Abstract
The high mobility group I (HMG) box is proposed to mediate DNA binding in a novel group of transcription-regulating proteins. Two of these, the proteins encoded by the T cell-specific TCF-1 and the mammalian sex-determining gene SRY, carry a single HMG box with specificity for the heptamer motif A/T A/T C A A A G. We have now analysed the mode of interaction of the HMG boxes of TCF-1 and SRY with this motif. Methylation interference footprinting revealed that both HMG boxes contacted adenines on both strands in the minor groove, whereas no major groove guanine contacts were discerned. Diethylpyrocarbonate (DEPC) carbethoxylation interference footprinting of TCF-1 indicated the absence of major groove contacts on positions 5, 6 and 7 of the motif. Carbethoxylation interference was observed, however, on positions 2, 3 and 4 and to a lesser extent on position 1 in the major groove. Combined T----C and A----I substitution, which changes the surface of the major groove but leaves the minor groove intact, did not interfere with sequence-specific binding by TCF-1 and SRY. These observations indicate that recognition of the heptamer motif by the HMG boxes of the distantly related TCF-1 and SRY proteins predominantly occurs through nucleotide contacts in the minor groove.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Affolter M., Percival-Smith A., Müller M., Leupin W., Gehring W. J. DNA binding properties of the purified Antennapedia homeodomain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jun;87(11):4093–4097. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.11.4093. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castrop J., van Norren K., Clevers H. A gene family of HMG-box transcription factors with homology to TCF-1. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Feb 11;20(3):611–611. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.3.611. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans R. M., Hollenberg S. M. Zinc fingers: gilt by association. Cell. 1988 Jan 15;52(1):1–3. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90522-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garnier J., Osguthorpe D. J., Robson B. Analysis of the accuracy and implications of simple methods for predicting the secondary structure of globular proteins. J Mol Biol. 1978 Mar 25;120(1):97–120. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90297-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giese K., Amsterdam A., Grosschedl R. DNA-binding properties of the HMG domain of the lymphoid-specific transcriptional regulator LEF-1. Genes Dev. 1991 Dec;5(12B):2567–2578. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.12b.2567. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gubbay J., Collignon J., Koopman P., Capel B., Economou A., Münsterberg A., Vivian N., Goodfellow P., Lovell-Badge R. A gene mapping to the sex-determining region of the mouse Y chromosome is a member of a novel family of embryonically expressed genes. Nature. 1990 Jul 19;346(6281):245–250. doi: 10.1038/346245a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harley V. R., Jackson D. I., Hextall P. J., Hawkins J. R., Berkovitz G. D., Sockanathan S., Lovell-Badge R., Goodfellow P. N. DNA binding activity of recombinant SRY from normal males and XY females. Science. 1992 Jan 24;255(5043):453–456. doi: 10.1126/science.1734522. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herr W. Diethyl pyrocarbonate: a chemical probe for secondary structure in negatively supercoiled DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(23):8009–8013. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.23.8009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jantzen H. M., Admon A., Bell S. P., Tjian R. Nucleolar transcription factor hUBF contains a DNA-binding motif with homology to HMG proteins. Nature. 1990 Apr 26;344(6269):830–836. doi: 10.1038/344830a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly M., Burke J., Smith M., Klar A., Beach D. Four mating-type genes control sexual differentiation in the fission yeast. EMBO J. 1988 May;7(5):1537–1547. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02973.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kissinger C. R., Liu B. S., Martin-Blanco E., Kornberg T. B., Pabo C. O. Crystal structure of an engrailed homeodomain-DNA complex at 2.8 A resolution: a framework for understanding homeodomain-DNA interactions. Cell. 1990 Nov 2;63(3):579–590. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90453-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landschulz W. H., Johnson P. F., McKnight S. L. The leucine zipper: a hypothetical structure common to a new class of DNA binding proteins. Science. 1988 Jun 24;240(4860):1759–1764. doi: 10.1126/science.3289117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee D. K., Horikoshi M., Roeder R. G. Interaction of TFIID in the minor groove of the TATA element. Cell. 1991 Dec 20;67(6):1241–1250. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90300-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leonard N. J., McDonald J. J., Henderson R. E., Reichmann M. E. Reaction of diethyl pyrocarbonate with nucleic acid components. Adenosine. Biochemistry. 1971 Aug 31;10(18):3335–3342. doi: 10.1021/bi00794a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine M., Hoey T. Homeobox proteins as sequence-specific transcription factors. Cell. 1988 Nov 18;55(4):537–540. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90209-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
