Abstract
In the fifteen years following the discovery of single-walled carbon nanotube (SWCNT) photoluminescence, investigators have made significant progress in their understanding of the phenomenon and towards the development of applications. The intrinsic potential of semiconducting carbon nanotubes – a family of bright, photostable near infrared (NIR) fluorophores (900–2100 nm) with tunable properties, has motivated their use as optical probes and sensors. In this perspective, we highlight the advances made in the synthesis, processing, modification, separation, and metrology of carbon nanotubes in the context of applications of their photoluminescence.
Single-walled carbon nanotubes are hollow cylinders of graphene, with diameters of approximately 1 nm and lengths that typically range from ~ 10 nm to 10 μm1. The hexagonal graphene lattice, composed entirely of sp2-bonded carbon, can be rolled at varying angles to create seamless cylinders representing different nanotube structures2. Each distinct nanotube structure, or helicity, is uniquely identifiable by a pair of (n,m) integers, known as its chiral indices. Additionally, nanotubes exist as enantionmers, with (n,m) and (m,n) corresponding to the same chirality but different handedness3.
The electronic bandgap between valence and conducting bands in the density of states determines whether a SWCNT is metallic (0 meV bandgap), semi-metallic (<100 meV bandgap) or semi-conducting (> 500 meV)3. One-third of nanotube chiralities are metallic1,4. As quasi-one dimensional nanomaterials, semi-conducting SWCNTs contain sharp peaks known as van Hove singularities in their density of states, and the optical properties of SWCNTs are determined by these singularities. For semi-conducting nanotubes, photoexcitation at distinct absorption transitions (Eii, i = 1 to 4) can result in intrinsic bandgap photoluminescence which occurs only at the lowest energy transition (E11) at the band edge, in the near-infrared spectral region.
Since the original observation of near-infrared emission from carbon nanotubes5, investigations of nanotube photoluminescence have spanned several areas: 1) understanding and enhancing carbon nanotube photoluminescence, 2) the development of experimental tools to optically characterize the NIR emission of carbon nanotubes at the ensemble and single-molecule level, and 3) the application of the imaging and sensing capabilities of nanotubes in increasingly complex environments. Regarding their synthesis, a number of techniques have been developed to increase the yield and purity of single-walled carbon nanotubes6. Relatively pristine, defect-free nanotubes, required to observe photoluminescence, were synthesized via several methods, including the high-pressure carbon monoxide (HiPco) process7. Most methods generate a mixture of nanotube chiralities that must be separated to obtain a structurally pure sample, although methods, such as the CoMoCAT process, have been developed to narrow the distribution of chiralities synthesized8. An alternative ‘bottom up’ approach proposes a small molecule structural template for synthesizing nanotubes of a particular chirality9. Recently, single chirality growth with over 90% specificity10, and elongation of single chirality nanotube precursors to several hundred nanometers in length11 was accomplished. As work on increasing the yield and scalability of these synthesis processes continues, pre-dispersed carbon nanotubes of a specific chirality may be available for a variety of research applications.
Semiconducting carbon nanotubes quench upon contact with metallic nanotubes5, necessitating methods to individually disperse SWCNT mixtures in solutions or composites. However, the hydrophobic graphitic surface of as-produced carbon nanotubes renders them insoluble in water, while strong inter-tube van der Waals interactions cause the formation of bundles/aggregates12. Investigations into the individual dispersal of SWCNTs to result in luminescent suspensions found that certain dispersants facilitate aqueous suspension, including charged and non-ionic surfactants13. To allow for stable suspensions upon removal of unbound dispersants, molecules with greater binding affinity were needed. Studies found dispersants including lipids, polymers, and biomolecules, including DNA and proteins, which could stably suspend SWCNTs. Modular materials, such as polyethylene glycol-lipid conjugates14, derivatizable polymer libraries15, 16, and single-stranded DNA17, have been used to construct numerous SWCNT complexes for imaging and sensor applications.
