 8.04 (s, 1H), 7.78 (m, 1H), 7.66 (s, 1H), 7.59 (s, 1H), 7.43 (d, J = 8.4 Hz, 1H), 7.32 (t, J = 8.1 Hz, 1H), 7.17 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 1H), 6.84 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 1H), 6.28 (d, J = 7.3 Hz, 1H), 4.67–4.63 (m, 1H), 3.57–3.55 (m, 1H), 2.11–2.09 (m, 2H), 1.95–1.93 (m, 2H), −1.67–1.61 (m, 2H), 1.43–1.36 (m, 2H); 13C NMR (125 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 165.2, 158.0, 154.3, 148.7, 142.2, 130.2, 129.0 (q, J = 3.8 Hz), 127.8 (q, J = 4.3 Hz), 124.4, 124.2 (q, J = 271.5 Hz), 120.9 (q, J = 32.6 Hz), 120.1 (q, J = 256.2 Hz), 116.1, 115.0, 112.8, 109.5, 76.1, 46.9, 29.7, 29.2; LC-MS (ESI+): m/z calcd for C22H21F6N3O4: 505.14; found: 506.09 [M+H]+; HR-MS (ESI+): m/z calcd for C22H21F6N3NaO4: 528.1334; found: 528.1318 [M+Na]+; AHPLC (RP): tR = 16.6 min, 95.8%.
2-((1,4-trans)-4-(3-(3-(Trifluoromethoxy)phenyl)ureido)cyclohexyl)oxy)-5-(trifluoromethyl)benzamide (3n)
Prepared according to general procedure C. White powder, 26% yield; mp 202 °C; 1H NMR (500 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 8.64 (s, 1H), 7.91 (s, 1H), 7.67 (s, 1H), 7.64 (d, J = 8.8 Hz, 1H), 7.56 (s, 1H), 7.32 (t, J = 8.1 Hz, 1H), 7.16 (m, 2H), 7.03 (s, 1H), 6.85 (d, J = 8.1 Hz, 1H), 6.26 (d, J = 7.3 Hz, 1H), 4.54–4.50 (m, 1H), 3.57–3.52 (m, 1H), 2.08–2.06 (m, 2H), 1.95–1.93 (m, 2H), 1.54–1.48 (m, 2H), 1.43–1.36 (m, 2H); 13C NMR (125 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 168.9, 159.8, 154.5, 148.9, 142.3, 130.3, 128.3, 124.1 (q, J = 272.0 Hz), 120.2 (q, J = 256.2 Hz), 117.7 (q, J = 32.3 Hz), 116.2, 115.6, 115.1, 112.9, 109.6, 74.6, 47.2, 29.9, 29.6 ; LC-MS (ESI+): m/z calcd for C22H21F6N3O4: 505.14; found: 506.15 [M+H]+; HR-MS (ESI+): m/z calcd for C22H21F6N3NaO4: 528.1334; found: 528.1309 [M+Na]+; AHPLC (RP): tR = 17.9 min, 98.1%.
N-(2-(((1,4-trans)-4-(3-(3-(Trifluoromethoxy)phenyl)ureido)cyclohexyl)oxy)-5-(trifluoromethyl) phenyl)acetamide (3o)
Prepared according to general procedure C. White powder, 36%. mp 160 °C; 1H NMR (500 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 9.11 (s, 1H), 8.66 (s, 1H), 8.38 (s, 1H), 7.67 (s, 1H), 7.38 (d, J = 8.4 Hz, 1H), 7.33 (d, J = 8.4 Hz, 1H), 7.30 (d, J = 9.5 Hz, 1H), 7.17 (d, J = 8.1 Hz, 1H), 6.84 (d, J = 7.7 Hz, 1H), 6.29 (d, J = 7.3 Hz, 1H), 4.53–4.49 (m, 1H), 3.56–3.53 (m, 1H), 2.15 (s, 3H), 2.07–2.05 (m, 2H), 1.98–1.96 (m, 2H), 1.66–1.60 (m, 2H), 1.40–1.34 (m, 2H); 13C NMR (125 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 162.2, 154.4, 150.1, 148.8, 142.3, 130.3, 128.8, 124.5 (q, J = 271.1 Hz), 121.2 (m), 120.5 (q, J = 31.9 Hz), 120.2 (q, J = 255.1 Hz), 118.3 (m), 116.2, 113.6, 112.9, 109.6, 75.8, 47.3, 29.9, 29.5, 24.1; LC-MS (ESI+): m/z calcd for C23H23F6N3O4: 519.16; found: 520.11 [M+H]+; HR-MS (ESI+): m/z calcd for C23H23F6N3NaO4: 542.1490; found: 542.1495 [M+Na]+; AHPLC (RP): tR = 17.9 min, 97.4%.
