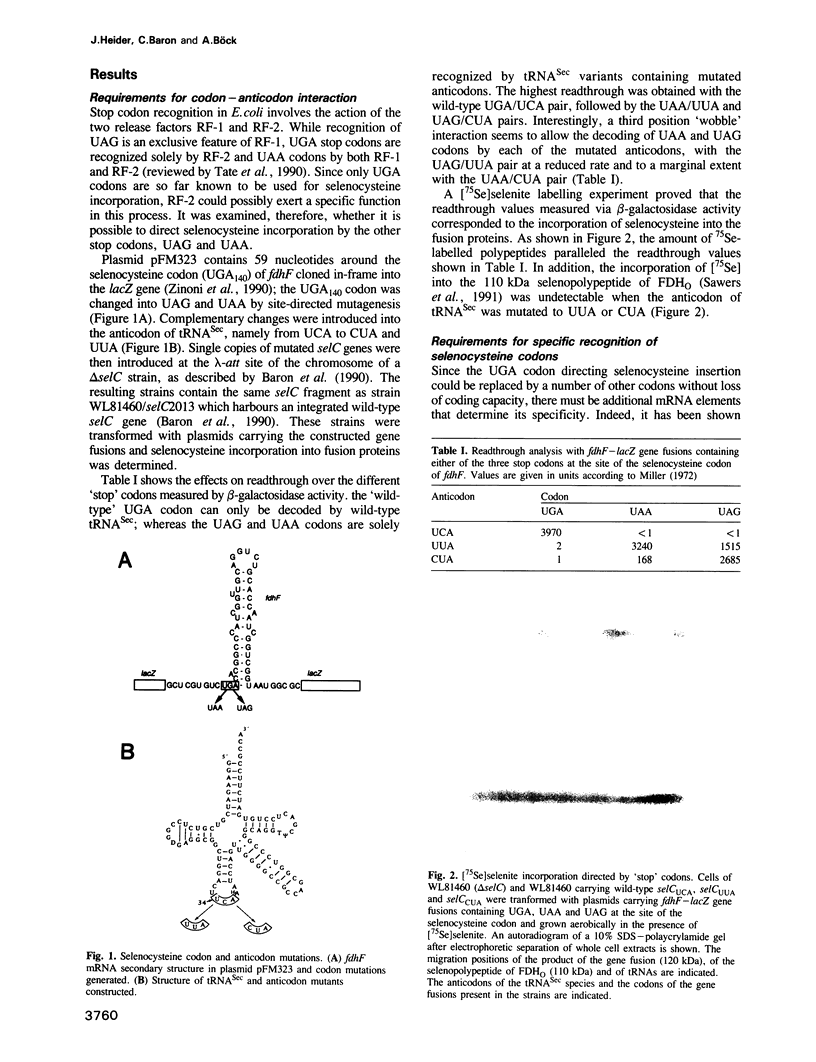
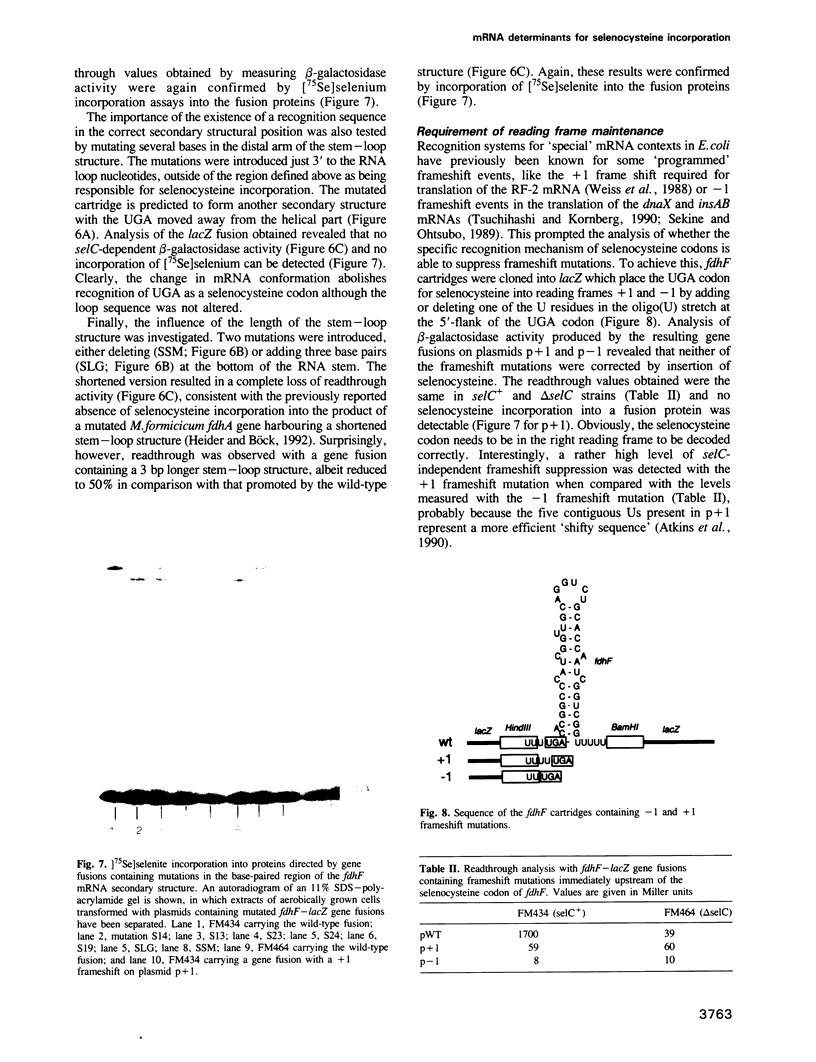
Abstract
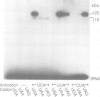
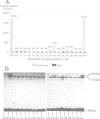
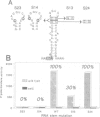
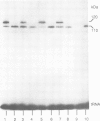
Incorporation of selenocysteine into proteins is directed by specifically 'programmed' UGA codons. The determinants for recognition of the selenocysteine codon have been investigated by analysing the effect of mutations in fdhF, the gene for formate dehydrogenase H of Escherichia coli, on selenocysteine incorporation. It was found that selenocysteine was also encoded when the UGA codon was replaced by UAA and UAG, provided a proper codon-anticodon interaction was possible with tRNA(Sec). This indicates that none of the three termination codons can function as efficient translational stop signals in that particular mRNA position. The discrimination of the selenocysteine 'sense' codon from a regular stop codon has previously been shown to be dependent on an RNA secondary structure immediately 3' of the UGA codon in the fdhF mRNA. It is demonstrated here that the correct folding of this structure as well as the existence of primary sequence elements located within the loop portion at an appropriate distance to the UGA codon are absolutely required. A recognition sequence can be defined which mediates specific translation of a particular codon inside an mRNA with selenocysteine and a model is proposed in which translation factor SELB interacts with this recognition sequence, thus forming a quaternary complex at the mRNA together with GTP and selenocysteyl-tRNA(Sec).
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Atkins J. F., Weiss R. B., Gesteland R. F. Ribosome gymnastics--degree of difficulty 9.5, style 10.0. Cell. 1990 Aug 10;62(3):413–423. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90007-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baron C., Heider J., Böck A. Mutagenesis of selC, the gene for the selenocysteine-inserting tRNA-species in E. coli: effects on in vivo function. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Dec 11;18(23):6761–6766. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.23.6761. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berg B. L., Baron C., Stewart V. Nitrate-inducible formate dehydrogenase in Escherichia coli K-12. II. Evidence that a mRNA stem-loop structure is essential for decoding opal (UGA) as selenocysteine. J Biol Chem. 1991 Nov 25;266(33):22386–22391. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berg B. L., Li J., Heider J., Stewart V. Nitrate-inducible formate dehydrogenase in Escherichia coli K-12. I. Nucleotide sequence of the fdnGHI operon and evidence that opal (UGA) encodes selenocysteine. J Biol Chem. 1991 Nov 25;266(33):22380–22385. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Böck A., Forchhammer K., Heider J., Baron C. Selenoprotein synthesis: an expansion of the genetic code. Trends Biochem Sci. 1991 Dec;16(12):463–467. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(91)90180-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen E. Y., Seeburg P. H. Supercoil sequencing: a fast and simple method for sequencing plasmid DNA. DNA. 1985 Apr;4(2):165–170. doi: 10.1089/dna.1985.4.165. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheong C., Varani G., Tinoco I., Jr Solution structure of an unusually stable RNA hairpin, 5'GGAC(UUCG)GUCC. Nature. 1990 Aug 16;346(6285):680–682. doi: 10.1038/346680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox J. C., Edwards E. S., DeMoss J. A. Resolution of distinct selenium-containing formate dehydrogenases from Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1981 Mar;145(3):1317–1324. doi: 10.1128/jb.145.3.1317-1324.