The optical properties of carbon nanotubes depend on their (n,m) chirality (species). Spectrofluorimetric measurements on individual SWCNT suspensions initially identified over 33 semi-conducting nanotube chiralities18, and an empirical model followed which predicted optical transitions for over 100 different chiralities19. For electronic applications in particular, separating metallic and semi-conducting nanotubes is critical20, and biological imaging studies would benefit from highly purified photoluminescent samples with well-defined optical absorption and emission bands21. Early successes, including the separation of metallic and semi-conducting nanotubes22, and concomitant length and diameter separation23, suggested that the sorting problem would be fundamentally solvable. Promising solutions for obtaining a high yield of dispersed chirality-sorted nanotube samples include separation by density gradient ultracentrifugation24, DNA recognition of specific chiralities25, gel chromatography26, and aqueous two phase systems (23), in addition to intrinsically selective dispersions27. Nanotube samples enriched in a few specific chiralities, along with highly pure metallic and semiconducting preparations, are now commercially available.
Photoluminescence from semi-conducting nanotubes is due to the generation and recombination of excitons28. During their short excited-state lifetime29, mobile excitons sample thousands of atomic sites to efficiently sense their local environment30. Defects in the sp2 carbon surface and certain small molecule adsorbents can provide a non-radiative relaxation pathway which directly causes exciton quenching31. The initial estimates of nanotube quantum yield in solution were relatively low (<0.1 %) and heterogeneous32. However, subsequent single molecule studies33 showed that nanotube emission is significantly brighter in air34. The addition of reducing agents to nanotubes in solution35, removal of water from the internal volume of a nanotube36, reduction of oxygen in contact with the nanotube surface37, and controlled endohedral filling of the nanotube38 have significantly increased the experimentally observed nanotube quantum yield.
Chemical modifications of the nanotube surface can controllably modulate their optical properties. Covalent doping of the nanotube surface with a low concentration of oxygen atoms resulted in emission at longer wavelengths by up to hundreds of nanometers39. An immediate benefit of such a red-shift is the ability to excite the nanotube at its E11 peak and detect emission at the shifted E11 peak. In live cells, the increase in detected signal and decrease in autofluorescence led to a 20-fold increase in image contrast, when compared with the pristine nanotubes39. The controlled introduction of sp3 defects into the sp2 nanotube lattice can create a new optically allowed defect state, from which nanotube emission is red-shifted and can be over 28-fold brighter40. By tailoring the surface functional group used to introduce the defect state, nanotube emission from a specific chirality is tunable over a shift of ~ 70 nm41. An exciting possibility from these chemical modifications is that the ability to excite each nanotube chirality at both E22 and E11 transitions, combined with the tunability of the E11* emission, nearly triples the number of available spectrally distinct NIR imaging probes.
Spectrofluorometric techniques have been developed to characterize nanotube suspensions at both the ensemble and single-nanotube levels. The chiral distribution of photoluminescent carbon nanotubes can be determined by acquiring two-dimensional photoluminescence excitation emission plots18, which can now be acquired in a high-throughput manner42, 43. Single carbon nanotube photoluminescence was first imaged using InGaAs cameras coupled with a fluorescence microscope44. Advanced techniques which combine single-particle tracking with statistical variations in a dilute sample can accurately determine the absorption cross-section45 and length distribution46 of carbon nanotubes in solution, while single nanotube-counting techniques can directly determine molarity47. A recently developed spectral imaging technique, hyperspectral microscopy, can acquire the full spectra from each pixel in an entire field of view – thus allowing the spectral analysis of single nanotubes48. The increasing availability of instruments for the optical characterization and imaging of carbon nanotube emission will expand the abilities of diverse researchers to make contributions to the field.