1-((1,4-trans)-4-(4-(Trifluoromethoxy)phenoxy)cyclohexyl)-3-(3-(trifluoromethoxy)phenyl)urea (3p)
Prepared according to general procedure C. White powder, 27% yield; mp 176 °C; 1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 8.62, (s, 1H), 7.66 (s, 1H), 7.32 (t, J = 8.5 Hz, 1H), 7.26 (d, J = 8.4 Hz, 2H), 7.16 (d, J = 8.1 Hz, 1H), 7.04 (d, J = 8.8 Hz, 2H), 6.84 (d, J = 7.7 Hz, 1H), 6.24 (d, J = 7.7 Hz, 1H), 4.37–4.34 (m, 1H), 3.56–3.51 (m, 1H), 2.06–2.04 (m, 2H), 1.95–1.93 (m, 2H), 1.51–1.45 (m, 2H), 1.40–1.33 (m, 2H); 13C NMR (125 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 156.2, 154.3, 148.7, 142.2, 141.6, 130.17, 122.5, 120.2 (q, J = 255.3 Hz), 120.1 (q, J = 256.0 Hz), 116.8, 116.0, 112.7, 109.4, 74.6, 47.2, 29.9, 29.6; LC-MS (ESI+): m/z calcd for C21H20F6N2O4: 478.13 ; found: 479.04 [M+H]+; HR-MS (ESI+): m/z calcd for C21H20F6N2NaO4: 501.1225; found: 501.1242 [M+Na]+; AHPLC (RP): tR = 20.3 min, 96.3%.
1-((3-(Trifluoromethoxy)phenyl)-3-(1,4-trans)-4-(4-(trifluoromethyl)phenoxy)cyclohexyl)urea (3q)
Prepared according to general procedure C. White powder, 25% yield; mp 173 °C; 1H NMR (500 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 8.63 (s, 1H), 7.67, (s, 1H), 7.63 (d, J = 8.4 Hz, 2H), 7.33 (t, J = 8.1 Hz, 2H), 7.18 (d, J = 7.4 Hz, 1H), 7.14 (d, J = 8.4 Hz, 2H), 6.85 (d, J = 7.7 Hz, 1H), 6.26 (d, J = 7.3 Hz, 1H), 4.50–4.46 (m, 1H), 3.57–3.53 (m, 1H), 2.08–2.06 (m, 2H), 1.96–1.94 (m, 2H), 1.54–1.47 (m, 2H), 1.42–1.35 (m, 2H); 13C NMR (125 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 160.3, 154.3, 148.7, 142.2, 130.2, 127.1 (q, J = 3.6 Hz), 124.6 (q, J = 271.1 Hz), 121.1, 120.8 (q, J = 32.1 Hz), 116.0, 115.8, 112.7, 109.4, 74.4, 47.2, 29.8, 29.5; LC-MS (ESI+): m/z calcd for C21H20F6N2O3: 462.14; found: 463.10 [M+H]+; HR-MS (ESI+): m/z called for C21H20F6N2O3: 462.1378; found: 462.1390 [M]+;AHPLC (RP): tR = 20.1 min, 97.0%.
General Procedure D for the Synthesis of N-Aryl phenylcarbamates19 4a-c
Phenyl chloroformate (1.2 eq or 2 eq, as indicated below for the specific compound) was added to a solution of the appropriate aniline (0.27 mmol, 1 eq) and pyridine (2 eq) in dichloromethane (4 ml) at 0 °C. The reaction mixture was stirred at room temperature for 30 minutes. Water (10 ml) and hydrochloric acid (1N, 1 ml) were added, the organic phase dried (Na2SO4) and the solvent evaporated under vacuum to produce the aryl phenylcarbamate that was used in the next step without further purification.
Phenyl (3-cyano-5-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)carbamate (4a)
Prepared according to general procedure D using phenyl chloroformate (84 mg, 0.54 mmol), 3-amino-5-(trifluoromethyl) benzonitrile (50 mg, 0.27 mmol) and pyridine (44 uL, 0.54 mmol) in dichloromethane (4 ml) at 0 °C. Used in the next step without further purification.
Phenyl (3,4-dicyanophenyl)carbamate (4b)
Prepared according to general procedure D using phenyl chloroformate (66 mg, 0.42 mmol), 4-aminophthalonitrile (50 mg, 0.35 mmol) and pyridine (35 uL, 0.54 mmol) in dichloromethane (4 ml). The obtained phenyl (3,4-dicyanophenyl)carbamate was used in the next step without further purification.
Phenyl (3,5-dicyanophenyl)carbamate (4c)
Prepared according to general procedure D using phenyl chloroformate (94 mg, 0.60 mmol), 3,5-dicyanoaniline (90 mg, 0.50 mmol) and pyridine (50 ul, 0.60 mmol) in dichloromethane (4 ml). The obtained phenyl (3,5-dicyanophenyl)carbamate was used in the next step without further purification. Preparation of 3,5-dicyanoaniline: To an ice cold solution of 5-aminoisophthalamide hydrochloride (100 mg, 0.46 mmol) in dichloromethane (6 mL), was added dry pyridine (0.23 ml, 2.77 mmol). The reaction mixture was stirred at 0 °C for 10 minutes followed by dropwise addition of trifluoroacetic anhydride (0.32 ml, 2.3 mmol). The reaction mixture was stirred for an additional hour. After completion of reaction as monitored by TLC, saturated sodium bicarbonate was added and reaction mixture was extracted using dichloromethane, dried over sodium sulfate, and evaporated under vacuum to obtain light yellow solid, which was column chromatographed using hexane and ethyl acetate gradient to obtain 3,5-dicyanoaniline as white solid in quantitative yield. 1H NMR (CDCl3) δ 8.19 (s, 2H), 7.82 (s, 1H); 13C NMR (DMSO-d6) δ 137.94, 132.71, 128.57, 116.68, 113.43.
