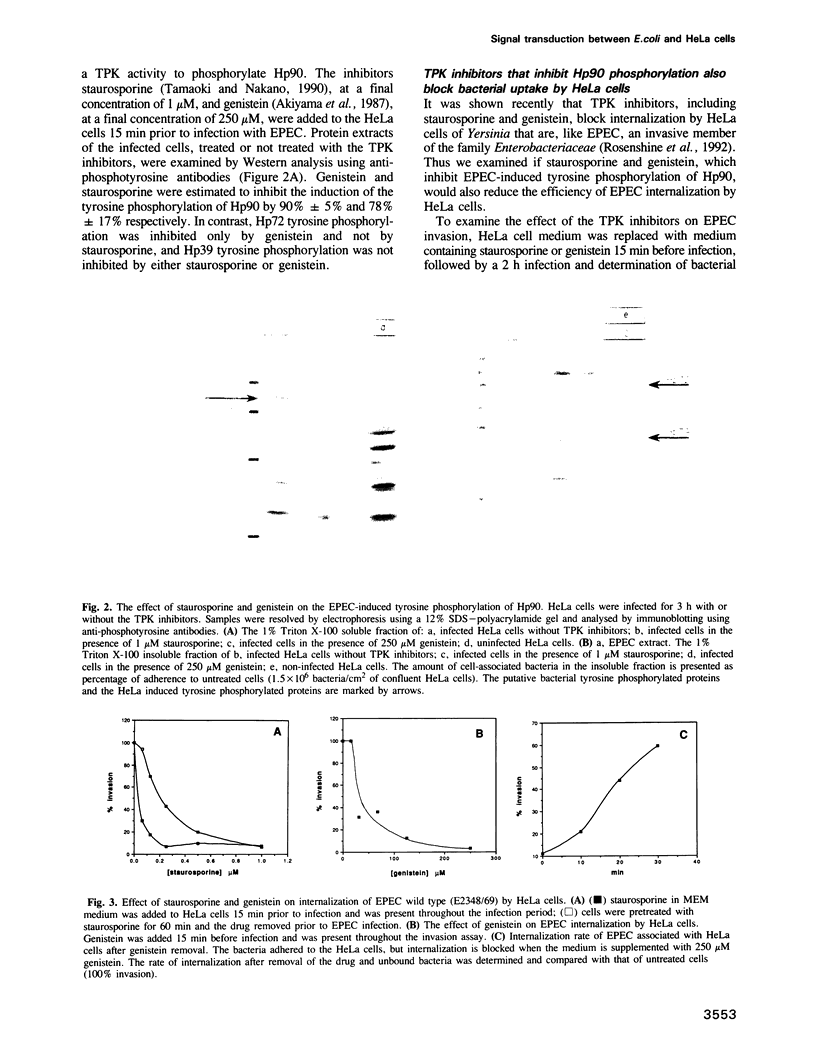
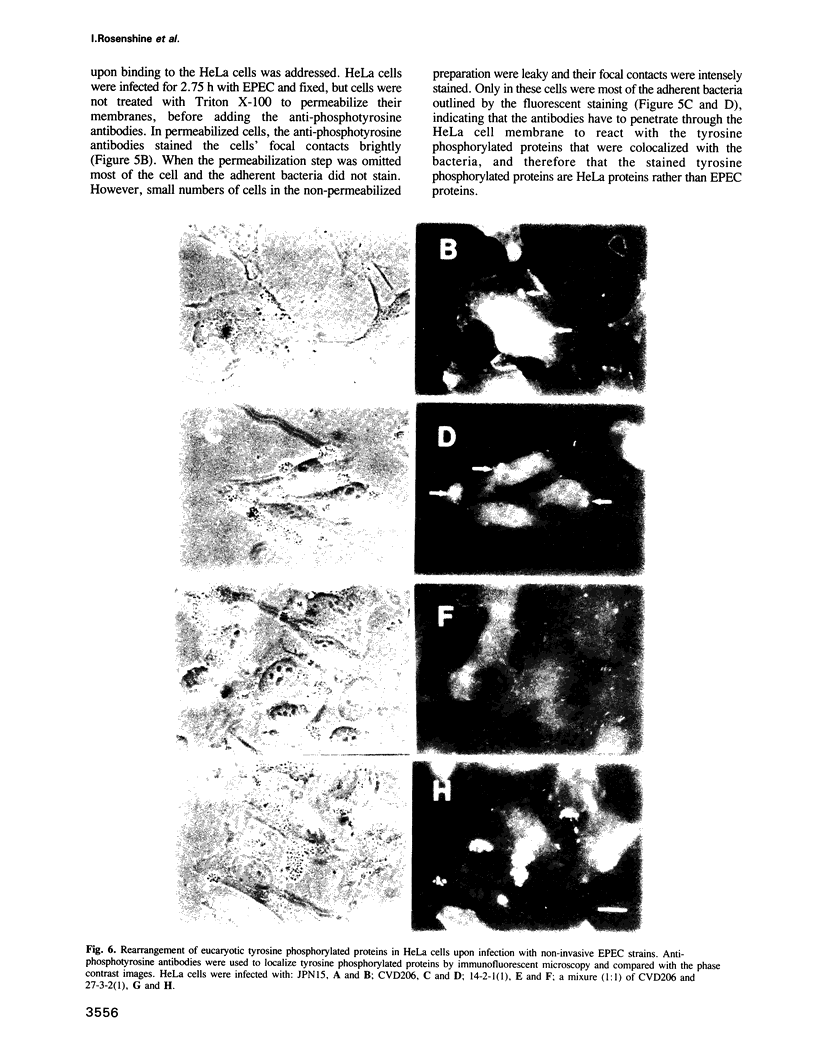
Abstract
Upon attachment to cultured HeLa cells, enteropathogenic Escherichia coli (EPEC) induces assembly of a complex cytoskeletal structure within the eucaryotic cell, localized beneath the adherent bacterium. In addition, EPEC induces its own internalization by non-phagocytic epithelial cells. We found that after binding to the epithelial cell surface, EPEC induces tyrosine phosphorylation of three eucaryotic proteins. The major phosphorylation substrate is a 90 kDa protein (Hp90). In correlation with Hp90 tyrosine phosphorylation, the EPEC-induced cytoskeletal structure also contained tyrosine phosphorylated proteins. Using tyrosine protein kinase inhibitors and EPEC mutants (cfm) that fail to induce Hp90 phosphorylation, we demonstrate that induction of Hp90 phosphorylation is involved in initiation of the cytoskeletal structure assembly and in bacterial uptake. Other non-invasive EPEC mutants (eae) are still able to induce Hp90 tyrosine phosphorylation and to initiate aggregation of the tyrosine phosphorylated proteins and some cytoskeleton components. However, eae mutants are deficient in nucleating the aggregates into an organized structure.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akiyama T., Ishida J., Nakagawa S., Ogawara H., Watanabe S., Itoh N., Shibuya M., Fukami Y. Genistein, a specific inhibitor of tyrosine-specific protein kinases. J Biol Chem. 1987 Apr 25;262(12):5592–5595. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andrade J. R., Da Veiga V. F., De Santa Rosa M. R., Suassuna I. An endocytic process in HEp-2 cells induced by enteropathogenic Escherichia coli. J Med Microbiol. 1989 Jan;28(1):49–57. doi: 10.1099/00222615-28-1-49. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baldini M. M., Kaper J. B., Levine M. M., Candy D. C., Moon H. W. Plasmid-mediated adhesion in enteropathogenic Escherichia coli. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 1983;2(3):534–538. doi: 10.1097/00005176-198302030-00023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baldwin T. J., Brooks S. F., Knutton S., Manjarrez Hernandez H. A., Aitken A., Williams P. H. Protein phosphorylation by protein kinase C in HEp-2 cells infected with enteropathogenic Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1990 Mar;58(3):761–765. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.3.761-765.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baldwin T. J., Ward W., Aitken A., Knutton S., Williams P. H. Elevation of intracellular free calcium levels in HEp-2 cells infected with enteropathogenic Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1991 May;59(5):1599–1604. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.5.1599-1604.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bliska J. B., Guan K. L., Dixon J. E., Falkow S. Tyrosine phosphate hydrolysis of host proteins by an essential Yersinia virulence determinant. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Feb 15;88(4):1187–1191. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.4.1187. