Abstract
Phage T4-induced anticodon nuclease triggers cleavage-ligation of the host tRNA(Lys). The enzyme is encoded in latent form by the optional Escherichia coli locus prr and is activated by the product of the phage stp gene. Anticodon nuclease latency is attributed to the masking of the core function prrC by flanking elements homologous with type I restriction-modification genes (prrA-hsdM and prrD-hsdR). Activation of anticodon nuclease in extracts of uninfected prr+ cells required synthetic Stp, ATP and GTP and appeared to depend on endogenous DNA. Stp could be substituted by a small, heat-stable E. coli factor, hinting that anticodon nuclease may be mobilized in cellular situations other than T4 infection. Hsd antibodies recognized the anticodon nuclease holoenzyme but not the prrC-encoded core. Taken together, these data indicate that Hsd proteins partake in the latent ACNase complex where they mask the core factor PrrC. Presumably, this masking interaction is disrupted by Stp in conjunction with Hsd ligands. The Hsd-PrrC interaction may signify coupling and mutual enhancement of two prokaryotic restriction systems operating at the DNA and tRNA levels.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amitsur M., Levitz R., Kaufmann G. Bacteriophage T4 anticodon nuclease, polynucleotide kinase and RNA ligase reprocess the host lysine tRNA. EMBO J. 1987 Aug;6(8):2499–2503. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02532.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amitsur M., Morad I., Kaufmann G. In vitro reconstitution of anticodon nuclease from components encoded by phage T4 and Escherichia coli CTr5X. EMBO J. 1989 Aug;8(8):2411–2415. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08371.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chambliss G. H., Henkin T. M., Leventhal J. M. Bacterial in vitro protein-synthesizing systems. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:598–605. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01040-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chapman D., Morad I., Kaufmann G., Gait M. J., Jorissen L., Snyder L. Nucleotide and deduced amino acid sequence of stp: the bacteriophage T4 anticodon nuclease gene. J Mol Biol. 1988 Jan 20;199(2):373–377. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90320-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- David M., Borasio G. D., Kaufmann G. Bacteriophage T4-induced anticodon-loop nuclease detected in a host strain restrictive to RNA ligase mutants. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Dec;79(23):7097–7101. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.23.7097. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Depew R. E., Cozzarelli N. R. Genetics and physiology of bacteriophage T4 3'-phosphatase: evidence for involvement of the enzyme in T4 DNA metabolism. J Virol. 1974 Apr;13(4):888–897. doi: 10.1128/jvi.13.4.888-897.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jabbar M. A., Snyder L. Genetic and physiological studies of an Escherichia coli locus that restricts polynucleotide kinase- and RNA ligase-deficient mutants of bacteriophage T4. J Virol. 1984 Aug;51(2):522–529. doi: 10.1128/jvi.51.2.522-529.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufmann G., David M., Borasio G. D., Teichmann A., Paz A., Amitsur M. Phage and host genetic determinants of the specific anticodon loop cleavages in bacteriophage T4-infected Escherichia coli CTr5X. J Mol Biol. 1986 Mar 5;188(1):15–22. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90476-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
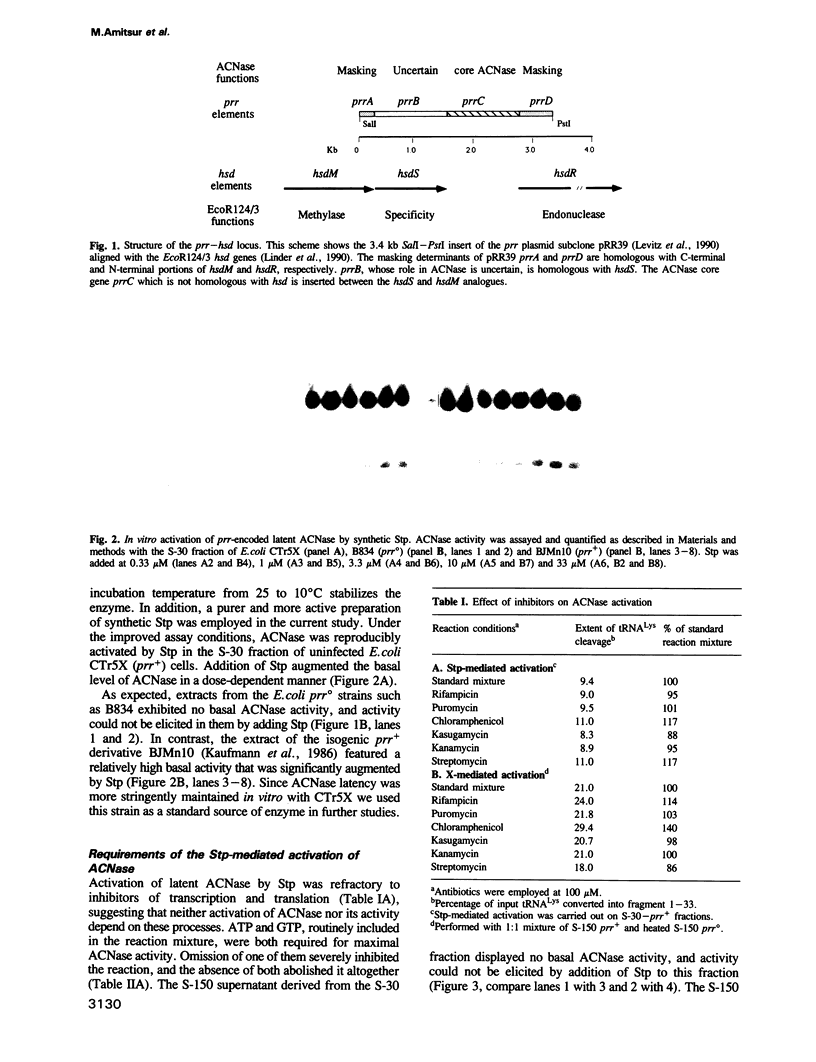
- Levitz R., Chapman D., Amitsur M., Green R., Snyder L., Kaufmann G. The optional E. coli prr locus encodes a latent form of phage T4-induced anticodon nuclease. EMBO J. 1990 May;9(5):1383–1389. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08253.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linder P., Doelz R., Gubler M., Bickle T. A. An anticodon nuclease gene inserted into a hsd region encoding a type I DNA restriction system. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Dec 11;18(23):7170–7170. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.23.7170. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raleigh E. A., Trimarchi R., Revel H. Genetic and physical mapping of the mcrA (rglA) and mcrB (rglB) loci of Escherichia coli K-12. Genetics. 1989 Jun;122(2):279–296. doi: 10.1093/genetics/122.2.279. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Runnels J. M., Soltis D., Hey T., Snyder L. Genetic and physiological studies of the role of the RNA ligase of bacteriophage T4. J Mol Biol. 1982 Jan 15;154(2):273–286. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90064-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sirotkin K., Cooley W., Runnels J., Snyder L. R. A role in true-late gene expression for the T4 bacteriophage 5' polynucleotide kinase 3' phosphatase. J Mol Biol. 1978 Aug 5;123(2):221–233. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90322-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabor S., Richardson C. C. A bacteriophage T7 RNA polymerase/promoter system for controlled exclusive expression of specific genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(4):1074–1078. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.4.1074. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]