General Procedure E for the Synthesis of Ureas (3r-t)
trans-4-(4-(Trifluoromethyl)phenoxy)cyclohexanamine, 4f (1 eq) was added to a solution of the appropriate phenylcarbamate (1–1.65 eq, as indicated for each compound) and pyridine (anhydrous, 4 mL) under N2 atmosphere. The mixture was stirred at 80 °C for 3 hours, unless otherwise indicated. The solvent was evaporated and the product was purified by silica gel using hexane and ethyl acetate gradient to obtain the desired product.
1-(3-Cyano-5-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)-3-((1,4-trans)-4-(4-(trifluoromethyl)phenoxy)cyclohexyl)urea (3r)
Prepared according to general procedure E using phenyl (3-cyano-5-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)carbamate (70 mg, 0.23 mmol), dry pyridine (4 mL) and 4-(4-(trifluoromethyl)phenoxy)cyclohexan-1-amine (60 mg, 0.23 mmol). White amorphous solid, 83% yield; mp 205 °C. 1H NMR (500 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 9.11 (s, 1H), 8.17 (m, 1H), 8.00 (s, 1H), 7.78 (s, 1H), 7.62 (d, J = 8.5 Hz, 2H), 7.14 (d, J = 8.5 Hz, 2H), 6.68 (d, J = 7.6 Hz, 1H), 4.49–4.45 (m, 1H), 3.58–3.52 (m, 1H), 2.08–2.06 (m, 2H), 1.95–1.93 (m, 2H), 1.53–1.46 (m, 2H), 1.45–1.38 (m, 2H); 13C NMR (125 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 160.2, 154.1, 142.4, 130.7 (q, J = 32.8 Hz), 128.9 (q, J = 3.1 Hz), 124.5 (q, J = 271.5 Hz), 123.8, 123.1 (q, J = 272.3 Hz), 120.8 (q, J = 31.1 Hz), 120.6 (m), 117.9 (m), 117.6, 115.8, 112.8, 74.4, 47.4, 29.7, 29.5. 19F NMR (470 MHz, DMSO) δ −58.8, −60.9; LC-MS (ESI+): m/z calcd for C19H20F6N3O2: 471.14; found: 472.03 [M+H]+; HR-MS (ESI+): m/z calcd for C22H19F6N3O2: 471.1381; found: 471.1397 [M]+; AHPLC (RP): tR = 19.9 min, 96.4%.
1-(3,4-Dicyanophenyl)-3-((1,4-trans)-4-(4-(trifluoromethyl)phenoxy)cyclohexyl)urea (3s)
Prepared according to general procedure E using phenyl (3,4-dicyanophenyl)carbamate (140 mg, 0.53 mmol), dry pyridine (4 mL) and 4-(4-(trifluoromethyl)phenoxy)cyclohexan-1-amine, 4f (96 mg, 0.37 mmol). White amorphous solid, 91% yield; mp 242 °C. 1H NMR (500 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 9.18 (s, 1H), 8.12 (d, J = 1.5 Hz, 1H), 7.95 (d, J = 8.8 Hz, 1H), 7.76 (dd, J = 8.8, 1.5 Hz, 1H), 7.63 (d, J = 8.5 Hz, 2H), 7.14 (d, J = 8.5 Hz, 2H), 6.64 (d, J = 7.3 Hz, 1H), 4.50–4.46 (m, 1H), 3.57–3.55 (m, 1H), 2.07–2.05 (m, 2H), 1.95–1.93 (m, 2H), 1.55–1.48 (m, 2H), 1.45–1.40 (m, 2H); 13C NMR (125 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 160.3, 153.6, 145.2, 134.8, 126.9 (q, J = 4.1 Hz), 124.6 (q, J = 271.1 Hz), 121.21 (q, J = 2.4 Hz), 120.8 (q, J = 32.1 Hz), 116.5, 116.1, 115.8, 115.3, 104.9, 74.3, 47.4, 29.6, 29.4. 19F NMR (470 MHz, DMSO) δ −58.8; LC-MS (ESI+): m/z calcd for C22H19 F3N4O2: 428.15; found: 429.03 [M+H]+; HRMS calcd for C22H23F3N5O2 m/z 446.1804, found: 446.1816 (M+NH4)+; AHPLC (RP): tR = 18.3 min, 95.6%.