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burridge K., Fath K., Kelly T., Nuckolls G., Turner C. Focal adhesions: transmembrane junctions between the extracellular matrix and the cytoskeleton. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1988;4:487–525. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.04.110188.002415. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis S., Lu M. L., Lo S. H., Lin S., Butler J. A., Druker B. J., Roberts T. M., An Q., Chen L. B. Presence of an SH2 domain in the actin-binding protein tensin. Science. 1991 May 3;252(5006):712–715. doi: 10.1126/science.1708917. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donnenberg M. S., Calderwood S. B., Donohue-Rolfe A., Keusch G. T., Kaper J. B. Construction and analysis of TnphoA mutants of enteropathogenic Escherichia coli unable to invade HEp-2 cells. Infect Immun. 1990 Jun;58(6):1565–1571. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.6.1565-1571.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donnenberg M. S., Donohue-Rolfe A., Keusch G. T. A comparison of HEp-2 cell invasion by enteropathogenic and enteroinvasive Escherichia coli. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1990 May;57(1-2):83–86. doi: 10.1016/0378-1097(90)90417-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donnenberg M. S., Donohue-Rolfe A., Keusch G. T. Epithelial cell invasion: an overlooked property of enteropathogenic Escherichia coli (EPEC) associated with the EPEC adherence factor. J Infect Dis. 1989 Sep;160(3):452–459. doi: 10.1093/infdis/160.3.452. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donnenberg M. S., Kaper J. B. Construction of an eae deletion mutant of enteropathogenic Escherichia coli by using a positive-selection suicide vector. Infect Immun. 1991 Dec;59(12):4310–4317. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.12.4310-4317.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finlay B. B., Falkow S. Comparison of the invasion strategies used by Salmonella cholerae-suis, Shigella flexneri and Yersinia enterocolitica to enter cultured animal cells: endosome acidification is not required for bacterial invasion or intracellular replication. Biochimie. 1988 Aug;70(8):1089–1099. doi: 10.1016/0300-9084(88)90271-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finlay B. B., Rosenshine I., Donnenberg M. S., Kaper J. B. Cytoskeletal composition of attaching and effacing lesions associated with enteropathogenic Escherichia coli adherence to HeLa cells. Infect Immun. 1992 Jun;60(6):2541–2543. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.6.2541-2543.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finlay B. B., Ruschkowski S., Dedhar S. Cytoskeletal rearrangements accompanying salmonella entry into epithelial cells. J Cell Sci. 1991 Jun;99(Pt 2):283–296. doi: 10.1242/jcs.99.2.283. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foster R., Thorner J., Martin G. S. Nucleotidylation, not phosphorylation, is the major source of the phosphotyrosine detected in enteric bacteria. J Bacteriol. 1989 Jan;171(1):272–279. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.1.272-279.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Francis C. L., Jerse A. E., Kaper J. B., Falkow S. Characterization of interactions of enteropathogenic Escherichia coli O127:H6 with mammalian cells in vitro. J Infect Dis. 1991 Oct;164(4):693–703. doi: 10.1093/infdis/164.4.693. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Girón J. A., Ho A. S., Schoolnik G. K. An inducible bundle-forming pilus of enteropathogenic Escherichia coli. Science. 1991 Nov 1;254(5032):710–713. doi: 10.1126/science.1683004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldschmidt-Clermont P. J., Kim J. W., Machesky L. M., Rhee S. G., Pollard T. D. Regulation of phospholipase C-gamma 1 by profilin and tyrosine phosphorylation. Science. 1991 Mar 8;251(4998):1231–1233. doi: 10.1126/science.1848725. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guan K. L., Dixon J. E. Protein tyrosine phosphatase activity of an essential virulence determinant in Yersinia. Science. 1990 Aug 3;249(4968):553–556. doi: 10.1126/science.2166336. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill T. D., Dean N. M., Mordan L. J., Lau A. F., Kanemitsu M. Y., Boynton A. L. PDGF-induced activation of phospholipase C is not required for induction of DNA synthesis. Science. 1990 Jun 29;248(4963):1660–1663. doi: 10.1126/science.2163545. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isberg R. R., Leong J. M. Multiple beta 1 chain integrins are receptors for invasin, a protein that promotes bacterial penetration into mammalian cells. Cell. 1990 Mar 9;60(5):861–871. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90099-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jerse A. E., Kaper J. B. The eae gene of enteropathogenic Escherichia coli encodes a 94-kilodalton membrane protein, the expression of which is influenced by the EAF plasmid. Infect Immun. 1991 Dec;59(12):4302–4309. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.12.4302-4309.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jerse A. E., Martin W. C., Galen J. E., Kaper J. B. Oligonucleotide probe for detection of the enteropathogenic Escherichia coli (EPEC) adherence factor of localized adherent EPEC. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Dec;28(12):2842–2844. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.12.2842-2844.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jerse A. E., Yu J., Tall B. D., Kaper J. B. A genetic locus of enteropathogenic Escherichia coli necessary for the production of attaching and effacing lesions on tissue culture cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Oct;87(20):7839–7843. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.20.7839. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kellie S., Horvath A. R., Elmore M. A. Cytoskeletal targets for oncogenic tyrosine kinases. J Cell Sci. 1991 Jun;99(Pt 2):207–211. doi: 10.1242/jcs.99.2.207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knutton S., Baldwin T., Williams P. H., McNeish A. S. Actin accumulation at sites of bacterial adhesion to tissue culture cells: basis of a new diagnostic test for enteropathogenic and enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1989 Apr;57(4):1290–1298. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.4.1290-1298.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koch C. A., Anderson D., Moran M. F., Ellis C., Pawson T. SH2 and SH3 domains: elements that control interactions of cytoplasmic signaling proteins. Science. 1991 May 3;252(5006):668–674. doi: 10.1126/science.1708916. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine M. M., Edelman R. Enteropathogenic Escherichia coli of classic serotypes associated with infant diarrhea: epidemiology and pathogenesis. Epidemiol Rev. 1984;6:31–51. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.epirev.a036274. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manjarrez-Hernandez H. A., Amess B., Sellers L., Baldwin T. J., Knutton S., Williams P. H., Aitken A. Purification of a 20 kDa phosphoprotein from epithelial cells and identification as a myosin light chain. Phosphorylation induced by enteropathogenic Escherichia coli and phorbol ester. FEBS Lett. 1991 Nov 4;292(1-2):121–127. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(91)80848-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manoil C., Beckwith J. TnphoA: a transposon probe for protein export signals. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(23):8129–8133. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.23.8129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moon H. W., Whipp S. C., Argenzio R. A., Levine M. M., Giannella R. A. Attaching and effacing activities of rabbit and human enteropathogenic Escherichia coli in pig and rabbit intestines. Infect Immun. 1983 Sep;41(3):1340–1351. doi: 10.1128/iai.41.3.1340-1351.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nataro J. P., Baldini M. M., Kaper J. B., Black R. E., Bravo N., Levine M. M. Detection of an adherence factor of enteropathogenic Escherichia coli with a DNA probe. J Infect Dis. 1985 Sep;152(3):560–565. doi: 10.1093/infdis/152.3.560. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenshine I., Duronio V., Finlay B. B. Tyrosine protein kinase inhibitors block invasin-promoted bacterial uptake by epithelial cells. Infect Immun. 1992 Jun;60(6):2211–2217. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.6.2211-2217.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scaletsky I. C., Silva M. L., Trabulsi L. R. Distinctive patterns of adherence of enteropathogenic Escherichia coli to HeLa cells. Infect Immun. 1984 Aug;45(2):534–536. doi: 10.1128/iai.45.2.534-536.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamaoki T., Nakano H. Potent and specific inhibitors of protein kinase C of microbial origin. Biotechnology (N Y) 1990 Aug;8(8):732–735. doi: 10.1038/nbt0890-732. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu J., Kaper J. B. Cloning and characterization of the eae gene of enterohaemorrhagic Escherichia coli O157:H7. Mol Microbiol. 1992 Feb;6(3):411–417. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1992.tb01484.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]