The exceptional optical properties of nanotube photoluminescence have been employed for a number of sensing and bioimaging applications49, 50. NIR emission from an individual nanotube48 can be detected in cells51. Recently, single nanotube tracking was used in live cells to resolve intracellular fluctuations52, and in tissues to map the composition of extracellular space in the live brain53. As E11 emission lies within the near-infrared window in biological tissue54, nanotubes in whole organisms were detectable in a live invertebrate55, and then a live mammal14. Advancements in optical techniques have now led to surgical guidance56 and through-skull imaging21 in live mice. In parallel, the use of carbon nanotubes as optical sensors57 was extended to the measurement of strain in composites58, multimodal optical sensing in live cells59, and measurements in live plants60. Excitingly, SWCNT optical sensors were also shown to function in live mice for over 400 days61.
Conclusions and Outlook
The use of carbon nanotube photoluminescence for applications in imaging and sensing is motivated by the goal of approaching scientific and technological problems that are currently intractable or extremely difficult. Such problems may be addressed by the unique properties of nanotube photoluminescence, including high photostability, NIR emission range, narrow bandwidths, large Stokes shift, large number of optically separable emission bands, and environmental sensitivity. Applications of SWCNT optical probes will require high quantum yields, homogeneous samples of essentially one chirality, well-defined and narrow length distributions, and the ability to independently choose the dispersant/coating.
The understanding of the photophysics governing the modulation of carbon nanotube emission is critical for the rational design of sensitive and specific sensors. As detection platforms, nanotubes can function as both the recognition and signal transduction element. A general set of rules for predicting the effect of a specific non-covalent functionalization on the optical response of the sensor prototype would be valuable. Similarly, our understanding of how covalent modifications affect the optical response of the nanotube is still preliminary.
For biological applications, a key concern is the potential toxicity of single walled carbon nanotubes. Although it is clear to many researchers that the major sources of carbon nanotube-associated toxicity i.e. metallic catalyst impurities, length, diameter, chemical functionalization, and aggregation state – are completely dependent on how the sample is processed, studies that systematically explore cellular toxicity as a function of these parameters are limited. Investigations that map the range of nanotube parameters with respect to biocompatability will be extremely useful and could preemptively answer questions concerning toxicity in future applications.
The last 15 years of research into single walled carbon nanotube photoluminescence have resulted in notable progress towards applications. A convergence between our conceptual understanding of nanotube photoluminescence and its modulation, the breadth of instruments for optical characterization, and the range of applications currently under development by multiple investigators, suggest greater expansion of the field and convergence with multiple disciplines.
Supplementary Material
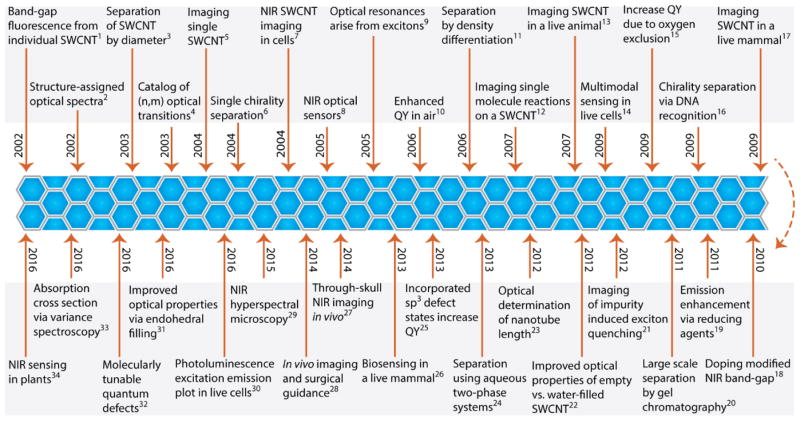
Figure 1.