1-(3,5-Dicyanophenyl)-3-((1,4-trans)-4-(4-(trifluoromethyl)phenoxy)cyclohexyl)urea (3t)
Prepared according to general procedure E using phenyl 3,5-dicyanophenyl)carbamate (100 mg, 0.38 mmol), dry pyridine (4 mL) and 4-(4-(trifluoromethyl)phenoxy)cyclohexan-1-amine, 4f (60 mg, 0.23 mmol). The mixture was heated at 80 °C for 24h. White amorphous solid, 62% yield; mp 260 °C. 1H NMR (500 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 8.92 (s, 1H), 8.09 (s, 1H), 7.92 (s, 1H), 7.62 (d, J = 7.9 Hz, 2H), 7.13 (d, J = 8.2 Hz, 2H), 6.61 (d, J = 7.3 Hz, 1H), 4.49 – 4.45 (m, 1H), 3.57 – 3.55 (m, 1H), 2.07 – 2.05 (m, 2H), 1.95–1.93 (m, 2H), 1.54–1.47, (m, 2H), 1.44–1.37 (m, 2H); 13C NMR (125 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 160.3, 154.0, 142.2, 127.6, 126.9 (q, J = 3.8 Hz), 124.6 (q, J = 271.1 Hz), 124.58, 120.8 (q, J = 31.6 Hz), 117.34, 115.8, 113.1, 74.4, 47.4, 29.8, 29.5; 19F NMR (470 MHz, DMSO) δ −58.8; LC-MS (ESI+): m/z calcd for C22H19 F3N4O2: 428.15; found: 429.03 [M+H]+; HR-MS (ESI+): m/z calcd for C22H19F6N3O2: 429.1538; found: 429.1530 [M+H]+; AHPLC (RP): tR = 18.4 min, 94.6%.
4-(4-(Trifluoromethyl)phenoxy)aniline (5)
Light pink powder, 53% yield; 1H NMR (500 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 7.65 (d, J = 8.1 Hz, 2H), 7.00 (d, J = 8.4 Hz, 2H), 6.82 (d, J = 7.7 Hz, 2H), 6.62 (d, J = 8.1 Hz, 2H), 5.08 (s, 2H); 13C NMR (125 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 162.2, 146.3, 144.0, 127.2 (m), 124.5 (q, J = 271.1 Hz), 122.0 (q, J = 32.1 Hz), 121.4, 116.3, 114.9; LC-MS (ESI+): m/z calcd for C13H10F3NO: 253.07; found: 253.83 [M+H]+.
1-(4-(4-(Trifluoromethyl)phenoxy)phenyl)-3-(3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)urea (6a)
Prepared according to general procedure B. White needles, 45% yield; mp 178 °C; 1H NMR (500 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 9.05 (s, 1H), 8.88 (s, 1H), 8.02 (s, 1H), 7.71 (d, J = 8.4 Hz, 2H), 7.59 (d, J = 8.1 Hz, 1H), 7.55 (d, J = 8.8 Hz, 2H), 7.51 (t, J = 8.1 Hz, 1H), 7.31 (d, J = 7.3 Hz, 1H), 7.10 (d, J = 8.8 Hz, 4H); 13C NMR (125 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 161.1, 152.6, 149.3, 140.6, 136.4, 129.9, 129.5, (q, J = 31.4 Hz), 127.3 (q, J = 3.6 Hz), 124.3 (q, J = 271.3 Hz), 124.2 (q, J = 272.3 Hz), 122.8 (q, J = 32.1 Hz), 121.8, 120.8, 120.3, 118.0 (q, J = 4.1 Hz), 117.2, 114.1 (q, J = 4.1 Hz), ; LC-MS (ESI+): m/z calcd for C21H14F6N2O2: 440.10; found: 441.14 [M+H]+; HR-MS (ESI+): m/z calcd for C21H14F6N2O2: 440.0959; found: 440.0971 [M]+;AHPLC (RP): tR = 20.5 min, 96.9%.
1-(3-(Trifluoromethoxy)phenyl)-3-(4-(4-(trifluoromethyl)phenoxy)phenyl)urea (6a)
Prepared according to general procedure C. White needles, 47% yield; mp 126 °C; 1H NMR (500 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 9.10 (s, 1H), 8.93 (s, 1H), 7.71 (d, J = 8.1 Hz, 3H), 7.54 (d, J = 8.8 Hz, 2H), 7.40 (t, J = 8.1 Hz, 1H), 7.31 (d, J = 8.1 Hz, 1H), 7.10 (d, J = 8.4 Hz, 4H), 6.94 (d, J = 7.7 Hz, 1H); 13C NMR (125 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 161.1, 152.5, 149.3, 148.7, 141.5, 136.4, 130.4, 127.3 (m), 124.3 (q, J = 271.1 Hz), 122.8 (q, J = 32.3 Hz), 120.9, 120.3, 120.1 (q, J = 255.6 Hz), 117.2, 116.8, 113.7, 110.2; 19F NMR (376 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ −56.7, −60.2; LC-MS (ESI+): m/z calcd for C21H14F6N2O3: 456.09; found: 457.21 [M+H]+; HR-MS (ESI+): m/z calcd for C21H14F6N2O3: 456.0909; found: 456.0916 [M]+; AHPLC (RP): tR = 20.9 min, 99.7%.
Biology
Plasmids and Ternary complex assay
The dual luciferase expression vector and other plasmids used for these studies are described in15a. The ternary complex assay, surrogate of eIF2α phosphorylation, has been described elsewhere15b. Briefly, a dual Renilla and Firefly luciferase mammalian reporter vector that transcribes both mRNAs from the same bi-directional enhancer/promoter complex was utilized for generation of surrogate eIF2α phosphorylation assay15a. Both mRNAs contain the same 90 nucleotide plasmid derived 5′UTR. In addition 5′UTR of the Firefly luciferase mRNA also have in-frame fusion of the 267 nucleotide ATF-4 5′UTR15b.
