Abstract
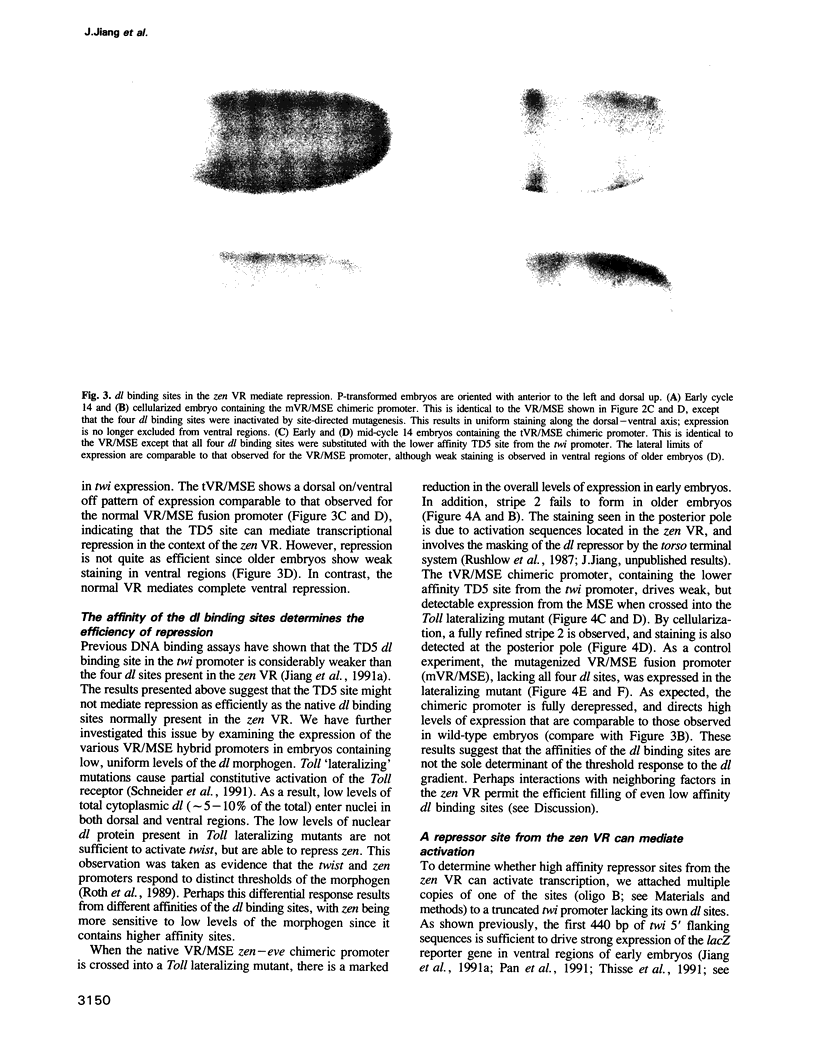
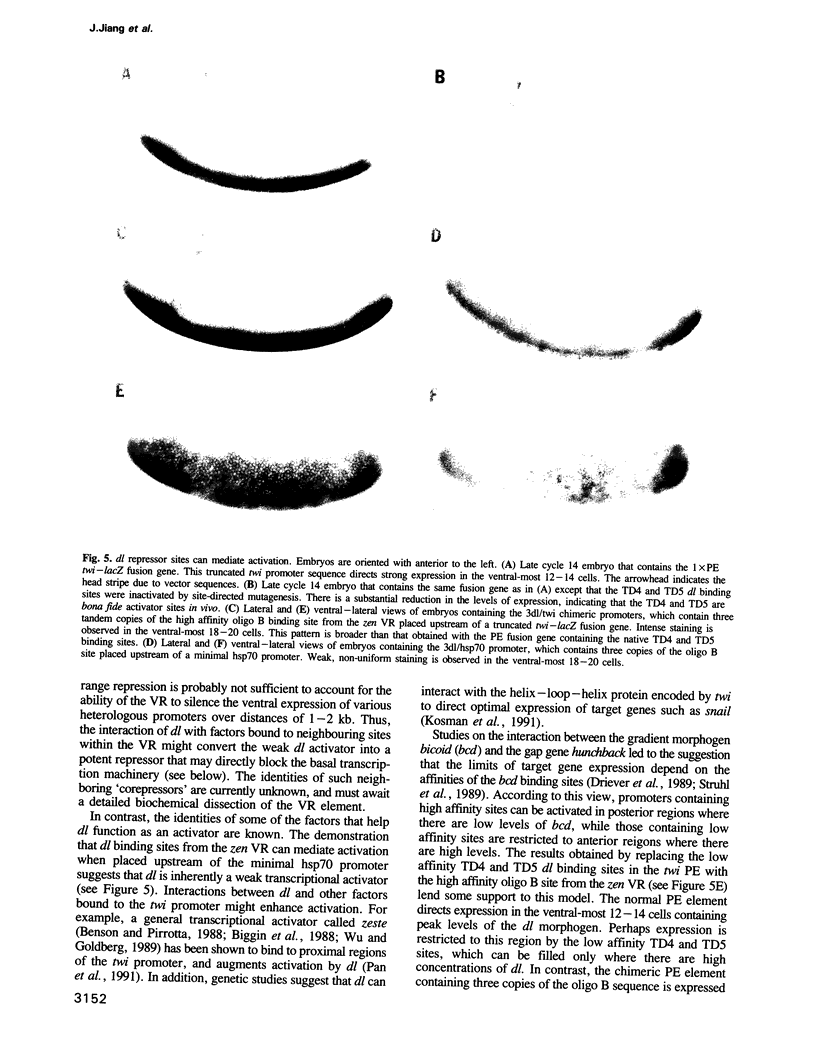
The dorsal (dl) morphogen gradient is responsible for initiating the differentiation of the mesoderm, neuroectoderm and dorsal ectoderm in the Drosophila embryo. dl encodes a sequence-specific DNA binding protein that belongs to the Rel family of transcription factors. Previous studies have shown that dl activates the mesoderm determinant twist (twi); here we use a combination of site-directed mutagenesis and P-transformation assays to demonstrate that it also functions as a direct transcriptional repressor of a second target gene, zerknüllt (zen). By exchanging dl binding sites between the promoters we show that activator sites from twi can mediate repression when placed in the context of the zen promoter, and that repressor sites from zen can mediate activation in the context of the twi promoter. This represents the first demonstration that common binding sites for any DNA binding protein can mediate both activation and repression in a developing embryo. Evidence is also presented that the affinities of dl binding sites are important for the efficiency of repression, but are not the sole determinants of the threshold response to the dl gradient.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Benson M., Pirrotta V. The Drosophila zeste protein binds cooperatively to sites in many gene regulatory regions: implications for transvection and gene regulation. EMBO J. 1988 Dec 1;7(12):3907–3915. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03277.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biggin M. D., Bickel S., Benson M., Pirrotta V., Tjian R. Zeste encodes a sequence-specific transcription factor that activates the Ultrabithorax promoter in vitro. Cell. 1988 Jun 3;53(5):713–722. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90089-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doyle H. J., Kraut R., Levine M. Spatial regulation of zerknüllt: a dorsal-ventral patterning gene in Drosophila. Genes Dev. 1989 Oct;3(10):1518–1533. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.10.1518. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Driever W., Nüsslein-Volhard C. The bicoid protein is a positive regulator of hunchback transcription in the early Drosophila embryo. Nature. 1989 Jan 12;337(6203):138–143. doi: 10.1038/337138a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh S., Gifford A. M., Riviere L. R., Tempst P., Nolan G. P., Baltimore D. Cloning of the p50 DNA binding subunit of NF-kappa B: homology to rel and dorsal. Cell. 1990 Sep 7;62(5):1019–1029. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90276-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Govind S., Steward R. Dorsoventral pattern formation in Drosophila: signal transduction and nuclear targeting. Trends Genet. 1991 Apr;7(4):119–125. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(91)90456-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ip Y. T., Kraut R., Levine M., Rushlow C. A. The dorsal morphogen is a sequence-specific DNA-binding protein that interacts with a long-range repression element in Drosophila. Cell. 1991 Jan 25;64(2):439–446. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90651-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jiang J., Hoey T., Levine M. Autoregulation of a segmentation gene in Drosophila: combinatorial interaction of the even-skipped homeo box protein with a distal enhancer element. Genes Dev. 1991 Feb;5(2):265–277. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.2.265. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jiang J., Kosman D., Ip Y. T., Levine M. The dorsal morphogen gradient regulates the mesoderm determinant twist in early Drosophila embryos. Genes Dev. 1991 Oct;5(10):1881–1891. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.10.1881. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kieran M., Blank V., Logeat F., Vandekerckhove J., Lottspeich F., Le Bail O., Urban M. B., Kourilsky P., Baeuerle P. A., Israël A. The DNA binding subunit of NF-kappa B is identical to factor KBF1 and homologous to the rel oncogene product. Cell. 1990 Sep 7;62(5):1007–1018. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90275-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kosman D., Ip Y. T., Levine M., Arora K. Establishment of the mesoderm-neuroectoderm boundary in the Drosophila embryo. Science. 1991 Oct 4;254(5028):118–122. doi: 10.1126/science.1925551. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine M., Manley J. L. Transcriptional repression of eukaryotic promoters. Cell. 1989 Nov 3;59(3):405–408. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90024-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pan D. J., Huang J. D., Courey A. J. Functional analysis of the Drosophila twist promoter reveals a dorsal-binding ventral activator region. Genes Dev. 1991 Oct;5(10):1892–1901. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.10.1892. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth S., Stein D., Nüsslein-Volhard C. A gradient of nuclear localization of the dorsal protein determines dorsoventral pattern in the Drosophila embryo. Cell. 1989 Dec 22;59(6):1189–1202. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90774-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rushlow C., Frasch M., Doyle H., Levine M. Maternal regulation of zerknüllt: a homoeobox gene controlling differentiation of dorsal tissues in Drosophila. Nature. 1987 Dec 10;330(6148):583–586. doi: 10.1038/330583a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider D. S., Hudson K. L., Lin T. Y., Anderson K. V. Dominant and recessive mutations define functional domains of Toll, a transmembrane protein required for dorsal-ventral polarity in the Drosophila embryo. Genes Dev. 1991 May;5(5):797–807. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.5.797. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Small S., Kraut R., Hoey T., Warrior R., Levine M. Transcriptional regulation of a pair-rule stripe in Drosophila. Genes Dev. 1991 May;5(5):827–839. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.5.827. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- St Johnston D., Nüsslein-Volhard C. The origin of pattern and polarity in the Drosophila embryo. Cell. 1992 Jan 24;68(2):201–219. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90466-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- St Johnston R. D., Gelbart W. M. Decapentaplegic transcripts are localized along the dorsal-ventral axis of the Drosophila embryo. EMBO J. 1987 Sep;6(9):2785–2791. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02574.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanojevic D., Small S., Levine M. Regulation of a segmentation stripe by overlapping activators and repressors in the Drosophila embryo. Science. 1991 Nov 29;254(5036):1385–1387. doi: 10.1126/science.1683715. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steward R. Dorsal, an embryonic polarity gene in Drosophila, is homologous to the vertebrate proto-oncogene, c-rel. Science. 1987 Oct 30;238(4827):692–694. doi: 10.1126/science.3118464. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Struhl G., Struhl K., Macdonald P. M. The gradient morphogen bicoid is a concentration-dependent transcriptional activator. Cell. 1989 Jun 30;57(7):1259–1273. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90062-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thisse B., Stoetzel C., Gorostiza-Thisse C., Perrin-Schmitt F. Sequence of the twist gene and nuclear localization of its protein in endomesodermal cells of early Drosophila embryos. EMBO J. 1988 Jul;7(7):2175–2183. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03056.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thisse C., Perrin-Schmitt F., Stoetzel C., Thisse B. Sequence-specific transactivation of the Drosophila twist gene by the dorsal gene product. Cell. 1991 Jun 28;65(7):1191–1201. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90014-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thummel C. S., Boulet A. M., Lipshitz H. D. Vectors for Drosophila P-element-mediated transformation and tissue culture transfection. Gene. 1988 Dec 30;74(2):445–456. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90177-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu C. T., Goldberg M. L. The Drosophila zeste gene and transvection. Trends Genet. 1989 Jun;5(6):189–194. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(89)90074-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]