A timeline of advancements in the measurement, processing, separation, modifications, and applications of photoluminescent single-walled carbon nanotubes. References are listed in the Supplementary Information.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported in part by the NIH New Innovator Award (DP2-HD075698), the Cancer Center Support Grant (P30 CA008748), the Anna Fuller Fund, the Louis V. Gerstner Jr. Young Investigator’s Fund, the Frank A. Howard Scholars Program, the Honorable Tina Brozman Foundation for Ovarian Cancer Research, Cycle for Survival, the Alan and Sandra Gerry Metastasis Research Initiative, Mr. William H. Goodwin and Mrs. Alice Goodwin and the Commonwealth Foundation for Cancer Research, the Experimental Therapeutics Center, the Imaging & Radiation Sciences Program, and the Center for Molecular Imaging and Nanotechnology of Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer (MSKCC). P.V.J was supported by an NIH NCI T-32 fellowship (2T32CA062948-21). D.R. was supported by an American Cancer Society 2013 Roaring Fork Valley Research Fellowship and an RI-INBRA grant (P20GM103430). We acknowledge J. Bartlett for help with manuscript preparation.
References
- 1.Jones DEH. Nature. 1996;381:384. [Google Scholar]
- 2.Iijima S. Nature. 1991;354:56. [Google Scholar]
- 3.Zheng M. Topics in Current Chemistry. 2017 doi: 10.1007/s41061-016-0098-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Naumov AV, Kuznetsov OA, Harutyunyan AR, Green AA, Hersam MC, Resasco DE, Nikolaev PN, Weisman RB. Nano Lett. 2009;9:3203. doi: 10.1021/nl9014342. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.O’Connell MJ, Bachilo SM, Huffman CB, Moore VC, Strano MS, Haroz EH, Rialon KL, Boul PJ, Noon WH, Kittrell C, Ma JP, Hauge RH, Weisman RB, Smalley RE. Science. 2002;297:593. doi: 10.1126/science.1072631. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Prasek J, Drbohlavova J, Chomoucka J, Hubalek J, Jasek O, Adam V, Kizek R. J Mater Chem. 2011;21:15872. [Google Scholar]
- 7.Bronikowski MJ, Willis PA, Colbert DT, Smith KA, Smalley RE. J Vac Sci Technol A. 2001;19:1800. [Google Scholar]
- 8.Bachilo SM, Balzano L, Herrera JE, Pompeo F, Resasco DE, Weisman RB. J Am Chem Soc. 2003;125:11186. doi: 10.1021/ja036622c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Segawa Y, Ito H, Itami K. Nat Rev Mater. 2016;1 [Google Scholar]
- 10.Yang F, Wang X, Zhang DQ, Yang J, Luo D, Xu ZW, Wei JK, Wang JQ, Xu Z, Peng F, Li XM, Li RM, Li YL, Li MH, Bai XD, Ding F, Li Y. Nature. 2014;510:522. doi: 10.1038/nature13434. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Sanchez-Valencia JR, Dienel T, Groning O, Shorubalko I, Mueller A, Jansen M, Amsharov K, Ruffieux P, Fasel R. Nature. 2014;512:61. doi: 10.1038/nature13607. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Huang YY, Terentjev EM. Polymers-Basel. 2012;4:275. [Google Scholar]
- 13.Moore VC, Strano MS, Haroz EH, Hauge RH, Smalley RE, Schmidt J, Talmon Y. Nano Lett. 2003;3:1379. [Google Scholar]
- 14.Welsher K, Liu Z, Sherlock SP, Robinson JT, Chen Z, Daranciang D, Dai H. Nat Nanotechnol. 2009;4:773. doi: 10.1038/nnano.2009.294. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Budhathoki-Uprety J, Jena PV, Roxbury D, Heller DA. J Am Chem Soc. 2014;136:15545. doi: 10.1021/ja505529n. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Zhang JQ, Landry MP, Barone PW, Kim JH, Lin SC, Ulissi ZW, Lin DH, Mu B, Boghossian AA, Hilmer AJ, Rwei A, Hinckley AC, Kruss S, Shandell MA, Nair N, Blake S, Sen F, Sen S, Croy RG, Li DY, Yum K, Ahn JH, Jin H, Heller DA, Essigmann JM, Blankschtein D, Strano MS. Nat Nanotechnol. 2013;8:959. doi: 10.1038/nnano.2013.236. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Zheng M, Jagota A, Strano MS, Santos AP, Barone P, Chou SG, Diner BA, Dresselhaus MS, McLean RS, Onoa GB, Samsonidze GG, Semke ED, Usrey M, Walls DJ. Science. 2003;302:1545. doi: 10.1126/science.1091911. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Bachilo SM, Strano MS, Kittrell C, Hauge RH, Smalley RE, Weisman RB. Science. 2002;298:2361. doi: 10.1126/science.1078727. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Weisman RB, Bachilo SM. Nano Lett. 2003;3:1235. [Google Scholar]