Dual luciferase reporter (DLR) assay
Cells expressing firefly and renilla luciferases were assayed with a dual glow luciferase assay kit, per manufacturer’s instruction (Promega Inc., Madison, WI). The data calculations were carried out as the ratio of firefly to renilla luciferase signal. Dose-response curves were obtained and triplicate data points were fitted to the logistical sigmoidal model using nonlinear least-squares regression performed in GraphPad Prism 6.
Stable transfection
Stable cell lines utilized in this study are generated as described elsewhere17. Briefly, cells were seeded at the density of 105 in 60-mm dish and transfected one day later using the Lipofectamine 2000 (Invitrogen). For selection of stable cell lines, transfected cells were transferred to 100-mm plates and selected with appropriate antibiotics15b.
Western blotting
Cells cultured under recommended media conditions, were plated and maintained in serum-containing media without antibiotics in 14-cm plates (Nunc) until reaching 70% confluence. Cells were then treated with compounds for 6 hours, washed with cold PBS once, and lysed with M-PER Mammalian Protein Extraction Reagent (Pierce) for 30 minutes on ice. The cell lysates were centrifuged at 12,000 RPM for 15 min and the supernatants were transferred to fresh tubes and the concentrations were determined by BCA (Pierce). Equal amount of proteins were mixed with Laemmli Sample Buffer, heated at 100°C for 5 min and separated by SDS-PAGE and probed with anti-phosphoserine-51-eIF2α (Phos-eIF2α), anti-total eIF2α-specific antibodies (Total-eIF2α) (Biosource International, Hopkinton, MA), anti-CHOP, anti-cyclin D1 or anti-actin (Santa Cruz Biotechnology, CA) essentially as described22.
Cell Growth Inhibition Assay
Cells were seeded in 96-well plates and maintained for 5 days in the presence of 0.5 to 20 μM of individual compound, and cell proliferation was measured by the sulforhodamine B (SRB) assay as described23: briefly, at the end of a 5-day treatment, cells were fixed in 10% cold trichloroacetic acid. Cell number was estimated by measuring the remaining bound dye of sulforhodamine B after washing. The percentage of growth was calculated by using the equation: 100× [(T−T0)/(C−T0)], where T and C represent the absorbance in treated and control cultures at Day 5, and T0 at time zero, respectively. If T is less than T0, cell death has occurred and can be calculated from 100× [(T−T0)/T0].
In vivo PK and anti-tumor studies
All animal studies were performed in accordance with institutional guidelines as defined by Harvard Longwood-Area Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee per protocol 03757. For tumor studies NU 088 male nude mice (nine animals per group) were injected subcutaneously with the CRL-2813 human melanoma cancer cell line and mice bearing 100–150 mm3 tumors were distributed randomly into three groups and were treated q.d. with cHAU 3r at 150 mg/kg and 37.5 mg/kg doses for four days followed by four days off and three days on schedule for a total of 28 days. For 150 mg/kg dose group 55 mg of 3r was dissolved in 55 μl of N-methylmorpholine (NMP), by heating with a heat gun until transparent solution was obtained, followed by sequential addition of 190 μl of Chromophore EL and 30 μl of dd-H2O and subsequent heating of the mixture after each addition to obtain a clear solution. This solution was injected i.p. at 1 μl/gram body weight. The solution of 3r for 37.5 mg/kg group was prepared by dissolving 11.25 mg of 3r, similarly, in the above mixture of NMP, chromophore EL and dd-H2O. As vehicle control we injected a group of tumor bearing mice with 1 μl/gram body weight of the same mixture of NMP. Chromophore EL, and dd-H2O. To determine if 3r causes eIF2α phosphorylation in the tumors, mice bearing ~200 mm3 tumors were injected three consecutive days with same doses of compound 3r or vehicle, tumors were excised and phosphorylated and total eIF2α levels were determined by Western blot analysis. For PK studies mice were given a single IP injection of 40 mg/kg 3r and blood was drawn before injection or 0.5, 1, 2, 4, 6, 24, 48, or 72 hours after injection. Concentration of 3r was then determined by LC-MS using a standard curve. Briefly 10uL blood collected at the indicated time was transferred into a 1.5mL microcentrifuge tube containing 50uL 0.1% EDTA solution (acetic acid, AA). The blood samples were mixed with 10uL of 200nM TAPU (internal standard) in methanol and vortexed strongly for 2min. The samples were then extracted with 200uL of ethyl acetate twice. The extraction solution (organic layer) was then transferred to a 1.5mL microcentrifuge tube, and dried using speed vacuum. The residues were reconstituted in 50uL of 100nM –[(cyclohexylcarbamoyl)amino]dodecanoic acid (CUDA, external standard) in methanol. The samples were vortexed for 5 minutes, transferred to auto-sampler vials with low volume inserts and analyzed by LC/MS/MS. Calibration standards for LC/MS/MS analysis were prepared with a range of 0.5 ng/mL to 500 ng/mL. The LC/MS/MS analysis was performed on a 4000 QTrap tandem mass spectrometer (Applied Biosystems Instrument Corporation, Foster city, CA) equipped with an electrospray ion source coupled to an Agilent 1200SL liquid chromatography series (Agilent Corporation, Palo Alto, CA USA) equipped with a Kinetex C18 2.1 × 50 mm 2.6 um column held at 45 °C. The samples were kept in the auto-sampler at 4 °C, and 3uL of samples were injected on the column. Mobile phase A was water with 0.1% glacial acetic acid. Mobile phase B consisted of acetonitrile with 0.1% glacial acetic acid. The gradient was shown in Table 3. The flow rate was 400 uL/min. The mass spectrometer was operated in negative MRM mode. For optimization of multiple reaction monitoring (MRM) transitions and source parameters, samples were directly infused into the mass spectrometer. Optimized conditions for mass spectrometry and MRM transitions are in Table 4 and Table 5, respectively. Quantification analysis was performed with the software of Analyst 1.5.