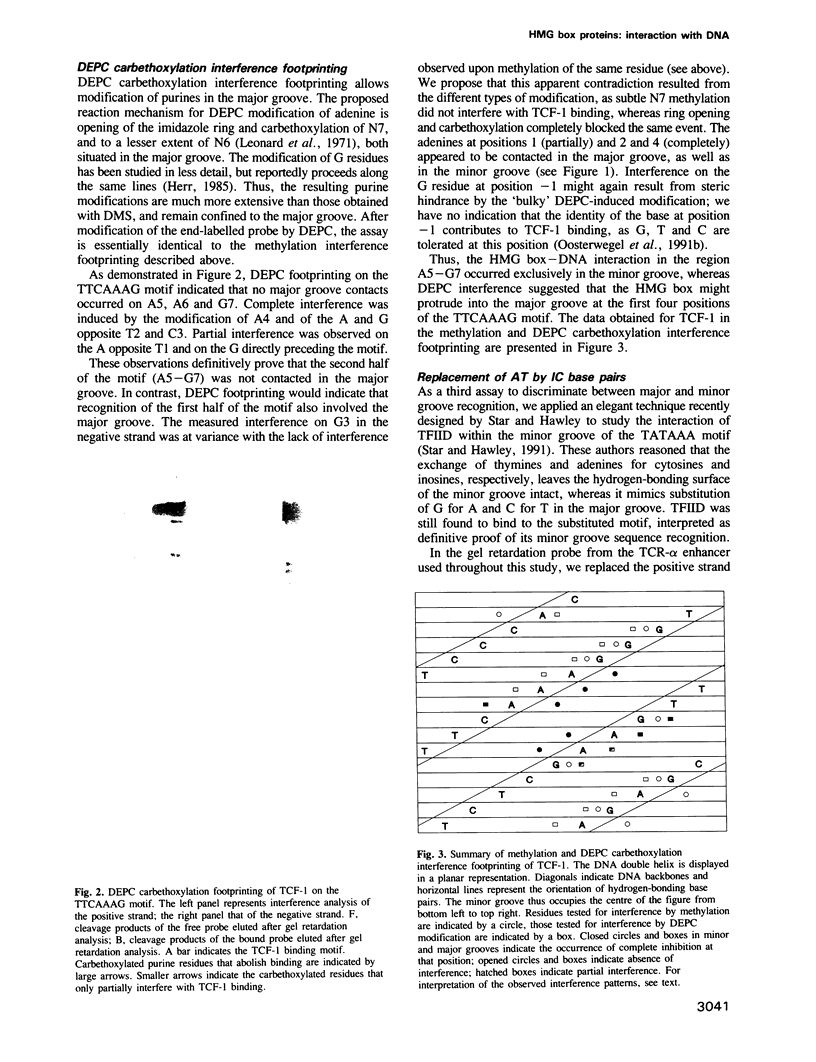
- Murre C., McCaw P. S., Baltimore D. A new DNA binding and dimerization motif in immunoglobulin enhancer binding, daughterless, MyoD, and myc proteins. Cell. 1989 Mar 10;56(5):777–783. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90682-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nash H. A., Granston A. E. Similarity between the DNA-binding domains of IHF protein and TFIID protein. Cell. 1991 Dec 20;67(6):1037–1038. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90280-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nasrin N., Buggs C., Kong X. F., Carnazza J., Goebl M., Alexander-Bridges M. DNA-binding properties of the product of the testis-determining gene and a related protein. Nature. 1991 Nov 28;354(6351):317–320. doi: 10.1038/354317a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oosterwegel M. A., van de Wetering M. L., Holstege F. C., Prosser H. M., Owen M. J., Clevers H. C. TCF-1, a T cell-specific transcription factor of the HMG box family, interacts with sequence motifs in the TCR beta and TCR delta enhancers. Int Immunol. 1991 Nov;3(11):1189–1192. doi: 10.1093/intimm/3.11.1189. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oosterwegel M., van de Wetering M., Dooijes D., Klomp L., Winoto A., Georgopoulos K., Meijlink F., Clevers H. Cloning of murine TCF-1, a T cell-specific transcription factor interacting with functional motifs in the CD3-epsilon and T cell receptor alpha enhancers. J Exp Med. 1991 May 1;173(5):1133–1142. doi: 10.1084/jem.173.5.1133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parisi M. A., Clayton D. A. Similarity of human mitochondrial transcription factor 1 to high mobility group proteins. Science. 1991 May 17;252(5008):965–969. doi: 10.1126/science.2035027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seeman N. C., Rosenberg J. M., Rich A. Sequence-specific recognition of double helical nucleic acids by proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Mar;73(3):804–808. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.3.804. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siebenlist U., Gilbert W. Contacts between Escherichia coli RNA polymerase and an early promoter of phage T7. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jan;77(1):122–126. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.1.122. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sinclair A. H., Berta P., Palmer M. S., Hawkins J. R., Griffiths B. L., Smith M. J., Foster J. W., Frischauf A. M., Lovell-Badge R., Goodfellow P. N. A gene from the human sex-determining region encodes a protein with homology to a conserved DNA-binding motif. Nature. 1990 Jul 19;346(6281):240–244. doi: 10.1038/346240a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staben C., Yanofsky C. Neurospora crassa a mating-type region. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jul;87(13):4917–4921. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.13.4917. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starr D. B., Hawley D. K. TFIID binds in the minor groove of the TATA box. Cell. 1991 Dec 20;67(6):1231–1240. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90299-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takanami M. RNA polymerase nascent product analysis. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):497–499. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65058-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka I., Appelt K., Dijk J., White S. W., Wilson K. S. 3-A resolution structure of a protein with histone-like properties in prokaryotes. Nature. 1984 Aug 2;310(5976):376–381. doi: 10.1038/310376a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Travis A., Amsterdam A., Belanger C., Grosschedl R. LEF-1, a gene encoding a lymphoid-specific protein with an HMG domain, regulates T-cell receptor alpha enhancer function [corrected]. Genes Dev. 1991 May;5(5):880–894. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.5.880. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waterman M. L., Fischer W. H., Jones K. A. A thymus-specific member of the HMG protein family regulates the human T cell receptor C alpha enhancer. Genes Dev. 1991 Apr;5(4):656–669. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.4.656. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang C. C., Nash H. A. The interaction of E. coli IHF protein with its specific binding sites. Cell. 1989 Jun 2;57(5):869–880. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90801-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van de Wetering M., Oosterwegel M., Dooijes D., Clevers H. Identification and cloning of TCF-1, a T lymphocyte-specific transcription factor containing a sequence-specific HMG box. EMBO J. 1991 Jan;10(1):123–132. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07928.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]