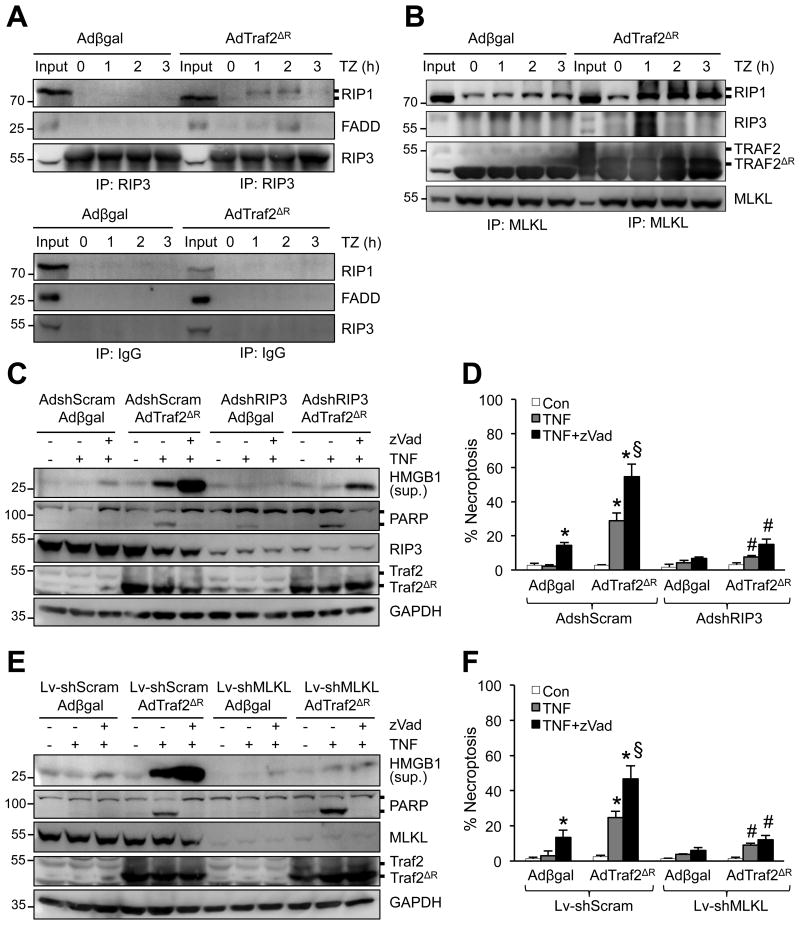
Figure 5. Loss of Traf2 promotes necroptotic signaling through RIP1-RIP3-MLKL.
A and B, Western blotting for the indicated proteins following IP with anti-RIP3 (A, top panel), anti-MLKL (B), or pre-immune IgG control (A, bottom panel) from extracts of cardiomyocytes infected with Adβgal or AdTraf2ΔR, then treated with TNFa plus zVad for 0-3 h. C, Western blotting for the indicated proteins from cardiomyocytes infected with the indicated adenoviral vectors then treated with vehicle control, TNF, or TNF+zVad for 4 h. D, Quantification of necroptosis (PI positive without chromatin condensation) from cells treated as in C. *P < 0.05 versus vehicle control; #P < 0.05 versus Ad-shScram in the corresponding group; §P < 0.05 versus Ad-shScram Adβgal TNF+zVad. E, Western blotting for the indicated proteins from cardiomyocytes infected with the indicated adenoviral and lentiviral vectors then treated with vehicle control, TNF, or TNF+zVad for 4 h. F, Quantification of necroptosis (PI positive without chromatin condensation) from cells treated as in E. *P < 0.05 versus vehicle control; #P < 0.05 versus Lv-shScram in the corresponding group; §P < 0.05 versus Ad-shScram Adβgal TNF+zVad. Data were from at least 3 independent experiments with ≥ 900 cells per group analyzed for cell death. One-way ANOVA with Bonferroni's post-hoc test was performed in D and F.