Table 3.
HPLC gradient
| Total Time (min) | Flow Rate (μL/min) | B (%) |
|---|---|---|
| 0.00 | 400 | 35 |
| 0.25 | 400 | 35 |
| 2.00 | 400 | 80 |
| 3.50 | 400 | 98 |
| 4.00 | 400 | 98 |
| 4.10 | 400 | 35 |
| 5.00 | 400 | 35 |
Table 4.
Optimized mass spectrometric parameters on Q-trap
| Parameters | Value |
|---|---|
| CUR | 30 psi |
| TEM | 600 °C |
| GS1 | 50 psi |
| GS2 | 60 psi |
| iHe | ON |
| CAD | Medium |
| IS | 4500 V |
| EP | 10 V |
Table 5.
Optimized mass transitions and collision energy for 3r, TAPU and CUDA
| Compounds | Q1 Mass (Da) | Q3 Mass (Da) | CE | DP | CXP |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CUDA | 339.1 | 214.3 | −32 | −65 | −4.0 |
| TAPU | 327.9 | 159.8 | −24 | −100 | −11 |
| 3r | 470.2 | 161.1 | −32 | −96 | −8 |
Supplementary Material
Figure 4.
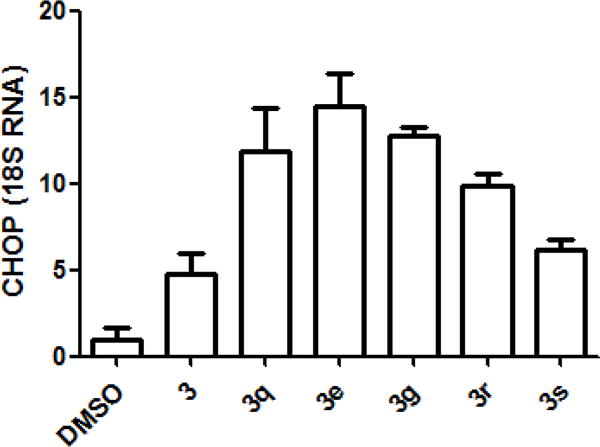
Induction (fold increase) of CHOP mRNA by selected cHAUs at 5μM concentration (normalized to 18S RNA).
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by NCI grant #1RO1CA152312 to B.H. Aktas and NIEHS RO1ES002710 to B.D. Hammock
ABBREVIATIONS
- AA
Acetic Acid
- AHPLC
Analytical high-performance liquid chromatography
- CHAUs
N-cyclohexyl-N′-arylureas
- CHOP
C/EBP homologous protein
- DLR
dual-luciferase eIF2α phosphorylation reporter
- DMF
Dimethylformamide
- DMSO
Dimethyl sulfoxide
- eIF2α
Eukaryotic Initiation Factor 2 alpha
- eIF2B
Eukaryotic Initiation Factor 2 B
- ESI
Electron spray ionization
- GCMS
Gas chromatography mass spectrometer
- GDP
Guanosine-5′-diphosphate
- GTP
Guanosine-5′-triphosphate
- HRI
Heme-regulated inhibitor
- IND
Investigational new drugs
- LC–MS
Liquid chromatography mass spectrometer
- NADPH
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate
- NMP
N-methyl morpholine
- NMR
Nuclear magnetic resonance
- PKR
Protein kinase R
- PERK
PKR-like endoplasmic reticulum kinase
- RP-HPLC
Reverse-phase high-performance liquid chromatography
- SAR
Structure-activity relationship
- SRB
sulforhodamine B
- TFA
Trifluoracetic acid
- uORF
Upstream open reading frame
- UTRs
Untranslated regions
Footnotes
Supporting Information available: NMR and HRMS analysis data of the synthesized compounds is available free of charge via the internet at http://pubs.acs.org.