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehrenreich A., Forchhammer K., Tormay P., Veprek B., Böck A. Selenoprotein synthesis in E. coli. Purification and characterisation of the enzyme catalysing selenium activation. Eur J Biochem. 1992 Jun 15;206(3):767–773. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1992.tb16983.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forchhammer K., Böck A. Selenocysteine synthase from Escherichia coli. Analysis of the reaction sequence. J Biol Chem. 1991 Apr 5;266(10):6324–6328. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forchhammer K., Leinfelder W., Boesmiller K., Veprek B., Böck A. Selenocysteine synthase from Escherichia coli. Nucleotide sequence of the gene (selA) and purification of the protein. J Biol Chem. 1991 Apr 5;266(10):6318–6323. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forchhammer K., Leinfelder W., Böck A. Identification of a novel translation factor necessary for the incorporation of selenocysteine into protein. Nature. 1989 Nov 23;342(6248):453–456. doi: 10.1038/342453a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Förster C., Ott G., Forchhammer K., Sprinzl M. Interaction of a selenocysteine-incorporating tRNA with elongation factor Tu from E.coli. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Feb 11;18(3):487–491. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.3.487. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heider J., Böck A. Targeted insertion of selenocysteine into the alpha subunit of formate dehydrogenase from Methanobacterium formicicum. J Bacteriol. 1992 Feb;174(3):659–663. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.3.659-663.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jukes T. H. Genetic code 1990. Outlook. Experientia. 1990 Dec 1;46(11-12):1149–1157. doi: 10.1007/BF01936925. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel T. A., Roberts J. D., Zakour R. A. Rapid and efficient site-specific mutagenesis without phenotypic selection. Methods Enzymol. 1987;154:367–382. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)54085-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neidhardt F. C., Bloch P. L., Smith D. F. Culture medium for enterobacteria. J Bacteriol. 1974 Sep;119(3):736–747. doi: 10.1128/jb.119.3.736-747.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawers R. G., Ballantine S. P., Boxer D. H. Differential expression of hydrogenase isoenzymes in Escherichia coli K-12: evidence for a third isoenzyme. J Bacteriol. 1985 Dec;164(3):1324–1331. doi: 10.1128/jb.164.3.1324-1331.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schön A., Böck A., Ott G., Sprinzl M., Söll D. The selenocysteine-inserting opal suppressor serine tRNA from E. coli is highly unusual in structure and modification. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Sep 25;17(18):7159–7165. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.18.7159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sekine Y., Ohtsubo E. Frameshifting is required for production of the transposase encoded by insertion sequence 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jun;86(12):4609–4613. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.12.4609. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapira S. K., Chou J., Richaud F. V., Casadaban M. J. New versatile plasmid vectors for expression of hybrid proteins coded by a cloned gene fused to lacZ gene sequences encoding an enzymatically active carboxy-terminal portion of beta-galactosidase. Gene. 1983 Nov;25(1):71–82. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90169-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simons R. W., Houman F., Kleckner N. Improved single and multicopy lac-based cloning vectors for protein and operon fusions. Gene. 1987;53(1):85–96. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(87)90095-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabor S., Richardson C. C. DNA sequence analysis with a modified bacteriophage T7 DNA polymerase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jul;84(14):4767–4771. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.14.4767. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsuchihashi Z., Kornberg A. Translational frameshifting generates the gamma subunit of DNA polymerase III holoenzyme. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Apr;87(7):2516–2520. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.7.2516. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veres Z., Tsai L., Scholz T. D., Politino M., Balaban R. S., Stadtman T. C. Synthesis of 5-methylaminomethyl-2-selenouridine in tRNAs: 31P NMR studies show the labile selenium donor synthesized by the selD gene product contains selenium bonded to phosphorus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Apr 1;89(7):2975–2979. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.7.2975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vieira J., Messing J. The pUC plasmids, an M13mp7-derived system for insertion mutagenesis and sequencing with synthetic universal primers. Gene. 1982 Oct;19(3):259–268. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90015-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogelstein B., Gillespie D. Preparative and analytical purification of DNA from agarose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Feb;76(2):615–619. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.2.615. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss R. B., Dunn D. M., Dahlberg A. E., Atkins J. F., Gesteland R. F. Reading frame switch caused by base-pair formation between the 3' end of 16S rRNA and the mRNA during elongation of protein synthesis in Escherichia coli. EMBO J. 1988 May;7(5):1503–1507. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02969.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss R. B., Dunn D. M., Shuh M., Atkins J. F., Gesteland R. F. E. coli ribosomes re-phase on retroviral frameshift signals at rates ranging from 2 to 50 percent. New Biol. 1989 Nov;1(2):159–169. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanisch-Perron C., Vieira J., Messing J. Improved M13 phage cloning vectors and host strains: nucleotide sequences of the M13mp18 and pUC19 vectors. Gene. 1985;33(1):103–119. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90120-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zinoni F., Birkmann A., Leinfelder W., Böck A. Cotranslational insertion of selenocysteine into formate dehydrogenase from Escherichia coli directed by a UGA codon. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 May;84(10):3156–3160. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.10.3156. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zinoni F., Heider J., Böck A. Features of the formate dehydrogenase mRNA necessary for decoding of the UGA codon as selenocysteine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jun;87(12):4660–4664. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.12.4660. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]