- 20.Wang C, Takei K, Takahashi T, Javey A. Chem Soc Rev. 2013;42:2592. doi: 10.1039/c2cs35325c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Hong G, Diao S, Chang J, Antaris AL, Chen C, Zhang B, Zhao S, Atochin DN, Huang PL, Andreasson KI, Kuo CJ, Dai H. Nature Photonics. 2014;8:723. doi: 10.1038/nphoton.2014.166. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Krupke R, Hennrich F, von Lohneysen H, Kappes MM. Science. 2003;301:344. doi: 10.1126/science.1086534. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Heller DA, Mayrhofer RM, Baik S, Grinkova YV, Usrey ML, Strano MS. J Am Chem Soc. 2004;126:14567. doi: 10.1021/ja046450z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Arnold MS, Green AA, Hulvat JF, Stupp SI, Hersam MC. Nat Nanotechnol. 2006;1:60. doi: 10.1038/nnano.2006.52. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Tu X, Manohar S, Jagota A, Zheng M. Nature. 2009;460:250. doi: 10.1038/nature08116. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Liu H, Nishide D, Tanaka T, Kataura H. Nature Communications. 2011:2. doi: 10.1038/ncomms1313. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Khripin CY, Fagan JA, Zheng M. J Am Chem Soc. 2013;135:6822. doi: 10.1021/ja402762e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Wang F, Dukovic G, Brus LE, Heinz TF. Science. 2005;308:838. doi: 10.1126/science.1110265. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Wang F, Dukovic G, Brus LE, Heinz TF. Phys Rev Lett. 2004:92. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.92.177401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Cognet L, Tsyboulski DA, Rocha JDR, Doyle CD, Tour JM, Weisman RB. Science. 2007;316:1465. doi: 10.1126/science.1141316. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Crochet JJ, Duque JG, Werner JH, Doorn SK. Nat Nanotechnol. 2012;7:126. doi: 10.1038/nnano.2011.227. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Crochet J, Clemens M, Hertel T. J Am Chem Soc. 2007;129:8058. doi: 10.1021/ja071553d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Lefebvre J, Fraser JM, Finnie P, Homma Y. Phys Rev B. 2004:69. [Google Scholar]
- 34.Lefebvre J, Austing DG, Bond J, Finnie P. Nano Lett. 2006;6:1603. doi: 10.1021/nl060530e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Lee AJ, Wang X, Carlson LJ, Smyder JA, Loesch B, Tu X, Zheng M, Krauss TD. Nano Lett. 2011;11:1636. doi: 10.1021/nl200077t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Cambre S, Santos SM, Wenseleers W, Nugraha ART, Saito R, Cognet L, Lounis B. Acs Nano. 2012;6:2649. doi: 10.1021/nn300035y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Ju SY, Kopcha WP, Papadimitrakopoulos F. Science. 2009;323:1319. doi: 10.1126/science.1166265. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Campo J, Piao Y, Lam S, Stafford CM, Streit JK, Simpson JR, Walker ARH, Fagan JA. Nanoscale Horiz. 2016;1:317. doi: 10.1039/c6nh00062b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Ghosh S, Bachilo SM, Simonette RA, Beckingham KM, Weisman RB. Science. 2010;330:1656. doi: 10.1126/science.1196382. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Piao Y, Meany B, Powell LR, Valley N, Kwon H, Schatz GC, Wang Y. Nature Chemistry. 2013;5:840. doi: 10.1038/nchem.1711. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Kwon H, Furmanchuk M, Kim M, Meany B, Guo Y, Schatz GC, Wang YH. J Am Chem Soc. 2016;138:6878. doi: 10.1021/jacs.6b03618. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Lefebvre J. Acs Nano. 2016;10:9602. doi: 10.1021/acsnano.6b05077. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Roxbury D, Jena PV, Shamay Y, Horoszko CP, Heller DA. Acs Nano. 2016;10:499. doi: 10.1021/acsnano.5b05438. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Tsyboulski DA, Bachilo SM, Weisman RB. Nano Lett. 2005;5:975. doi: 10.1021/nl050366f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Sanchez SR, Bachilo SM, Kadria-Vili Y, Lin CW, Weisman RB. Nano Lett. 2016;16:6903. doi: 10.1021/acs.nanolett.6b02819. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Streit JK, Bachilo SM, Naumov AV, Khripin C, Zheng M, Weisman RB. Acs Nano. 2012;6:8424. doi: 10.1021/nn3032744. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Galassi TV, Jena PV, Roxbury D, Heller DA. Analytical Chemistry. 2017 doi: 10.1021/acs.analchem.6b04091. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Roxbury D, Jena PV, Williams RM, Enyedi B, Niethammer P, Marcet S, Verhaegen M, Blais-Ouellette S, Heller DA. Sci Rep-Uk. 2015;5 doi: 10.1038/srep14167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Hong GS, Diao SO, Antaris AL, Dai HJ. Chem Rev. 2015;115:10816. doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.5b00008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Yang W, Ratinac KR, Ringer SR, Thordarson P, Gooding JJ, Braet F. Angewandte Chemie - International Edition. 2010;49:2114. doi: 10.1002/anie.200903463. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Cherukuri P, Bachilo SM, Litovsky SH, Weisman RB. J Am Chem Soc. 2004;126:15638. doi: 10.1021/ja0466311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Fakhri N, Wessel AD, Willms C, Pasquali M, Klopfenstein DR, MacKintosh FC, Schmidt CF. Science. 2014;344:1031. doi: 10.1126/science.1250170. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Godin AG, Varela JA, Gao Z, Danne N, Dupuis JP, Lounis B, Groc L, Cognet L. Nat Nanotechnol. 2016 doi: 10.1038/nnano.2016.248. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Won N, Jeong S, Kim K, Kwag J, Park J, Kim SG, Kim S. Mol Imaging. 2012;11:338. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Leeuw TK, Reith RM, Simonette RA, Harden ME, Cherukuri P, Tsyboulski DA, Beckingham KM, Weisman RB. Nano Lett. 2007;7:2650. doi: 10.1021/nl0710452. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Ghosh D, Bagley AF, Na YJ, Birrer MJ, Bhatia SN, Belcher AM. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 2014;111:13948. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1400821111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Barone PW, Baik S, Heller DA, Strano MS. Nature Materials. 2005;4:86. doi: 10.1038/nmat1276. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Leeuw TK, Tsyboulski DA, Nikolaev PN, Bachilo SM, Arepalli S, Weisman RB. Nano Lett. 2008;8:826. doi: 10.1021/nl072861c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Heller DA, Jin H, Martinez BM, Patel D, Miller BM, Yeung TK, Jena PV, Hobartner C, Ha T, Silverman SK, Strano MS. Nat Nanotechnol. 2009;4:114. doi: 10.1038/nnano.2008.369. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Wong MH, Giraldo JP, Kwak SY, Koman VB, Sinclair R, Lew TTS, Bisker G, Liu P, Strano MS. Nature Materials. 2016 doi: 10.1038/nmat4771. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Iverson NM, Barone PW, Shandell M, Trudel LJ, Sen S, Sen F, Ivanov V, Atolia E, Farias E, McNicholas TP, Reuel N, Parry NMA, Wogan GN, Strano MS. Nat Nanotechnol. 2013;8:873. doi: 10.1038/nnano.2013.222. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.