References
- 1.(a) Krishnamoorthy T, Pavitt GD, Zhang F, Dever TE, Hinnebusch AG. Tight binding of the phosphorylated alpha subunit of initiation factor 2 (eIF2α) to the regulatory subunits of guanine nucleotide exchange factor eIF2B is required for inhibition of translation initiation. Mol Cell Biol. 2001;21:5018–5030. doi: 10.1128/MCB.21.15.5018-5030.2001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (b) Kimball SR, Fabian JR, Pavitt GD, Hinnebusch AG, Jefferson LS. Regulation of guanine nucleotide exchange through phosphorylation of eukaryotic initiation factor eIF2α. Role of the α- and δ-subunits of eIF2b. J Biol Chem. 1998;273:12841–12845. doi: 10.1074/jbc.273.21.12841. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Donnelly N, Gorman AM, Gupta S, Samali A. The eIF2α kinases: their structures and functions. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2013;70:3493–3511. doi: 10.1007/s00018-012-1252-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Proud CG. eIF2 and the control of cell physiology. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2005;16:3–12. doi: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2004.11.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.(a) Shi Y, Taylor SI, Tan SL, Sonenberg N. When translation meets metabolism: multiple links to diabetes. Endocr Rev. 2003;24:91–101. doi: 10.1210/er.2002-0018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (b) Biason-Lauber A, Lang-Muritano M, Vaccaro T, Schoenle EJ. Loss of kinase activity in a patient with Wolcott-Rallison syndrome caused by a novel mutation in the EIF2AK3 gene. Diabetes. 2002;51:2301–2305. doi: 10.2337/diabetes.51.7.2301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.(a) Chen JJ. Regulation of protein synthesis by the heme-regulated eIF2α kinase: relevance to anemias. Blood. 2007;109:2693–2699. doi: 10.1182/blood-2006-08-041830. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (b) Chen JJ. Heme-regulated eIF2α Kinase. In: Sonenberg N, Hershey JWB, Mathews MB, editors. Translational Control of Gene Expression. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press; New York: 2000. pp. 529–546. [Google Scholar]; (c) Han AP, Fleming MD, Chen JJ. Heme-regulated eIF2α kinase modifies the phenotypic severity of murine models of erythropoietic protoporphyria and β-thalassemia. J Clin Invest. 2005;115:1562–1570. doi: 10.1172/JCI24141. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.(a) Wang L, Popko B, Roos RP. An enhanced integrated stress response ameliorates mutant SOD1-induced ALS. Hum Mol Genet. 2014;23:2629–2638. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddt658. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (b) Kim HJ, Raphael AR, LaDow ES, McGurk L, Weber RA, Trojanowski JQ, Lee VM, Finkbeiner S, Gitler AD, Bonini NM. Therapeutic modulation of eIF2α phosphorylation rescues TDP-43 toxicity in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis disease models. Nat Genet. 2014;46:152–160. doi: 10.1038/ng.2853. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (c) Couturier J, Page G, Morel M, Gontier C, Claude J, Pontcharraud R, Fauconneau B, Paccalin M. Inhibition of double-stranded RNA-dependent protein kinase strongly decreases cytokine production and release in peripheral blood mononuclear cells from patients with Alzheimer’s disease. J Alzheimer’s Dis. 2010;21:1217–1231. doi: 10.3233/jad-2010-100258. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (d) Donze O, Jagus R, Koromilas AE, Hershey JW, Sonenberg N. Abrogation of translation initiation factor eIF-2 phosphorylation causes malignant transformation of NIH 3T3 cells. EMBO J. 1995;14:3828–3834. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1995.tb00052.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.(a) Aktas BH, Qiao Y, Ozdelen E, Schubert R, Sevinc S, Harbinski F, Grubissich L, Singer S, Halperin JA. Small-Molecule targeting of translation initiation for cancer therapy. Oncotarget. 2013;4:1606–1617. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.1186. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (b) Aktas BH, Bordelois P, Peker S, Merajver S, Halperin JA. Depletion of eIF2·GTP·Met-tRNAi translation initiation complex up-regulates BRCA1 expression in vitro and in vivo. Oncotarget. 2015;6:6902–6914. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.3125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.(a) Sidrauski C, McGeachy AM, Ingolia NT, Walter P. The small molecule ISRIB reverses the effects of eIF2α phosphorylation on translation and stress granule assembly. eLife. 2015;4 doi: 10.7554/eLife.05033. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (b) Suragani RN, Zachariah RS, Velazquez JG, Liu S, Sun CW, Townes TM, Chen JJ. Heme-regulated eIF2α kinase activated Atf4 signaling pathway in oxidative stress and erythropoiesis. Blood. 2012;119:5276–5284. doi: 10.1182/blood-2011-10-388132. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (c) Tenkerian C, Krishnamoorthy J, Mounir Z, Kazimierczak U, Khoutorsky A, Staschke KA, Kristof AS, Wang S, Hatzoglou M, Koromilas AE. mTORC2 Balances AKT Activation and eIF2α Serine 51 Phosphorylation to Promote Survival under Stress. Mol Cancer Res. 2015;13:1377–1388. doi: 10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-15-0184-T. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Chen T, Takrouri K, Hee-Hwang S, Rana S, Yefidoff-Freedman R, Halperin J, Natarajan A, Morisseau C, Hammock B, Chorev M, Aktas BH. Explorations of substituted urea functionality for the discovery of new activators of the heme-regulated inhibitor kinase. J Med Chem. 2013;56:9457–9470. doi: 10.1021/jm400793v. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Hwang SH, Tsai HJ, Liu JY, Morisseau C, Hammock BD. Orally bioavailable potent soluble epoxide hydrolase inhibitors. J Med Chem. 2007;50:3825–3840. doi: 10.1021/jm070270t. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.(a) Hua Z, Bregman H, Buchanan JL, Chakka N, Guzman-Perez A, Gunaydin H, Huang X, Gu Y, Berry V, Liu J, Teffera Y, Huang L, Egge B, Emkey R, Mullady EL, Schneider S, Andrews PS, Acquaviva L, Dovey J, Mishra A, Newcomb J, Saffran D, Serafino R, Strathdee CA, Turci SM, Stanton M, Wilson C, Dimauro EF. Development of novel dual binders as potent, selective, and orally bioavailable tankyrase inhibitors. J Med Chem. 2013;56:10003–10015. doi: 10.1021/jm401317z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (b) Hwang SH, Wecksler AT, Zhang G, Morisseau C, Nguyen LV, Fu SH, Hammock BD. Synthesis and biological evaluation of sorafenib- and regorafenib-like sEH inhibitors. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2013;23:3732–3737. doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2013.05.011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Zhang Y, Anderson M, Weisman JL, Lu M, Choy CJ, Boyd VA, Price J, Sigal M, Clark J, Connelly M, Zhu F, Guiguemde WA, Jeffries C, Yang L, Lemoff A, Liou AP, Webb TR, Derisi JL, Guy RK. Evaluation of Diarylureas for Activity Against Plasmodium falciparum. ACS Med Chem Lett. 2010;1:460–465. doi: 10.1021/ml100083c. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Zhang L, Xia W, Wang B, Luo Y, Lu W. Convenient Synthesis of Sorafenib and Its Derivatives. Synth Commun. 2011;41:3140–3146. [Google Scholar]
- 14.Lemieux M, Popovici-Muller J, Travins J, Cai Z, Cui D, Zhou D. US 20130190249 A1. Oxopyrrolidine- heterocycles as isocitrate dehydrogenase 1 inhibitors and their preparation, therapeutically active compositions and their methods of use. 2013
- 15.(a) Ziegeler G, Ming J, Koseki JC, Sevinc S, Chen T, Ergun S, Qin X, Aktas BH. Embryonic lethal abnormal vision-like HuR-dependent mRNA stability regulates post-transcriptional expression of cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p27Kip1. J Biol Chem. 2010;285:15408–15419. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.113365. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (b) Chen T, Ozel D, Qiao Y, Harbinski F, Chen L, Denoyelle S, He X, Zvereva N, Supko JG, Chorev M, Halperin JA, Aktas BH. Chemical genetics identify eIF2α kinase heme-regulated inhibitor as an anticancer target. Nat Chem Biol. 2011;7:610–616. doi: 10.1038/nchembio.613. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Aktas H, Fluckiger R, Acosta JA, Savage JM, Palakurthi SS, Halperin JA. Depletion of intracellular Ca2+ stores, phosphorylation of eIF2α, and sustained inhibition of translation initiation mediate the anticancer effects of clotrimazole. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1998;95:8280–8285. doi: 10.1073/pnas.95.14.8280. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Bai H, Chen T, Ming J, Sun H, Cao P, Fusco DN, Chung RT, Chorev M, Jin Q, Aktas BH. Dual activators of protein kinase R (PKR) and protein kinase R-like kinase PERK identify common and divergent catalytic targets. ChemBioChem. 2013;14:1255–1262. doi: 10.1002/cbic.201300177. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Denoyelle S, Chen T, Chen L, Wang Y, Klosi E, Halperin JA, Aktas BH, Chorev M. In vitro inhibition of translation initiation by N,N′-diarylureas–potential anti-cancer agents. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2012;22:402–409. doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2011.10.126. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Aktas H, Halperin JA. Translational regulation of gene expression by omega-3 fatty acids. The Journal of nutrition. 2004;134(9):2487S–2491S. doi: 10.1093/jn/134.9.2487S. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Palakurthi SS, Fluckiger R, Aktas H, Changolkar AK, Shahsafaei A, Harneit S, Kilic E, Halperin JA. Inhibition of translation initiation mediates the anticancer effect of the n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acid eicosapentaenoic acid. Cancer Res. 2000;60:2919–2925. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Gelev V, Aktas H, Marintchev A, Ito T, Frueh D, Hemond M, Rovnyak D, Debus M, Hyberts S, Usheva A, Halperin J, Wagner G. Mapping of the auto-inhibitory interactions of protein kinase R by nuclear magnetic resonance. J Mol Biol. 2006;364:352–363. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2006.08.077. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Aktas H, Cai H, Cooper GM. Ras links growth factor signaling to the cell cycle machinery via regulation of cyclin D1 and the Cdk inhibitor p27KIP1. Mol Cell Biol. 1997;17:3850–3857. doi: 10.1128/mcb.17.7.3850. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Palakurthi SS, Fluckiger R, Aktas H, Changolkar AK, Shahsafaei A, Harneit S, Kilic E, Halperin JA. Inhibition of translation initiation mediates the anticancer effect of the n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acid eicosapentaenoic acid. Cancer Res. 2000;60:2919–2925. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.


